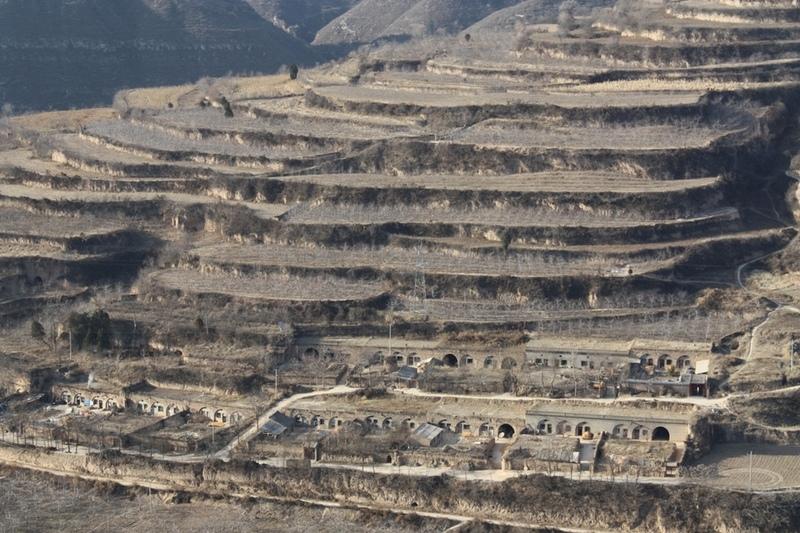
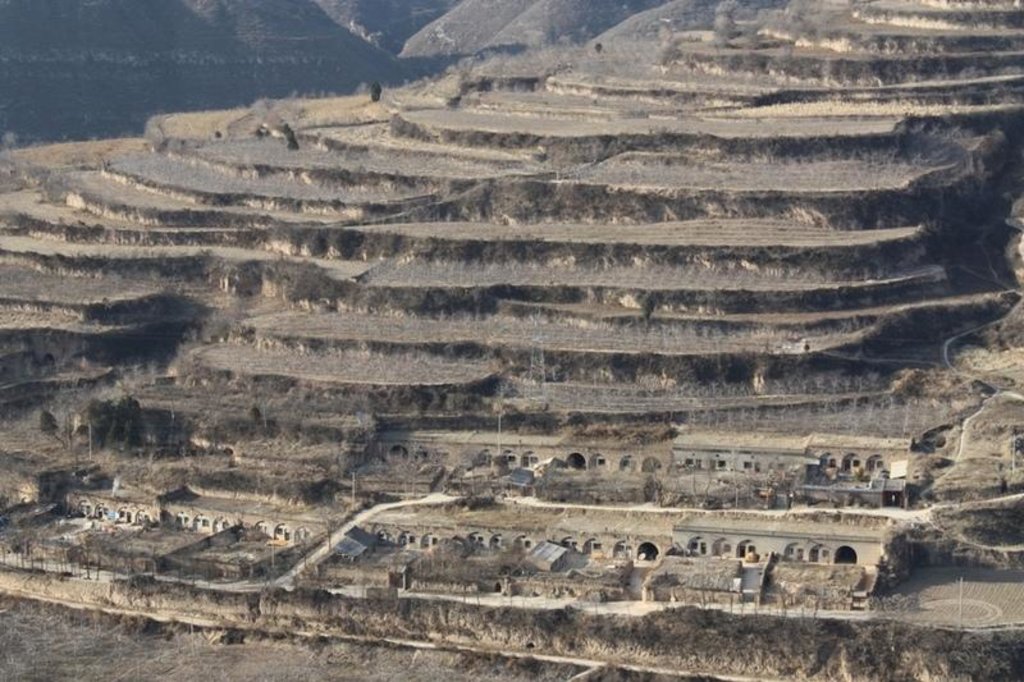
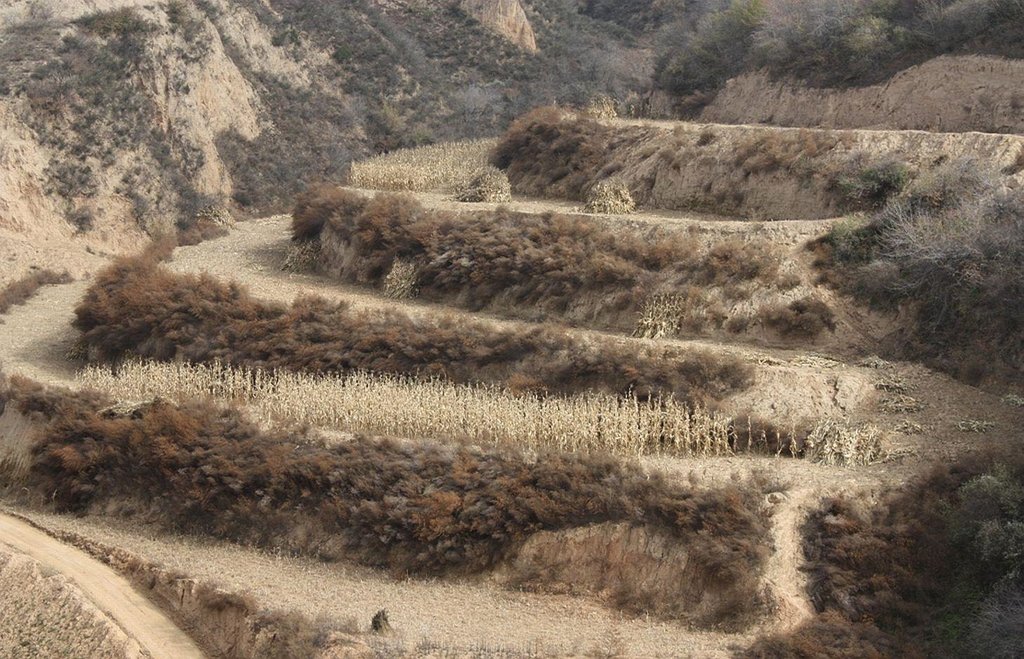
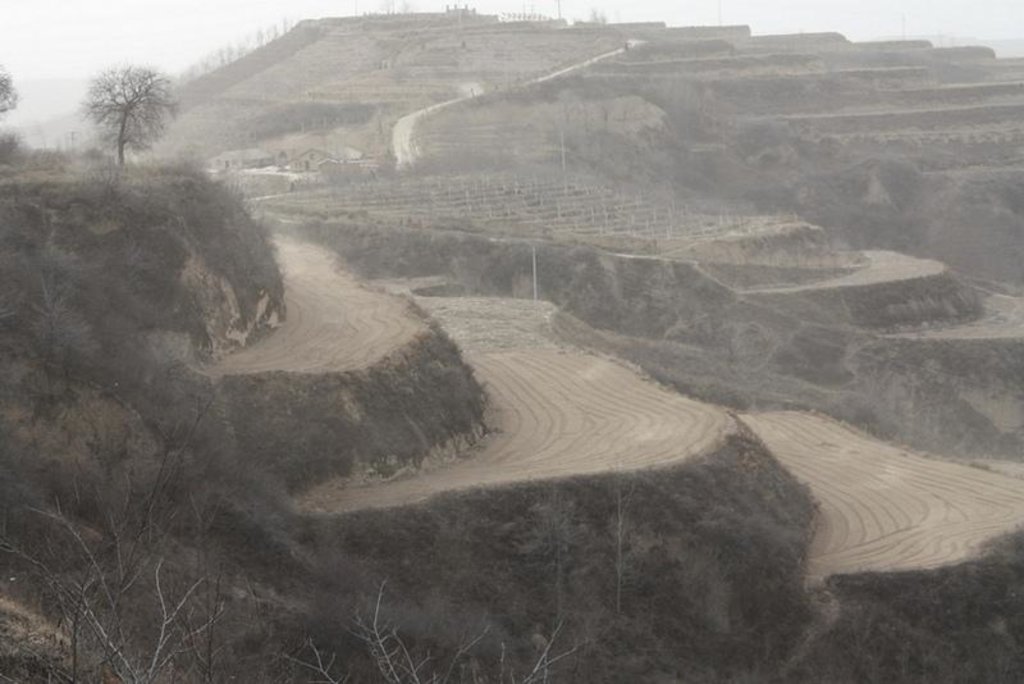
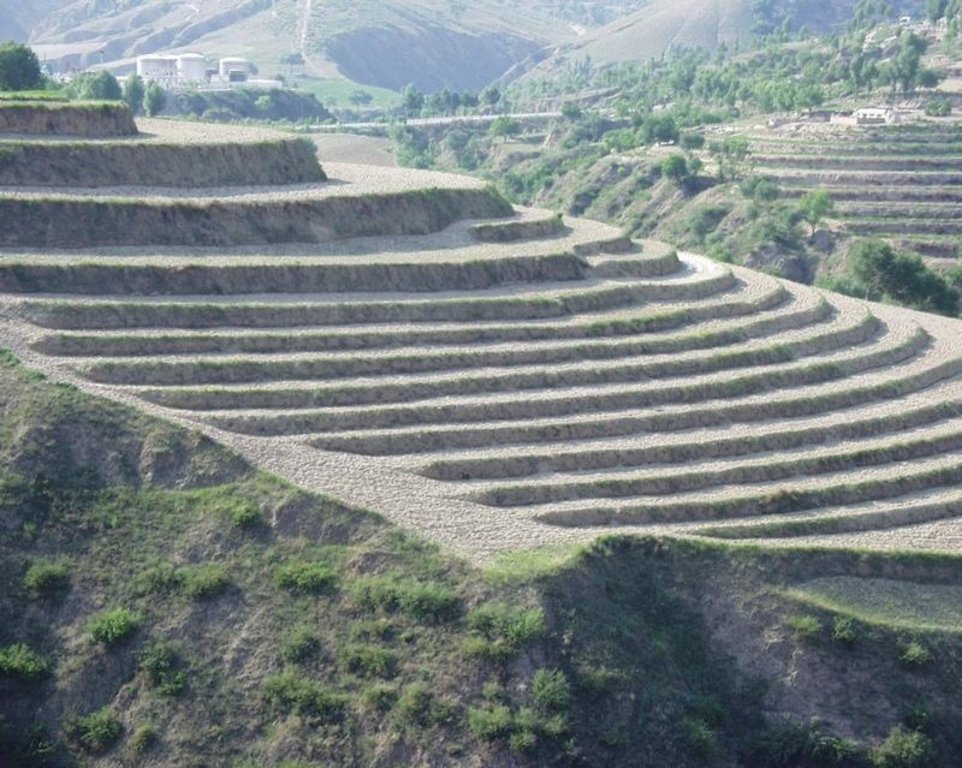
Bench terraces on loess soil [Китай]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Fei WANG
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
土坎梯田,梯地
technologies_1445 - Китай
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Специалист по УЗП:
1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
A Terrace is a structural SLM practice with a raised flat platform built on the slope to reduce soil loss and runoff on the slope, increase the rainfall infiltration and yield.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
A terrace is a leveled section of a hilly cultivated area, designed as a method of soil conservation to slow or prevent the rapid surface runoff and erosion of topsoil. Often such land is formed into multiple terraces, giving a stepped appearance.
Purpose of the Technology: To change the landform for better agricultural condition of operation of tillage and harvasting, reduction of soil erosion and water loss and finally for higher production.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The building of a terrace in the loess plateau takes long because loess is very soft and deep and the severe soil erosion and shortage of water in agriculture hinders the process, as well. Previously, terraces were constructed by hand. These terraces weres narrow and damaged by the great storms. Now, the machinery is used to build wide terrace with high bank size in the loess plateau. The establishment of terrace needs a lot of money but it is a long-term investment. The maintenance of terrace is considerable economic because the major efforts are the annually improvment of terrace bunds.
Natural / human environment: The soil erosion is very severe because of the cohesionless loess soil and very intensive rainfall storms in the summer and autumn that would destroy the land surface into broken hilly area. Terrace is a kind of measure to resolve it combining with crops. The human activities here is very intensive because they must plant on the slopes that would make the soil erosion greater.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Китай
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Shaanxi Province
Более точная привязка места:
Yanhe River Basin
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если технология равномерно занимает территорию, укажите площадь покрытия (в км2):
253,3
Пояснения:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 253.3 km2.
The total area with different measures is till to 2000. Yanhe River is a first class branch of Yellow River, China. The average channel slope is 3.26‰, and the area of whole basin is 7,687 km2. It is in the semi-arid North Temperate Zone with an average annual precipitation varying from 500 to 550 mm, and an average annual air temperature ranging from 8.5 to 11.4℃. It is in hilly gully area of the Loess Plateau covered by loess. The landform is seriously broken by cutting gullies induced by water erosion. The gully density (the length of channel in one km2) is amount to 2.1 to 4.6 km•km-2. The soil loss is severe all along.
The Ganguyi Hydrology Station (109°48′E, 36°42′N) located in the Ganguyi Town, Baota Country, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province. The area up Ganguyi Hydrology Station is 5,891 km2, including of Jingbian County(256km2), Zhidan County(708km2), Ansai County(2,699km2) and Baota County(2,228km2). The average annual runoff is 0.22 billion m3, and the runoff modulus accounting for 4,776.36 m3•km-2•yr-1. The average annual sediment flow is 4.776
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- более 50 лет назад (традиционная)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- как часть традиционной системы землепользования (более 50 лет назад)
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
The terrace in this site has been formed since 1994 with machinery. The land is quite wide and large enough for agriculture in the hilly loess region,
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Да
Укажите сочетания типов землепользования (посевы / пастбища / деревья):
- Агролесоводство

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
- Многолетние (недревесные) культуры
- Древесные и кустарниковые культуры
Ежегодный урожай - Уточните культуры:
- зерновые культуры - кукуруза
- зерновые культуры - просо
- цветочные культуры
- кормовые культуры - люцерна
- бобовые - бобы
- масличные культуры - подсолнечник, рапс, другие
- корневые / клубнеплодные культуры - картофель
- овощи - другие
Древесные и кустарниковые культуры - Уточните культуры:
- даты
- семечковые плоды (яблоки, груши, айва и т. д.)
Число урожаев за год:
- 1
Поясните:
Longest growing period in days: 300Longest growing period from month to month: March to NovemberSecond longest growing period in days: 200Second longest growing period from month to month: April to October
Пояснения:
Main cash crops: Beans, sunflower, apple, Chinese date, alfalfa
Main food crops: Potato, millets, maize, buckwheat
other crops: vegetable
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil and water losses are alarming in this region. The loose loess, steep slopes, and intensive storms in the summer and autumn, accelerates this process. Aditionally, the lack of rainfall negatively impacts agriculture and vegatation. Sediment deposition could increase the river bed and diminish capacity of reservoirs. On one hand side floods occur frequently because of fast and large runoff and on other hand side sedimentation in rivers reduce their water carring capacity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The low yield of crops and the low income from land is more important for the local people. It is necessary to improve the agricultural conditions. The land, especially the tableland and gentle slope land could be convert into terrace.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: The composation of agriculture is very simple here.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
- Да (Пожалуйста, заполните нижеприведенные вопросы относительно использования земель до внедрения Технологии)

Пастбищные угодья
- Intensive grazing/ fodder production
3.4 Водоснабжение
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
3.5 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- мероприятия по влагозадержанию и снижению эрозии почв на склонах
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Мероприятия с использованием растительности
- Р2: Злаковые и многолетние травянистые растения

инженерные мероприятия
- И1: Террасирование

управленческие мероприятия
- У1: Смена типа землепользования
Пояснения:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов

деградация водных ресурсов
- Вуп: изменение объема поверхностного стока
- Вб: снижение буферной способности водно-болотных угодий
Пояснения:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water, Hw: reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland areas
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (The natural vegetation in this region is grass on theslope and trees on the gully and alluvial land. After the destroy of natural, the soil loss increases greatly.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (About 70% of annual rainfall is in the summer and autumn. The storm is very intensive.), population pressure (The population density account for 71 capita per square km.)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (The rainfall varies greatly in different year and different seasons. The drought happened frenquently.)
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- снижение деградации земель
Пояснения:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
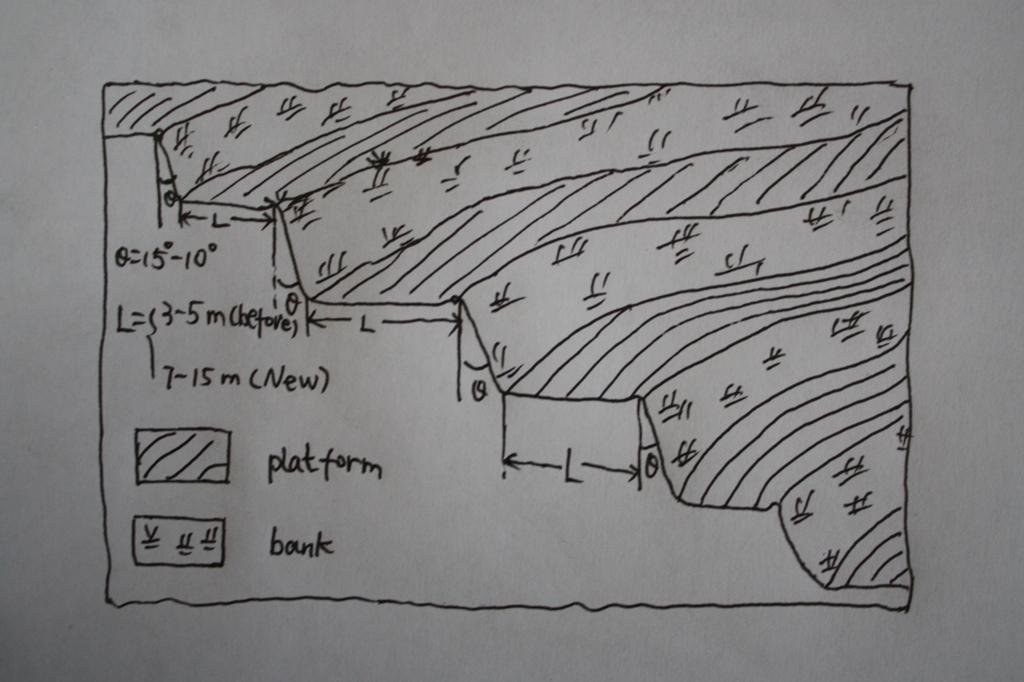
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
The brief structure of terrace in the Yanhe River Basin.
Location: Zhifanggou Watershed. Ansai County, Shaanxi, China
Date: 2008-12-15
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (The location selection and how to build a good terrace need special knowledge on soil engineering.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (It is easy to know the benefit for all the local farmers.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 50000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Grass species: Natural grass to protect the bank of terrace.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 1.00%
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2.5
Spacing between structures (m): 8
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 2.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 8
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-100
Construction material (earth): The terrace in the Loess Plateau are used local soil/earth directly.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 30-60%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Wild grassland or range land before mostly. Some time the cropland on the slope.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: The labor is less intensive on the plain platform.
Автор:
Wang Fei, Yangling, Shaanxi, China
4.2 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Укажите денежные единицы, использованные для подсчета затрат:
- Доллары США
Если это необходимо, укажите обменный курс от доллара США к местной валюте (например, 1 доллар США = 79,9 бразильского реала): 1 доллар США =:
0,83
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
8.8
4.3 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Время (сессия) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey and design | Before construction |
| 2. | Move the topsoil to other place | 1st step of construction |
| 3. | Built the platform and bank with soil digged | 2nd step of construction |
| 4. | Backcover the topsoil on the surface of platform | 3rd step of construction |
| 5. | Check and accept the terrace | After the terrace finished |
4.4 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Survey and design | Person/day | 45,0 | 8,8 | 396,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Building terraces (machine price included) | Person/day | 75,0 | 19,0 | 1425,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 1821,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на создание Технологии в долларах США | 2193,98 | |||||
Пояснения:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.5 month(s)
4.5 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Reinforce the bank | annually |
| 2. | Fill the erosion hole of the landform | annually |
| 3. | Build the edge in some terraces | annually |
| 4. | Reinforce the bank | annually |
| 5. | Fill the erosion hole of the landform | annually |
| 6. | Build the edge in some terraces | annually |
4.6 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Keep Terraces in shape | Person/day | 30,0 | 8,8 | 264,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 264,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на поддержание Технологии в долларах США | 318,07 | |||||
Пояснения:
Machinery/ tools: Crawl dozer and small traditional hand tool., crawler tractor, spade
In general condition, slope and soil, in the middle reaches of Yan River Basin. The prices of labour-day and Machine-hour are around 2005.
4.7 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
The terrace on the steep slope need more input for more soil and earth should be moved. It is the most important factor.The soil depth is not so important for the deep soil layer here.The cost of labour increases greatly in the last several years and the cost of construction of terrace increased.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Пояснения/ комментарии по осадкам:
The mean annual rainfall in the basin is 515.2 mm in the duration from 1952 to 2000. The rainfall from May to Oct accounts for 446.8 mm, up to 86.7%; and that from Jun to Sep accounts for 367.6 mm, up
Агроклиматическая зона
- полузасушливая
Thermal climate class: temperate. The accumulating time that temperature above 0 ℃ about 3800 hours, and that above 10 ℃ is more than 3200 hours.
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Укажите, приурочено ли применение Технологии к специфическим условиям:
- в условиях выпуклого рельефа
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
Landforms also: mountain slopes and hill slopes
Slopes on average also very steep
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- низкое (< 1%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil texture: There are more than 50% soil particle are fine sand with size between 0.05 and 0.1 mm.
Soil fertility very low: Lack of N, P and SOM.
Topsoil organic matter: The average Top-SOM of cropland is about 0.05%
Soil drainage / infiltration good: The inflitration of Loess is very fast, but it is prone to sealing when flashing.
Soil water storage capacity low: It is easy to evaporation and drainage.
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
5-50 м
Доступность поверхностных вод:
средняя
Качество воды (без обработки):
питьевая вода плохого качества (необходима обработка)
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по качеству и количеству воды:
Availability of surface water medium: It is very stable in this region.
Availability of surface water also poor/none: Nearly all the branches of Yanhe are seasonal river.
Ground water table: It depends on the landform. In valley and alluvial land, it is shallow.
Water quality: Good quality for there are few pollution sources.
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- средняя
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по биоразнообразию:
It is very stable in this region.
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- смешанный (натуральный / коммерческий)
- товарное/ рыночное хозяйство
Доходы из других источников:
- 10-50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- средний
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
- тягловая сила
Пол:
- женщины
- мужчины
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No clear difference.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
80% of the land users are average wealthy (The terrace are build together in some villages for all the people funded by national subsidy.).
Off-farm income specification: The yield of terrace is much high and stable.
Level of mechanization manual work: The harvesting and other management are by hand, even the tillage on the nerrow terrace
Level of mechanization animal traction: Tillage with animal power mostly in the wider terrace.
Market orientation mixed subsistence/ commercial: Some production for themselves, but most of production is exchanged on the market.
5.7 Средняя площадь земель, используемых землепользователями с применением Технологии
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- мелкое
Пояснения:
According to 0.054 ha per capita.
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- государственная
- общинная/ поселковая
Право землепользования:
- индивидуальное
Право водопользования:
- неограниченное (неконтролируемое)
Пояснения:
Like other rural area in China.
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
Количество до применения УЗП :
600
Количество после применения УЗП:
2200
производство продуктов животноводства
производство древесины
риск потери продуктивности
разнообразие продукции
площадь, используемая для производства продукции
Доступность и качество воды
доступность питьевой воды
качество питьевой воды
Доходы и затраты
доходы хозяйства
Количество до применения УЗП :
43.9
Количество после применения УЗП:
120
разнообразие источников дохода
объем работ
Социальное и культурное воздействие
продовольственная безопасность/ самообеспечение
смягчение конфликтов
Livelihoods and human well-being
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
сбор воды/ водоудержание
поверхностный сток
испарение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Evaporation form the wall of terrace, Especially for the narrow terrace
Почвы
влажность почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
More inflitration of rainfall, but the evaporation near to the wall increases
почвенный покров
утрата почв
Количество до применения УЗП :
10000t/km^
Количество после применения УЗП:
2000t/km^2
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
биомасса/ содержание углерода в надземной биомассе
разнообразие флоры
Другие экологические последствия
Hazards towards adverse events
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
надежность и постоянство водотоков
подтопление ниже по течению
отложение наносов ниже по течению
буферная/ фильтрационная способность
отложения, переносимые ветром
ущерб прилегающим полям
ущерб объектам инфраструктуры общего/ частного пользования
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | увеличение или уменьшение | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| среднегодовые температуры | увеличилось | хорошо |
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Погодные стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| местные ливневые дожди | плохо |
| местные ураганы | хорошо |
Стихийные бедствия климатического характера
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| засухи | не известно |
Гидрологические стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| регулярные наводнения (выход рек из берегов) | хорошо |
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| сокращение вегетационного периода | не известно |
Пояснения:
Loess is very prone to erosion and extreme storms would destory the bank of terrace. In the study site sesonal rainfall increased and the loess terrace could retain more soil water and reduce the runoff.
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Пояснения:
The yield of terrace is stable and relative higher. The income from terrace is high and the maintain cost is low.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
- 1-10%
Если возможно, дайте количественную характеристику (число домохозяйств и/или площадь применения):
100 households
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 0-10%
Пояснения:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
95 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Most land farmers have some terrace. I do not know the exact number of land user families who adopted the technology.
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
5 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: the old narrow terraces, now a very small area left, are build voluntarily.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nearly all the people know the benefit of terrace. the benefits of terraces are very good for crops and orchards are high enough in this region.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
|
Increase yield and income. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the terrace is maintained well, the water condition would be better than that on the slope land even in dry year with low precipitation. |
|
Convenient to till and harvest How can they be sustained / enhanced? Tillage and harvesting is much easier on the plain flat land than on the slope. The maintainance of terrace is important. |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
|
Reduce soil erosion on the slope. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The loess soil is prone to erosion because of its loose character induced by fine sand content and low soil organic matter. The plain flat makes the dispersion and transportation of soil particls difficult. |
|
Reduce runoff and increase the soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? The runoff generation is smaller on the plain than on the slope. Slow movement of surface water lead to more soil infiltration. |
|
Increase yield. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Water is the limit factor in the loess plateau. The yield would increase if there is enough water available. |
|
Decrease flood risk. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It is a kind of off-site benefits because less runoff generation and gentle process of runoff decrease flooding. Reduction of sediment also diminish flood risk because the drainage capacity of channel and adjusting capacity of reservior increase when sedimentation decrease. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| The output is also low in contrast with other industries. | No way to overcome it. The total and net income is too low because the area of terrace per capita is very small. |
| The income is relative compared with other industries. | No way to overcome it. The net income is low because the labour costs are increasing, and the total income because labour cost and very small area of terrace per capita. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| There is possible damage of terraces because the loess is very loosen and prone to collapse. | Keep upmaintaining the bank and land well. |
| Decrease runoff of lower stream. | No way to overcome it, but it also could decrease the risk of floods. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Soil and water conservation records of Shaanxi Province. 2000. Shaanxi People's Press, Xi'an City, China
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Library of ISWC, CAS
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
The soil and agriculture of the Loess Plateau. 1989. Zhu Xianmo, Agriculture Press, Beijing City, China
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Library of ISWC, CAS
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Statistical tearbook of Yan'an. 2003. Compiled by Editorial Board of Statistical tearbook of Yan'an
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Library of ISWC, CAS
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Impact of human activities on runoff and sediment change of Yanhe River based on the periods divided by sediment concentration. 2008. WANG Fei , MU Xing-min ,JIAO Ju-ying, LI Rui. Journal of Sediment Research
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
http://159.226.100.28/asp/Detail.asp
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Changes of soil erosion intensity due to conversion of farmland to forest and grassland in Yanhe River. 2007. BasinWang Bangwen, yang Qinke, Liu Zhihong, Meng Qingxiang, Science of Soil and Water Conservation
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
http://159.226.100.28/asp/Detail.asp
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей