Afforestation [Кабо-Верде]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Jacques Tavares
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: David Streiff
Arborização / floresta (Portuguese)
technologies_1523 - Кабо-Верде
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Специалист по УЗП:
Varela Larissa
INIDA
Кабо-Верде
Специалист по УЗП:
Amarós Regla
INIDA
Кабо-Верде
Специалист по УЗП:
Bentub Jailson
INIDA
Кабо-Верде
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
INIDA (INIDA) - Кабо-Верде1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
03/04/2009
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.5 Ссылка на Анкету (-ы) по Подходам УЗП

Protection des versants [Кабо-Верде]
Cette approche consiste à mettre à profit les eaux d'écoulement superficiel
- Составитель: Jacques Tavares
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
Afforestation is one of the key technologies to address the fragility of ecosystems: it provides better protection against erosion and makes better use of rainfall in order to maintain the sustainability of agricultural systems.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
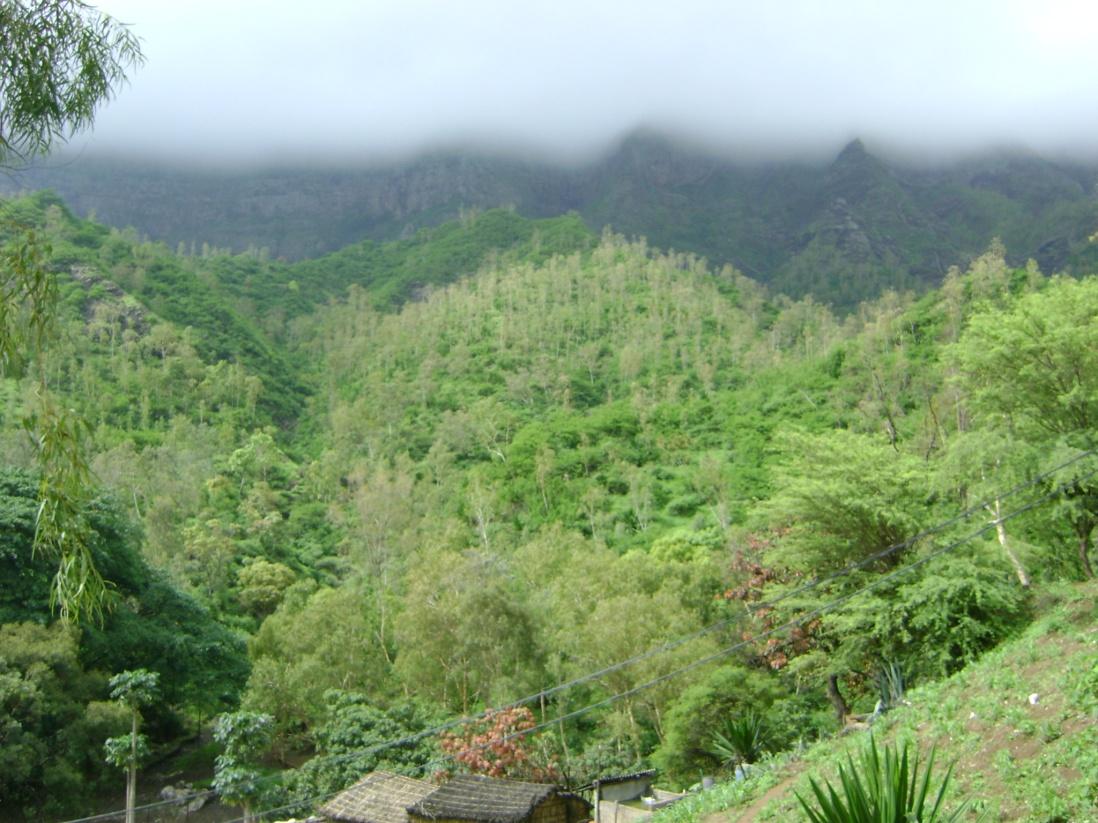
Mountain forest areas are considered protective due to their role in regulating water (infiltration of storm water, regulation of surface runoff, and ground water recharge) within the watershed. The main species used are Prosopis juliflora, Parkinsonia aculeata, Jatropha curcas, Atriplex spp, Acacia holosericea, Acacia victoriae, Lantana camara and others, in arid areas and Eucalyptus camaldulensis, Grevillea robusta, Pinus and Cupressus ssp. in highland and humid areas.
Purpose of the Technology: The climatic conditions are characterized by high spatial and temporal variability of the rainfall. The rains are concentrated in two or three months (August and September or October); the highlands and the N-NE parts are wetter compared to the low lands or coastal areas, which are very dry. The average annual rainfall is about 225 mm over the whole island; it has declined since the 1960s, with negative effects on farming conditions, and water supply. However, in areas located more than 500 m above sea level and exposed to trade winds, rainfall can exceed 700 mm. About 20% of the precipitation is lost through runoff, 13% infiltrates the soil and recharges aquifers and 67% evaporates. The evaporation loss is a limiting factor for any agriculture or forestry. Therefore, it is necessary to adapt the afforestation implementation to the specific local conditions (slope, stone cover, climate, etc). To overcome and minimize the problem of water scarcity, several measures are applied: (a) caldeira or half-moon structures achieved with earth or stone; (b) contour furrows or level bench terraces with stone walls arranged along the contour; (c). small dams to protect gullies. The aim is to maximize retention of water and control surface runoff. This not only allows better infiltration of water for the tree plantations, but also protects against soil erosion and facilitates groundwater recharge.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The success of the reforestation may be indicated not only by the area covered but also by the number of introduced plants. In 1975, there were about 3,000 ha of afforested land. By 2011, there are over 90,000 ha of afforested land with almost 50 million trees. Afforestation has focused mainly on the island of Santiago and Santo Antão, (13% of the total area reforested). Nowadays, more than 20% of the country is afforested. The forest has had a great importance in the context of combating desertification, rehabilitation of vegetation cover, in meeting energy needs and forage production and in developing agrosilvopastoral systems, as well as having undoubtedly contributed to a significant modification of the landscape in Cape Verde. The afforestation activities also contributed to increase biodiversity of some species of birds, including “Galinha di mato” (Numida meleagris), “Codorniz” (Coturnix coturnix), “Passarinha” (Halcyon leucocephala) and others.
Natural / human environment: The forest species are mainly used for land protection and for production of fuel wood and coal. Because of the poor growing conditions, the forest species are not well suited to the construction industry or wood processing.
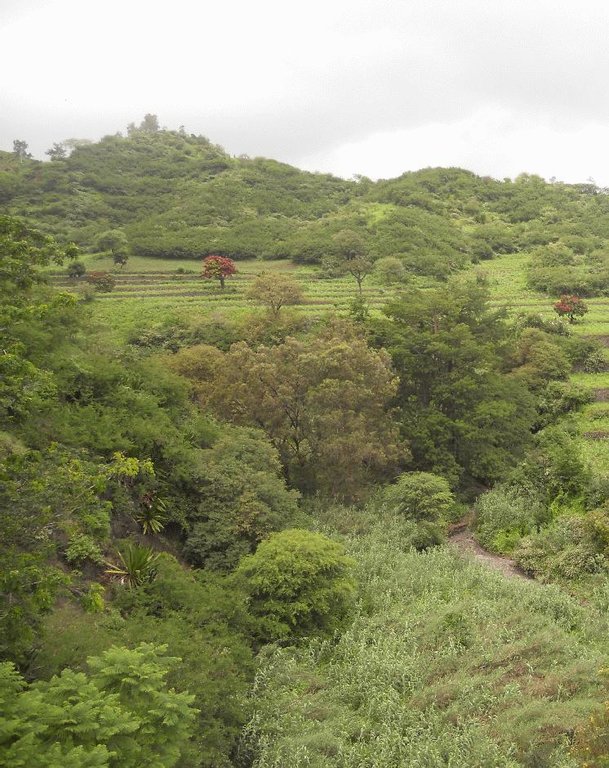
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Кабо-Верде
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Santiago Island, Cape Verde
Более точная привязка места:
Ribeira Seca
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- 10-50 лет назад
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
Before 1975, the forestry production was directed to the market of wood, after 1975 began to stock in order to protect the environment
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
- сохранение экосистем
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология

Пастбищные угодья
Интенсивный выпас/ выращивание кормов:
- Стойловое содержание/ нулевой выпас
Основные породы скота и виды продукции:
goats and cows

Леса/ лесистая местность
Лесопосадки, облесение:
- Смешанные культуры
Продукции и услуги:
- Природоохранные/ защитные
Пояснения:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The loss of soil by runoff, influenced by its low coverage, reducing their fertility and their thickness
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion by runoff, low productive soils, low organic matter, low soil cover, fertility and depth particularly in the agro-systems with rainfed agriculture.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: goats/ cows
Grazingland comments: production is characterized as extensive, although made in a closed expaço
Plantation forestry: Few trees are cut, since the main objective of which is the forest canopy. The dead are removed, make's some clean and plant new trees every year.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Before 1975, date of independence of Cape Verde, began to stock the areas discovered. The forest is more dense at high altitudes but also introduced
Forest products and services: nature conservation / protection
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Ms: Silvo-pastoralism
Type of grazing system comments: production is characterized as extensive, although made in a closed expaço
Если использование земель изменилось с началом применения Технологии, укажите тип землепользования до применения Технологии:
Mixed: Mo: Other
3.3 Дополнительная информация о землепользовании
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
Число урожаев за год:
- 1
Поясните:
Longest growing period in days: 90; Longest growing period from month to month: August untill October
Поголовье скота на единицу площади (если применимо):
25-50 LU /km2
3.4 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- лесное хозяйство в естественных и измененных лесах
- Управление орошением (включая водоснабжение и дренаж)
3.5 Распределение Технологии по площади
Пояснения:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 71.5 km2.
The forest with the greatest density of trees occupies an area of 2.51 km2 and is located in the area of higher altitude. The density decreases with decrease in altitude
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Мероприятия с использованием растительности
- Р1: Древесный и кустарниковый покров

инженерные мероприятия
- И2: Насыпи, валы
Пояснения:
Secondary measures: structural measures
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов
- ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование

биологическая деградация
- Бр: сокращение растительного покрова
- Бм: утрата местообитаний

деградация водных ресурсов
- Вуг: изменения уровня грунтовых вод/ водоносных горизонтов
Пояснения:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
Main causes of degradation: soil management (It is cultivated maize and peanuts on land slopes very pronounced and boot up the plants by the root in end of the cycle), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (The cleaning of the crop residues of corn is done pulling them by the root, negatively affecting soil stability), poverty / wealth (Leads sensitized peoples to advocate action against the landscape for survival of the family), education, access to knowledge and support services (Knowledge and technical training increase the options for means of survival of the community that acts on the forest, the degree of attending school is low and the illiteracy rate is 17%)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (Creation of the wild animals compact the soil, destroying the structures for the conservation of soil and water exists, and creates conflict), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Sometimes occur heavy rains intensity that associated with poor vegetation cover, increase soil erosion), governance / institutional (Lack of applicability of the laws that manage the land)
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- восстановление/ реабилитация нарушенных земель
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
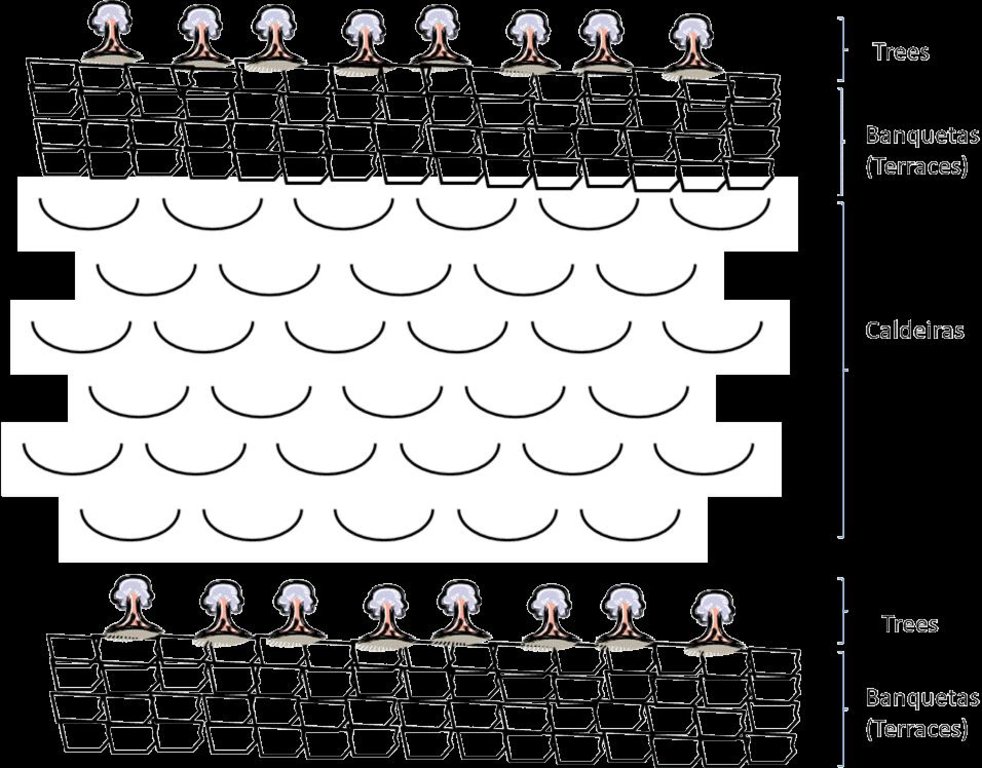
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
4.2 Спецификация / пояснения к техническому рисунку
Treatment of slope before afforestation
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (It's needed sufficient knowledge to choice species according to their suitability to the natural and human environment)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.8
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Construction material (earth): land from the local construction of the ditch is used in the construction of banks, that can be rein
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30 - 60%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:3
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.4 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Quantification of the area to be afforested | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | |
| 2. | Production of plants in nursery ( 500 - 1300 plants) | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | |
| 3. | Treatment of area (slope) with building terraces (15 m / person / day) | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | |
| 4. | Treatment of area (slope) with: Making half-moons “Caldeiras” (3 / person / day) | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | |
| 5. | 4. Excavating the pits (10 / person / day): 60x60x60 cm | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | |
| 6. | Planting (50 /person / day): 5 to 5 metres | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | |
| 7. | Initial maintenance (8 /persons / day) | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | |
| 8. | Cleaning and marking on curves level | Инженерные | In April |
| 9. | Construction of the retention / infiltration ditch and opening of the surface of culture | Инженерные | April to June |
4.5 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 28218,0 | 28218,0 | |
| Оборудование | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 410,0 | 410,0 | 10,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 942,0 | 942,0 | |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 29570,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | forest cleaning | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | |
| 2. | forest cleaning | Инженерные | In the dry session |
4.7 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Forest cleaning | ha | 1,0 | 142,0 | 142,0 | 52,0 |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 142,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
Machinery/ tools: Hoe, machete
Costs are estimated according to the time required for afforestation and the entity contracted for the implementation of the activities.
4.8 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
The labour affects the costs more than other factors. Paid labour is a way to achieve additional income for many people in this area. The employer (Directorate General of Agriculture, Sylviculture and Livestock of the Ministry of Rural Development) provides 90% of the cost of the equipment. The lifetime of the equipment is 10-15 years.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Укажите среднегодовое количество осадков (если известно), мм:
800,00
Агроклиматическая зона
- влажная
- Умеренно-влажная
- полузасушливая
- засушливая
Thermal climate class: tropics. average temperature equal to 26 º C
The exposure and altitude are factors diterminantes for agroclimatic estratização. the higher areas and targeted to the SE are more humid.
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Укажите, приурочено ли применение Технологии к специфическим условиям:
- не имеет значения
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
Altitudinal zone: 100-500 m a.s.l. belongs to the stratum semi-arid sub-humid. Is part of the stratum the highest percentage of the area of the basin. 1000-1500 m a.s.l. includes mainly the cliffs and ridges.
Landforms: Also ridges and footslopes. The hazards of a convex situations does not allow its application in mountain slopes.
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- грубый крупнозернистый/ лёгкий (песчаный)
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
- низкое (< 1%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil depth on average: Very shallow is associated with the sloping hillsides used for rainfull agriculture and shaloow is found mainly in the valley bottoms of the downstream.
Soil texture (topsoil): The soil overlay mainly basaltic rocks, piroclastic, conglomerates and aluvial deposits
Soil fertility is medium - low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good - medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium - low
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
5-50 м
Доступность поверхностных вод:
недостаточны/ отсутствуют
Качество воды (без обработки):
питьевая вода плохого качества (необходима обработка)
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по качеству и количеству воды:
Ground water table: In rain months, it is more superficial than in the dry months
Availability of surface water: There is some just when it rains.
Water quality (untreated): Salinization of water due to over exploitation of wells and boreholes
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- средняя
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Доходы из других источников:
- < 10% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- плохой
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- использующее наемных работников (компания, государство)
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%
and own 1% of the land (the tecnology is applyed by the state, and the state of that country is poor).
Off-farm income specification: forest production (mainly grass and wood) generate an annual income of approximately $2,500
Market orientation of production system: Mixed:Forest products are quite limited: lumber, firewood, charcoal and fodder from the pods. Firewood is the most important product but marketing is quite limited in time and space and subsistence are families who enter the forest for collection of grass and firewood. It is necessary for their survival. The state sells these products in order to finance other development projects.
5.7 Средний размер земельных участков, арендуемых или находящихся в собственности землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- крупное
Пояснения:
Also 50-100 ha, 100-500 ha and 100-500 ha,
The forest covers all the household
The grass production is made between the trees across the forest area if it's possible
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- государственная
- индивидуальная, оформленная в собственность
- Diocese
Право землепользования:
- общинное (контролируемое)
- индивидуальное
Право водопользования:
- общинное (контролируемое)
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
электроснабжение:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство кормов
качество кормов
производство электроэнергии
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Firewood to the community
Доступность и качество воды
доступность питьевой воды
Доходы и затраты
сельскохозяйственные издержки
экономическое неравенство
Социальное и культурное воздействие
продовольственная безопасность/ самообеспечение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
It reduces the options of land use
культурные возможности
смягчение конфликтов
положение социально и экономически уязвимых групп населения
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Any sex has the same opportunity on the assets of the forest
livelihood and human well-being
Комментарий/ пояснения:
It improves air quality, promotes the production of endemic species and its use as medicine
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
уровень грунтовых/ подземных вод
испарение
Почвы
влажность почв
почвенный покров
утрата почв
почвенное / подземное органическое вещество/ углерод
Климат и снижение риска стихийных бедствий
выбросы углекислого газа и парниковых газов
скорость ветра
Другие экологические последствия
Invasive species
competition
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
доступность воды
надежность и постоянство водотоков
подтопление ниже по течению
отложение наносов ниже по течению
буферная/ фильтрационная способность
отложения, переносимые ветром
ущерб прилегающим полям
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | Тип изменения климата/ экстремального явления | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| среднегодовые температуры | увеличилось | хорошо |
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Погодные стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| местные ливневые дожди | не известно |
| местные ураганы | плохо |
Стихийные бедствия климатического характера
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| засухи | плохо |
Гидрологические стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| регулярные наводнения (выход рек из берегов) | не известно |
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| сокращение вегетационного периода | хорошо |
Пояснения:
Tree species more tolerant of the climatic factors can be used, whilst retaining all the benefits that the existing species provide
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
отрицательно
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
влияние незаметно
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Пояснения:
The high costs are associated with its implementation; afterwards they are significantly reduced and the technology builds up the benefits.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
Если возможно, дайте количественную характеристику (число домохозяйств и/или площадь применения):
None. It's a project of the government
Пояснения:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Only the state has implemented this technology, because it changes the use of land and, without any subsidies, other land users are not encouraged to agree to it.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: there is a continuing campaign of afforestation of state land. There are voluntary associations working in this technology for a better environment
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
|
Production of firewood and grass How can they be sustained / enhanced? make more forest operations such as pruning or cutting of new seedlings |
|
Protection of soil How can they be sustained / enhanced? strengthen maintenance operations |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
|
Increases the quality of the landscape and reduces the loss of soil by runoff How can they be sustained / enhanced? increasing the tree cover in areas with low coverage |
|
Encourages the production of livestock, and fuel wood How can they be sustained / enhanced? integrate the community in managing the forest, and manage it in a sustainable way. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| impossibility of farming in the forest lands | off-farm income creation to compensate |
| Lack of involvement of farmers in the management of forest areas | capacity building of land users in forest management strategies, elaboration of contracts between State and land users for the management of forest perimeters |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Reduces the percentage of land for agricultural production | increase productivity in cultivated land and reduce the need for the use of forest land, and implement new production technologies such as greenhouses |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Desertification at the Santiago Island, DESIRE, 2008
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Relatório de avaliação inicial do impacto das realizações de conservação de solos e água em 1993 do projecto WDP, WDP project, 1995
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
www.ine.cv: Survey of family income and expenditure, INE, 2002
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
OCDE, CILSS, 1982. Análise do Sector Florestal e Propostas para Cabo Verde. Sahel D (82) 179
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Club do Sahel, pp 203.
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
MAAA/DGASP, 1996. Rapport de pays pour la Conférence Technique Internationale de la FAO sur les Ressources Phytogénétiques, Leipzig, 1996, pp 38.
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Leipzig, 1996, pp 38.
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Protection des versants [Кабо-Верде]
Cette approche consiste à mettre à profit les eaux d'écoulement superficiel
- Составитель: Jacques Tavares
Модули
Нет модулей