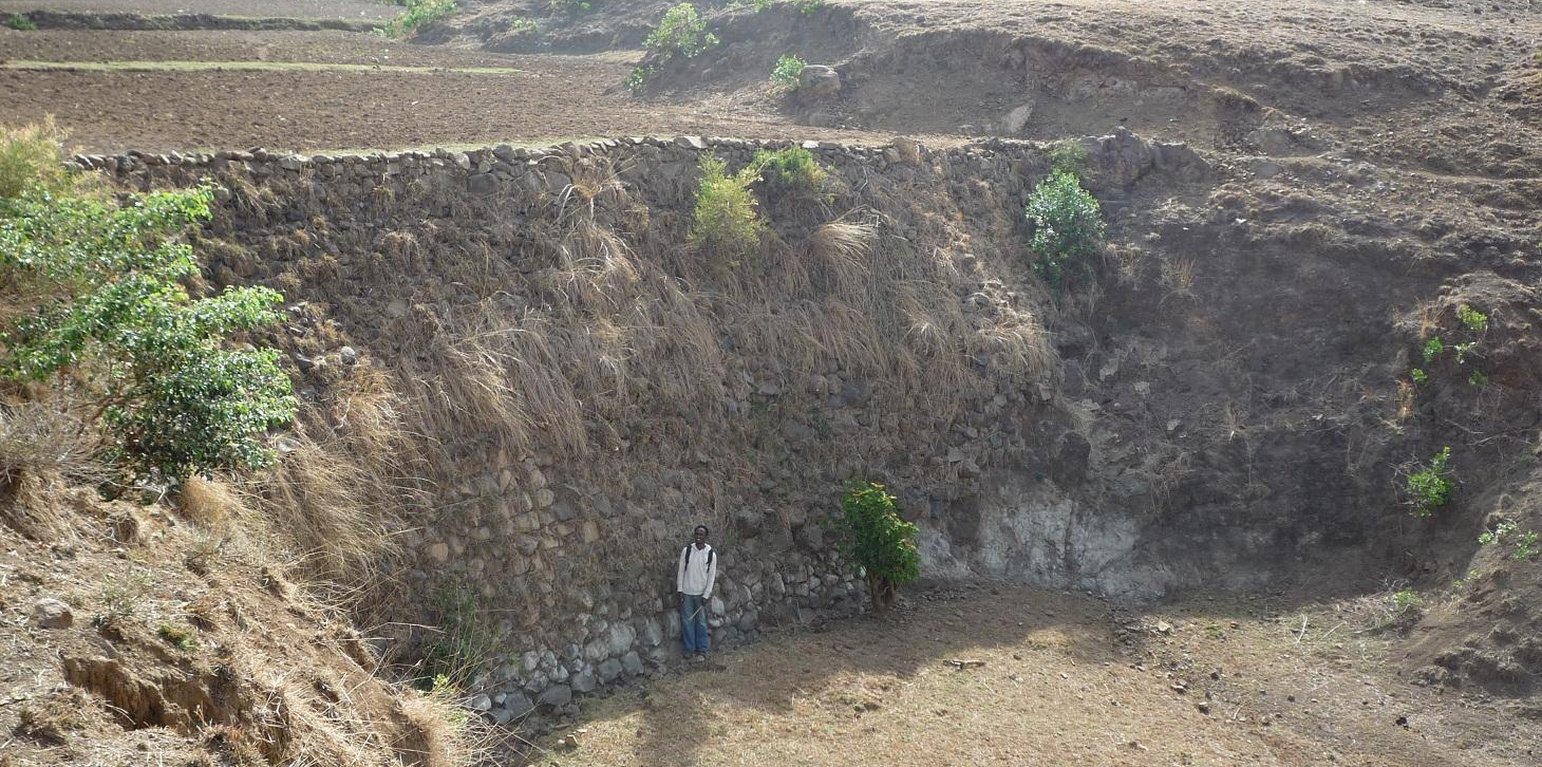




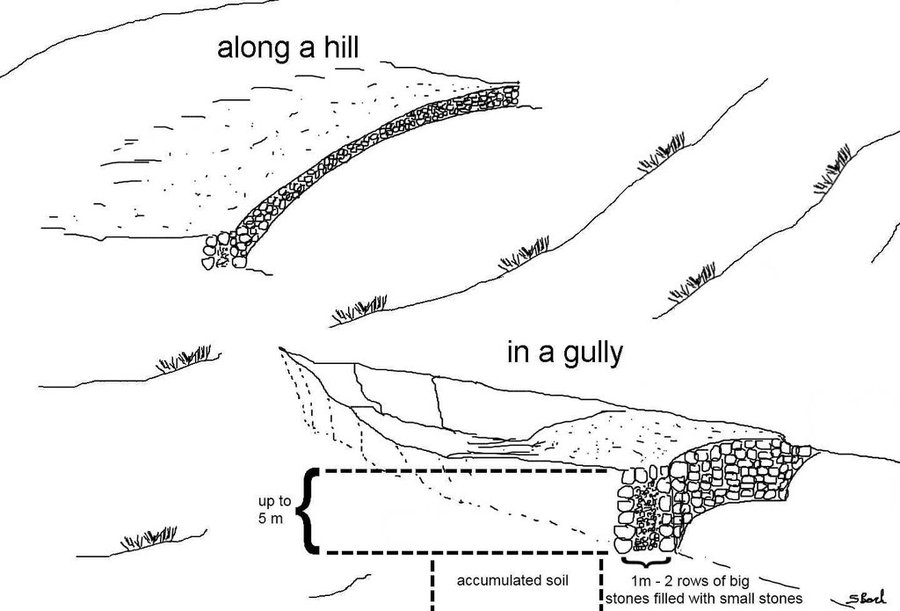
During the 1980s stone walls and terraces were introduced in Ethiopia in order to combat soil erosion. The technology of stone walls or terraces is used to stabilize hills or to refill gullies also in Bati, Ethiopia. Stone walls can form a very strong check dam to rehabilitate gullies even several meters deep.
Purpose of the Technology: Although stone walls can be used for different purposes, this case study is focusing on stone walls used to combat gully erosion. Farmers in the Bati region often use stone walls to rehabilitate gullies if the material is easily accessible, otherwise they may search for alternatives.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Following procedure is undertaken to build a stone wall check dam: After breaking the stones in the source-area they are transported to the target-area either by hand, by camels or by donkeys, depending on the distance. After digging a foundation for the wall of approximately 30 cm depth, the gap between two rows of big stones 1 m apart is filled up with smaller stones and gravel. These actions are repeated until the desired height and width of the wall are reached
Natural / human environment: The case study site, Bati, lays in an semiarid climatic zone on 1600 m a.s.l. Rainfalls are erratic and the rain sum per year is between 500-1000 mm. The landscape is very hilly with rather steep slopes. As almost in all Ethiopia, the area has a high population density and growth. The agricultural sector is very dominant and lead by a lot of small scale farming with a lot of livestock and small plots of cropland.
สถานที่: Bati, Ethiopia / Amhara Region, เอธิโอเปีย
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี:
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 10-50 ปี
ประเภทของการแนะนำ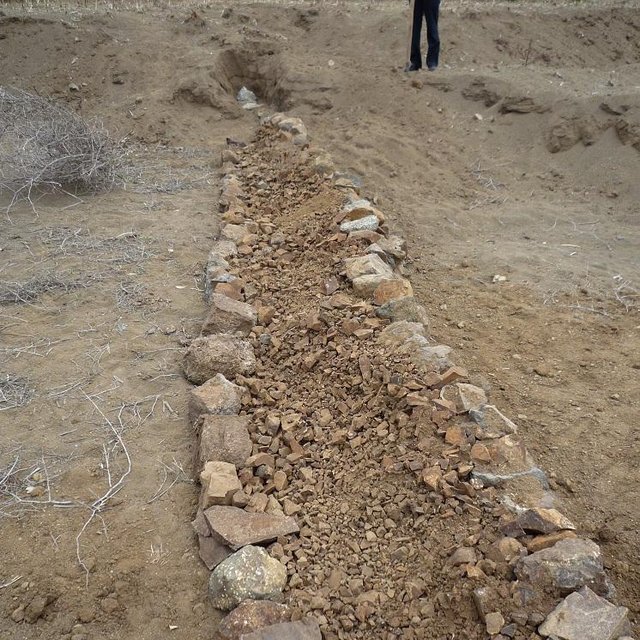




| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Ethiopian Birr) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Ethiopian Birr) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 1165.0 | 1165.0 | 50.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1'170.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 69.56 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Ethiopian Birr) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Ethiopian Birr) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 50.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 505.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 30.02 | ||||
Conservation of soil water
Gullies are transformed to fields. Structure needs space but also gains space
Structure as a new obstacle
alluvial soil is relatively fertile
new fields lead to higher productivity
additional income due to new fields
Gully is now flat land and traversable but needs establishment and maintenance work
Additional space for new fields
best practices may spread further on
upstream and downstream dialog
Accumulation of soil leads to new space for fields and additional food security or even income (if crop surplus is sold).
increased soil moisture
dam blocks water flow
increased infiltration, reduced flow velocity
increased infiltration
Dam blocks water flow but can lead to the fact that additional groundwater may be logged
alluvial accumulation behind the structure
new habitat for rodents etc.
flood controll by stone check dams
possibility of spring development
if a spring can develop
increased infiltration/reduced flooding but also less downstream river flow
trapping of the sediments by the structure
trapping of the sediments by the structure. No off site sediment yields available anymore.
increased infiltration
due to gully rehabilitation
due to gully rehabilitation