Integrated Wetlands Biodiversity Conservation Project [Зимбабве]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Kalulu Mumpande
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: William Critchley, Joana Eichenberger
IWBCP
approaches_7367 - Зимбабве
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Подхода
Ответственный (-ые) специалист (-ы)
co-compiler:
Mumpande Kalulu
+263773667529 / +263773667529
mumpandekalulu@yahoo.com / safesewa@gmail.com
Safe Environment & Wildlife Africa
Stand No. 1659 Medium Density Binga
Зимбабве
Специалист по УЗП:
Mumkombwe Jane
+263 773666246 / +263 773666246
katemunkombwe46@gmail.com / katemunkombwe46@gmail.com
Agriculture & Rural Development Advisory Services (ARDAS)
Binga medium Density Stand no// 872 Binga
Зимбабве
землепользователь:
Susan Mwembe
+263782644815 / +263782644815
Nil / Nil
Smallholder Farmer
Manjolo Primary School P.O Box 10 Binga
Зимбабве
землепользователь:
Mudenda Naison
+263771152184 / +263771152184
Nil / Nil
Smallholder Farmer
Manjolo Primary School P.O Box 10 Binga
Зимбабве
Indigenous Knowledge Guardian:
Mwembe Nomai
+263775256810 (Daughter) / +263775256810 (Daughter)
Nil / Nil
Community Elderly
Manjolo Primary School P.O Box 10 Binga
Зимбабве
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
Safe Environment & Wildlife Africa (SEWA)1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование собранных ВОКАТ данных
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
21/10/2024
Составитель и ответственный/-ые специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
2. Описание Подхода УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Подхода
The integrated wetlands biodiversity conservation project aims to restore wetlands and associated biodiversity. The approach strengthens the resilience of neighbouring marginalized groups to climate change through developing lifelong skills and providing livelihoods support.
2.2 Подробное описание Подхода
Подробное описание Подхода:
The Integrated Wetlands Biodiversity Conservation Project aims to restore wetlands and associated biodiversity. It is a 2-year project which started in June 2023 with the support of a USD 50,000.00 grant from the Global Environment Facility Small Grants Programme, implemented by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP-GEFSGP). The approach strengthens the resilience of neighbouring community to climate change through developing lifelong skills and providing livelihood support. It targets those marginalized groups surrounding protected areas, who experience severe droughts due to high cases of human-wildlife conflicts, making them highly food insecure. The approach is simultaneously improving sustainable management and utilization of the Masibinta wetland and its catchment.
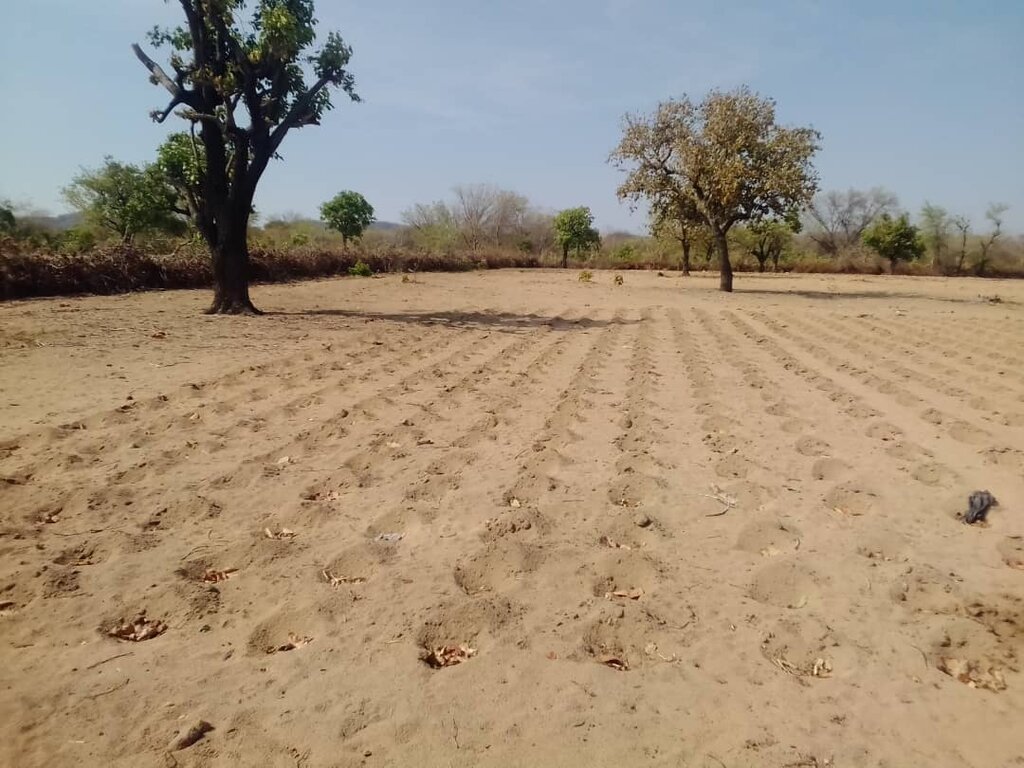
Technical activities are targeted at restoring Masibinta wetland’s ecological integrity by protecting the wetland, implementing conservation agriculture in its catchment, reforesting bare land, controlling and reshaping gullies to create small ponds, and removing a bushy invasive species (Ipomoea carnea) while making compost from its leaves and branches. The ponds increase the recharge of the wetland. This helps provide water to the community and at the same time acts as a barrier to soil erosion and epicenters for natural vegetative cover regeneration and biodiversity restoration. Land degradation neutrality is an overall goal.
Specific targets include:
(a) Protection, rehabilitation and conservation of 13 hectares of Masibinta wetlands, as well as reclamation of degraded land in and around the wetland, while increasing the capacity of the community members to conserve biodiversity.
(b) Increasing access of 387 households to adequate and clean water.
(c) Reduction of invasive species in the wetlands by 80%, and reclamation of 1000 m of gullies.
(d) Promotion of sustainable use and management of Masibinta wetland through regenerative agriculture, livelihood support and imparting lifelong skills to 50 youths (30 females and 20 males).
A variety of technical and social methods are employed:
(a) Grey and Green Infrastructure (GGI): hybrid restoration techniques that involve the combination of engineered structures and Nature-based Solutions (NbS).
(b) Regenerative agriculture: including mulching, mixed cultivation, crop rotation, agroforestry, use of organic manure in nutrition gardens, and zero tillage (“Maganko”).
(c) Incentives: monetary incentives to the community members who offer their labour.
(d) Self-mobilization.
(e) Peer-to-peer learning.
(f) Problem-solving.
The stages of implementation involved are:
(a) Baseline survey,
(b) Education and training of project support staff, stakeholders,
(c) Monitoring, Evaluation and Learning (MEL),
(d) Livelihood support,
(e) Protection of the wetland, then MEL,
(f) Borehole Drilling,
(g) Invasive species management, then MEL,
(h) Gully modification, and
(i) Evaluation and Learning.
The stakeholders involved and their roles are:
(a) Environmental Management Agency (EMA): Implement and monitor restoration activities in the wetland and assess the impact of barricading the gully on the environment.
(b) Forestry Commission (FC): Nursery establishment, management and tree planting.
(c) Agriculture and Rural Advisory Services (ARDAS): Train farmers on agroforestry, goat rearing, climate-smart agriculture, gully reclamation, and polyculture.
(d) Rural and Infrastructure Development Agency (RIDA): oversees all engineering work.
(e) Ministry of Youth Empowerment Development and Vocational Training (MYEDVT): Monitoring youth engagement and benefits.
(f) Ministry of Women Affairs Community Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MWACSMED): Tracked and monitored inclusion and entrepreneurship.
(h) United Nations Development Programme – Grant disbursement, monitoring and evaluating the implementation and sustainability of IWBCP at the national level in line with the GEFSGP expectations.
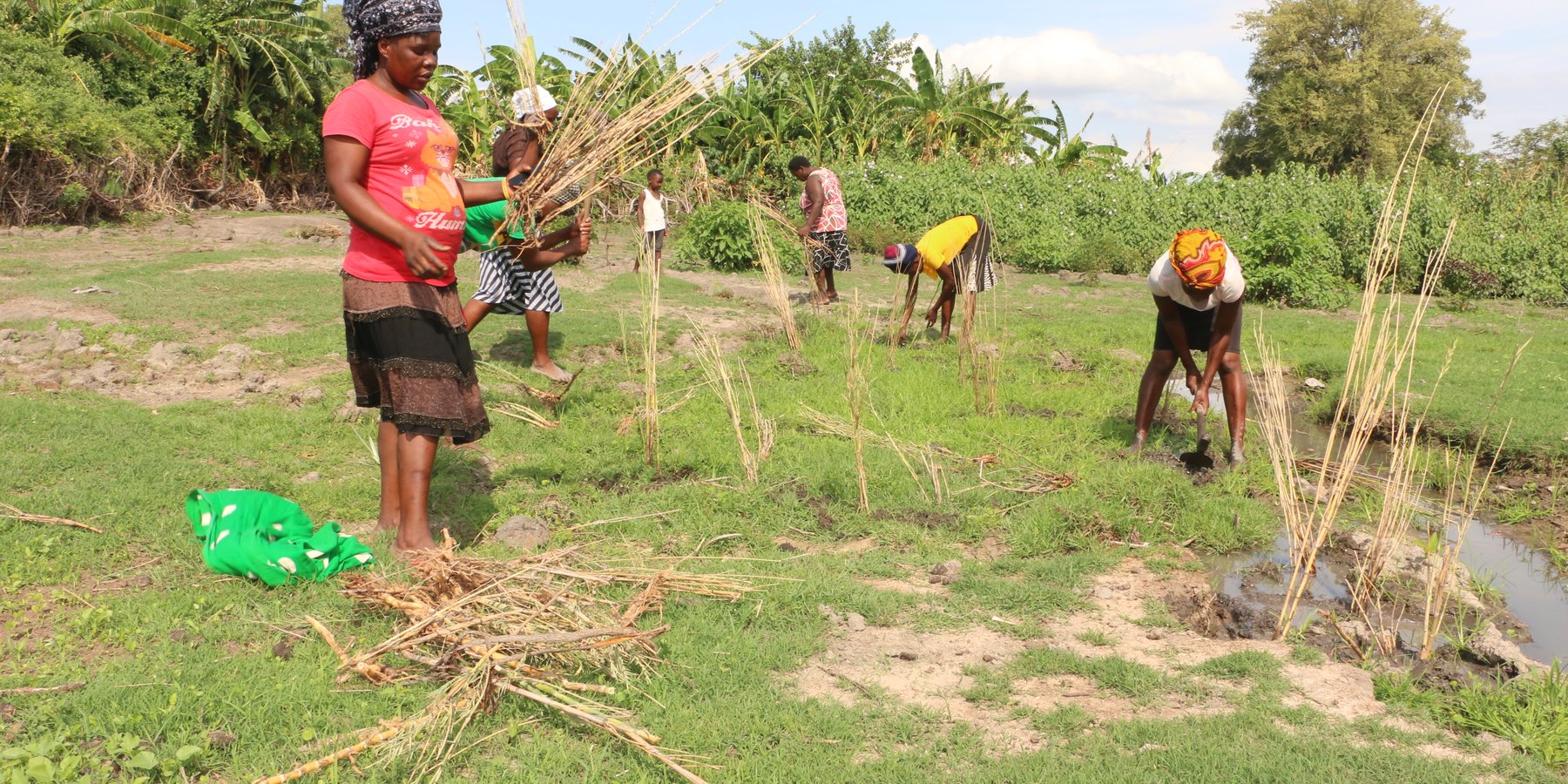
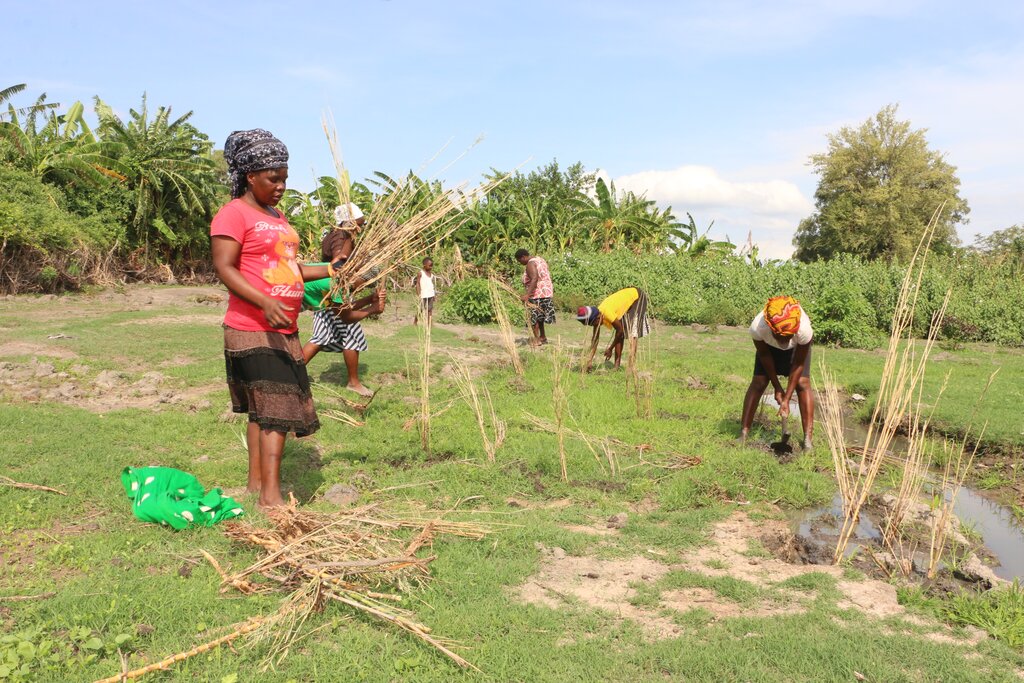
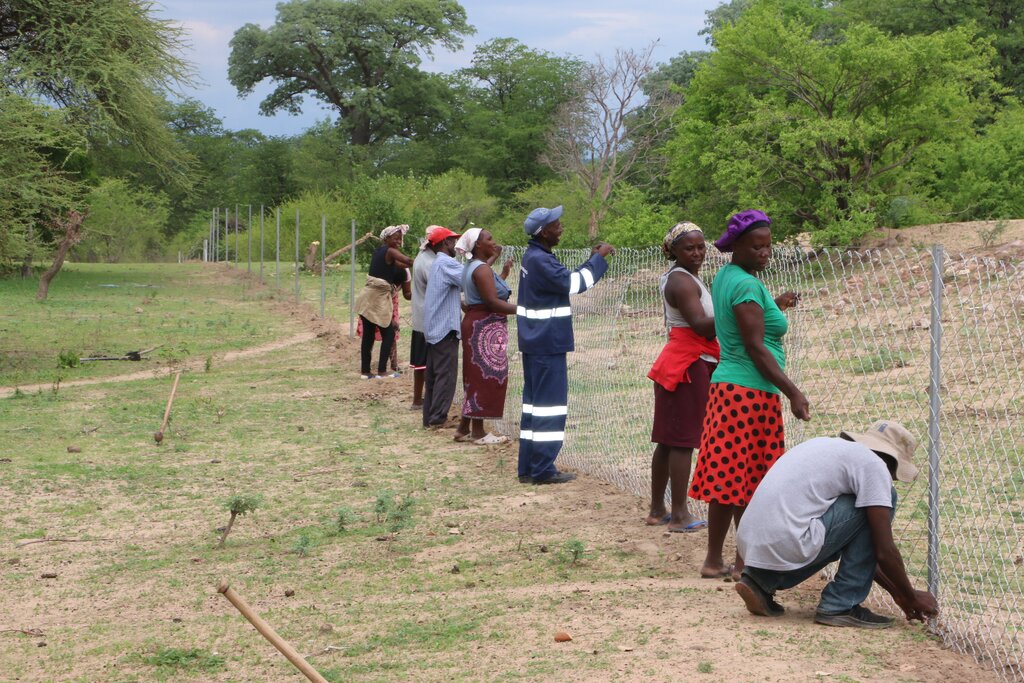
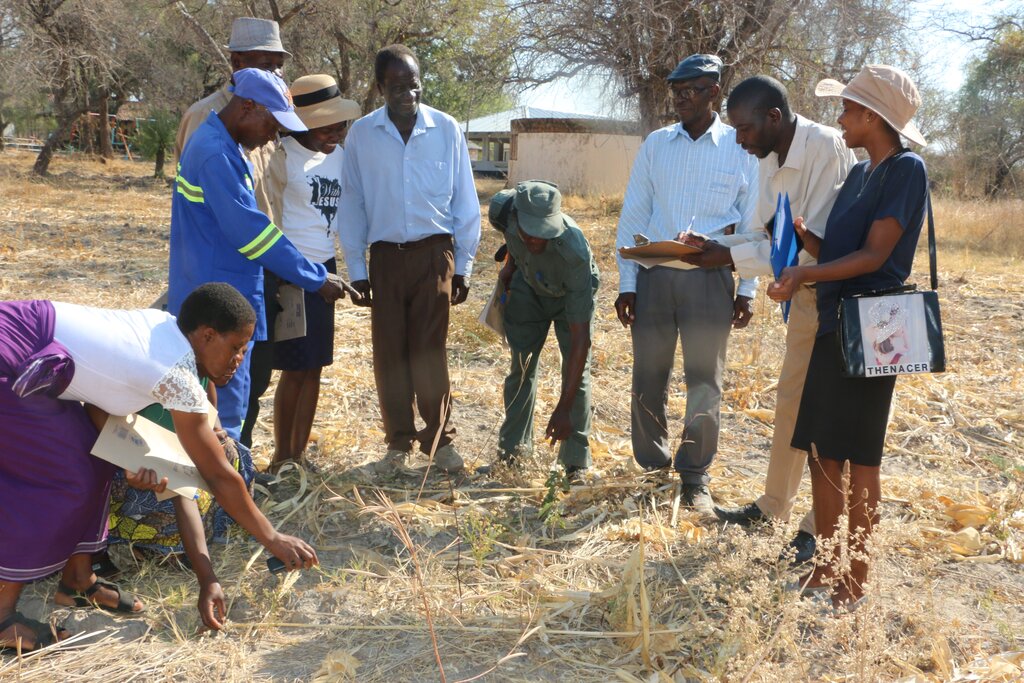
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Подход
2.4 Видеоматериалы по применению Подхода
Дата:
02/02/2024
Место:
Manjolo
Автор съемки:
Kalulu Mumpande
2.5 Страна/ регион/ место, где применялся Подход
Страна:
Зимбабве
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Matebeleland North
Более точная привязка места:
Binga
Комментарии:
Masibinta wetland, surrounded by bare catchment areas
Map
×2.6 Даты начала и окончания реализации Подхода
Год начала реализации:
2023
Если год начала реализации Подхода достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
менее 10 лет назад (недавняя)
Год окончания (Если Подход больше не применяется):
2025
2.7 Тип Подхода
- в рамках проекта/ программы
2.8 Каковы цели/ задачи Подхода
The Approach aimed at developing an environmentally responsive community, capable of managing and utilizing Masibinta Wetland most sustainably through:
(a)Increasing knowledge and skills in restoring degraded and conserving the restored land
(b)Improving perceptions on biodiversity and building best practices which promote sustainability of the natural resources capital
(c)Increasing conservation benefit sharing and improving governance of the natural resources
2.9 Условия содействующие применению Технологии/ Технологий в рамках Подхода или затрудняющие его
Сотрудничество/ координация действий
- содействуют
Collaboration between the stakeholder and the community enabled the Approach to win a Provincial Award: Excellence in Biodiversity Restoration and Social Impact.
Нормативно-правовая база (землевладение, права на земле- и водопользование)
- затрудняют
Land is owned along family lines which make it difficult to restore. For example a 100-meters portion of a gully which was reclaimed was later cleared to paved a way for a garden by the family member.
Программные документы/ руководящие установки
- затрудняют
Lack of policy on conservation cultivation
Осведомленность в области УЗП, доступность технической поддержки
- затрудняют
The stakeholders have limited knowledge on disaster risk reduction and regenerative farming
Рынки (для приобретения материалов и услуг, продажи продукции) и цены
- затрудняют
Limited access to markets which offers competitive prices for the landers as producers.
Объем работ, доступность рабочей силы
- затрудняют
The work load is huge and the manpower is limited. The support staff were on a voluntary contract.
3. Участие и распределение ролей заинтересованных сторон
3.1 Заинтересованные стороны, участвующие в реализации Подхода и их роли
- местные землепользователи/ местные сообщества
Traditional leaders and community members
Community members provided labour and security of materials and food during the Approach's activities. They also monitored and evaluated the Approach and provided valuable lessons. Traditional leadership provided the approach's local oversight role, whipped members into line, provided Indigenous knowledge, and guided the implementation process in accordance with the values and beliefs of the Manjolo community. Traditional leadership was key in information dissemination and resolution of issues which would otherwise affect the success of the Approach
- эксперты по УЗП/ сельскому хозяйству
Agriculture & Rural Development Advisory Services (ARDAS), ZimParks, Forest Commission, Environmental Management Agency (EMA), Small to Medium Enterprises, Ministry of Youth, Social Development, Ministry of Information, Ministry of Health and Child Welfare
Provided technical support, training community members, and local management committees. Supervising activities and evaluating the Approach
- местные власти
Binga District Development Committee
Monitoring and Evaluation of the Approach
Providing supportive framework and ensuring that the Approach keep in line with the district's development agenda
Если участвовало несколько заинтересованных сторон, назовите ведущую организацию:
Environment Management Agency (EMA) and Agriculture & Rural Development Advisory Services (ARDAS)
3.2 Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ на разных стадиях реализации Подхода
| Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ | Перечислите участников и опишите их вовлеченность | |
|---|---|---|
| инициирование/ мотивация | самоорганизация | Smallholder farmers The initiation began in October 2022 where the organized a meeting and invited SEWA. At this meeting the farmer highlighted the degradation of Masibinta wetland and how the degradation was negatively affecting their lives. The farmers gave suggestion on possible solutions to the challenges faced. |
| планирование | интерактивное | Smallholder farmers, youth, traditional leaders, local business community, church leaders, teachers, Rural Care Givers, Health Workers, Resources Monitors, Counsellors, People with Disability In December 2022, the farmers who initiated the Approach mobilized community members to a planning meetings, developed activities, pledged own contribution to the Approach, outlined roles of each social group in the Approach, developed ways of mobilizing locally available materials and selected management committees and local lines of communication. They also identified potential challenges and suggested ways of dealing with the challenges that could otherwise arise from the Approach |
| выполнение | интерактивное | The smallholder farmers, traditional leaders, local business community, youth, church leaders, teachers, Rural Care Givers, Health Workers, Resources Monitors, Counsellors, People with Disability The implementation started in July 2023 after GEFSGP had supported the Approach with a grant of $50,000.00 through the UNDP. The community members worked together and provided labour and security of materials and food during the Approach's activities. They also monitored and evaluated the Approach and provided valuable lessons. Traditional leadership provided the approach's local oversight role, whipped members into line, provided Indigenous knowledge, and guided the implementation process in accordance with the values and beliefs of the Manjolo community. Traditional leadership was key in information dissemination and resolution of issues which would otherwise affect the success of the Approach |
| мониторинг/ оценка | интерактивное | Small holder farmers, youth, traditional leaders, local business community, church leaders, teachers, Rural Care Givers, Health Workers, Resources Monitors, Counsellors, and People with Disability, These provided the views on how the Approach impacted their lives and also on what needed to be changed. |
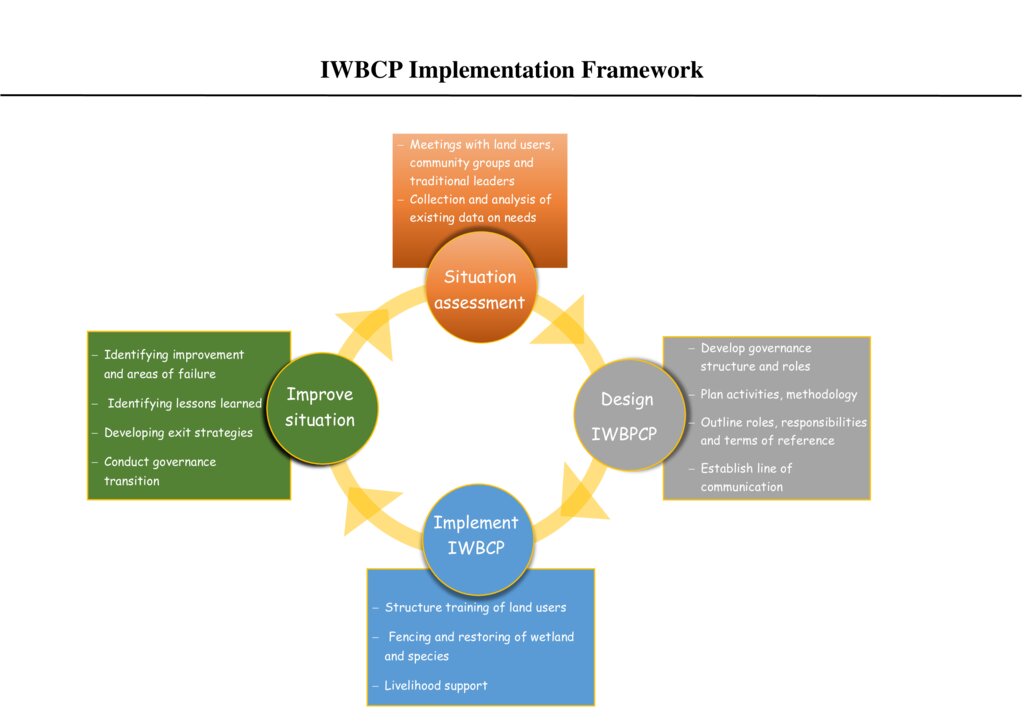
3.3 Схема реализации (если имеется)
Описание:
Integrated Wetland Biodiversity Conservation Project (IWBCP) Implementation framework
Автор:
Mumpande Kalulu
3.4 Принятие решений по выбору Технологии/ Технологий УЗП
Укажите, кто принимал решение по выбору применяемой Технологии/ Технологий:
- все участники как часть процесса совместных действий
Поясните на чём было основано принятие решений:
- личный опыт и мнения (незадокументированные)
4. Техническая поддержка, повышение компетенций и управление знаниями
4.1 Повышение компетенций/ обучение
Проводилось ли обучение землепользователей/ других заинтересованных лиц?
Да
Если существенно, укажите гендерный и возрастной состав, статус, этническую принадлежность и т.д.
124 smallholder farmers (69 females, 55 males), 10 Village Heads (2 females, 11males), and 2 Ward-based Environment Monitors (all males) were capacity developed from the 32 hours structured training on land and biodiversity restoration and conservation. During the training the participants were engaged through presentations, drama, role plays, scenarios, problem-solving and field trips. The key stakeholders drawn from government line ministries, and Binga Rural District Council trained the the beneficiaries.
Тип обучения:
- в ходе работы
- обмен опытом между фермерами
- общие собрания
Рассматриваемые темы:
Biodiversity conservation, project infrastructure management, sustainable land management, agroforestry, gully reclamation, conservation farming, climate change, and environmental policies
Комментарии:
The training sessions were not enough due to limited budget. Each training was conducted conducted over for 8hrs and the participants had little time for hands-on participation.
4.2 Консультационные услуги
Есть ли у землепользователей возможность получать консультации?
Да
Укажите, где именно оказываются консультационные услуги:
- на полях землепользователей
- в постоянно функционирующих центрах
Описание/ комментарий:
The Rural & Infrastrure Development Agency , Forest Commission and Agriculture & Rural Development Advisory Services provided advisory services to land users crop fields preparation, gully reclamation, tree planting, and wetland management
4.3 Институциональная (организационная) поддержка
В ходе реализации Подхода были ли организованы новые институциональные структуры или поддержаны уже существующие?
- да, умеренно
Укажите уровень, на котором структуры были укреплены или вновь созданы:
- местные
Опишите организацию, функции и ответственность, членство и т.д.
Community Management Committee and local constitution
Supervision of the land users and enforcing constitution
Укажите тип поддержки:
- повышение компетенций/ обучение
Подробнее:
The management committee was trained once on their roles. However, more structured training would enhance their discharge of duties
4.4 Мониторинг и оценка
Являются ли мониторинг и оценка частью Подхода?
Да
Комментарии:
Continuous monitoring was carried out by the Approach support staff. Monitoring and Evaluation was done quarterly, involving all key stakeholders
Если да, будет ли данный документ использоваться для мониторинга и оценки?
Нет
4.5 Научные исследования
Были ли научные исследования частью Подхода?
Нет
5. Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка
5.1 Годовой бюджет мероприятий по УЗП в рамках Подхода
Укажите годовой бюджет мероприятий УЗП в рамках Подхода в долларах США :
25000,00
Комментарий (например, основные источники финансирования/ ключевые доноры):
-Co-funding
-Global Environment Facility Small Grants Programme, implemented by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP_GEFSGP)
5.2 Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка, предоставляемая землепользователям
Предоставлялась ли землепользователям финансовая/ материальная поддержка для применения Технологии /Технологий?
Да
Если да, укажите тип(-ы) поддержки, кто ее предоставил и условия предоставления:
Fencing materials, stationary, cement, goats, seed inputs
Provider: UNDP_GEFSGP
5.3 Субсидии на отдельные затраты (включая оплату труда)
- оборудование
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| инвентарь/ инструменты | профинансированы частично | |
| Fencing material | профинансированы полностью | |
- сельскохозяйственные
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| семена | профинансированы частично | |
- инфраструктура
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| Fence | профинансированы полностью | |
Если труд землепользователя был существенным вкладом, укажите, был ли этот вклад:
- добровольный
Комментарии:
The land user provided voluntary work during the fencing of the wetland. An additional funding of $15,000.00 for the management of the Ipomoea carnea and gully medication has been secured from he G20 Global Land Restoration Initiative. Under these activities, the land users will be provided and an incentive of $1.50 per day per individual for the provision of labour. The activities are yet to be implemented once the funds are disbursement into SEWA's bank account.
5.4 Кредитование
Предоставлялись ли в рамках Подхода кредиты на мероприятия УЗП?
Нет
5.5 Другие методы или инструменты стимулирования
Использовались ли другие методы или инструменты стимулирования для продвижения Технологий УЗП?
Да
Если да, поясните:
Monetary incentive (for activities which are yet to be done using the additional support from the G20 Global Land Restoration Initiative)
6. Анализ влияния и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Подхода
Сумел ли Подход расширить возможности местных землепользователей, повысить участие заинтересованных сторон?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
124 land users were trained, supported with seed imputes, and goats.
Сумел ли Подход дать возможность принимать решения на основе подтвержденных фактов?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Decisions were made based on data gathered from community engagements, lessons learned from the before projects in the area and the surveys conducted as a baseline.
Сумел ли Подход помочь землепользователям внедрить и поддерживать технологии УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Land users have reclaimed 100 metres of gullies, implemented conservation cultivation, used nature-based approaches to restore the wetland
Сумел ли Подход улучшить согласованность действий и повысить рентабельность применения практик УЗП:
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
The use of Nature-based Solutions and indigenous knowledge reduced the cost of implementing the SLM as such approaches are cheaper in terms of cost. Approach improved coordination between the project management and land users through clearly defined roles and lines of communication
Сумел ли Подход мобилизовать/ расширить доступ к финансовым ресурсам для применения практик УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Mobilized finances from the Global Environment Facility Small Grants Programme through the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP-GEFSGP). Finances have also been mobilized from the G20 Global Land Initiative, though yet to be disbursed into SEWA's bank account.
Сумел ли Подход расширить знания и возможности землепользователей в применении практик УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
124 land users were trained on SLM and were given kowledge material such as brochures.
Сумел ли Подход расширить знания и возможности других заинтересованных сторон?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Not much training of stakeholders was done. However the stakeholders drew lessons from the project and shared their experience during project progress update meetings.
Сумел ли Подход укрепить сотрудничество между заинтересоваными сторонами/ выстроить механизмы сотрудничества?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Each and every stakeholder involved in the project had clearly defined roles and synergies
Сумел ли Подход снизить остроту конфликтов?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
The fencing of wetland including the nutrition gardens and the development of the land users' constitution mitigated conflicts
Сумел ли Подход расширить возможности социально и экономически уязвимых групп?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Assisted women, youth and people with disability with female goats. These groups were trained under the same rood
Сумел ли Подход стимулировать молодежь/ будущее поколение землепользователей заниматься УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Financial limitation reduced the engagement of youth in Manjolo as the effective method of engaging youth in Manjolo require a reasonable budget
Сумел ли Подход разрешить правовые проблемы землевладения/ землепользования, препятствующие использованию технологий УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
The Approach has not yet tackled the issue
Сумел ли Подход способствовать улучшению продовольственой безопасности/ качества питания?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Through crop yields, and income generation projects.
Сумел ли Подход расширить доступ к рынкам?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Local market. Land users are supply Boarding School and a hospital with green vegetables
Сумел ли Подход улучшить санитарные условия и доступ к водоснабжению?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Boreholes Drilling couldn't find water.
Сумел ли Подход привести к более эффективному использованию электроэнергии/ возобновляемых источников энергии?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
The Approach did not look at energy
Сумел ли Подход улучшить способность землепользователей адаптироваться к изменениям климата и смягчать последствия катастрофических погодных явлений?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Through training and livelihoods support
2 youth were employed for fencing
6.2 Основные причины, побуждающие землепользователей внедрять УЗП
- рост продуктивности
Improved protection of their crops in nutrition gardens, increased crop production, ownership and management of the wetland.
- рост прибыли (доходности) и рентабельности
81 out of 144 wetland users reported an average increase of 32% from their incomes over the last cropping season. 79 out of 144 reported an average increase of 40 kg of maize production in the last between November 2023 and March 2024. All wetland user reported reduced destruction of their crops by livestock over the past cropping season.
- снижение деградации земель
67 Farmers adopted the use of organic fertilizers and 23 were involved in the demo plots for poly cropping. The wetland user protected 13 seeps using the reeds. 15 farmers have since abandoned the use of brash wood fencing adopting the edible hedging. These practices have reduced land degradation. However restoration is still ongoing to realize full impact of the Approach.
- снижение риска катастрофических погодных явлений
89 out 144 households which used to miss at least a meal per day during the drought months (July to February) reported that they never missed a meal between July 2024 and October 2024.
- снижение объёма работ
The fencing of wetland has significantly reduced the workload particularly for women and girls who used to spend about 27% of their 24-Hour Day manning their gardens from animals. A 12% decrease in time spend looking after crops has been observed.
- нормативно-правовое регулирование (штрафы)/ контроль
As way of improving sustainability of Masibinta wetland, the community have set rule and regulations for the management of the resources. The trespassers are liable to a commensurate fines and the rules are enforces at local level by the Community Management Committee (CMC) and the traditional leadership. The community members participate in the enforcement of the rules through being own police.
- престиж, общественное давление/ солидарность
Masibinta Wetland saves support 2400 community members and 3 schools with water, livelihoods and income for feeds and health needs. The restoration of the wetland by the Approach has unified different groups in the community by working and living together for a common cause. It has improved social relationships, pride and reduced poverty
- причастность к движению/ проекту/ группе/ сети
As a result of the Approach, SEWA has joined the UNCCD and WOCAT Network.
- экологическая сознательность
The Land Users have formed the Manjolo Environment Defenders Club (MEDC). The MEDC was formed as community initiative led by women after being educated by the Approach on land restoration and Protection. The club carries out peer-to -peer education on best environmental practices, such as encouraging fellow Land Users to use organic fertilizers, stop cutting of trees, accouraging safe use of wetland and monitoring the wetland health. The club started with 4 women but now the membership has grown to 15. This shows improved environmental consciousness as a result of the Approach
- традиции и верования, нравственные ценности
The Approach has improved the Land Users' awareness of the importance of conserving land resources. This motivated them to explore beyond what they were taught. They now value nature more that before the implementation of the approach.
- приобретение знаний и опыта в области УЗП
The training reconceived by the Land Users has equipped them with skills to contract gabions, plants trees, raise tree nurseries for commercial purpose. Two of the youth who were trained in fence installation got contracts on fencing. The farmers who were trained on regenerative agriculture, are now practicing on their crop fields.
- улучшение эстетической привлекательности
The Approach's innovativeness and novelty made to appeal o the Land Users
- снижение остроты конфликтов
Conflicts caused by livestock destroying crops in nutritional gardens have been reduced. However due to the improved habitat conditions, crocodiles and pythons have since invaded the wetland and new conflicts have arisen between these species and the farmers. How, SEWA is working with the Community Resources, Communal Areas Management Programmes For Indigenous Resources (CAMPFIRE) and Zimbabwe Parks & Wildlife Management Authority (ZimParks) in monitoring and relocating the crocodiles and pythons.
6.3 Долгосрочная устойчивость мероприятий в рамках Подхода
Могут ли землепользователи самостоятельно (без внешней поддержки) продолжать применение того, что было реализовано в рамках Подхода?
- да
Если да, опишите как:
In terms of human sustainability, the training that the Land Users have received, skills and knowledge that they have gained will enable them to continue with the project activities without any external support. The involvement of the Land Users in decision making structures and programmes will enable Land Users to make and implement key decisions beyond the external support. The income generating projects and the Internal Savings and Lending Schemes introduced under the Approach will ensure financial sustainability. The training of the stakeholders by the Approach provide the technical sustainability.
6.4 Сильные стороны/ преимущества Подхода
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| The Approach is providing women with financial independence and choices. |
| The Approach is empowering the marginalized community groups with climate resilient and bankable assets. For example 12 youth, 3 people with disability and 10 women have been assisted with 2 female goats, increasing conservation benefits. |
| The land Users view the Approach as their out of hunger and poverty |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| Views the Approach as sustaible and transformative development. |
| The Approach is viewed as practical demonstration of sustainable land management |
| Viewed as a sources of lessons for the partners and environmentalists |
6.5 Слабые стороны/ недостатки Подхода и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| The Approach has a limited thrust on influencing policy and land tenure | Involving policy makers at local level |
| The Approach has not identified learning areas | Identify learning areas through monitoring and evaluation sessions |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| The ponds may cause risk of drowning of children as kids love playing in water | Constructing shallow ponds |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
24
- опросы землепользователей
6
- опросы специалистов/экспертов по УЗП
1
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
None
7.3 Ссылки на материалы, доступные онлайн
Название/ описание:
None
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей