Improved Kibanja cropping system [แทนซาเนีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Jasson Rwazo
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Ekibanja ekiine emikolele emirungi (Haya/Nyambo)
technologies_1183 - แทนซาเนีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
Government:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Government:
Makung'uto Iddi
Missenyi District Council
แทนซาเนีย
Government:
Kagaruki Anna Grace
Missenyi District Council
แทนซาเนีย
Government:
Subira John
Missenyi District Council
แทนซาเนีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Kaihura Fidelis
Kagera TAMP
แทนซาเนีย
Government:
Kitundu Elizabeth
Missenyi District Council
แทนซาเนีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO Food and Agriculture Organization) - อิตาลีชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - แทนซาเนีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Integrated farm knowledge adoption [แทนซาเนีย]
The way and means through which a performing farmers adopt and use a combination of indigenous and scientific to maximaze production.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Jasson Rwazo
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
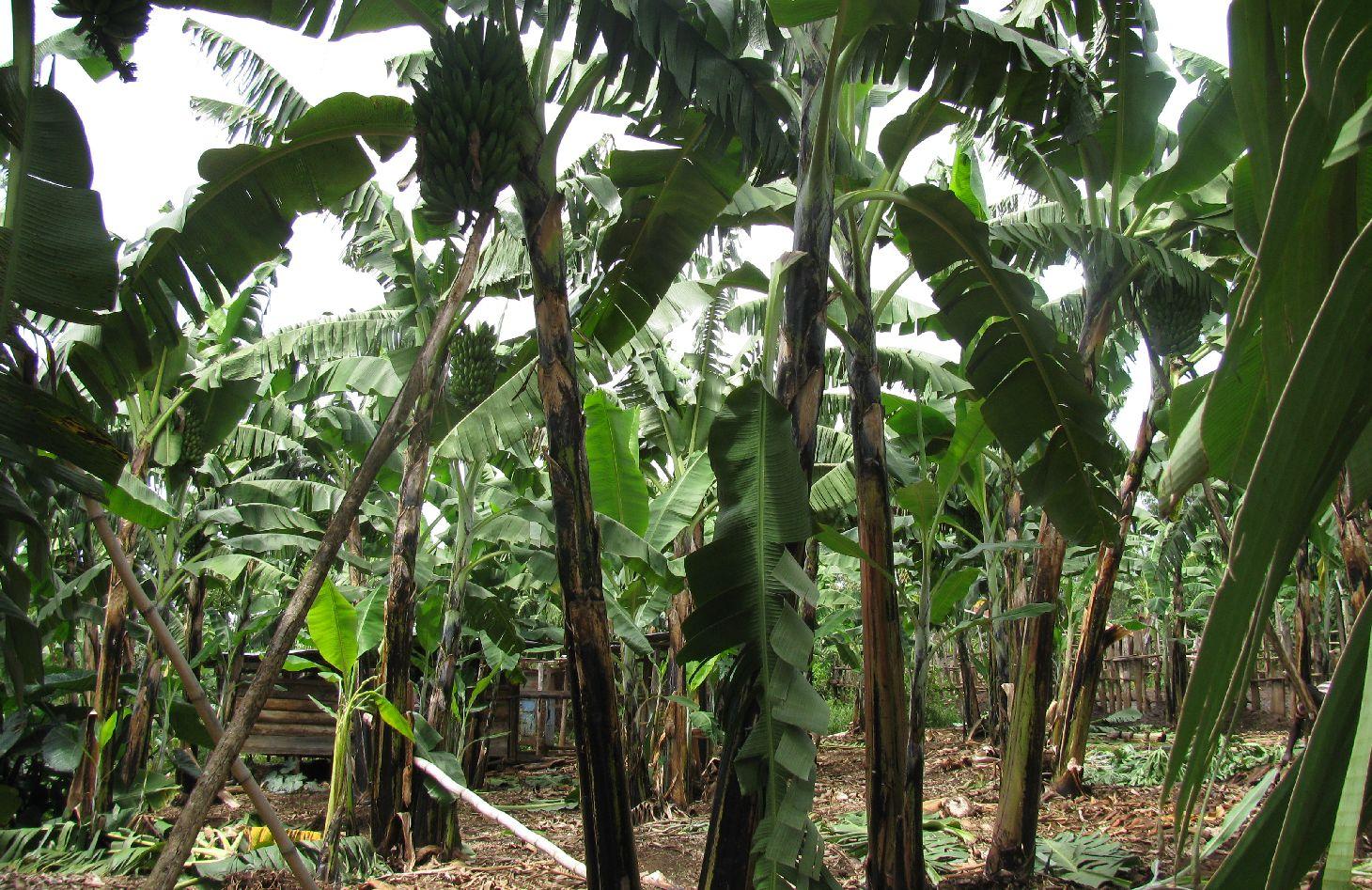
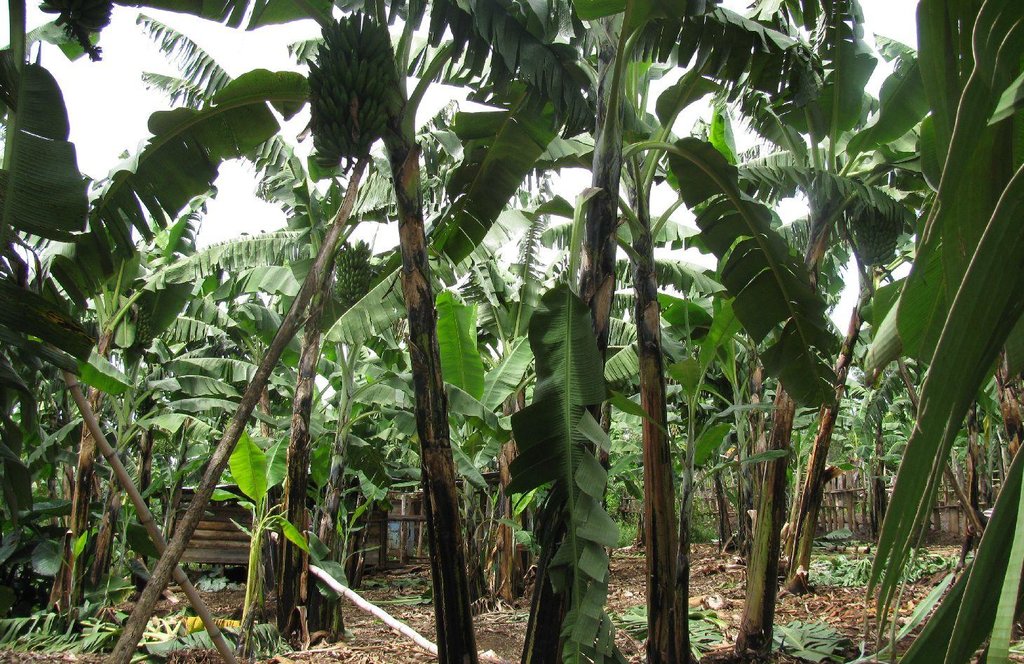
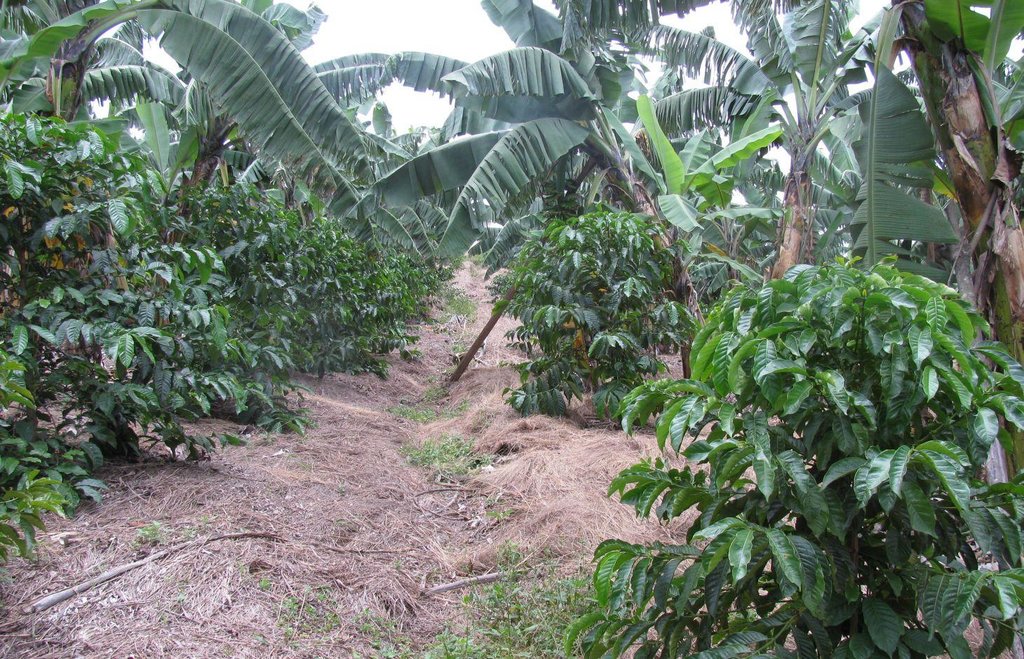
This is a traditional banana and coffee complex cropping system interplanted with annual crops, trees,shrubs, vegetables and other diverse plants of social economic importance.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
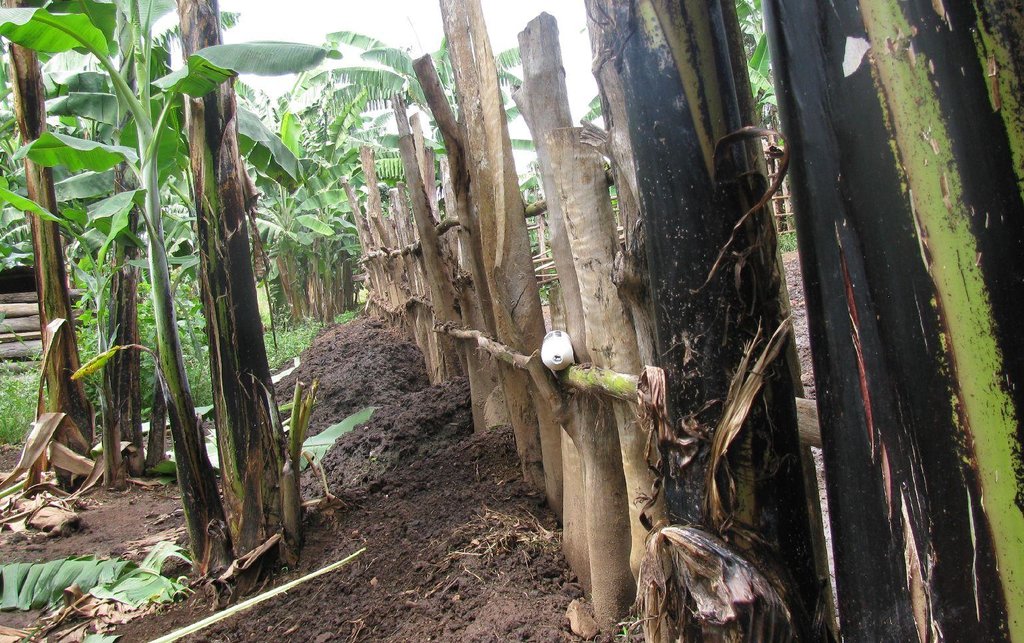
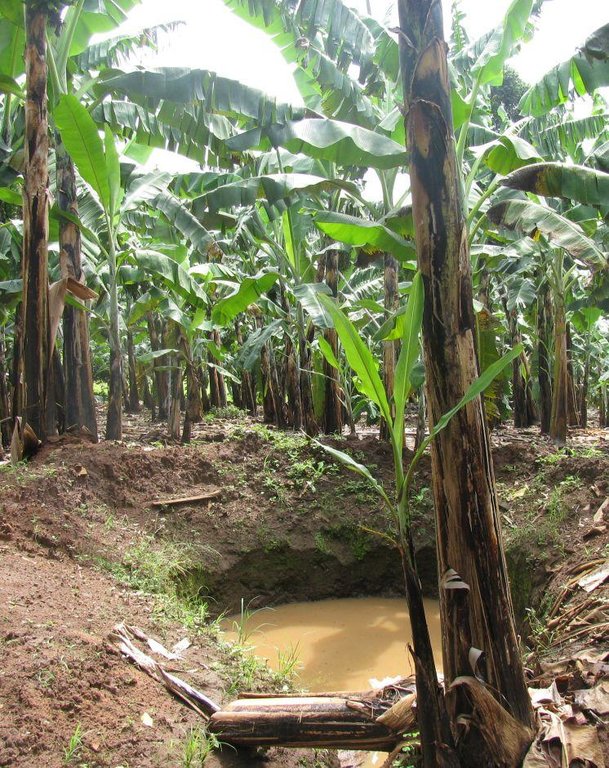
Improved traditional multi-cropping system that combines banana and coffee as main crops planted in a specific spacing to optimize plant stands. Banana and coffee are intercropped with; 1. annuals crops: Maize, beans, yams, coco-yams;2. Vegetables: Lycoperscum esculentum, Amaranthus spp, Cucumis communis and Solanum aethopium ;3. Shrubs of social economic value. Trees (e.g Maesopsis eminii, Makhcamia lutea, Ricinus comunis, Ficus thorninghii) and shrubs (Dracaena usambarensis) are planted on the farm edge. These serve as live fence, wind breaker, source of timber, fuel wood, medicine and protect the field against erosion. To optimize farm production, application of 15cm thick mulch ( grass mulch and banana prunnings), farmyard or compost manure and interplanting with soil fertility and/or soil moisture improvement trees are ensured. With problems of climate change, water harvesting ditches and trenches are constructed. Water harvesting ditches are constructed to collect water from micro catchments like roads or homestead. Sustainability of the Improved Kibanja system has always been assured through crop/livestock integration approaches.The cropping system is typical in high rainfall areas along foot slopes, valley bottoms or hilltops preferably on fertile and deep soils.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose is improve soil fertility,moisture, controlling soil erosion (wind and water) and suppressing weeds in order to improve the production banana, coffee and other inter planted crops.
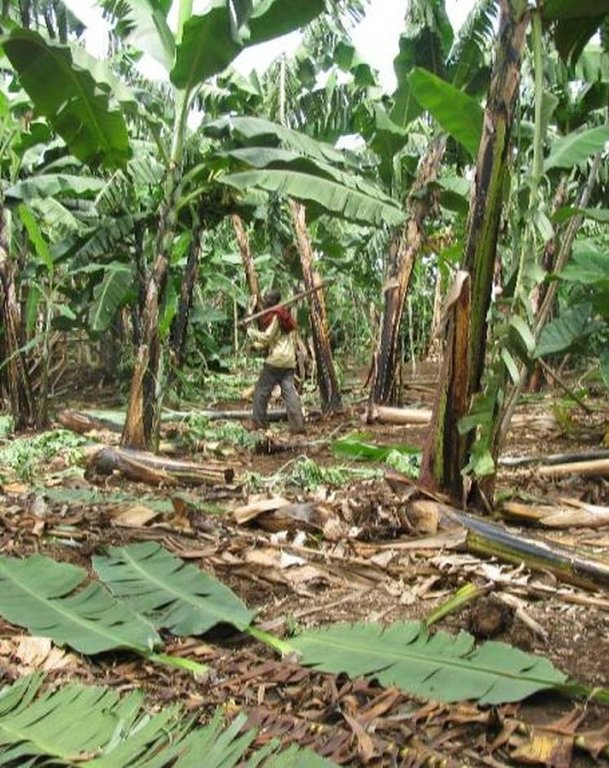
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities: 1. Land clearing and preparation: Slashing, uprooting tree stumps, ploughing and pitting 60cm x 90cm banana hole and 60cm x 60cm coffee (Mid June to August) using simple farm implements; 2.Farm Yard Manure application: 60 Kg per banana holes and 36 Kg per coffee hole (August to early September); 2. Planting: 308 banana suckers at 3.6m x 8m spacing, 830 coffee seedlings at 3m x 8m spacing in alternating row, edge row trees seedling at 10m spacing and 15cm spacing for shrubs e.g. Dracaena usambarensis (September to November);4. Excavation of water retention structure ( after planting mainly in Novermber). Full establishment of Improved Kibanja cropping system can be attained in three years.
Maintenance activities:1. Weeding:Done two times per year (mid January to February / July to augost) before planting annual crops; 2.FYM enrichment: Every after 3 years; iii. banana dethrashing and desuckering ,topping mulch, coffee pruning and harvesting (Immediately after weeding); 4. Other maintenence activities: Disease control (nematode, banana weevils, Banana Xanthamonas Wilt) and Propping (using pole to support banana plant with heavy bunches against wind); 5.Inputs: Labour, farmyard manure, propping poles, mulch; 6. Simple farm implements:Hand hoe,machete and wheel barrow.
Natural / human environment: The technology is implemented in mixed land use type under sub humid condition receiving 1000-1500mm of rains per year. A combination of soil and water improvement measures (FYM application, Mulching, water retention ditches and live fencing) complement each other to minimize risk of crop failure and hence improve production. The slope is gentle to moderate , soil depth is moderate and soil texture loam. Simple hand tools are traditional used,Land ownership is individual not titled. Application of this technology determined by high establishment and maintenence cost.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แทนซาเนีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Tanzania
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Missenyi District, Kyazi Village
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.062 km2.
2ha approximately
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Improved traditional land use system: The use of combination of measures in Improved Kibanja Cropping system in Kagera has been existing for more than 100 year ago.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- improve soil fertility
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
- Ficus thoninji,Markhamia lutea,Maesopesis eminii
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- legumes and pulses - beans
- Lycoperscum esculentum, Amaranthus spp, Cucumis communis and Solanum aethopium
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- avocado
- Orange, Paw paw, Maesopsis eminii, Makhcamia lutea, Ricinus comunis, Ficus thorninghii, Dracaena usambarensis
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: Short rains (September to December); Second longest growing period in days: 65; Second longest growing period from month to month: Long rains (March to June)
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
banana, coffee

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง
- ผลิตภัณฑ์อื่น ๆ จากป่า
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil nutrient loss, decline of soil moisture and soil erosion by wind and fast water runoff.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Reduced crop production, loss of indigenous medicinal plants, reduced water water quatity in natural water sources.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Due to mixed farming and agroforestry there is high nutrient cycling resulting in high productivity
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- แนวกันลมหรือแนวต้านลม
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S4: คูน้ำแนวระดับ หลุม

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M3: การวางผังตามสิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมของมนุษย์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, retaining more vegetation cover, mulching, manure / compost / residues, minimum tillage, pits
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind, aligned: -along boundary, aligned: -linear
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Cultivation along the slope and overcultivation), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Cultivation of season crop without reprenishing of soil nutrients), change of seasonal rainfall (Fractuation in rain season), droughts, population pressure, education, access to knowledge and support services
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), land tenure, poverty / wealth, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Location: Kyazi Village. Missenyi District, Kagera Region, Tanzania
Date: 2012.08.28
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (The technology requires moderate technical knowledge for adoption)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (The technology requires moderate technical knowledge for adoption)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Banana
Quantity/ density: 304
Remarks: 3.6 m by 8m
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: Beans
Remarks: Random
Mulching
Material/ species: Grass mulch, banana(Prooning) trashes mulch
Quantity/ density: 10000
Remarks: Spreading the mulch
Material/ species: Coffee
Quantity/ density: 830
Remarks: 3m by 8m
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Farmyard manure, farm residure,
Quantity/ density: 40 tone
Remarks: Spreading on the pit
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Hand hoe,matechette
Pits
Material/ species: Hand hoe,matechette
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 277
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): Random
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): Random
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): Random
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 100000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.01
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.01
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 100000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.01
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.01
Trees/ shrubs species: Maeesopsis Eminii, Dracaena usambalensis,Erythrina abysinica
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Pawpaw, Orange, Avocado
Perennial crops species: Banana, Coffee, Vanilla
Other species: Carisa edulis (shrubs)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 6.3%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 6.3%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.4
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.15
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.15
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Waterway
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.4
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.75
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 5
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.4
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.75
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 5
Construction material (earth): 2.25 m3 of earth material used per ditch
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 6%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 8%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 10m3
Catchment area: 1.6Ham2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:3.5
ผู้เขียน:
Jasson Rwazo, P.O.BOX 38 Misseny Tanzania, rjrwazo@gmail.com
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land clearing and preparation:Slashing,uprooting tree stumps, ploughing and pitting | June to August |
| 2. | Availing and applying 54 tone Farm Yard | August to early September |
| 3. | Planting: 308 banana suckers 830 coffee and tree edge low tree seedlings | From September |
| 4. | Construction of water harvesting ditches | Once year |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Land clearing | persons/day | 202.0 | 1.18316 | 239.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Construction of water harvesting ditches | persons/day | 4.0 | 0.937 | 3.75 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 61.56 | 61.56 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | pieces | 1138.0 | 0.0468 | 53.26 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Manure | tons | 54.0 | 34.7222 | 1875.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Cuttings | ha | 1.0 | 2234.6 | 2234.6 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 4467.17 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 4467.17 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Topping grass mulch | 3 times per year |
| 2. | Farm yard manure enrichment | 2 times per year |
| 3. | Removal of sediments and debris in water retention ditches. | Every year |
| 4. | To replacement propping Poles | Every 1.5 year |
| 5. | To corve transportation cost | Manure |
| 6. | Replacement of propping pole and live hedges | Every 1.5 year |
| 7. | Removal of sediments and debris in water retention ditches | Once per year |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Topping grass mulch | persons/day | 10.0 | 4.101 | 41.01 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Applying FYM | persons/day | 10.0 | 3.906 | 39.06 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Removal of sediments | persons/day | 4.0 | 0.9375 | 3.75 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | To replacement propping Poles | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 3.906 | 39.06 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | per ha | 4.0 | 1.875 | 7.5 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Farm yard manure | tons | 20.833 | 46.8 | 974.98 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wood | pieces/ha | 600.0 | 0.625 | 375.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Mulching material | bundle | 300.0 | 1.875 | 562.5 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Transportation | trips | 19.0 | 61.673 | 1171.79 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 3214.65 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 3214.65 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Machetes, Mattocks, Hand hoe, spade, wheel barrow, Machete,Hand hoes, spade, Hand hoe,Machete, Spade
Cost assesment completed in June 2012
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Manure is most determinate factor high transportation cost especially during establishment
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Avarage rainfall 1200mm, Bimode rainfall, 5 month dry season
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics. Annual temperature 23C
Length of growing period 120 -300 days
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zonation: 1270m a.s.l
Slopes on average: Movement of soil due to erosion, exposure of parent rock on some part of the farm
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Shallow on the hill slope and moderately deep on the valley bottom, also deep sometimes
Soil texture (topsoil): Sandy loam
Topsoil organic matter: Due to the high use of organic manure (farm yard manure) and mulch
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium due to the high use of organic manure (farm yard manure), mulch, good aeration
Soil water storage capacity is medium due to the high use of organic manure (farm yard manure) and mulch
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Different species of soil micro organisms and plant species
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The land inheritance is mainly dominated by male, women mostly use the land for production of understory crops such as beans; banana and coffee production is dominated by men
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%; 3%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 30% of the land (Own 2.5-5 acre land, car, 10-20 catlle,brick wall house).
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land (Own 1-2.5 acre of land,2-5 cattle, brick wall house).
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land (Own 0.5-1 acre of land,2-3 goats,mud wall house with corrugarated iron roof).
15% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land (Own 0-0.5 acre of land, no livestock, mud house withgrass roofing).
5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land (Does not own land or own less than 0.5 acre of land, work as casual labour).
Off-farm income specification: 90% of land users income depends on on- income
Market orientation of production system: Mainly for substence for commecial
Level of mechanization: Using hand tools
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
50
หลังจาก SLM:
300
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Bunch of banana with 70 kg each
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Depend mainly on banana sell
การจัดการที่ดิน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1875 $
หลังจาก SLM:
1406 $
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
6250
หลังจาก SLM:
25000
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Annual income in dollar
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Solery depend on farm
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced weeding, but technology is labour intensive.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1000
หลังจาก SLM:
4000
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increase in bunch of banana produde annually
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
5
หลังจาก SLM:
2
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Frequency of attedndence to hospital due to edequate food supply
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Adoption by neighbouring farmers
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
10
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to water harvesting dithchers along the foot path in the farm
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to the use of mulch and corver crops
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to corver crop and mulch
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Use of banana trash mulch and other corver crops
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to mulching material
ความเร็วของลม
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Use drainage trenches
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Depending on regular application of manure and mulch plus good management of the farm
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
317 households (70 percent of all land users in the area)
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
317 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Limited with high labour and input cost (Manure)
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Increased house hold food security and income How can they be sustained / enhanced? Schedule regular maintenance activities |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Soil moisture conservation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance of water harvesting ditches and replacement of mulching materials |
|
Soil fertility improvement How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular application of manure and mulch |
|
Improvement of soil structure and aeration How can they be sustained / enhanced? Manure and mulch application |
|
Control of soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance of plant cover and water retention ditches, manure and mulch application |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High labour and capital demand | Phase in implementation and regular maintenance of the technology |
| High risk of fire | Use of fire breaks |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Improving Productivity of Field Crops and Post Harvest Management in North west Tanzania,United Republic of Tanzania Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Cooperatives,2008
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Kagera TAMP project website
URL:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Integrated farm knowledge adoption [แทนซาเนีย]
The way and means through which a performing farmers adopt and use a combination of indigenous and scientific to maximaze production.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Jasson Rwazo
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล