Ecograze [Австралия]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Andrew Ash
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1332 - Австралия
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
CSIRO (CSIRO) - Австралия1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Декларация по устойчивости описываемой Технологии
Вызывает ли описанная здесь Технология проблемы деградации земель настолько, что ее нельзя назвать природосберегающей?
Нет
1.5 Ссылка на Анкету (ы) по Подходам УЗП (документируется с использованием ВОКАТ)

Development and promotion of Ecograze [Австралия]
Research-based development and promotion of Ecograze principles and practices through on-farm testing and demonstration.
- Составитель: Andrew Ash
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
An ecologically sound and practical grazing management system, based on rotation and wet season resting.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
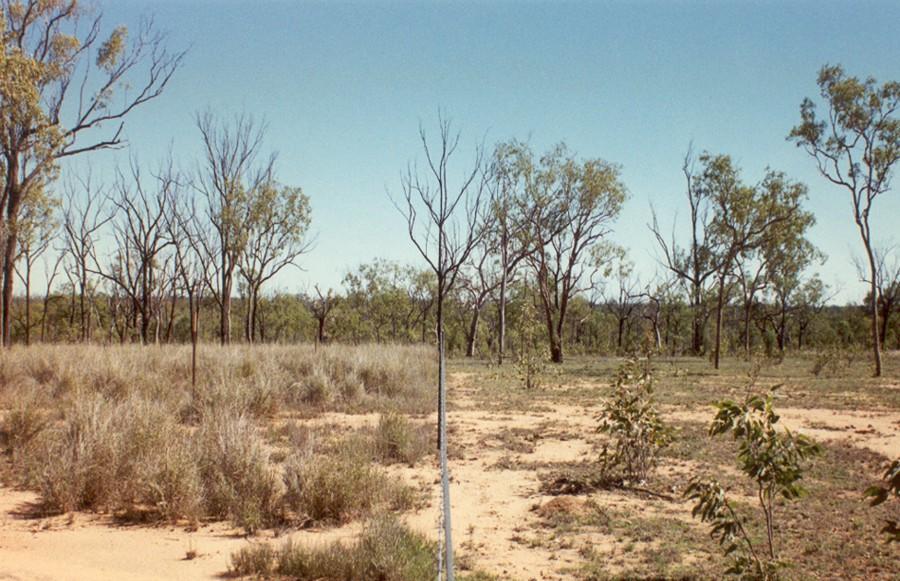
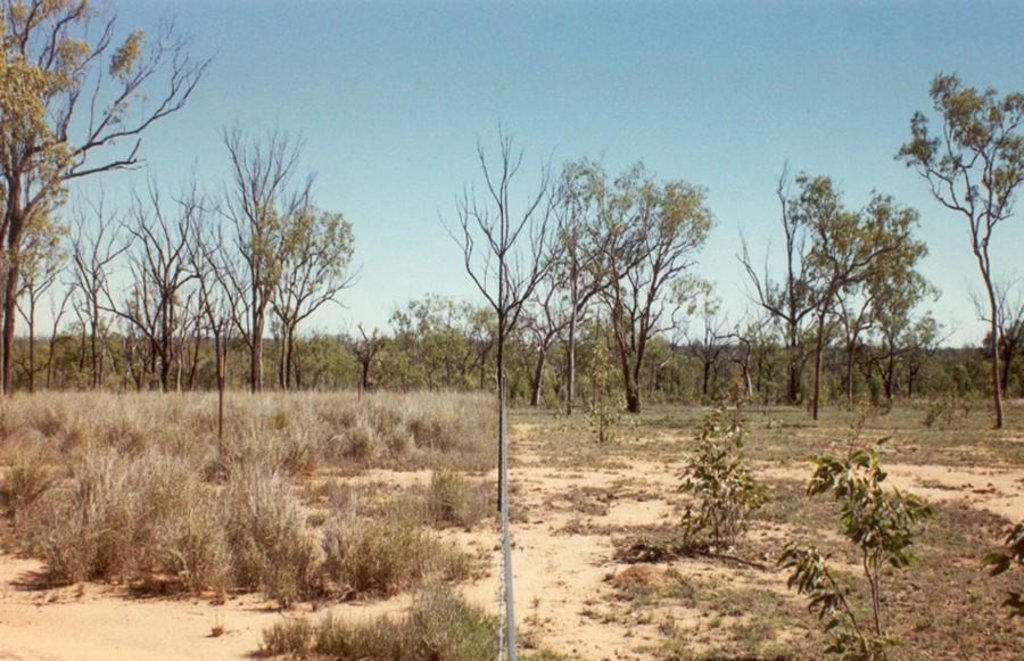
Open eucalypt woodlands cover approximately 15 million hectares in the semi-arid plains of north-east Australia, and support about a million head of cattle. Keeping these grazing lands productive and healthy demands good management, and getting the right balance between stock numbers and the forage resource is a considerable challenge.
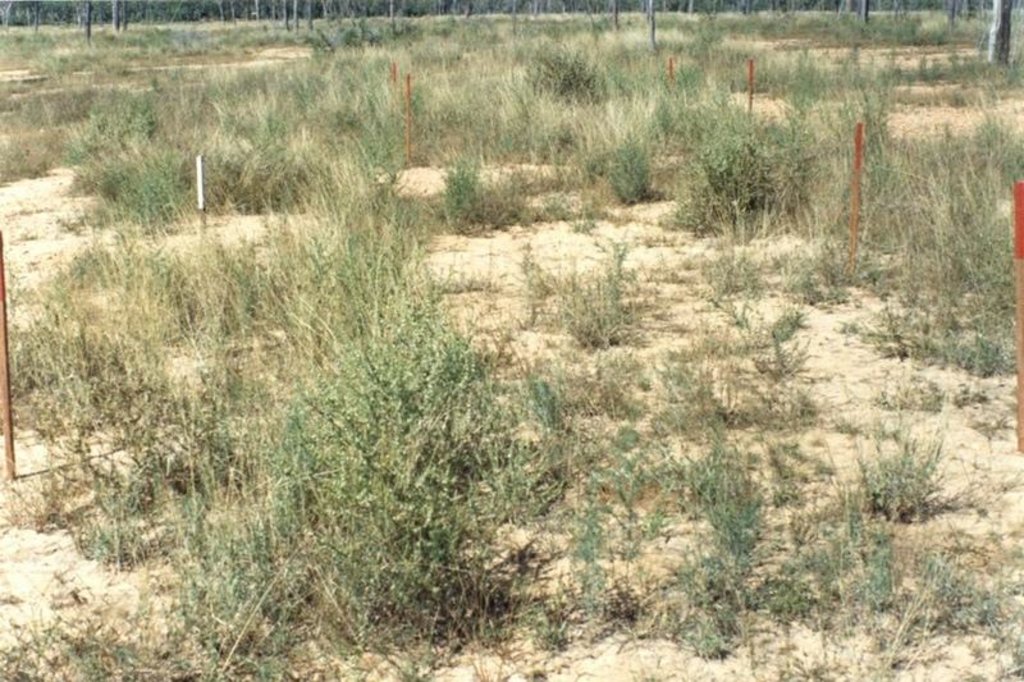
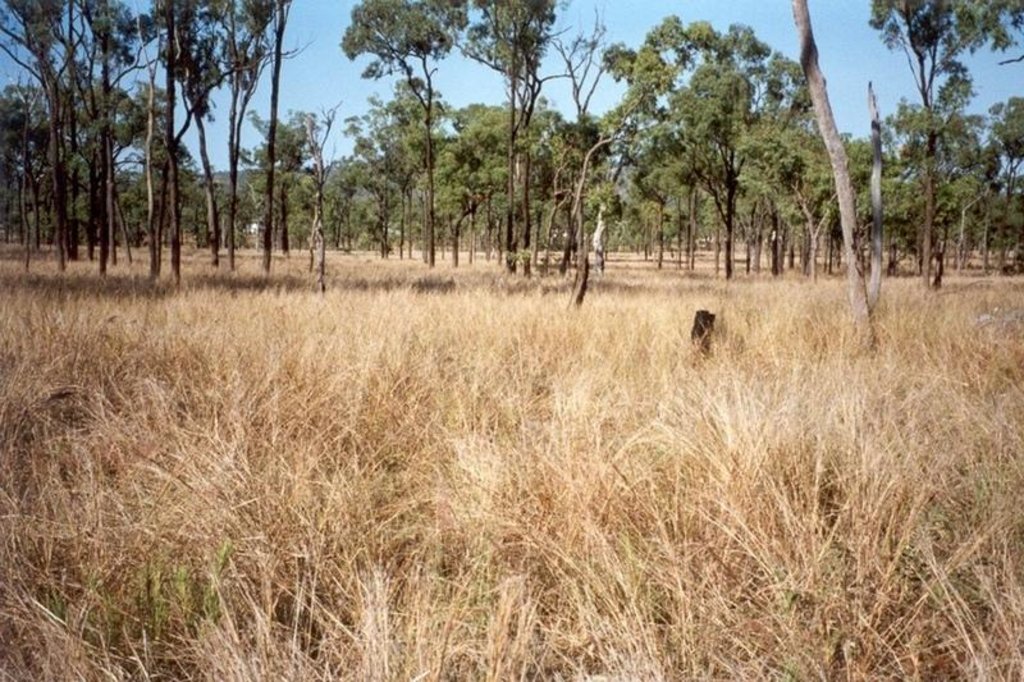
Land in good condition has a healthy coverage of so-called ‘3P grasses’: native perennial, productive and palatable grasses, important to cattle and to the health of the landscape. Less palatable plants include annual grasses, native and exotic forbs and shrubs. The heterogeneity of the pasture resource results in uneven utilisation, and thus overgrazing in parts.
In order to prevent pastures in good condition from degrading, or to restore/improve deteriorated pastures, utilisation needs to be adjusted according to climate and the state of the ‘3P grasses’. In practice, the only means of manipulating pasture composition over large areas are grazing, resting from grazing, and burning.
The flexible Ecograze system includes wet season resting, and is based on the establishment of three paddocks with two herds within a rotational system. The key is that all paddocks get some wet season rest two years out of three. Wet season rests are divided into two phases: (1) The early wet season rest starts after the first rains in November/December and continues for 6-8 weeks, it is particularly good for perennial grass recovery; (2) the late wet season rest lasts until March/April and aids both seed set and vegetative recovery.
Average paddocks of around 3,000 ha in size are sub-divided into three relatively equal sizes, though some flexibility is required to balance variation in the productive capacity of different land types within the paddock. The paddocks are fenced and extra water points through polythene piping and additional water troughs, and where required, pumps are established. The return on investment can be realised within a few years.
The main management challenges are: (1) the timing and length of the early wet season rest, which depends on how effectively the early rains promote vegetative growth of perennial grasses, and (2) the movement of animals during the wet season. The number of stock movements are fixed - but the timing is flexible and should be responsive to the situation: the challenge is to learn to assess the pasture condition, read the situation, and schedule the timing and length of the rest period accordingly. The main criterion is the recovery state of perennial grasses.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Австралия
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Queensland
Более точная привязка места:
North-eastern Queensland
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если технология равномерно занимает территорию, укажите площадь покрытия (в км2):
10,0
Если точная область неизвестна, укажите приблизительную площадь:
- 10-100 км2
Пояснения:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 10 m2.
study terminated after 8 years (2000-2001).
The paddocks of an average size of around 30 km2 are subdivided into three paddocks of an average size of 10 km2. The technology is therefore documented on one of the subdivided paddocks. The 10 km2 is the area per subdivided paddock, each farm (localities) has 10 km2 (respectively 3*10km2) area, where the technology is applied.
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- менее 10 лет назад (недавняя)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- в качестве научного/ полевого эксперимента
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
Meat and Livestock Australia initiated the project to improve the understanding of the effects of grazing, spelling, fire and climate on the condition and productivity of open eucalyptus woodlands in north-eastern Queensland.
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология

Пастбищные угодья
Экстенсивный выпас:
- Загонно-порционное
- Cattle
Пояснения:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Over the last 20 years there has been a decline in the condition of grazing lands in north-east Australia. The evidence is a decline of palatable, perennial, productive grasses (‘3P grasses’), reduced ground cover and an increase in sediment and nutrient movement into streams. As a consequence of economic pressures and over-optimistic expectations of good rains, stocking rates have often been too high.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): same as above (combined)
Ranching: Yes
3.4 Водоснабжение
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
3.5 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- ротационная система (севооборот, парование, переложное использование)
- Кочевое животноводство и пастбищное хозяйство
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

управленческие мероприятия
- У2: Изменение формы/ интенсивности хозяйствования
Пояснения:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов
- ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование
- ВЭд: косвенное воздействие водной эрозии

ухудшение физических свойств почв
- Фу: уплотнение
- Фк: растрескивание и коркообразование

биологическая деградация
- Бр: сокращение растительного покрова
- Бв: потеря природного разнообразия
Пояснения:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects, Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- снижение деградации земель
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
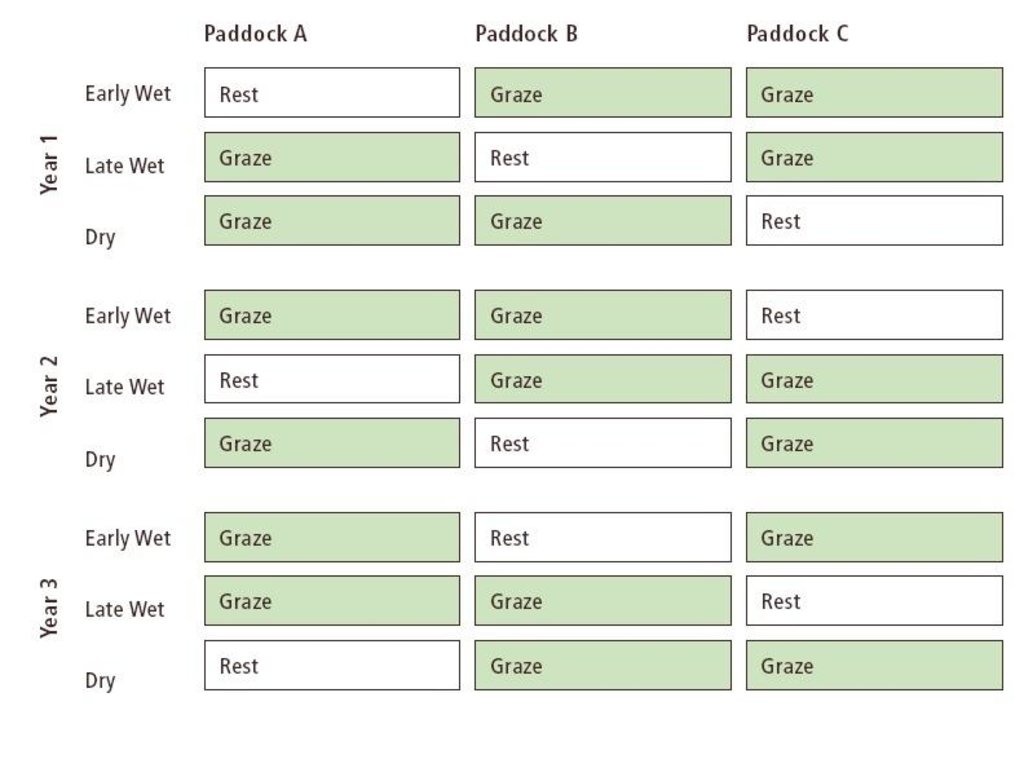
The drawing refers to the ‘two herd/three paddock Ecograze system’. Paddock A is rested in the early wet season, while Paddocks B and C are grazed. Paddock B is then rested for the late wet season while Paddocks A and C are razed. Paddock C is then rested for the dry season and the next early wet season while Paddocks A and B are grazed. Paddock A is then rested for the late wet season and the rotational cycle continues in this fashion for the three years of the full rotation. Early wet season spelling should commence after the first significant rains in November/December and should continue for 6-8 weeks, depending on how effectively the early rains promote vegetative growth of perennial grasses. Late wet season rest typically last until March/April, depending on length of growing season.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate; Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, increase in soil fertility
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: 3P grasses (native perennial, productive and palatable grasses)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: rotational system, timing and length of resting period, timing of animal movement
Control / change of species composition: grazing, (wet season) resting from grazing and burning
Автор:
Mats Gurtner
4.2 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Уточните, как рассчитывались затраты и вложения:
- на площадь, где применяется Технология
Укажите размер и единицу площади:
1 ha
Укажите денежные единицы, использованные для подсчета затрат:
- Доллары США
4.3 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Время (сессия) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Paddocks first need to be surveyed to understand the various plant communities and soils | |
| 2. | Paddocks first need to be surveyed to understand the various plant communities and soils. | |
| 3. | Based on the survey and location of water points, and the most practical location for fences, a paddock design is developed: paddocks are subdivided into relatively equal sizes. | |
| 4. | Fencing the paddocks Material: metal barbed wire or plain wire for electric fences, steel fence posts, wooden or steel end assemblies (poles) to strain the fence, energisers (for electric fences). | |
| 5. | Provision of extra water points through polythene piping and additional water troughs - and where required, pumps. |
4.4 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Tools | ha | 1,0 | |||
| Строительные материалы | others (specify): metal, wire, wood | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 80,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 10,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на создание Технологии в долларах США | 10,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
Duration of establishment phase: 48 month(s)
4.5 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Monitoring pastures and soils | |
| 2. | Mustering (gathering) and shifting (moving) livestock | |
| 3. | Monitoring pastures and soils. | |
| 4. | Repair fences (wire, poles, etc) |
4.6 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Tools | ha | 1,0 | |||
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 1,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на поддержание Технологии в долларах США | 1,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
Current average paddock size is 3,000 ha - commonly 6 km x 5 km. To sub-divide the paddock into three requires two internal fences, each of 5.0 km. Costs of fencing and associated gates are about US$1,200 per km. Labour for fencing is also approximately US$1,200 per km (Note: while this looks expensive, because of the large paddock size, on a per hectare basis this is equivalent to US$ 4.0 per hectare).
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Агроклиматическая зона
- полузасушливая
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
Landforms: Also hill slopes (ranked 2) and ridges (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Aslo moderate (ranked 2) and flat (ranked 3)
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
- тонкодисперсный/ тяжёлый (глинистый)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
- низкое (< 1%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil depth on average: Also Shallow (ranked 2) and deep (ranked 3)
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (ranked 1) and poor (ranked 2)
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- товарное/ рыночное хозяйство
Доходы из других источников:
- 10-50% всех доходов
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Off-farm income specification: usually constitutes off-farm financial investments (eg shares in companies, investment properties, etc)
5.7 Средняя площадь земель, используемых землепользователями с применением Технологии
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
- individual
Право землепользования:
- аренда
- индивидуальное
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство кормов
качество кормов
Доходы и затраты
доходы хозяйства
экономическое неравенство
объем работ
Социальное и культурное воздействие
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Экологическое воздействие
Почвы
влажность почв
почвенный покров
утрата почв
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
подтопление ниже по течению
отложение наносов ниже по течению
отложения, переносимые ветром
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
отрицательно
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо отрицательное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
Если возможно, дайте количественную характеристику (число домохозяйств и/или площадь применения):
15005
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 0-10%
Пояснения:
60% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
5 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
15000 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There are indications that around 700 (of a total of 15,000) farmers across northern Australia have already adopted some aspects. Surveys indicate spontaneous adoption beyond the region as well. In time a large number of farmers are expected to adopt it.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
|
Increased perennial grass cover, improved pasture productivity, increased animal carrying capacity and associated increased profit How can they be sustained / enhanced? Wide and long-term adoption of Ecograze system. |
|
Improved soil cover reduces erosion and sediment flow into streams and dams How can they be sustained / enhanced? Manage pasture condition through Ecograze to maintain ‘3P grasses’. |
|
Greater stability of forage supply leading to less problems and less stress in farm management How can they be sustained / enhanced? Wide and long-term adoption of Ecograze system. |
|
Soil carbon reserves maintained/improved How can they be sustained / enhanced? Wide and long-term adoption of Ecograze system. |
|
Plant biodiversity protected How can they be sustained / enhanced? Wide and long-term adoption of Ecograze system. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Adoption of technology needs long-term approach to accommodate for slow rate of change by ranchers | Continue to demonstrate the advantages of the technology. |
| Implementing rotational grazing incurs (moderate) investment costs in the form of fencing and new water points | Investigate government subsidies and educate about long-term economic benefits. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Ash A, Corfield J and Taoufik T (undated) The ECOGRAZE Project: developing guidelines to better manage grazing country. CSIRO, Meat and Livestock Commission and Queensland Government
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Tothill JC and Gillies C (1992) The pasture lands of northern Australia: their condition, productivity and sustainability Occasional Publication No.5, Tropical Grassland Society of Australia, Brisbane
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Tothill J and Partridge I (1998) Monitoring grazing lands in northern Australia - edited by Occasional Publication No.9, Tropical Grassland Society of Australia, Brisbane
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Development and promotion of Ecograze [Австралия]
Research-based development and promotion of Ecograze principles and practices through on-farm testing and demonstration.
- Составитель: Andrew Ash
Модули
Нет модулей