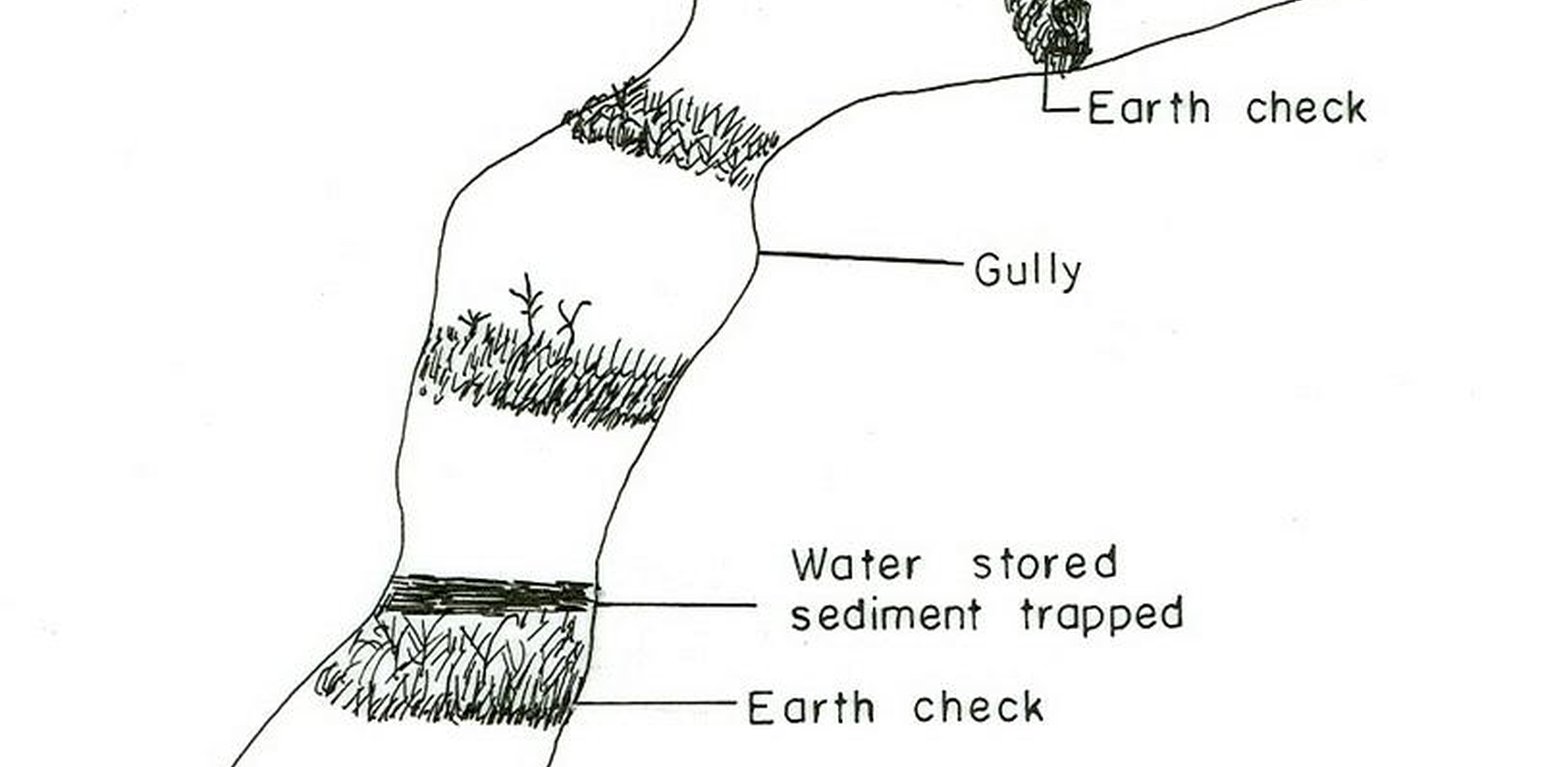



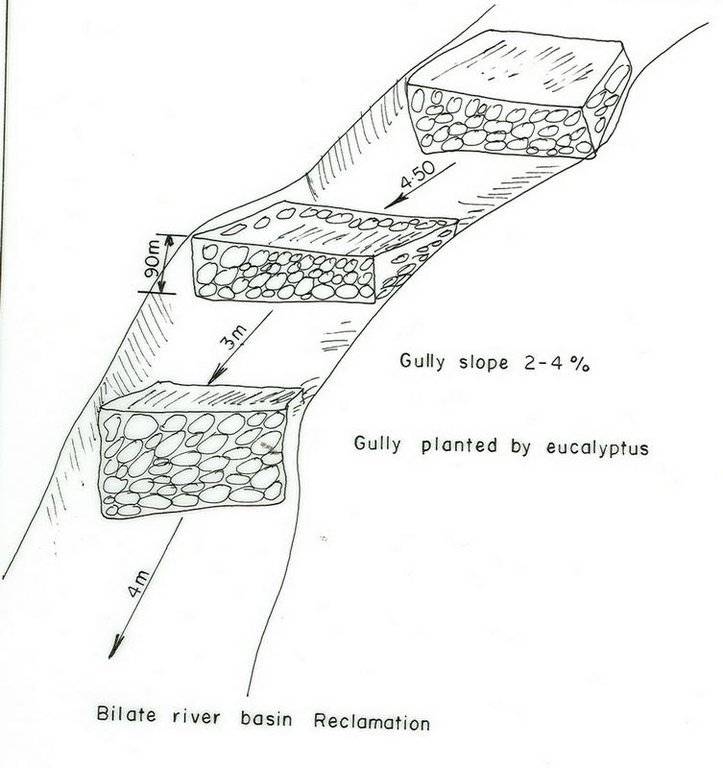
Active deep gullies are plugged by digging earth from the bottom as well as gully sides and embanked forming a barrier to runoff passing through it. The embankment is reinforced by planting useful plants such as banana, sesbania, gravillea, gesho, etc., The purpose is to rehabilitate gullies having depth and expand along sides and towards the head. By constructing earth checks the water is stored in the checks. The water percolates down the ground enriching the ground water. The soil is trapped in the checks and later brings up the gully gradient higher. As a result, a cultivable/cropable strip is formed. Weeding and cultivation done to plants established.The gully fence and breaks are repaired. The technology is seen to be suitable to humid highlands where land loss by gully is a serious problem and land under cultivation and grazing is getting here and there. In brief it is suitable in areas where land degradation problem is increasing with currently cultivated and grazed lands are encroched by gully expansion.
สถานที่: SNNPR/Damot Galle/Bilate, SNNPR, เอธิโอเปีย
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี:
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
ประเภทของการแนะนำ





| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Birr) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Birr) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 282.3 | 282.3 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 270.6 | 270.6 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 117.6 | 117.6 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 670.5 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 78.88 | ||||
Shortage of grazing land: Animals are thethered in a small plots
teams are formed
many wants to be beneficiaries but only the poor given the opportunities
all runoff retained
all soil trapped