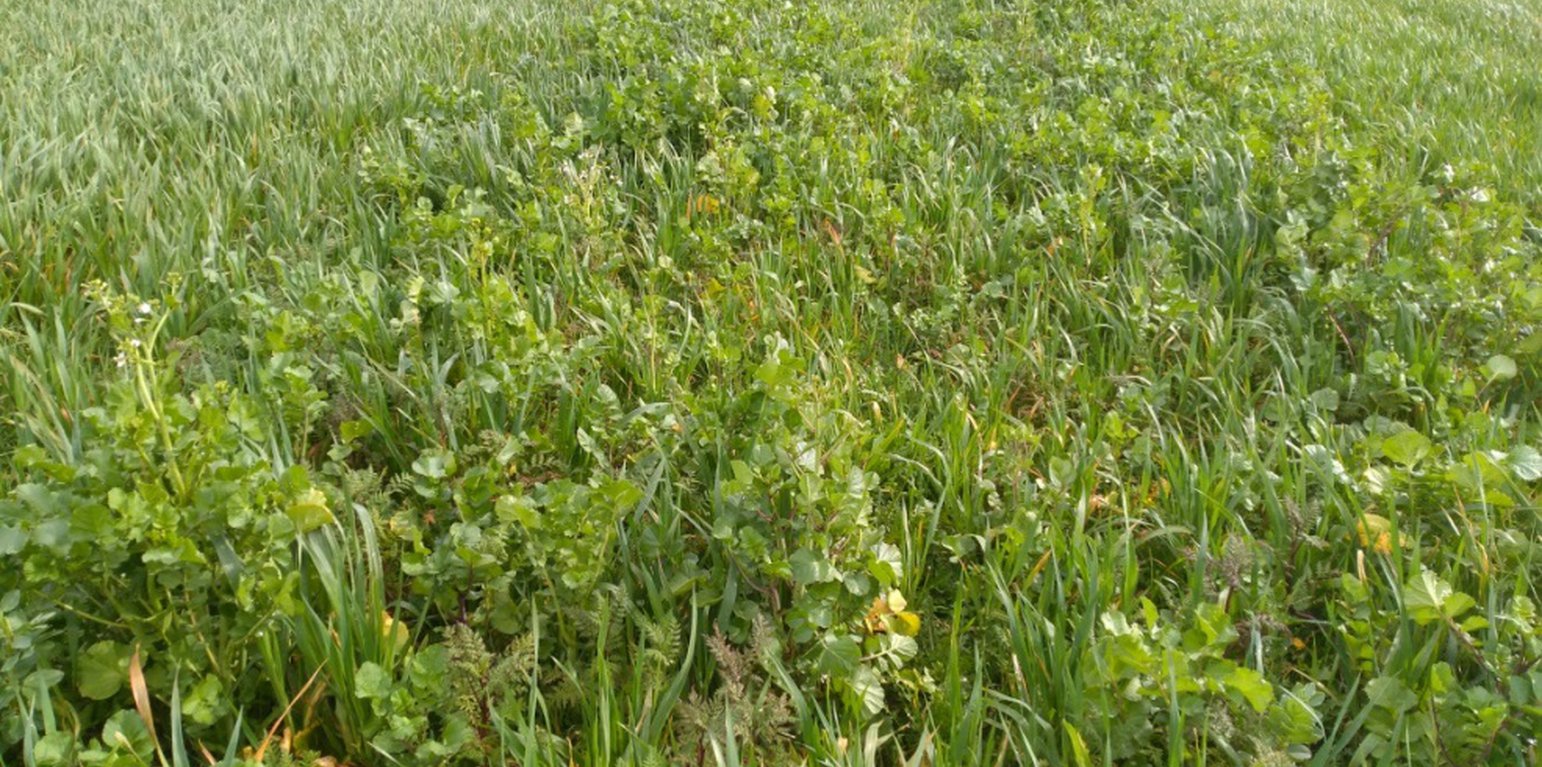
Vegetation cover management on an organic, mixed livestock-crop farm
(Франция)
Описание
Use of different mixes of plant cover for livestock fodder which are simultaneously favourable for biodiversity by improving soil health, and reducing the need for agrochemicals.
Agriculture in Brittany, in the north-west of France, is known for fish, beef, pork, poultry, vegetables and milk. Cover crops are used by farmers of Mauron, and the example described here is from a farm located in Morbihan in the basin known as Ploërmel. In this warm temperate area the average annual rainfall is 650-700 mm with an annual temperature of around 11°C.
There are three types of cover crops included in the rotation. These are selected on the basis of their benefits in relation to soil fertility and fodder production, in order to improve the farm's food self-sufficiency. There are three basic types of cover crops, as follows.
1) “Protein mixes” are composed of 35% faba (broad) beans, 26% oats, 17.5% peas, 17.5% vetch, and 4% clover. These are sown in early October after grass or maize are made into silage at the end of April.
2) "Green manure" cover crops are sown at the beginning of September after cereals, and are composed of various complementary species with the main objective of preserving and strengthening soil life (i.e. worm abundance), and winter feeding of heifers. For example, the commercial "Biomax" mix contains seeds of broad bean, vetch, clover, phacelia and radish. These cover crops are enriched by the presence of approximately 50% ryegrass regrowth, supporting the development of soil life.
3) Rapeseed is sown after cereals as a crop rotation feedstock and are made into silage.
Cover crops are either broadcast and rolled, or direct seeded depending on the conditions of the post-harvest plots. The seed drill used is equipped with discs to minimise soil disturbance as a reduced tillage technique, but more important in this respect is the presence of crop residues (i.e. straw). The seed drill is also equipped with tines.
The cover crops are grazed by heifers in a rotational 2-day paddock set-up. After grazing and regrowth of the ryegrass present, the fields may be left to develop into pasture, or seeded to crops using a minimum tillage drill.
The purposes are:
•Improved production
•Countered land degradation
•Protected watersheds
•Preserved biodiversity
•Adaptation to climate change/extreme events
The benefits are:
•Sustained ecosystem health: no pest and disease problems, good herd health
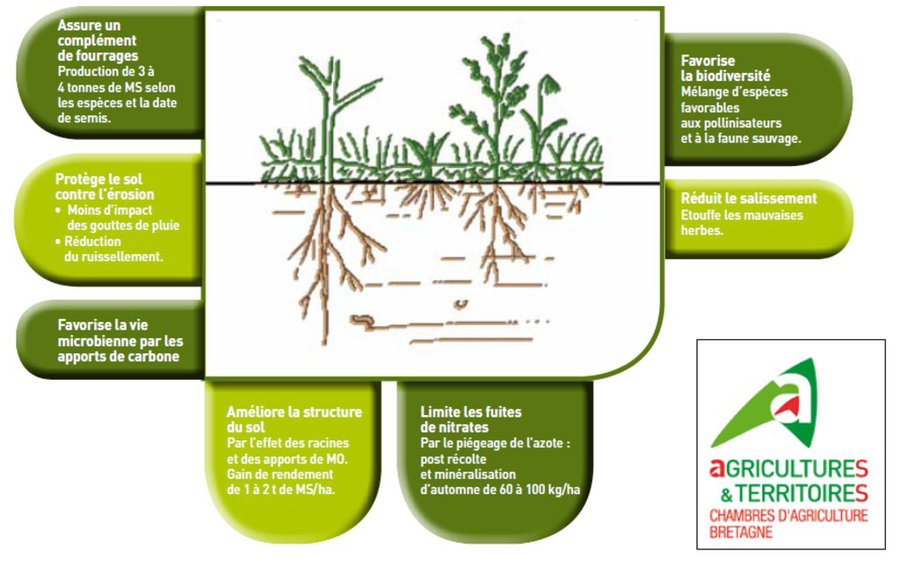
•Enrichment of the soil by the addition of carbon in organic matter and by the work of earthworms - favouring ecosystem functioning
•Protection of the soil and surface biodiversity because of maintained plant cover
•Increased weed control due to plant canopies and fertilisation effect of green manure
•Planted cover crops used as livestock feed during winter
The challenges are:
•Potential difficulties in establishing plant cover (especially in dry areas)
•Late sowing of cover crops reduces beneficial effects
•High costs of seed mixtures with high protein cover crops
Местоположение
Местоположение: Mauron, Brittany, Франция
Число исследованных участков, где применяется Технология: отдельный участок
Географическая привязка выбранных участков
Пространственное распространение Технологии: равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади (approx. 10-100 км2)
На постоянно охраняемой территории?: Нет
Продолжительность применения Технологии: 2019; менее 10 лет назад (недавняя)
Тип внедрения/ применения
-
как инновация (инициатива) землепользователей
-
как часть традиционной системы землепользования (более 50 лет назад)
-
в качестве научного/ полевого эксперимента
-
через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
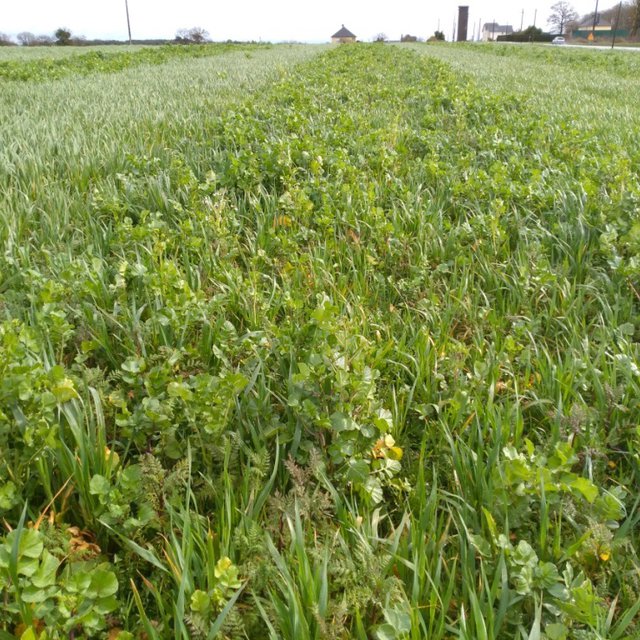

Cover crops in Brittany, France (Soil Care)

Cover crop mowing for its removal
Основная цель
-
повышение производства
-
снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
-
сохранение экосистем
-
защита бассейнов рек (приводораздельной части/ нижнего течения) – в сочетании с другими Технологиями
-
сохранение/ повышение биоразнообразия
-
снижение риска стихийных бедствий
-
адаптация к изменению климата / экстремальным погодным явлениям и их последствиям
-
смягчение последствий изменения климата
-
создание благоприятных экономических условий
-
создание благоприятных социальных условий
Землепользование
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы: Да - Агро-пастбищное хозяйство ( включая растениеводство-животноводство)
-
Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры: зерновые культуры - кукуруза, зерновые культуры - рожь, кормовые культуры - клевер, кормовые культуры - травы, кормовые культуры - другое, бобовые - бобы, масличные культуры - подсолнечник, рапс, другие
- Cover crops
Число урожаев за год: 1
Применяются ли посевы в междурядьях? Да
Применяется ли севооборот? Да
-
Пастбищные угодья
- Стойловое содержание/ нулевой выпас
- Улучшенные пастбища
Вид животных: крупный рогатый скот - молочный, домашняя птица
Используется ли комплексное земледельческо-животноводческое хозяйство? Да
| Виды | Счет |
| крупный рогатый скот - молочный | 115 |
| домашняя птица | 4500 |
Водоснабжение
-
богарные земли
-
сочетание богарных и орошаемых земель
-
полное орошение
Цель, связанная с деградацией земель
-
предотвращение деградации земель
-
снижение деградации земель
-
восстановление/ реабилитация нарушенных земель
-
адаптация к деградации земель
-
не применимо
Тип деградации, на борьбу с которым направлена
-
водная эрозия почв - ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов , ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование , ВЭд: косвенное воздействие водной эрозии
-
ухудшение химических свойств почв - Хп: Снижение плодородия и уменьшение содержания органического вещества (вызванное не эрозией, а другими причинами)
-
ухудшение физических свойств почв - Фу: уплотнение
-
биологическая деградация - Бр: сокращение растительного покрова, Бк: сокращение количества биомассы, Бв: потеря природного разнообразия , Бб: рост числа вредителей/болезней
-
деградация водных ресурсов - Взп: снижение качества поверхностных вод, Вб: снижение буферной способности водно-болотных угодий
Категория УЗП
-
Комлексное земледельческо-животноводческое хозяйство
-
Улучшение почвенного/ растительного покрова
-
Комплексная борьба с сельскохозяйственными вредителями и болезнями (включая органическое сельское хозяйство)
Мероприятия УЗП
-
Агрономические мероприятия - A1: Растительный/ почвенный покров, A2: Органическое вещество/ почвенное плодородие, A3: Поверхностная обработка почв, A4: Глубокая обработка почв
Технический рисунок
Технические характеристики
- broadcast sowing or direct sowing of species mixture in late August / early September or late September / early October
- protein mix: peas 40 kg / faba (broad) beans 80 kg / vetch 40 kg / clover 8 kg / oats 60 kg per hectare
- Biomax mix: radish 2 kg / clover 3 kg / faba (broad) bean 20 kg / phacelia 2 kg / vetch 10 kg per hectare
- Rapeseed mix: 8 to 10 kg per hectare
Author: Revue agricole Terra
Запуск и текущее обслуживание: мероприятия, необходимые ресурсы и затраты
Подсчет вложений и затрат
- Подсчитанные затраты: на площадь, где применяется Технология (размер и единица площади: 1 ha)
- Денежные единицы, использованные для подсчета затрат: €
- Обменный курс (к доллару США): 1 USD = 0.9 €
- Средний размер дневного заработка для нанятых работников: Gross hourly minimum wage: €10.15 on 1 January 2020, i.e. €1,539.42 monthly on the basis of the legal working week of 35 hours.
Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Direct sowing equipment, destruction with 2 passes of rolling spade, cost of purchasing "biomax" mixture
Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
-
Soil preparation and subsequent sowing of rapeseed/rapeseed after harvest cereals (Сроки/ повторяемость проведения: End of August)
-
Soil preparation and sowing of the Biomax mixture after harvest cereals (Сроки/ повторяемость проведения: End of August)
-
Soil preparation and sowing of meslin after grassland or corn on the cob (Сроки/ повторяемость проведения: End of October)
-
Rapeseed/rapeseed grazing and growing of green manure (Сроки/ повторяемость проведения: December to March)
-
Meslin silage (Сроки/ повторяемость проведения: April)
Стоимость вложений и затрат по запуску (per 1 ha)
| Опишите затраты |
Единица |
Количество |
Затраты на единицу (€) |
Общая стоимость на единицу (€) |
% затрат, оплаченных землепользователями |
|
Оборудование
|
| Direct seeding (compil) |
ha |
40,0 |
60,0 |
2400,0 |
100,0 |
| Broadcast sowing |
ha |
72,0 |
15,0 |
1080,0 |
100,0 |
| Roller spade before sowing (1 pass) |
ha |
72,0 |
23,0 |
1656,0 |
100,0 |
| Maceration by a roller with blades |
ha |
224,0 |
23,0 |
5152,0 |
100,0 |
|
Посадочный материал
|
| Seeds - protein blend |
ha |
60,0 |
394,0 |
23640,0 |
100,0 |
| Seeds - forage rapeseed |
ha |
17,0 |
28,0 |
476,0 |
100,0 |
| Seeds - green manure "biomax" fertilizer |
ha |
18,0 |
60,0 |
1080,0 |
100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии |
35'484.0 |
|
| Общие затраты на создание Технологии в долларах США |
39'426.67 |
|
Текущее обслуживание
n.a.
Природные условия
Среднегодовое количество осадков
-
< 250 мм
-
251-500 мм
-
501-750 мм
-
751-1000 мм
-
1001-1500 мм
-
1501-2000 мм
-
2001-3000 мм
-
3001-4000 мм
-
> 4000 мм
Агроклиматическая зона
-
влажная
-
Умеренно-влажная
-
полузасушливая
-
засушливая
Дополнительные характеристики климата
Среднегодовое количество осадков в мм: 675.0
The farm is located on the commune of Mauron in Morbihan and is in an early agro-climatic zone. The average annual rainfall of 650-700 mm is the lowest in Morbihan. The average annual temperature of around 11°C and is also the lowest in Morbihan.
Название метеостанции: Ploermel
The climate of Mauron is warm and temperate. It is in the basin known as Ploërmel, the most continental of Morbihan with colder winters, hotter summers and rainfall of around 650-700 mm/year. Heavy showers fall all year round in the area of Mauron. Even in the driest months, rainfall remains fairly heavy.
Склон
-
пологие (0-2%)
-
покатые (3-5%)
-
покато-крутые (6-10%)
-
крутые (11-15%)
-
очень крутые (16-30%)
-
чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
-
обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа
-
плато/ равнины
-
гребни хребтов/холмов
-
склоны гор
-
склоны холмов
-
подножья
-
днища долин
Высота над уровнем моря
-
0-100 м над уровнем моря
-
101-500 м н.у.м.
-
501-1000 м н.у.м.
-
1001-1500 м н.у.м.
-
1501-2000 м н.у.м.
-
2001-2500 м н.у.м.
-
2501-3000 м н.у.м.
-
3001-4000 м н.у.м.
-
> 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Технология применяется в
-
в условиях выпуклого рельефа
-
в ситуациях вогнутого рельефа
-
не имеет значения
Мощность почв
-
поверхностные (0-20 см)
-
неглубокие (21-50 см)
-
умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
-
глубокие (81-120 см)
-
очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта)
-
грубый крупнозернистый/ лёгкий (песчаный)
-
средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
-
тонкодисперсный/ тяжёлый (глинистый)
Гранулометрический состав (на глубине более 20 см)
-
грубый крупнозернистый/ лёгкий (песчаный)
-
средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
-
тонкодисперсный/ тяжёлый (глинистый)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем почвенном горизонте
-
высокое (> 3%)
-
среднее (1-3%)
-
низкое (< 1%)
Уровень грунтовых вод
-
на поверхности
-
< 5 м
-
5-50 м
-
> 50 м
Доступность поверхностных вод
-
избыток
-
хорошая
-
средняя
-
недостаточны/ отсутствуют
Качество воды (без обработки)
-
питьевая вода хорошего качества
-
питьевая вода плохого качества (необходима обработка)
-
исключительно для сельскохозяйственного использования (орошение)
-
непригодная для использования
Качество воды относится к: одновременно грунтовые и поверхностные воды
Является ли солёность воды проблемой?
Повторяемость затопления
Разнообразие местообитаний
Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Рыночная ориентация
-
натуральное хозяйство (самообеспечение)
-
смешанный (натуральный / коммерческий)
-
товарное/ рыночное хозяйство
Доходы из других источников
-
< 10% всех доходов
-
10-50% всех доходов
-
> 50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка
-
очень плохой
-
плохой
-
средний
-
обеспеченный
-
весьма обеспеченный
Уровень механизации
-
ручной труд
-
тягловая сила
-
механизировано/ есть автотранспорт
Осёдлый или кочевой
-
Осёдлый
-
Полукочевой
-
Кочевой
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство
-
частное/ домовладение
-
группа/ община
-
кооператив
-
использующее наемных работников (компания, государство)
Возраст
-
дети
-
молодёжь
-
средний возраст
-
пожилой
Площадь, используемая домохозяйством
-
< 0,5 га
-
0,5-1 га
-
1-2 га
-
2-5 га
-
5-15 га
-
15-50 га
-
50-100 га
-
100-500 га
-
500-1000 га
-
1000-10000 га
-
> 10000 га
Масштаб
-
мелкое
-
среднего размера
-
крупное
Собственность на землю
-
государственная
-
частной компании
-
общинная/ поселковая
-
коллективная
-
индивидуальная, не оформленная в собственность
-
индивидуальная, оформленная в собственность
Права на землепользование
-
неограниченное (неконтролируемое)
-
общинное (контролируемое)
-
аренда
-
индивидуальное
-
provisioning
Права на водовользование
-
неограниченное (неконтролируемое)
-
общинное (контролируемое)
-
аренда
-
индивидуальное
Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
занятость (вне хозяйства)
транспорт и дорожная сеть
водоснабжение и канализация
Влияние
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность сельскохозяйственных культур
Improved soil health and diversity with reduces pest issues
качество урожая
Improved soil health and diversity with reduces pest issues
производство кормов
Improved soil health and diversity with reduces pest issues
качество кормов
Improved soil health and diversity with reduces pest issues
производство продуктов животноводства
Better diversity of fodder available is producing healthier and better quality animals
разнообразие продукции
Sward mix in cover crop is very diverse
качество питьевой воды
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water quality related impacts
доступность воды для скота
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water related loss impacts
качество воды для скота
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water quality related impacts
доходы хозяйства
Improved crop and animal production
объем работ
Greater workload to rotationally graze and manage crop effectively in an organic system (i.e. can't rely on spraying to solve problems). Yet, benefits outweigh extra workload.
Социальное и культурное воздействие
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Vastly improved understanding through SLM expert advice and practical learning from doing SLM technology.
Экологическое воздействие
количество воды
Cover crops help maintain soil moisture and reduce runoff through root system, improving water quantity held in field.
качество воды
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water quality related impacts
поверхностный сток
Cover crops reduce soil wash-off and other water quality related impacts
испарение
Cover crops help maintain soil moisture and reduce runoff through root system, improving water quantity held in field.
влажность почв
Cover crops help maintain soil moisture and reduce runoff through root system, improving water quantity held in field.
почвенный покров
Cover crops design is to cover soil and reduce soil loss
утрата почв
Cover crops design is to cover soil and reduce soil loss
образование корки на поверхности почв/ запечатывание
Cover crops design is to cover soil and reduce soil crusting
уплотнение почв
Reduced tillage techniques and less passes across fields with machinery as no spraying due to organic system reduces compaction.
круговорот/ восполнение питательных веществ
Selected species of cover crops help recharge nutrient availability in the soil
почвенное / подземное органическое вещество/ углерод
Cover crop rooting system & waste inversion as green manure increases the soil organic matter below ground.
растительный покров
Cover crops design is to cover soil and reduce soil crusting
биомасса/ содержание углерода в надземной биомассе
Greater crop cover and thus more biomass above ground
разнообразие флоры
Well designed mixed cover crop seed mixes, although more expensive, provide a specialised plant diversity ideal for the farm system requirements.
полезные виды (дождевые черви, опылители, некоторые хищники)
Certain cover crops can attract beneficial species and help control pests and diseases
разнообразие местообитаний
A diverse vegetation supports greater habitat diversity
борьба с вредителями/ болезнями
Certain cover crops can attract beneficial species and help control pests and diseases
последствия наводнений
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing flood risk and impact
оползни и селевые потоки
Cover crops slow surface run off and can hold a greater water capacity reducing potential for debris flows in storm events
влияние засух
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing drought impacts
Влияние за пределами территории применения
затопление участков ниже по течению (нежелательное)
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing flood risk and impact
загрязнение подземных/ речных вод
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing potential for debris flows and nutrient leaching downstream
буферная/ фильтрационная способность (почв, растительности, водно-болотных угодий)
Cover crops slow surface runoff and can hold a greater water capacity reducing potential for debris flows and nutrient leaching downstream
Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе
крайне отрицательно
очень позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе
крайне отрицательно
очень позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с затратами на техническое обслуживание
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе
крайне отрицательно
очень позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе
крайне отрицательно
очень позитивное
Изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
среднегодовые температуры увеличилось
среднегодовое количество осадков увеличилось
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Внедрение и адаптация
Доля землепользователей (в процентах), применяющих Технологию
-
отдельные случаи/ эксперимент
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
Была ли Технология УЗП модифицирована в недавнее время с целью адаптации к меняющимся условиям среды?
К каким именно изменяющимся условиям среды?
-
изменения климата/ экстремальные погодные явления
-
изменяющиеся условия рынка
-
доступность рабочей силы (например, из-за миграции населения)
-
Livestock feeding, economic interest, societal expectations
Species are selected according to their ability to cover, feed and work the soil. To do this, species are chosen for their diversity and complementary according to their root system: tap roots, adventitious roots, surface lateral roots, etc.
For the past 2 years, the Biomax green manure + RGA regrowth mix has been grazed by heifers.
Заключительные положения и извлечённые уроки
Сильные стороны: по мнению землепользователей
-
Sustain ecosystem health: no pest and disease problems, good herd health.
-
Carbon sequestration by enrichment of the soil with organic matter and by the work of earthworms favouring ecosystem functioning.
-
Protection of the soil and surface biodiversity because of maintained plant cover.
-
Increased weed control due to plant canopies and fertilisation effect of green manure.
-
Planted cover crops used as livestock feed during winter.
-
Sustained ecosystem integrity reduces/counters ecosystem degradation by using multiple ecosystem functions: Complementarity, Continuity of soil life, Green fertilizer essential in the farming system, Feeding the livestock.
Сильные стороны: по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов
-
Multi-species cover is conducive to soil quality: production of a high above-ground and root biomass that promotes soil life, soil structuring at depth (tap roots) and on the surface (superficial roots) by the effect of organic matter inputs.
-
Multi-species cover provides shelter and cover for small fauna: seeds for the winter survival of the fauna, plants that are tiered at different heights without being too dense for wild game to move around while being protected.
-
The different families that can be planted under cover are:
- Grasses are generally easy to grow and are valued by animals (oats, rye and sorghum).
- Leguminous plants improve the performance of cover crops. They are regulating plants that trap nitrogen and fix it in the soil. This is then used by the crop that follows.
- Cruciferous plants are to be reserved for cereal rotations without rapeseed or vegetables.
- Compounds (nyger and sunflower) are interesting for biomass production.
-
Well-developed canopies have a competitive effect against weeds (germination inhibition, smothering, allelopathy). The aim is to have a rapidly developing canopy. It is necessary to limit the risks of shot blasting by sowing the canopy on clean soil, especially for early sowing (especially for short-cycle weeds: ragwort, bluegrass, Persian speedwell).
Some species have allelopathic effects, i.e. they secrete inhibiting substances (the intensity of the allelopathic effect is taken from the Sem-Partners catalogue, see bibliography):
- Diploid oats: allelopathic effect not demonstrated. Little is known about the mechanisms and molecules involved.
- Spring Oats, Fenugreek, Gesse, Moha : average allelopathic effect, mechanisms and molecules involved are not well known.
- Camelina, Radish: strong allelopathic effect (glucosinolates).
- Winter mustard, Spring mustard: action of glucosinolates against nematodes (Heterodera Schaati and Meloidogyne chitwoodi) in biofumigation.
- Buckwheat (Sarrazin): strong allelopathic effect. Little is known about the mechanisms and molecules involved.
-
A plant cover provides additional fodder, 3 to 4 tonnes of dry matter can be produced depending on the species and sowing date.
Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски: по мнению землепользователейвозможные пути преодоления
-
Difficulties in establishing cover: difficult lifting in dry areas
Conditions for successful plant cover
Sow as soon as possible
Take advantage of the humidity just after harvest
-
Late sowing of cover crops: no or little flowering and therefore little beneficial effect
Early establishment of complementary species
-
High cost of purchased seed of mixed protein cover crops
Self-production of farm-saved seed
Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски: по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистоввозможные пути преодоления
-
In order to increase the potential of the canopies for bees, it is necessary to sow in the first half of August for flowering in the autumn. Some species are rich in nectar or pollen: rapeseed, white mustard, phacelia, radish, sunflower, clover, vetch. However, some species have extra-floral nectar such as sunflower, vetch and faba beans. That is to say that they secrete nectar outside the flowering period.
Sow in the first half of August as soon as the cereals are harvested to take advantage of the residual moisture which is conducive to good emergence.
-
The development of RGA on the farm.
Ploughing can slow down the development of RGA.
-
The cost of destroying the canopy is high (45€/ha excluding labour) with the 2 cross passes of rolling spade.
3) Cost of some tools for destroying the cover crops:
Independent disc stubble cultivator 3m= 33€/ha
Cultivator 3.5m = 20€/ha
Mulcher 3m = 27 €/ha
Cambridge roller 8m = 16€/ha
Blade roller 3m = 17€/ha
Assumptions: replacement value depreciated over 10 years + maintenance, tractor cost 20€/hour, labour not included
-
Before grazing a multi-species canopy, it is advisable to check the absence of toxic species (e.g. buckwheat)
Not known
-
The doses and costs of implementing protein blend cutlery in interculture are high.
- Adjusting Mixed Doses
- Self-production of farm-saved seeds
- Mixture with recommended doses
(OBS: Do not exceed 120% pure dose)
Справочные материалы
Editors
-
David Robinson
-
David Norris
-
Sabine Reinsch
Рецензент
-
Rima Mekdaschi Studer
-
William Critchley
Продолжительность применения Технологии: 17 февраля 2020 г.
Последнее обновление: 16 августа 2021 г.
Ответственные специалисты
-
Christiane Joubioux - co-compiler
-
Patrice Le Callonnec - землепользователь
-
Sylvie Guiet - Специалист по УЗП
Полное описание в базе данных ВОКАТ
Документирование осуществлялось при участии
Организация
- Association des Chambres d’agriculture de l’Arc Atlantique (AC3A) - Франция
- UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (CEH) - Великобритания
Проект
- European Interreg project FABulous Farmers
Ключевые ссылки
-
Couvert végétal, une culture à part entière, Terra du 21 juin 2013: Terra (Réussir terragricoles de Bretagne) du 21 juin 2013
-
Couvert végétal, de réels avantages agronomiques, Terra 12 juin 2015: Terra 12 juin 2015
-
Couverts végétaux, la destruction possible dès le 1er février, Terra du 15 janvier 2016: Terra du 15 janvier 2016
Ссылки на материалы по теме, доступные онлайн















