Снижения затрата и предотвращения питательных вешеств с использованием ломом в садах и виноградников [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Rustam Kalandarov
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Farrukh Nazarmavloev
Гузоштани нурихои минерали бо воситаи лом барои сарфакори.
technologies_3673 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
land user:
Хусейнов Хасан
907 590 252
Дехканская хозяйство Хусейнов Хасан
район Рудаки,дж.Рохати ,кишлак Рохати.
Tajikistan
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Environmental Land Management and Rural Livelihoods (ELMAR)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Youth Ecological Centre Tajikistan (Youth Ecological Centre Tajikistan) - Tajikistan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
05/02/2018
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
Comments:
Технология является природосберегающем.
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
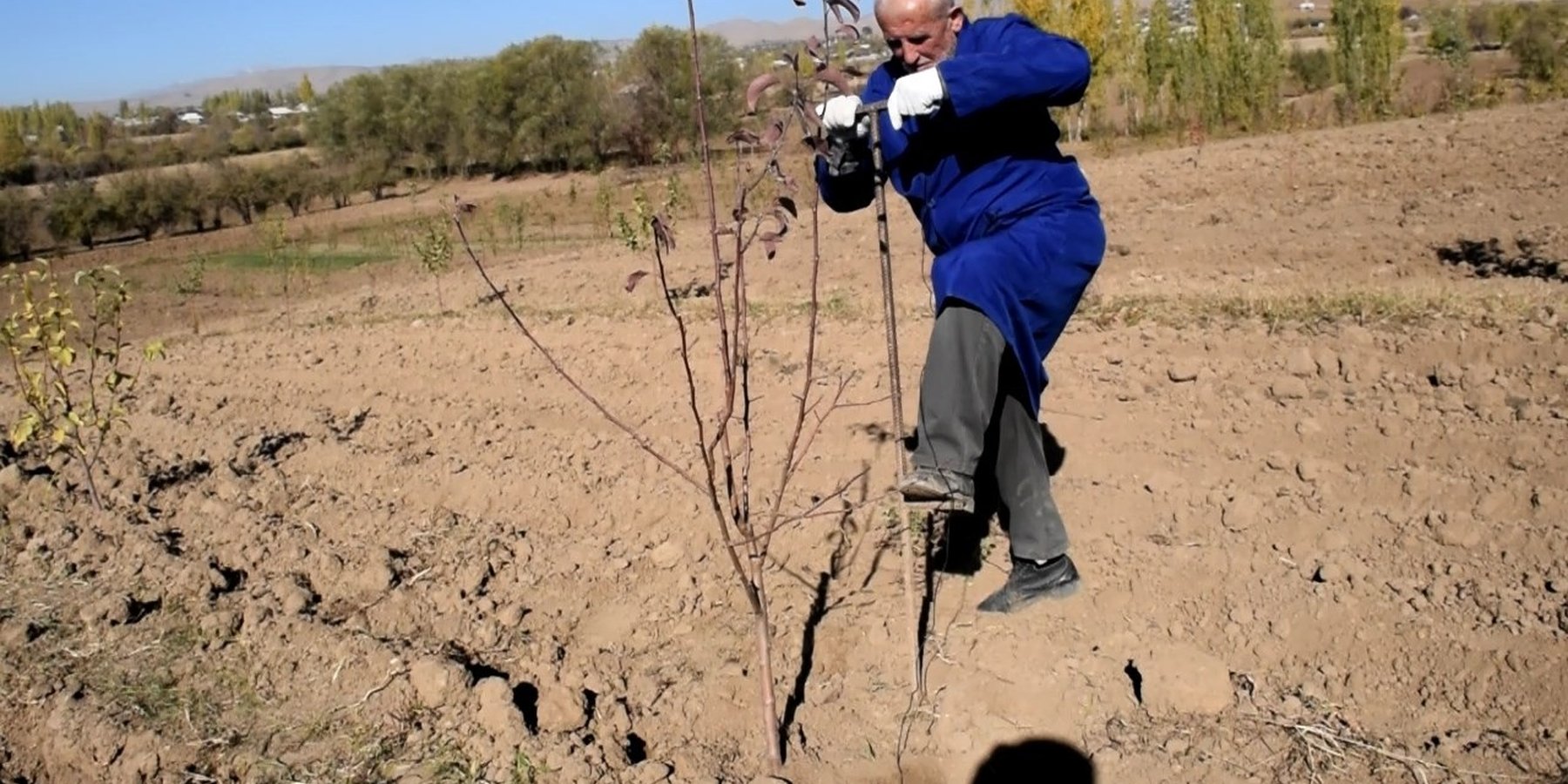
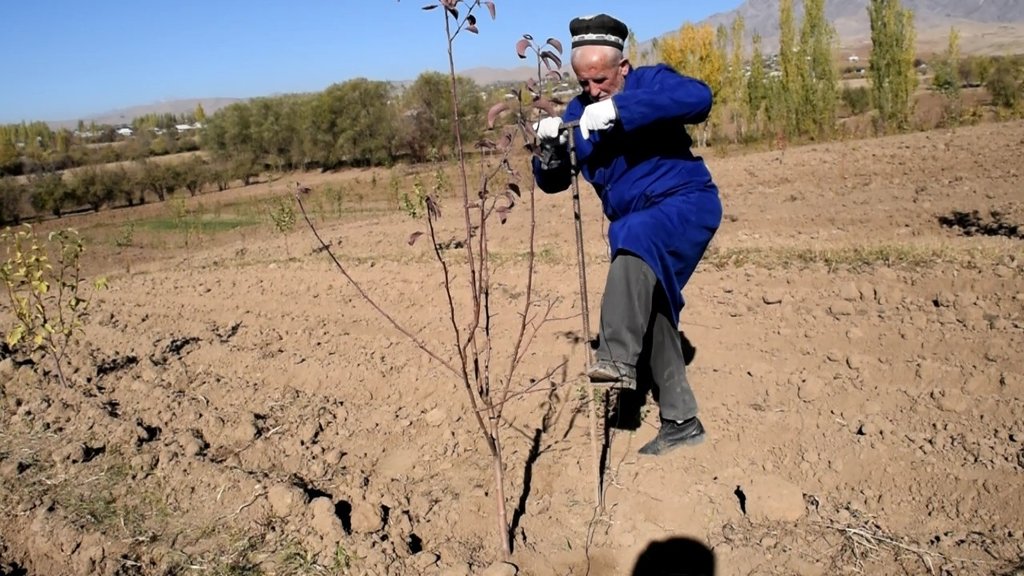
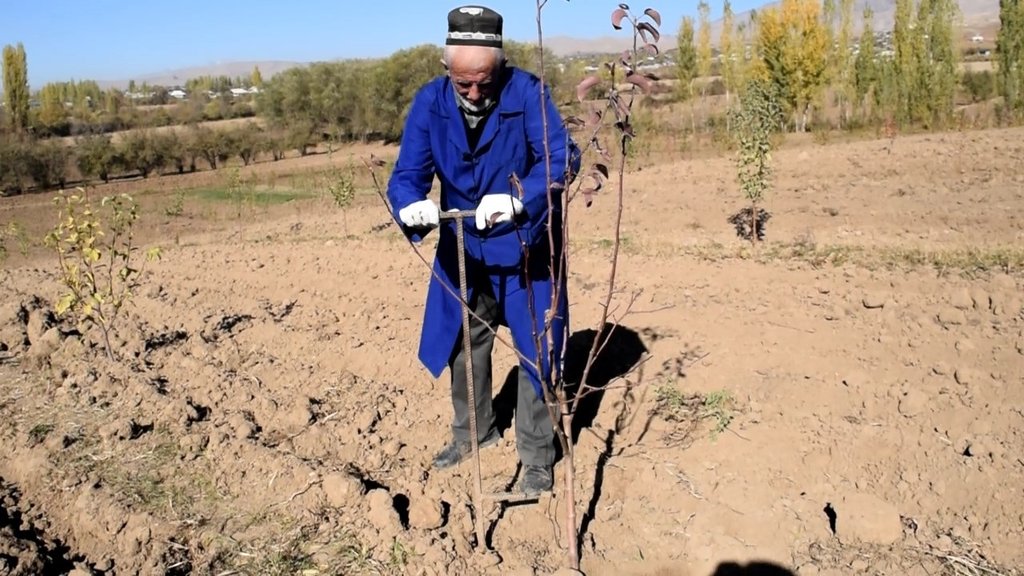
Удобрения выносятся ручным способом с использованием Лома . Ломом возле куста производят несколько (2-4 шт.) углубления на глубину 30 – 35 см и засыпают удобрения сохраняет почвенный кров без ущерба для корней, защищает ресурсы это от деградации и эрозии почвы.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Технология применяется в районе Рудаки, дж. Рохати, кишлак Рохати, в частном виноградарческом и садоводческом хозяйстве. Во многих садоводческих и виноградаческих частных хозяйствах применяется эта технология. Условия, где применяется технология богара и часть хозяйства - на условно поливных земледелиях. Основная хозяйственная деятельность здесь - это садоводство и виноградарство частично скотоводство. Основные работы в садах и виноградниках проводятся вручную техника используется только во время вспашки междурядий. Так как земельные участки находятся на склонах и по они рельефу покатые многие работы проводится вручную или мини трактором. В садах и виноградниках подкормку вносили вручную под каждым кустом копали лопатой и выносили удобрения. Уже более 20 лет землепользователи пользуется методом внесения удобрений под лом, который придумали сами. Сначала использовали деревянный кол длиной около1,5 м. который это часто ломался тогда решили использовать железный лом. Это очень простая технология, пр которой лом делается из обычной арматуры или гладкого метала длиной 1,5 м. С снизу на высате 50 см прикреплена для нажатия лома педаль , чтобы щель было до глубины 30-35 см, близко к корневой системы не повреждая её. Обычно, в зависимость от возраста куста производят от 4 до 6-7 щелей для внесения удобрения. Удобрения выносят два раза в год в каждую щель вносят определенную норму удобрения. В первый раз это фосфоро-калийные удобрения, вносят в декабре и январь. Второй раз в конце апреля, в начале цветения винограда выносятся азотные удобрения. Это метод для землепользователей стал приемлемым и удобным, экономно расходуются удобрения. Раньше использовали специальным оборудование клифер для внесения удобрений для садов и виноградников. Этим способом удобрения вносятся на глубину 15-20 см. Землепользователи сейчас этим методом не пользуются в связи с дороговизной трактора, горюче – смазочных материалов. Основная функция внесения удобрений именно ближе к корням, которые находятся в горизонте 50 см, а ломом можно вносит в до глубины 45-50см, где находятся всасывающие корни. Можно вносить за один день на площади одного гектара. Эта технология применяется в условиях, где затруднено использование техники. Техника вносит удобрения сплошную. А эта технология только вокруг куста. Для её запуска никаких затруднений нет. Только изготавливают лом с подножной педалью длиной 150 см и применяют ручной труд. Основное преимуществом том, что удобрения экономно выносятся. Удобрения засыпают именно по месту назначения, не нарушая плодородия почвы. Этот метод используют м маленьких частных хозяйствах и на приусадебных участках. Землепользователям этот метод нравится. они экономят затраты средств при технологии ручной труда. Сохраняется почвенный покров от эрозии и деградации, а также смыв плодородный части почвы на склонах. Технология является природа сберегающей не влияет на экосистему и окружающую среду.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
General remarks regarding photos:
Способ внесение удобрения ломом. Лом в тыкается в почву вокруг корней не задевая их по 4 - 5 шел до 35- 40 см. В каждый шел насыпают удобрения.
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Район Рудаки, РРП
Further specification of location:
Дж. Рохати кишлак Рохати уч. Хусейнов Хасан
Comments:
Технология где отмечено это восточный часть Района Рудаки в сторону Вахдатского района на предгорьях отмечено точкой.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
20
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Технология применяется уже более 20 лет как инновация землепользователя. считается очень удобным.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- conserve ecosystem
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Tree and shrub cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
культура является многолетние плодовые сады.
Comments:
Технология применялись на плантациях садов и виноградниках.
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
Тип землепользования до начало было зернобобовые культуры.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Comments:
Земля относится к богарным без применения поливного воды.
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Култура является многолетним. урожай получают один раз за вегетацию.
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- minimal soil disturbance
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 km2
Comments:
Применяемый площадь зависит от землеползоваптеля. Применяется по возможности целыми десятков гектаров.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
Comments:
Технология является агрономическим с использованием растительности.
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

chemical soil deterioration
Comments:
Технология применяется для обогащения минеральными питания растительности без ущерба почвенных эрозии и без экологического нарушения местности.
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Технология является природосберегающий окрестности и сохранения экосистемы.
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
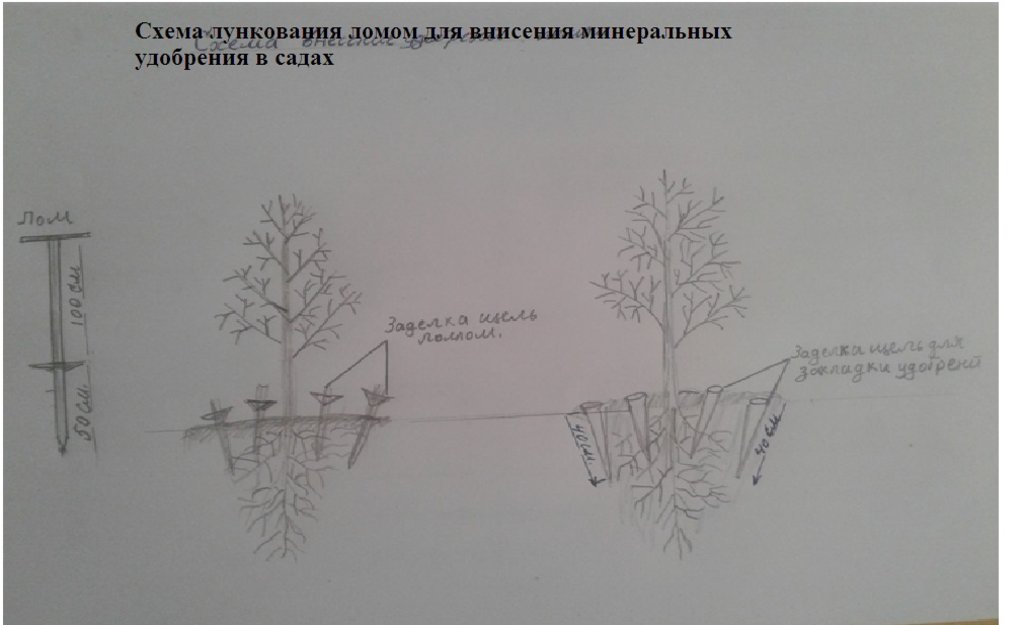
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
На схеме приведена лункования ломом для винесения минеральных удобрения в садах. размер лома 150 см. глубина 30-40 см вокруг корней .
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
единица площади измеряется на гектар
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare:
1 гектар 10000 м квадрат
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
4.9
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
3.0
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | изготовления лом | Structural | осенью |
| 2. | внисение удобрения по сезонам | Agronomic | осен и весна |
Comments:
Для начало реализации нужно подготовит лом и основная работа вносить удобрения по сроком.
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | внесение удобрения по сезонам | кг | 1200.0 | 0.45 | 540.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Ручная работа | чел | 3.0 | 3.0 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | изготовления лом | шт | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 552.0 | |||||
Comments:
Затраты оплачивается землепользователем так как он является основным владельцем.
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | внесение удобрения по сезонам | Agronomic | осень и весной |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | внисение удобрения по сезонам | кг | 1200.0 | 0.45 | 540.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 540.0 | |||||
Comments:
Так как землепользователь является владельцем земли
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
человеческий труд.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
Осадки выпадает в основном осеню зимой и весной зависимости от количества выпавших осадков.
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ГМС г. Душанбе
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
- arid
Зона является засушливым и полузасушливая так как зона пользования технологии является богарным.
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Технология можно принимать на любом рельефе.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Так как технология применяется на богарных условиях никаких поливных воды нет.
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
Местность является средней зоны биоразнообразии в основном стречаются кустарники полу кустарники и травянистые покровы
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
- elderly
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
В основном земле пользователи являются среднего и пожилые возраста. Постоянно живущие населения.
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
В основном землепользователи является частными и арендаторами.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- company
Land use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
- communal (organized)
Comments:
Землепользователи частными и арендаторы.
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
После применения технологии улучшилос за счет винисени норма удобрения
crop quality
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| seasonal temperature | winter | increase | well |
| annual rainfall | decrease | moderately | |
| seasonal rainfall | winter | increase | moderately |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | moderately |
| local thunderstorm | not well |
| local hailstorm | moderately |
Comments:
Технология заключается по внесением удобрение экстремальные явления погоды мало касается.
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Comments:
Технология не требует много затраты оно всегда окупается.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 10-50%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
более 10 более 10 га
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 10-50%
Comments:
Технологию применяет каждый землепользователь по собственному желанию.
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| снижения затрата на внесение удобрение. |
| целесообразно использование удобрения. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| снижения затрата на внесение удобрение. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ручной труд | только внисение техникой |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ручной труд | только внисение техникой |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
число опршенных 5
- interviews with land users
опршенных 5
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Удобрение богарных виноградников. Артаманова Н.П г.Душанбе
Available from where? Costs?
0,2
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules