Use of plastic mulch combined with a drip irrigation system for the cultivation of eggplants [Cambodia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Navin Chea
- Editor: Sophea Tim
- Reviewers: Alexandra Gavilano, Ursula Gaemperli, SO Than
HARVEST-drip irrigation system
technologies_3142 - Cambodia
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- Use of plastic mulch combined with a drip irrigation system for the cultivation of eggplants: Jan. 3, 2018 (inactive)
- Use of plastic mulch combined with a drip irrigation system for the cultivation of eggplants: Sept. 25, 2018 (inactive)
- Use of plastic mulch combined with a drip irrigation system for the cultivation of eggplants: Sept. 2, 2019 (public)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
Oun Leakana
Farmerd user
Cambodia
Chief Office of Agricultural Extension at Provincial Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Pursat:
Chief of District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Bakan:
Agronomic Official at District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Kandieng:
Seng Kompheak
District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Kandieng
Cambodia
Commune Extension Worker at Svay Luong Commune.
Moeun Khonnary
Svay Luong Commune Office
Cambodia
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Cambodia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
The cultivation of eggplants by using plastic mulch and a drip irrigation system in order to control weeds, retain soil moisture, save water and reduce labor for maintenance, weeding, watering, and the application of fertilizer for increase production and income.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
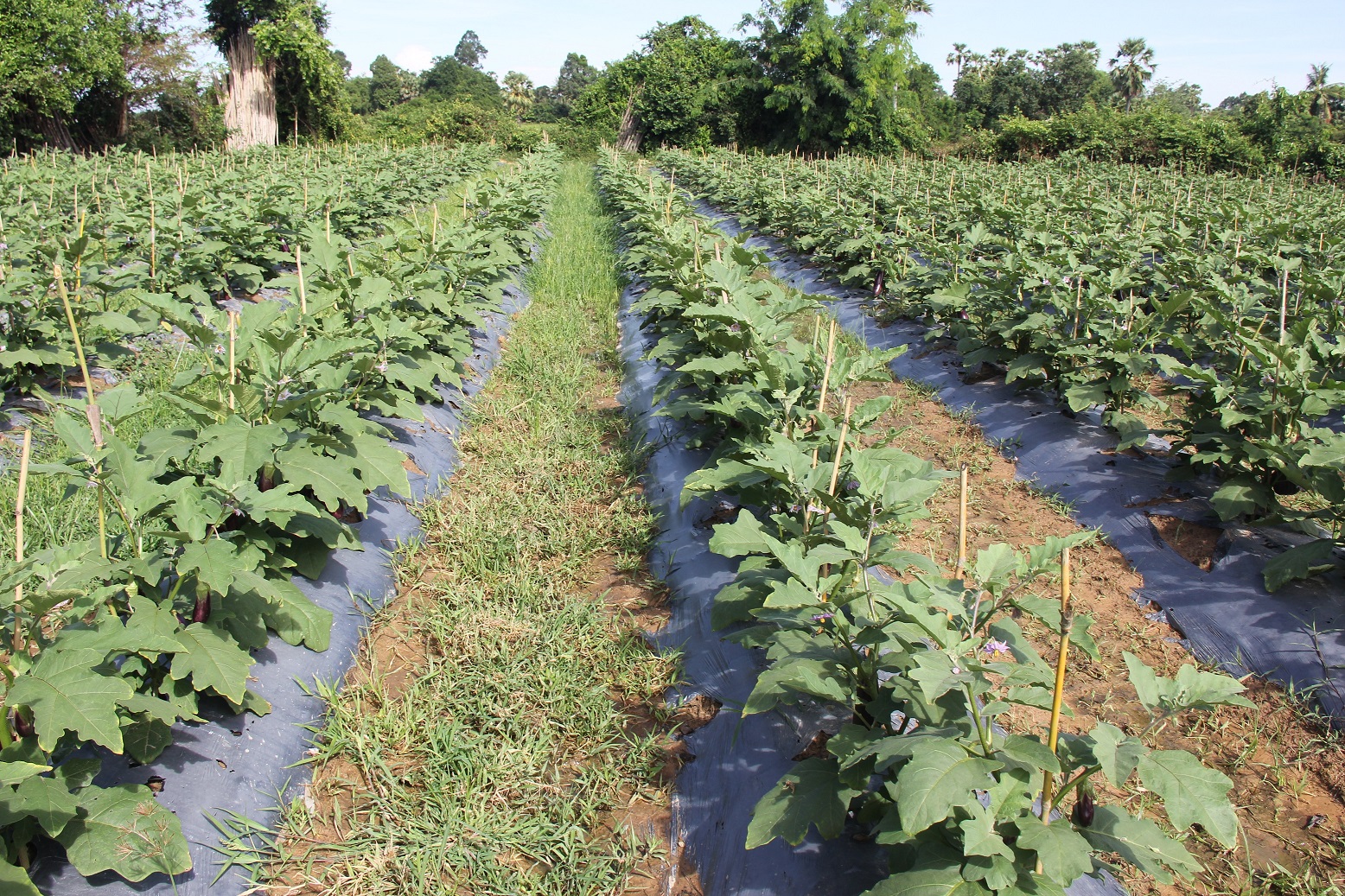
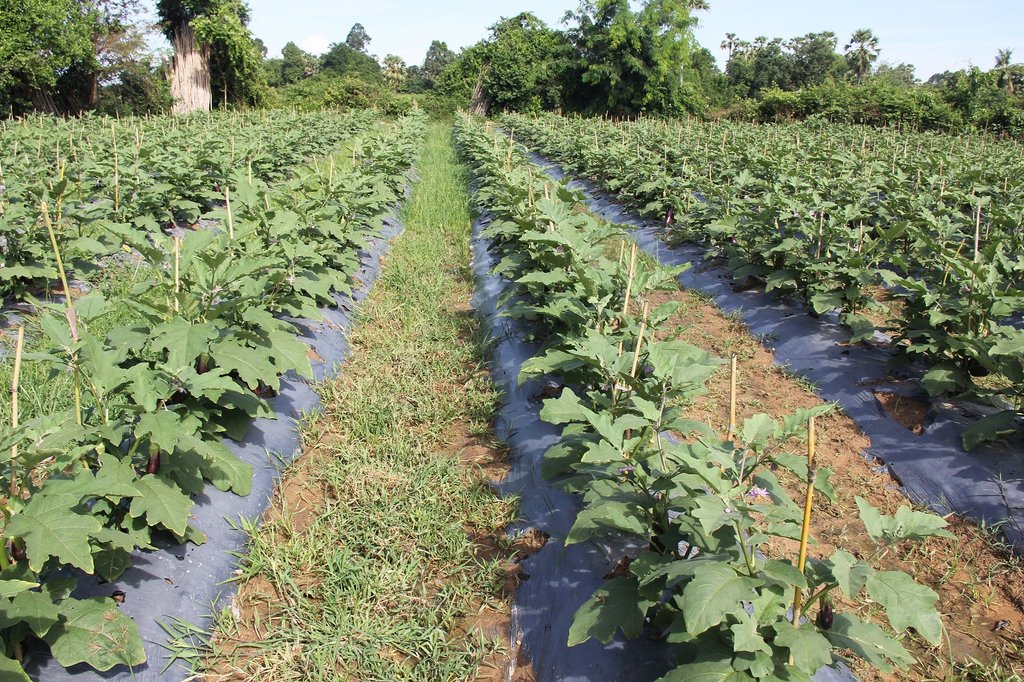
The use of organic materials such as rice straw, water hyacinth, woody herbs, and coconut leaves to retain soil moisture has been practiced by vegetable farmers for many years. Recently, with the availability of diverse industrial products the use of plastic has become a popular technology to cover soils. The impermeable plastic mulch prevents water evaporation. Furthermore condense water built under the impermeable plastic sheets drop back to soil; thus, plastic mulching in combination with the highly efficient drip irrigation substantially saves water for irrigation and it makes it as well suitable to areas faced by water shortage. Generally, black opaque plastic is used, which stops weed growth and in consequences also the attraction of harmful insects. Less weed mean also less competition for soil nutrients and therefore better growth of the crop. Another positive aspect of the weed control is the labor saving otherwise needed for weeding. In addition, plastic mulches play a role in preventing soil erosion and water saturation of the soil. At a nutshell, using plastic mulch combined with drip irrigation saves water for irrigation, reduces the number of harmful insects, and last but not least saves labor and time (FAO, 2017).
The eggplant cultivation in combination with plastic mulch and drip irrigation was introduced by the HARVEST project in 2014. This technology was employed on a farm which formerly grew rice on 1410 square meters of land. The farm comprised 1740 eggplants planted in 20 rows covered by plastic mulch. Eggplant is an annual vegetable plant that matures in well composted soil at temperatures above 20°C. The soil should be kept moist and at the same time water logging has to be avoided.
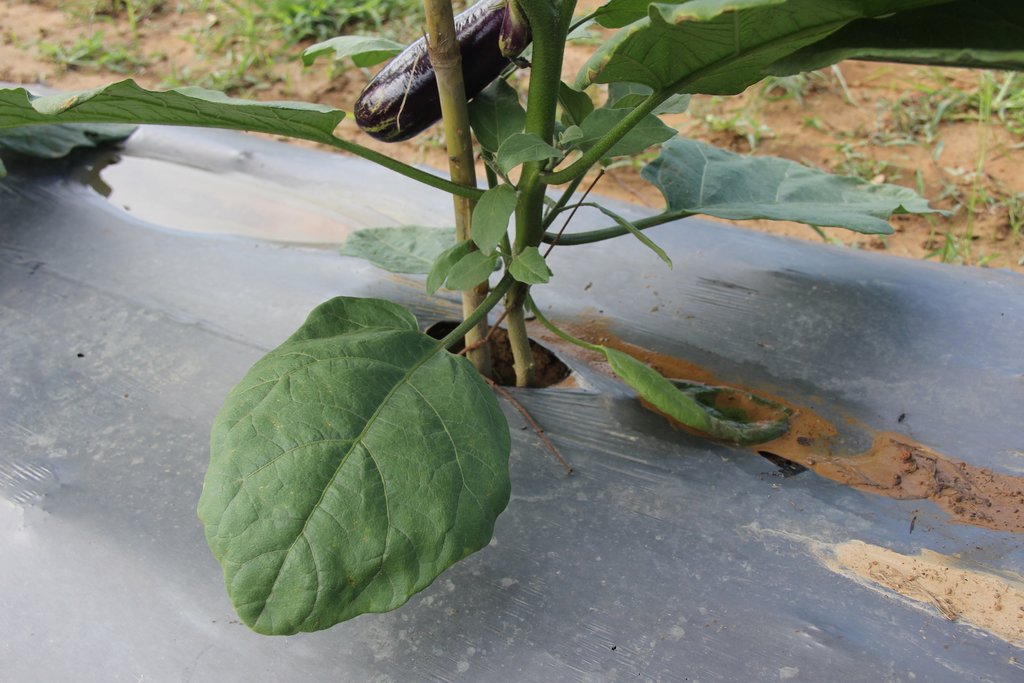
On the above mentioned farm the technology has been installed as follows: On the already prepared soil (the soil has been ploughed and dried at three separate times) the farmer created a ridge in each row that itself measures 1 meter in width and 20 centimeters in height. The distance between each row was 1 meter. The drip irrigation pipes run along the rows, which were watered after installation. Then, the rows were covered by the plastic mulch at 1.50 meters in width. Next, soil was placed on the plastic sides to hold and protect it against gusts of wind. In order to create a growing space for the eggplants the farmer cut out round windows of 8 cm in diameter along the plastic rows making sure that there is gap of 60 cm) between each window (matches with the holes of the drip irrigation). Finally, eggplant seedlings were planted in the holes. Bamboos sticks near each eggplant provided first support to the seedlings and later on, hold the plants when they are grown and bear fruit.
This technology is economically beneficial as can substantially increase his income. In the interviews the land users reported that without this technology, after deducting the investment and maintenance costs, they generated a net income of only 30%. However, after application of the technology their net income increased up to 70% (as long as the crop was not affected by disease). Furthermore it freed up the farmers’ time to fulfill other important tasks.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Cambodia
Region/ State/ Province:
Chreaeng Village, Svay Luong Commune, Kandieng District, Pursat Province
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2014
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Helping Address Rural Vulnerabilities and Ecosystem Stability Project (HARVEST)
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce risk of disasters
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- eggplant
Annual cropping system:
Vegetables - wheat/barley/oat/upland rice
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Comments:
គោមាន ០៥ក្បាលសម្រាប់យកលាមកផងដែរ។
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- rice
Annual cropping system:
Vegetables - wheat/barley/oat/upland rice
Comments:
ដីស្រែ
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
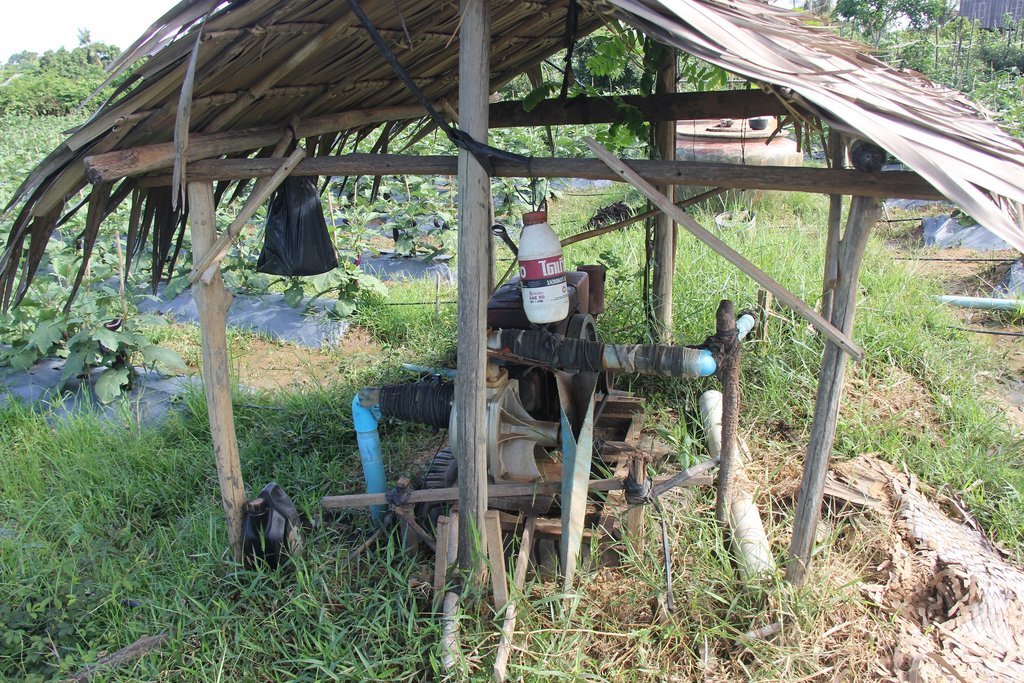
Drilled well
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility

structural measures
- S4: Level ditches, pits
Comments:
Eggplant seedlings are planted in rows on ridges. The farmer installed a drilled well to get water for drip irrigation during periods of water shortage.
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

physical soil deterioration
- Pw: waterlogging

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
- Bl: loss of soil life

water degradation
- Ha: aridification

other
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
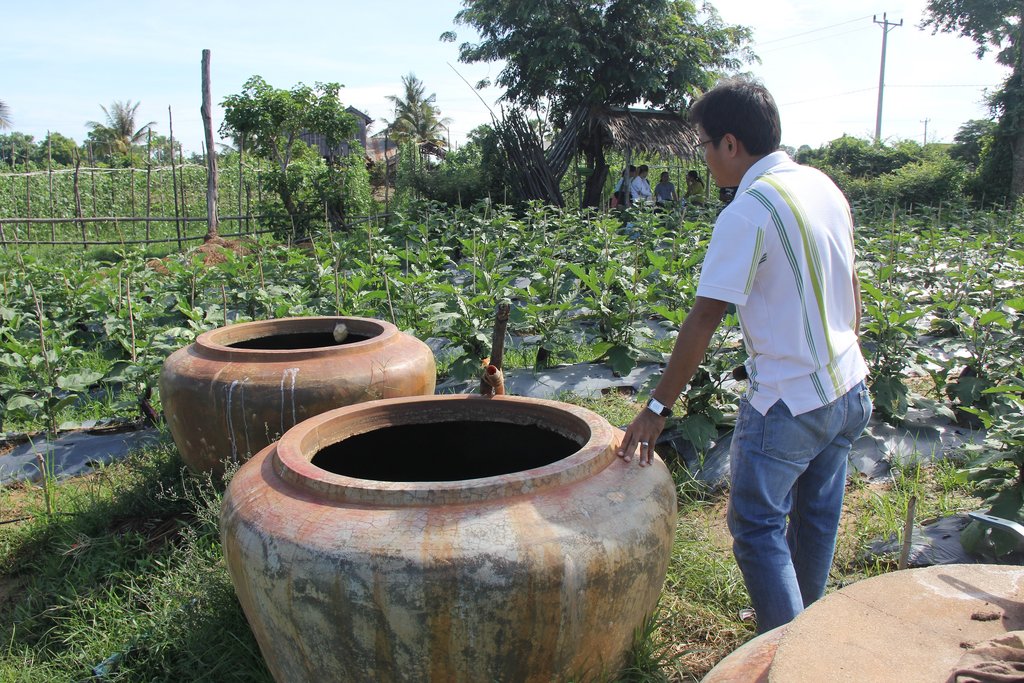
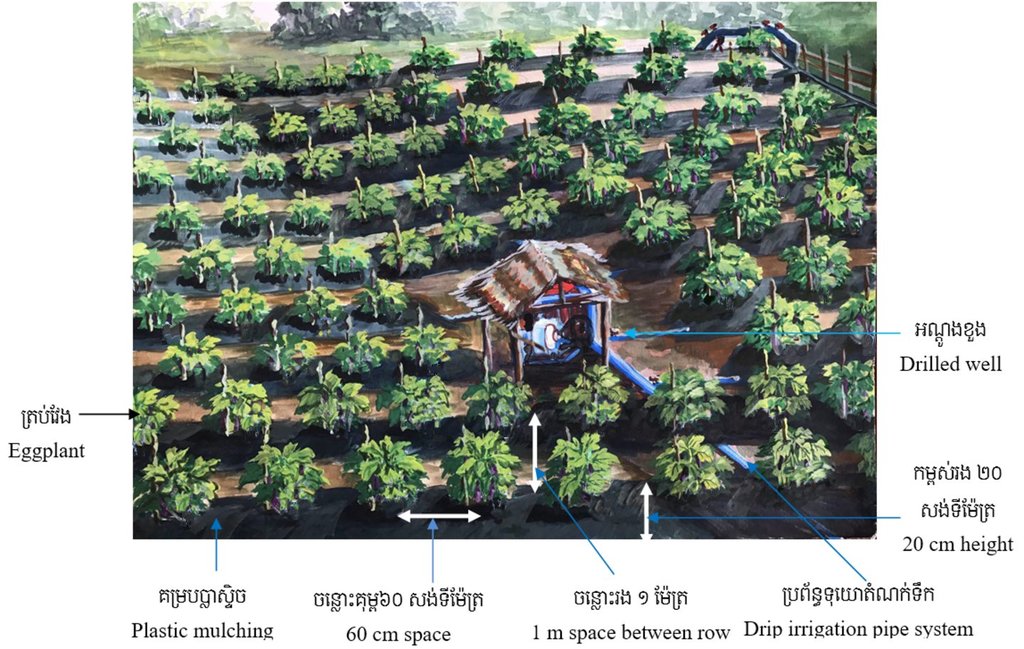
This technology is applied in an area measuring 1410 square meters where 1740 eggplants have been planted in 20 rows. In each row the farmer has created a ridge with a height of 20 cm, and a width of 1 meter, in which the eggplants are planted with a gap of 60 cm between them. All of the rows have a drip irrigation pipe running along the length of the row which is also covered by black plastic sheets of 1.5 meters in width. In the middle of the farm there is one drilled well which has a 1.50 meter house built over the top of it. The land user has also placed three big jars in the middle of the eggplant field with each jar being 1 meter in height and 1 meter in diameter. One of these is for mixing natural fertilizer for the crop, another is for making botanical pesticide and the other one is for water storage. Each eggplant is tied to a bamboo stick to prevent the plant from falling over, when fruits are growing.
Author:
Mr. Khuon Sophal
Date:
28/06/2017
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
1,410 square meters
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
0.14 hectare
other/ national currency (specify):
KHR
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
4000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
20000
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Eggplant nursery | April |
| 2. | Planting eggplant in the box produced by banana leaves | May |
| 3. | Plough the soil | May |
| 4. | Make the ridge of the row | May |
| 5. | Apply cow mannure | May |
| 6. | Set up drip irrigation system | May |
| 7. | Watering the rows of crop | May |
| 8. | Cover plastic sheets on the row | May |
| 9. | Planting eggplant | May |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Plough 3 times | Time | 3.0 | 50000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Eggplant nursery | person-day | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Make row, apply cow manure, set up drip irrigation system,water on row, plastic mulching. | person-day | 5.0 | 20000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Planting eggplant | person-day | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Two wheel tractor | Piece | 1.0 | 12300000.0 | 12300000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Pumping machine | set | 1.0 | 1400000.0 | 1400000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Hoe | Piece | 6.0 | 12000.0 | 72000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Spade | Piece | 1.0 | 12000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Tent | set | 1.0 | 40000.0 | 40000.0 | |
| Equipment | Pesticide sprayer by using hand | Piece | 1.0 | 280000.0 | 280000.0 | |
| Equipment | Tray for nursery of eggplant | Piece | 30.0 | 2500.0 | 75000.0 | |
| Equipment | Big baskets for harvesting crop | Piece | 3.0 | 15000.0 | 45000.0 | |
| Plant material | Eggplant seed | Package | 1.0 | 10000.0 | 10000.0 | |
| Construction material | Plastic sheet | set | 2.5 | 70000.0 | 175000.0 | |
| Construction material | Drip irrigation system | set | 1.5 | 160000.0 | 240000.0 | |
| Construction material | Jar | Piece | 3.0 | 45000.0 | 135000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | Waterproof boot shoes | Paires | 1.0 | 60000.0 | 60000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 15174000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 3793.5 | |||||
Comments:
Farmer uses her own cow manure which is difficult to calculate into cost. The main pipes were provided by the HARVEST project, so she doesn't know the cost of them. There are 100 piece of pipe provided by HARVEST, so she doesn't know the cost. Please also note that HARVEST project also supported other equipment such as eggplant seed, pesticide sprayer, nursery tray, big basket for harvesting the crop, waterproof boot shoes. The cost put in the table base on the price on the market and price estimation.
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering by pumping machine through drip irrigation system | Everyday |
| 2. | Weeding in between of eggplant rows. | Two times in one cycle of crop |
| 3. | Spaying botanical pesticide mixing with pesticides on eggplant | One time per week before first harvesting of eggplant |
| 4. | Apply fertilizer | One time in three days |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Weeding between the rows | Time | 2.0 | 240000.0 | 480000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Golden pesticide | Bottle | 1.0 | 15000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | Gasoline for pumping | Liter | 70.0 | 3000.0 | 210000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 705000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 176.25 | |||||
Comments:
Botanical pesticide is produced by herself which is difficult to calculate into cost.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Plastic and drip irrigation system are very expensive. The plastic can be used only once and drip irrigation system can be used for 2 years.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1225.70
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
Annual rainfall in 2015 is 1225.7 mm and in 2014 is 1128.1mm and in 2013 is 1316 mm.
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
Ministry of Water Resources and Meteorology in 2015
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Slight slope and new soil is added on the former rice field land.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
The soil texture below the surface soil is clay-loam.
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Yes
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Ground water table is 8 meters dept. pH = 6
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
Age of land users:
- youth
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
The land user is 22 years old.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
Rice field is 6 hectares
Other crop land is 1 hectare
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
Comments:
All land are tittle land.
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
The yield of eggplant is increased compared to conventional eggplant plantation (without using plastic mulch in combination with drip irrigation)
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
The eggplant fruit is bigger and look nicer. In addition, the eggplant provides a lot of fruits.
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
Reduce product failure due to efficiency of water supply and meet the requirement of market that need the product with quality. In addition, she could grow many crops year round. For example: she can use plastic and drip irrigation for growing cucumber, bitter melon etc.
Water availability and quality
drinking water availability
Comments/ specify:
Water available from the drilled well.
drinking water quality
Comments/ specify:
The water require boiling. The water contains corrosion particles.
water availability for livestock
Comments/ specify:
The water from the drilled well can also be used for cow raising.
irrigation water availability
Comments/ specify:
There is drilled well to get water for supplying crop during water shortage.
irrigation water quality
Comments/ specify:
The quality of water is good for growing crop but it contains corrosion particles which affect the drip irrigation system.
demand for irrigation water
Comments/ specify:
Reduced demand of water by using plastic mulch with drip irrigation system.
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
The cost of drip irrigation system and the plastic mulching are expensive. Drip irrigation system can be used for 2 years, but plastic mulch can be used only for one crop cycle.
farm income
Quantity before SLM:
300,000 Riels
Quantity after SLM:
700,000 Riels
diversity of income sources
Comments/ specify:
Save time to water, apply fertilizer, weeding, so the farmers could have time to do other works such as vegetable selling or rice cultivation.
workload
Comments/ specify:
The labor for watering and application of fertilizer was reduced. In addition, labor for weeding has been saved substantially. Using plastic mulch combined with a drip irrigation system save labor at about 70%.
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
The quality of product is good and meet of domestic and market needs. In addition, she could grow other also crops such as cucumber or bitter melon.
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
Thefamer learned by experience that the soil under the plastic is less compact and the texture looks like compost.
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
The soil under the plastic can be more easily kept moist.
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
Plastic mulch sheets serve as soil cover, which reduces evaporation to the atmosphere.
soil crusting/ sealing
Comments/ specify:
The soil under the plastic sheets is less compact and improves the soil structure.
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
pest/ disease control
Comments/ specify:
Weed is a driver of increasing the amount of insect. Plastic mulch, helps to control weed growing.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| seasonal temperature | wet/ rainy season | increase | well |
| seasonal temperature | dry season | increase | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
Some farmers who received support from the HARVEST project gave it up when the project finished because of spending too much money on the plastic and drip irrigation system.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
Farmer uses her own cow manure which is difficult to calculate into cost. The main pipes were provided by the HARVEST project, so she doesn't know the cost of them. There are 100 piece of pipe provided by HARVEST, so she doesn't know the cost. Please also note that HARVEST project supported also other equipment such as eggplant seed, pesticide sprayer, nursery tray, big basket for harvesting the crop, waterproof boot shoes. The cost estimation put in the table 4.5 bases on market prices and price estimations.
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Helps to control weeds. |
| Saves labor and time otherwise spent for weeding. |
| Saves water by using a drip irrigation system. |
| Generates better income for the household. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Weeds are unable to grow, which saves labor on weeding. |
| Reduce pest because there not many weed . |
| It is easy to maintain and use the drip irrigation system, which saves water and time. |
| Retain soil moisture through the use of plastic mulches. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Establishing this technology costs a lot of money. | Use rice straw instead of plastic mulch. |
| Difficult to collect the plastic waste. | Should manage plastic waste properly and set up a place to burn it. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Spend a lot of money buying plastic mulch and the drip irrigation system. | Seek external support and introduce budget management. |
| Plastic and waste from the plastic mulches and drip irrigation system can have an effect on the environment. | Proper plastic waste disposal. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
A place
- interviews with land users
A person
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
4 persons
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
28/06/2017
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
FAO. (2017). Rooftop water collection , drip irrigation and plastic mulching in home garden conditions in drought prone areas of Cambodia. Retrieved November 10, 2017, from
URL:
file:///C:/Users/HTPP ROYAL INV/Downloads/TECA - Rooftop water collection, drip irrigation and plastic mulching in home garden conditions in drought prone areas of Cambodia - 2017-05-31.pdf
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules