Haraghie Stone Bund [Ethiopia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Duagu ghagaa (Oromiya)
technologies_1076 - Ethiopia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Tadesse Getnet
Rural Land and Natural Resources Administration Authority.
Ethiopia
SLM specialist:
Mekonnen Daniel
Rural Land and Natural Resources Administration Authority.
Ethiopia
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
It is constructed along the contour to minimize soil erosion and prevent runoff damage from down stream fields.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
The technology is widely used by farmers in the area and also widely practiced. The structure is built from stone and/or soil. On the average 1m vertical interval is used on a slope of 20-40%.
Purpose of the Technology: The technology is used to increase and maintain crop productivity by promoting activities which improve production and conserve soil and water.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The embankment is constructed from stone/soil and a ditch is dug at the upper side of the bund and bund stablization technique is used and frequent maintenance made.
Natural / human environment: The technology is suitable to areas with gentle to undulating slope and in cultivated areas with moderate soil depth.
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Ethiopia
Region/ State/ Province:
Oromiya
Further specification of location:
Awash/Jalela
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 239.5 km2.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Originated locally-farmers developed it from years of experiences.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Dec Second longest growing period in days: 105 Second longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Jun
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Population pressure, deforestation, land degradation
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Comments:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- cross-slope measure
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (clearing forests and bushes for agricultural purpose), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (no vegetation cover/complete denudation), other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - continous farming with out apllying SWC), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of soil management skill), governance / institutional
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (high population/cattle pressure on the resources), poverty / wealth (lack of captial - unable to use improved technologies), land subdivision (small in size & fragmented), lack of enforcement of legislat./authority (legislation is not inplace)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
Comments:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
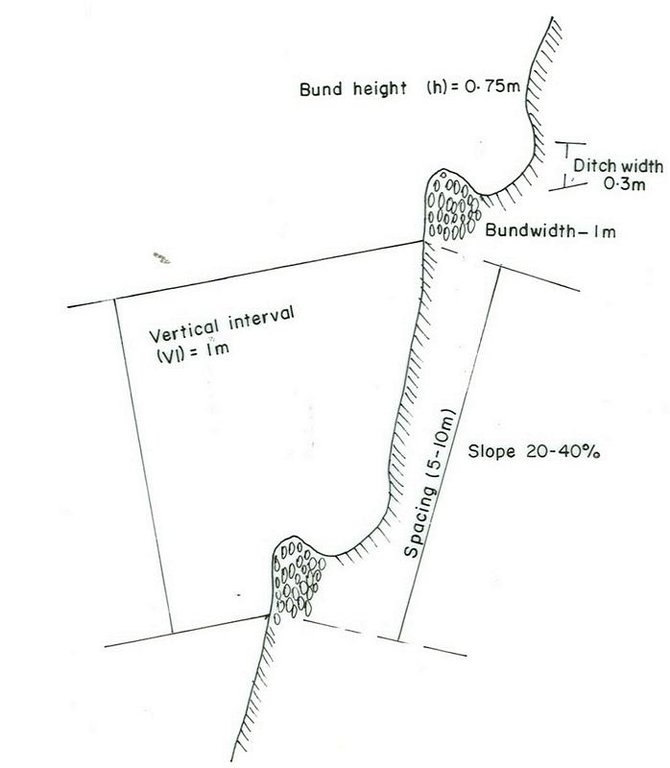
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Oromia
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Better crop cover
Material/ species: farm implements
Remarks: plough along the contour
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 5-10
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.75
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Construction material (earth): the excavated soil is used for making the embankment
Construction material (stone): used to construct stone/stone faced bunds
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Birr
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8.6
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
0.78
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Surveying | dry season |
| 2. | Collection of bund construction materilas | dry season |
| 3. | Excavation | dry season |
| 4. | Bund construction | dry season |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 169.0 | 169.0 | |
| Equipment | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 69.0 | 69.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | |||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 238.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 27.67 | |||||
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Contour plough | dry season & on set of rains / 3-5 times |
| 2. | Sowing | during rains / each cropping season |
| 3. | Weeding | during rains / each cropping season |
| 4. | Bund stablization | dry season/annual |
| 5. | Repair the breaks | dry season/annual |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 82.8 | 82.8 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 82.8 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 9.63 | |||||
Comments:
The cost is culculated for the stone/soil bund and trench per hectare of land.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Labour is the most important factor affecting the cost.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1), plateau/plains (ranked 2) and foot slopes (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Also rolling (ranked 2) and steep (ranked 3)
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1), low (ranked 2) and high (ranked 3)
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- very poor
- poor
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land.
50% of the land users are poor and own 45% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Farmers who have implemented SWC technologies on their farms have got better crop yields compared to those who have not implement SWC technologies.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Comments:
1-2 ha: Only few households
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
production area
land management
Income and costs
farm income
workload
Socio-cultural impacts
community institutions
national institutions
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
soil loss
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
reliable and stable stream flows in dry season
downstream flooding
downstream siltation
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
1049
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
Comments:
70% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
734 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
30% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
315 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
Reduce erosion and runoff How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Reduction of soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance |
| Increase infiltration rate |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules