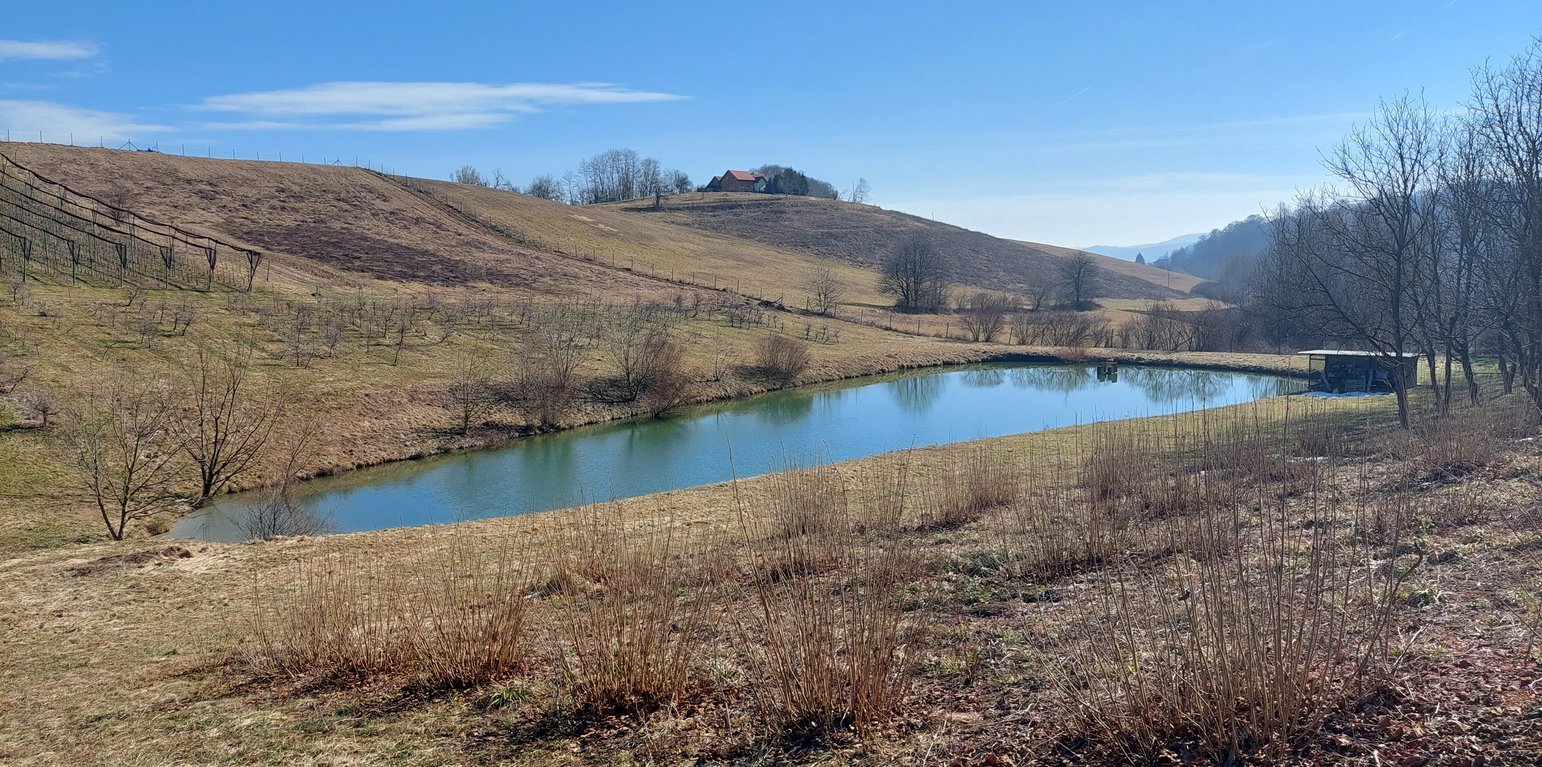




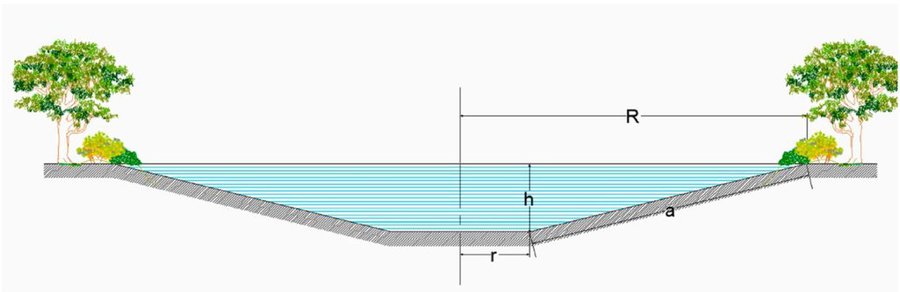
“Retention ponds” comprise both simple, small ponds (up to 2000 m3, up to 4 m deep) and larger, more complex reservoirs (greater than 2000 m3). Retention ponds are designed to provide storage capacity to attenuate surface runoff during rainfall events. Each consists of a permanent ponded area with landscaped banks. Retention ponds achieve both storm water attenuation and water quality treatment through supplementary storage capacity of runoff. Water is then released at a controlled rate once the risk of flooding has passed. The technology can be applied in a natural or human environment. Before construction of a pond it is essential to follow legislation, which covers conditions and restrictions for the given location. Once a site is selected, technical documentation is prepared: first the conceptual design, then documentation for obtaining opinion, consent and a building permit. Later there is also project documentation for implementation. If the water is to be used for other purposes as well (e.g. for irrigation), it is necessary to plan for usage and environmental impact. Retention and still water promotes pollutant removal through sedimentation, while aquatic vegetation and biological uptake mechanisms offer additional treatment. Retention ponds are effective in removing urban pollutants and improving water quality.
They are created either by using an existing natural depression, or by excavating a new depression, or by constructing embankments. Existing natural water bodies should not be used however, due to the risk that pollution events and poorer water quality might disturb/damage the natural ecology of the system. A great benefit of retention ponds is that they hold water when there is an excess of it, which can be used later when water is not available (e.g. for irrigation). Irrigation users are farmers, so they see the advantage of using a retention system. In addition to irrigation, water has also been needed in recent years for anti-frost systems (sprinkling a consistent layer of water on the crop during an entire frost event until temperatures are back to safe levels). Disadvantages are mainly restrictions in some areas (e.g. protected areas), preparation of demanding documentation and bureaucracy, and lengthy procedures for obtaining permits.
Местоположение: Pesnica, Podravska region, Slovenia, Словения
Число исследованных участков, где применяется Технология: 2-10 участков
Пространственное распространение Технологии: примененяется точечно/ на небольших участках
На постоянно охраняемой территории?: Нет
Продолжительность применения Технологии: 10-50 лет назад
Тип внедрения/ применения
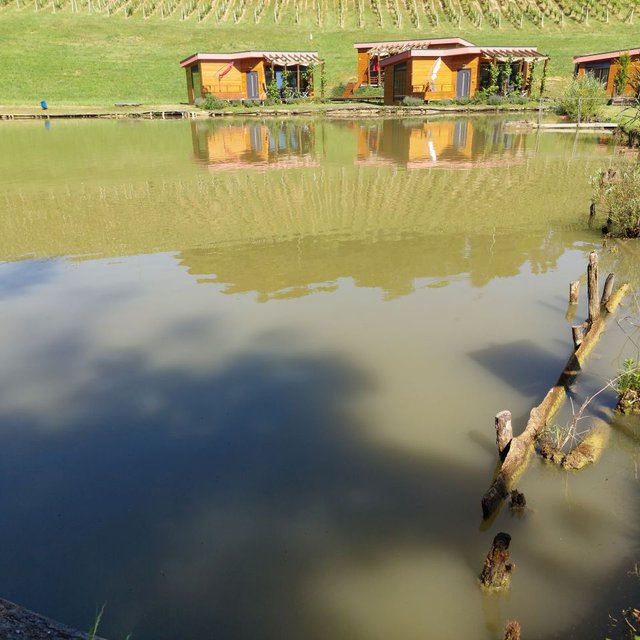






Irrigation has avoided reduction in production due to drought and frost
Improved fruit health (protection against drought and frost)
Protection against drought and frost
Change of land use (from agricultural land to water body).
Increased the complexity of management.
Production and income stability.
Possible diversification on farm (tourism and recreation).
Demanding maintenance and increased complexity of management.
Lower risk of production failure, stability in business, motivation to do business in agriculture
Possible additional activities on farm.
An example of good practice for the community.
With positive effects more interest of the farmer in sustainable production.
Water available in dry months.
Increased in case of irrigation
Planting species near/around the pond.
Danger in case of improper maintenance.
For a green reservoir, a lot of green infrastructure is placed next to it, which serves as protection for animals and plants (beneficial).
Proximity to water.
It affects the microclimate, more humidity, slower temperature fluctuations
It is slightly increased as the ponds provide water during dry periods.
Improved mainly due to water retention during wet seasons for use in dry periods.
Reduced due to the capacity of ponds to retain excess water during times when rivers may flood.
The reservoir also enables sediment retention, preventing sediment from reaching downstream watercourses.
Many studies indicate that ponds can trap harmful substances, causing them to settle or undergo processes (acting as natural purification systems, especially when appropriate plant species are involved). This helps maintain cleaner downstream flows in terms of pollutants.
The pond's ability to retain pollutants also contributes to its buffering and filtering capacity.