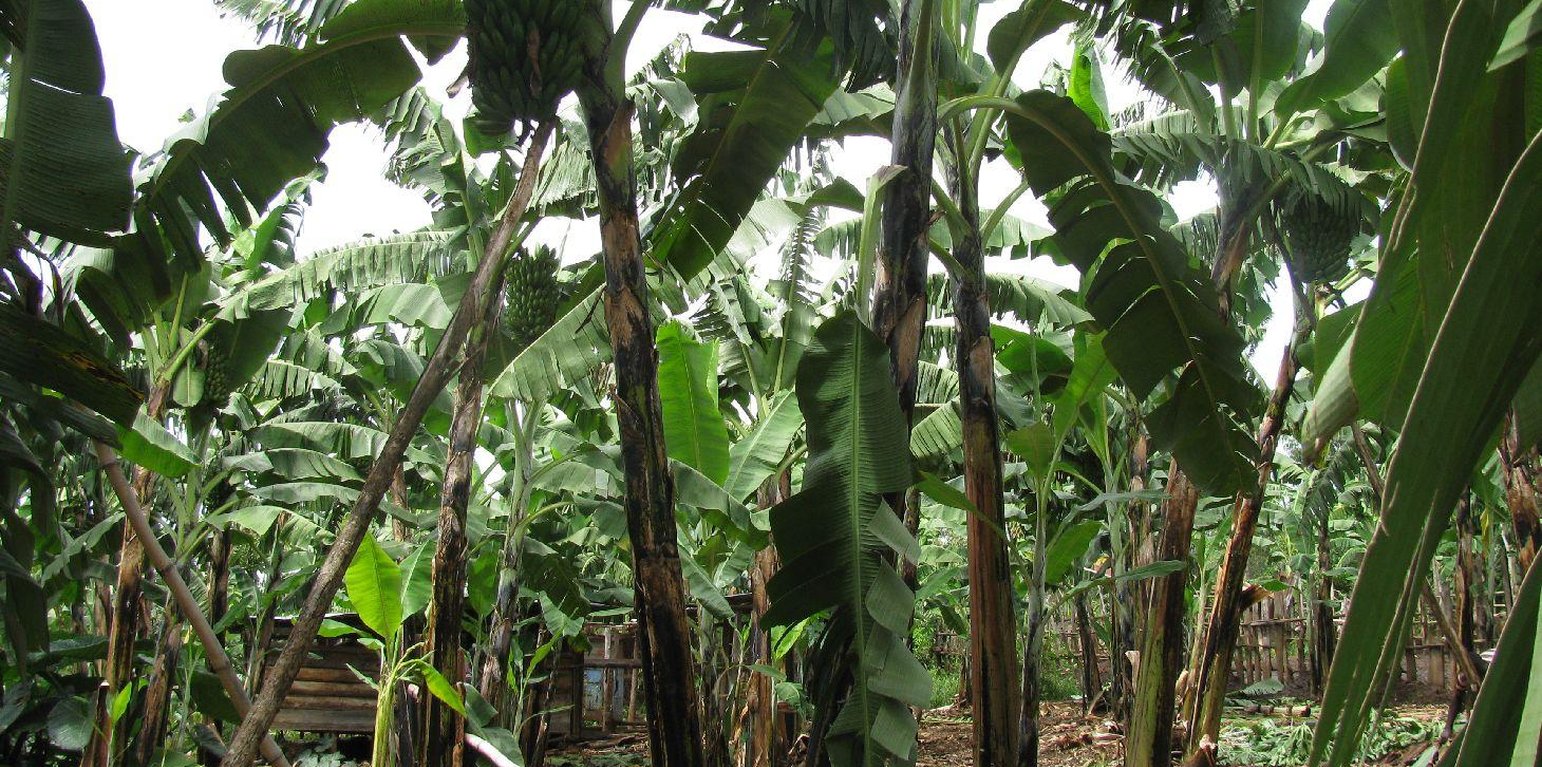




Improved traditional multi-cropping system that combines banana and coffee as main crops planted in a specific spacing to optimize plant stands. Banana and coffee are intercropped with; 1. annuals crops: Maize, beans, yams, coco-yams;2. Vegetables: Lycoperscum esculentum, Amaranthus spp, Cucumis communis and Solanum aethopium ;3. Shrubs of social economic value. Trees (e.g Maesopsis eminii, Makhcamia lutea, Ricinus comunis, Ficus thorninghii) and shrubs (Dracaena usambarensis) are planted on the farm edge. These serve as live fence, wind breaker, source of timber, fuel wood, medicine and protect the field against erosion. To optimize farm production, application of 15cm thick mulch ( grass mulch and banana prunnings), farmyard or compost manure and interplanting with soil fertility and/or soil moisture improvement trees are ensured. With problems of climate change, water harvesting ditches and trenches are constructed. Water harvesting ditches are constructed to collect water from micro catchments like roads or homestead. Sustainability of the Improved Kibanja system has always been assured through crop/livestock integration approaches.The cropping system is typical in high rainfall areas along foot slopes, valley bottoms or hilltops preferably on fertile and deep soils.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose is improve soil fertility,moisture, controlling soil erosion (wind and water) and suppressing weeds in order to improve the production banana, coffee and other inter planted crops.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities: 1. Land clearing and preparation: Slashing, uprooting tree stumps, ploughing and pitting 60cm x 90cm banana hole and 60cm x 60cm coffee (Mid June to August) using simple farm implements; 2.Farm Yard Manure application: 60 Kg per banana holes and 36 Kg per coffee hole (August to early September); 2. Planting: 308 banana suckers at 3.6m x 8m spacing, 830 coffee seedlings at 3m x 8m spacing in alternating row, edge row trees seedling at 10m spacing and 15cm spacing for shrubs e.g. Dracaena usambarensis (September to November);4. Excavation of water retention structure ( after planting mainly in Novermber). Full establishment of Improved Kibanja cropping system can be attained in three years.
Maintenance activities:1. Weeding:Done two times per year (mid January to February / July to augost) before planting annual crops; 2.FYM enrichment: Every after 3 years; iii. banana dethrashing and desuckering ,topping mulch, coffee pruning and harvesting (Immediately after weeding); 4. Other maintenence activities: Disease control (nematode, banana weevils, Banana Xanthamonas Wilt) and Propping (using pole to support banana plant with heavy bunches against wind); 5.Inputs: Labour, farmyard manure, propping poles, mulch; 6. Simple farm implements:Hand hoe,machete and wheel barrow.
Natural / human environment: The technology is implemented in mixed land use type under sub humid condition receiving 1000-1500mm of rains per year. A combination of soil and water improvement measures (FYM application, Mulching, water retention ditches and live fencing) complement each other to minimize risk of crop failure and hence improve production. The slope is gentle to moderate , soil depth is moderate and soil texture loam. Simple hand tools are traditional used,Land ownership is individual not titled. Application of this technology determined by high establishment and maintenence cost.
สถานที่: Missenyi District, Kyazi Village, Tanzania, แทนซาเนีย
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์))
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
ประเภทของการแนะนำ










| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (USD) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (USD) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Land clearing | persons/day | 202.0 | 1.18316 | 239.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction of water harvesting ditches | persons/day | 4.0 | 0.937 | 3.75 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 61.56 | 61.56 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| Seedlings | pieces | 1138.0 | 0.0468 | 53.26 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | |||||
| Manure | tons | 54.0 | 34.7222 | 1875.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | |||||
| Cuttings | ha | 1.0 | 2234.6 | 2234.6 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 4'467.17 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 4'467.17 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (USD) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (USD) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Topping grass mulch | persons/day | 10.0 | 4.101 | 41.01 | 100.0 |
| Applying FYM | persons/day | 10.0 | 3.906 | 39.06 | 100.0 |
| Removal of sediments | persons/day | 4.0 | 0.9375 | 3.75 | 100.0 |
| To replacement propping Poles | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 3.906 | 39.06 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Tools | per ha | 4.0 | 1.875 | 7.5 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | |||||
| Farm yard manure | tons | 20.833 | 46.8 | 974.98 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | |||||
| Wood | pieces/ha | 600.0 | 0.625 | 375.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | |||||
| Mulching material | bundle | 300.0 | 1.875 | 562.5 | 100.0 |
| Transportation | trips | 19.0 | 61.673 | 1171.79 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 3'214.65 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 3'214.65 | ||||
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 50
หลังจาก SLM: 300
Bunch of banana with 70 kg each
Depend mainly on banana sell
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 1875 $
หลังจาก SLM: 1406 $
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 6250
หลังจาก SLM: 25000
Annual income in dollar
Solery depend on farm
Reduced weeding, but technology is labour intensive.
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 1000
หลังจาก SLM: 4000
Increase in bunch of banana produde annually
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 5
หลังจาก SLM: 2
Frequency of attedndence to hospital due to edequate food supply
Adoption by neighbouring farmers
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 0
หลังจาก SLM: 10
Due to water harvesting dithchers along the foot path in the farm
Due to the use of mulch and corver crops
Due to corver crop and mulch
Use of banana trash mulch and other corver crops
Due to mulching material