Planting pits and stone lines [Нигер]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Charles Bielders
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
Tassa avec cordon pierreux (french)
technologies_1100 - Нигер
- Полная аннотация в формате PDF
- Полная аннотация в формате PDF для вывода на печать
- Полная аннотация в формате интернет-страницы
- Полная аннотация (неотформатированно)
- Planting pits and stone lines: 6 июня 2019 г. (public)
- Planting pits and stone lines: 4 апреля 2018 г. (inactive)
- Planting pits and stone lines: 4 апреля 2018 г. (inactive)
- Planting pits and stone lines: 4 мая 2017 г. (inactive)
- Planting pits and stone lines: 28 апреля 2017 г. (inactive)
- Planting pits and stone lines: 28 апреля 2017 г. (inactive)
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Специалист по УЗП:
Специалист по УЗП:
Oudou Noufou Amadou
PDRT
Нигер
Специалист по УЗП:
Специалист по УЗП:
Oudou Noufou Amadou
PDRT
Oudou Noufou Amadou
PDRT
Специалист по УЗП:
Oudou Noufou Amadou
PDRT
Нигер
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Projet de développement rural de Tahoua, Niger (PDRT)Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Université catholique de Louvain (Université catholique de Louvain) - БельгияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Centre for Agriculture in the Tropics and Subtropics (Centre for Agriculture in the Tropics and Subtropics) - ГерманияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
ICRISAT International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) - Нигер1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
01/08/1999
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.5 Ссылка на Анкету (-ы) по Подходам УЗП

Approche participative de réhabilitation des terres individuelles et … [Нигер]
Planification et gestion des terres individuelles et villageoises sur la base d’une participation des usagers ; promotion simultanée des activités des femmes.
- Составитель: Eric Tielkes
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
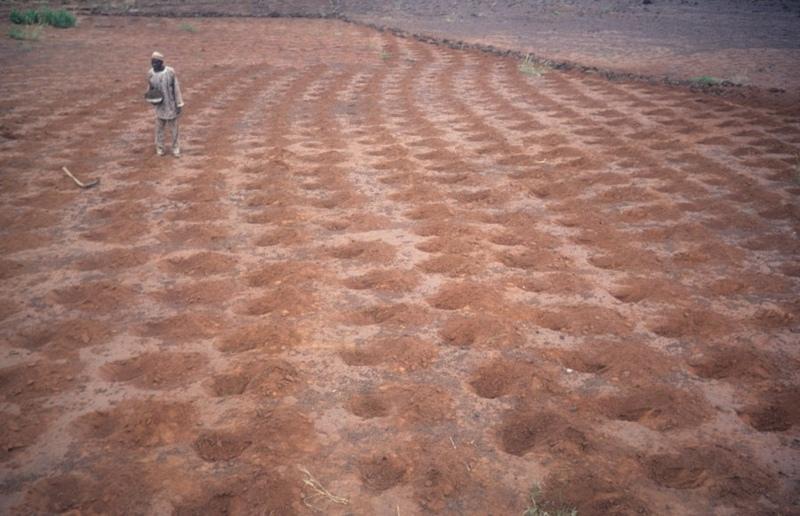
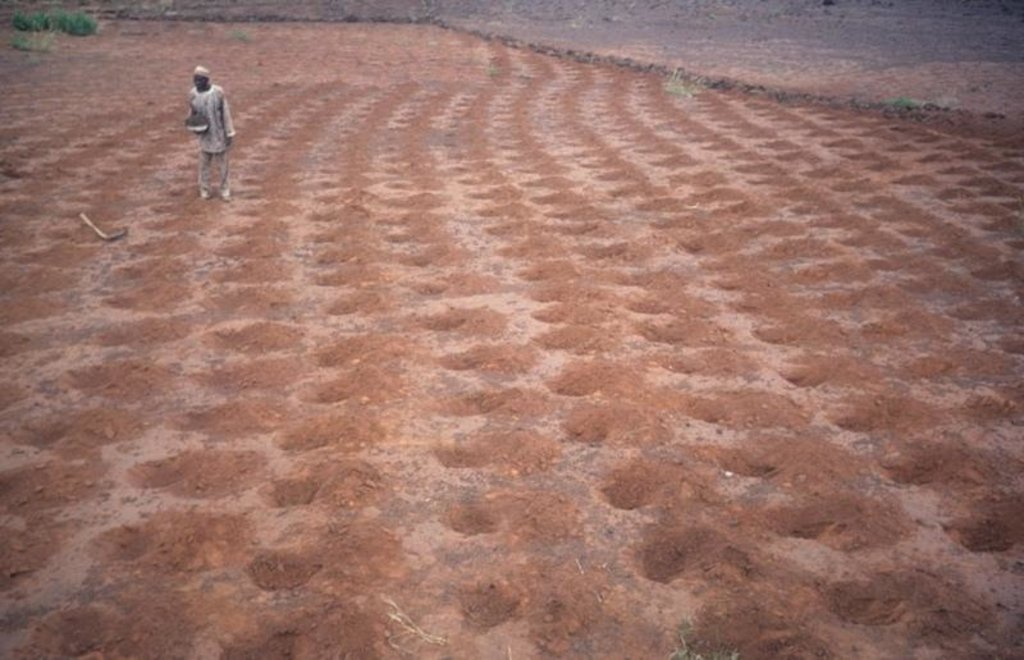
Rehabilitation of degraded land through manured planting pits, in combination with contour stone lines. The planting pits are used for millet and sorghum production on gentle slopes.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
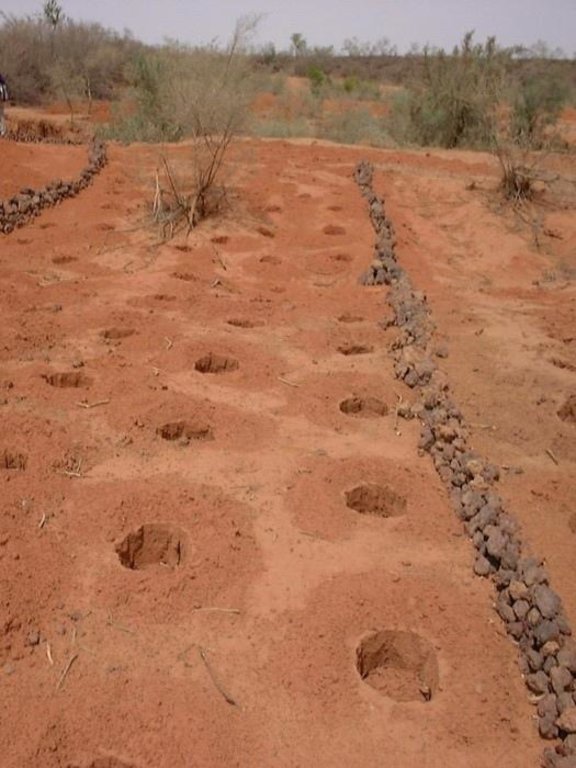
The combination of planting pits (tassa) with stone lines is used for the rehabilitation of degraded, crusted land. This technology is mainly applied in semi-arid areas on sandy/loamy plains, often covered with a hard pan, and with slopes below 5%. These denuded plains are brought into crop cultivation by the combination of tassa and stone lines. Planting pits are holes of 20-30 cm diameter and 20-25 cm depth, spaced about 1 m apart in each direction. The excavated earth is formed into a small ridge downslope of the pit. Manure is added to each pit, but its availability is sometimes a problem. At the start of the rainy season, millet or sorghum is sown in these pits. The overall aim of the system is to capture and hold
rainfall and runoff, and thereby improve water infiltration, while increasing nutrient availability.
Stone lines are small structures, at most three stones wide and sometimes only one stone high. The distance between the lines is a function of the slope and availability of stone. Typically they are sited 25-50 m apart on 2-5% slopes. Stones are usually collected from nearby sites - though sometimes up to 5-10 km away and brought to the fields by donkey carts or lorries (when a project is involved). They are positioned manually, along the contour. Stone lines are intended to slow down runoff. They thereby increase the rate of infiltration, while simultaneously protecting the planting pits from sedimentation.
Often grass establishes between the stones, which helps increase infiltration further and accelerates the accumulation of fertile sediment. Wind-blown particles may also build up along the stone lines due to a local reduction in wind velocity. The accumulation of sediment along the stone lines in turn favours water infiltration on the upslope side. This then improves plant growth, which further enhances the effect of the system. Construction does not require heavy machinery (unless the stones need to be brought from afar by lorry).
The technique is therefore favourable to spontaneous adoption. Stone lines may need to be repaired annually, especially if heavy rains have occurred. Manure is placed every second (or third) year into the previously dug pits and sand is removed annually: normally the highest plant production is during the second year after manure application.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Нигер
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Niger, Tahoua
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
Основные сельскохозяйственные культуры (товарные и продовольственные):
major food crop: Millet and sorghum
Пояснения:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil fertility decline is the basic problem: this is due to degradation and nutrient mining. Loss of limited rainwater by runoff and loss of soil cover result in low crop production and food insufficiency. This occurs in combination with lack of pasture, resulting in shortage of manure.
3.3 Дополнительная информация о землепользовании
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
3.4 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- сбор атмосферных осадков
- Управление орошением (включая водоснабжение и дренаж)
3.5 Распределение Технологии по площади
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Пояснения:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 40 km2.
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Агрономические мероприятия
- A6: Другие

инженерные мероприятия
- И11: Другие
Пояснения:
Specification of other agronomic measures: Manure application (supplementary)
Specification of other structural measures: stone lines, planting pits
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов

ветровая эрозия почв
- Эп: утрата плодородного слоя почвы

ухудшение химических свойств почв
- Хп: Снижение плодородия и уменьшение содержания органического вещества (вызванное не эрозией, а другими причинами)

ухудшение физических свойств почв
- Фу: уплотнение
- Фк: растрескивание и коркообразование
Пояснения:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- восстановление/ реабилитация нарушенных земель
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
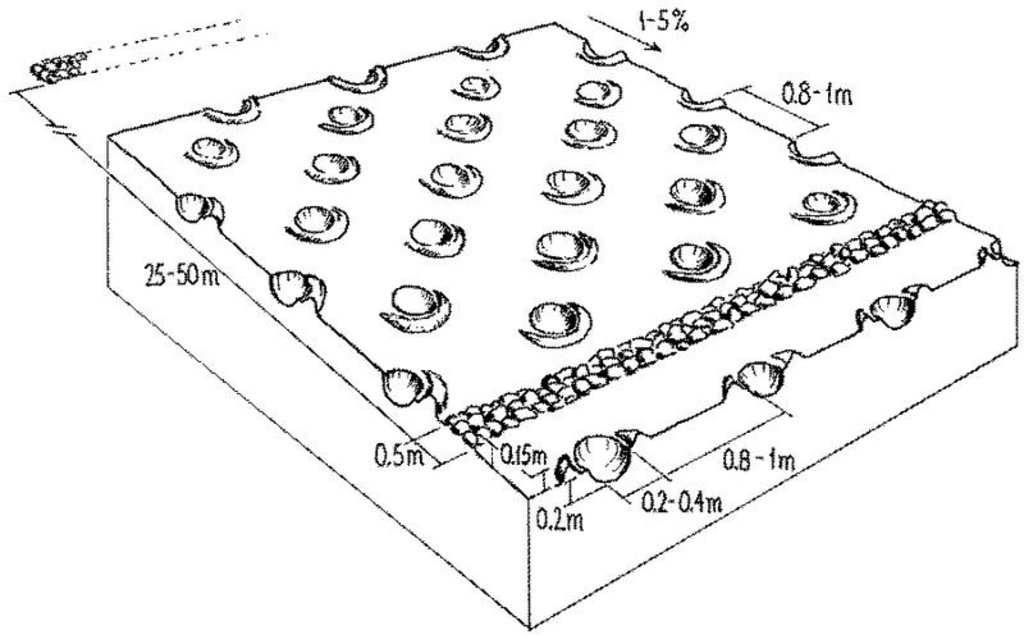
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
4.2 Спецификация / пояснения к техническому рисунку
Planting pits (tassa) capture rainfall runoff for cultivation of annual crops, and the stone lines - spaced at 25-50 metres apart - help hold back moisture and eroded soil.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, increase in soil fertility, increases natural regeneration of trees
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, improvement of soil structure
Manure / compost / residues
Quantity/ density: 2.5 t/ha
Structural measure: stone lines
Spacing between structures (m): 25-50planting pits
Structural measure: planting pits
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 1
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2-0.25
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2-0.3
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): <5%
4.3 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Укажите денежные единицы, использованные для подсчета затрат:
- Доллары США
4.4 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging pits (tassa): the excavated earth | Инженерные | dry season (November to May) |
| 2. | Digging out stones from nearby sites | Инженерные | dry season (November to May) |
| 3. | Transporting stones | Инженерные | dry season (November to May) |
| 4. | Aligning the stones along the contour with the help of a ‘water tube | Инженерные | dry season (November to May) |
4.5 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Digging tassa | persons/day/ha | 100,0 | 1,5 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Building stone lines | persons/day/ha | 26,666 | 1,5 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Tools for tassa | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Tools for stone lines | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 75,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Transporting stones with lorri | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 245,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Manuring the pits with approx 250 g per pit | Агрономические | dry season (November to May) / initial establishment |
| 2. | Manuring the pits with about 250 g per pit (2.5 t/ha) | Агрономические | October/November or March-May / every second year |
| 3. | Removing sand from the tassa | Инженерные | March-May/annual |
| 4. | Check and repair stone lines | Инженерные | annually and after heavy rains. |
4.7 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Labour | persons/day/ha | 21,0 | 1,5 | 31,5 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Tools for tassa | ha | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 35,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, pick-axe, shovel, donkey cart, (lorries)
The costs are based on 300 m of stone lines per hectare (on a 3-4% slope). Maintenance costs refer to removing
sand from the pits from the second year onwards, and to the application of manure every second year (costs are spread on an annual basis). If applicable, costs for transporting the manure need to be added. The general assumption in these calculations is that adequate manure is readily available close by. The availability of stones is the main factor in determining costs - though labour availability can affect prices also. If stones are not available in the field or nearby (from where they can be transported by donkey cart), they have to be carried by lorries, which is much more expensive. The costs here refer to fuel costs only, paid by a project: they do not include depreciation of lorries.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Укажите среднегодовое количество осадков (если известно), мм:
390,00
Агроклиматическая зона
- полузасушливая
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- грубый крупнозернистый/ лёгкий (песчаный)
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- низкое (< 1%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil depth on average: Also deep
Soil fertility is low - very low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good, though infiltration is low where there is a crust
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- натуральное хозяйство (самообеспечение)
- смешанное (самообеспечение/ товарное хозяйство
Доходы из других источников:
- > 50% всех доходов
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
- тягловая сила
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Off-farm income specification: remittances from out-migration of labour, commerce and crafts
5.7 Средний размер земельных участков, арендуемых или находящихся в собственности землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- индивидуальное
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
Доходы и затраты
доходы хозяйства
объем работ
Другое социально-экономическое воздействие
input contstraints
Социальное и культурное воздействие
местное самоуправление
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Through mutual aid in technology implementation
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
смягчение конфликтов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Land use rights conflicts of rehabilitated land and conflicts between farmers and pastoralists, because pasture land is being turned into cultivated fields
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
водный дренаж
Почвы
влажность почв
утрата почв
почвенное / подземное органическое вещество/ углерод
Другие экологические последствия
soil fertility
long-term soil cover
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
подтопление ниже по течению
отложение наносов ниже по течению
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
Пояснения:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is moderate growing spontaneous adoption (for rehabilitation of the plains), but there are no estimates available regarding the extent.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
|
Simple technology, individually applicable in the dry season, requiring only very little training/knowledge and no special equipment. |
| Making best use of manure, which is a limiting resource. |
| Increase in agricultural production. |
| Rehabilitation of degraded and denuded land: bringing back into production formerly uncultivated land; extension of farm land to the plateaus. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Labour demanding technology for implementation and maintenance | Mechanisation of tasks: transportation of stones and manure. However, this would raise the cost. |
| Instability of planting pits in loose soil, increased erosion on steeper slopes and with heavier rains |
Avoid loose sandy soils and steep slopes. |
|
The effectiveness can be compromised if the various geo-morphological units (plateaus, slopes) are not treated simultaneously |
Catchment area approach if downstream flooding is an issue. |
|
Possibility of land use conflicts concerning rehabilitated land, in particular with pastoralists |
Better coordination/consultation before implementing the technology in an area. |
| Implementation constraint: availability of manure and/or stones and transporting manure/stones to the plateaus and slopes |
Subsidise transport means (or supply donkey carts) or/and apply stone lines only in areas where there are stones available close to the fields. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Bety A, Boubacar A, Frölich W, Garba A, Kriegl M, Mabrouk A, Noufou O, Thienel M and Wincker H: Gestion durable desressources naturelles. Leçons tirées du savoir des paysans de l’Adar. Ministère de l’agriculture et de l’élevage, Niamey, 142 pp.. 19
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Hassane A, Martin Pand Reij C:Water harvesting, land rehabilitation and household food security in Niger: IFAD’s Soil and Water Conservation Project in IllelaDistrict. IFAD, Rome, 51 pp.. 2000.
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Mabrouk A, Tielkes E and Kriegl M: Conservation des eaux et des sols: Leçons des connaissances traditionnelles de la région de Tahoua, Niger. In: Renard, G., Neef, A,. Becker, K. and Von Oppen, M. (eds). de la région de Tahoua, Niger. 1998.
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Mabrouk A, Tielkes E and Kriegl M: Conservation des eaux et des sols: Leçons des connaissances traditionnelles de la région de Tahoua, Niger. In: Renard, G., Neef, A,. Becker, K. and Von Oppen, M. (eds). de la région de Tahoua, Niger. 1998.
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Mabrouk A, Tielkes E and Kriegl M: Conservation des eaux et des sols: Leçons des connaissances traditionnelles de la région de Tahoua, Niger. In: Renard, G., Neef, A,. Becker, K. and Von Oppen, M. (eds). de la région de Tahoua, Niger. 1998.
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Mabrouk A, Tielkes E and Kriegl M: Conservation des eaux et des sols: Leçons des connaissances traditionnelles de la région de Tahoua, Niger. In: Renard, G., Neef, A,. Becker, K. and Von Oppen, M. (eds). de la région de Tahoua, Niger. 1998.
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Mabrouk A, Tielkes E and Kriegl M: Conservation des eaux et des sols: Leçons des connaissances traditionnelles de la région de Tahoua, Niger. In: Renard, G., Neef, A,. Becker, K. and Von Oppen, M. (eds). de la région de Tahoua, Niger. 1998.
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Mabrouk A, Tielkes E and Kriegl M: Conservation des eaux et des sols: Leçons des connaissances traditionnelles de la région de Tahoua, Niger. In: Renard, G., Neef, A,. Becker, K. and Von Oppen, M. (eds). de la région de Tahoua, Niger. 1998.
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Mabrouk A, Tielkes E and Kriegl M: Conservation des eaux et des sols: Leçons des connaissances traditionnelles de la région de Tahoua, Niger. In: Renard, G., Neef, A,. Becker, K. and Von Oppen, M. (eds). de la région de Tahoua, Niger. 1998.
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Mabrouk A, Tielkes E and Kriegl M: Conservation des eaux et des sols: Leçons des connaissances traditionnelles de la région de Tahoua, Niger. In: Renard, G., Neef, A,. Becker, K. and Von Oppen, M. (eds). de la région de Tahoua, Niger. 1998.
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Approche participative de réhabilitation des terres individuelles et … [Нигер]
Planification et gestion des terres individuelles et villageoises sur la base d’une participation des usagers ; promotion simultanée des activités des femmes.
- Составитель: Eric Tielkes
Модули
Нет модулей