Использование конденсационной водоснабжение садов и виноградников в условиях богары и маловодия. [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Rustam Kalandarov
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Farrukh Nazarmavloev
Истифолабарии оби конденсационы дар богу токзорхо дар шароити лалмию камоби.……………………………………………………………………… Страна: Таджикистан
technologies_3683 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
land user:
Хусейнов Хасан
907 590 252
Дехканская хозяйствоа Х.Хасан
Район Рудаки,дж.Рохати, хозяйства Х.Хасан.
Tajikistan
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Environmental Land Management and Rural Livelihoods (ELMAR)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan (Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan) - Tajikistan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
Comments:
Технология является природоохранным не вызывает опасность к деградации и эрозии почвы.
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
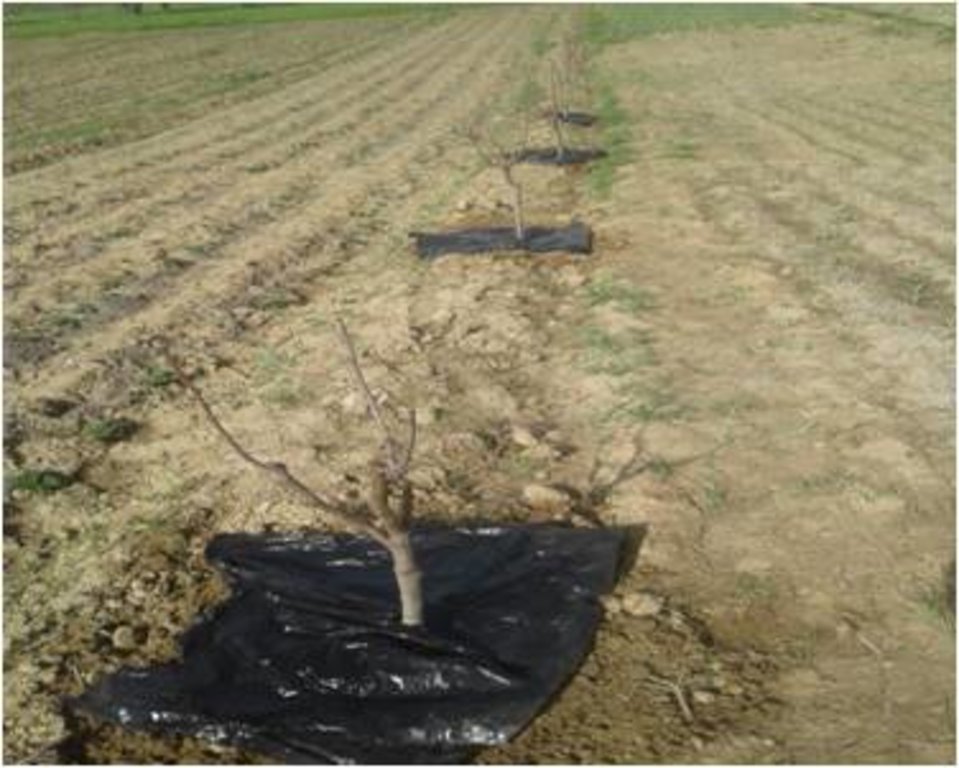
Технология заключается, в использование черной полиэтиленовой пленки, которой после рыхления и внесения подкормки покрывают почву . При нагревание днем поднимается пар с приставленной круга растений вечером этот кондисат с пленки капает на почву и увлажняет её. Технология используется на богаре, применяется в богарных условиях в садах, виноградниках для сохранения влажности почвы для содержания корневой системы растений во влажной почве дехкане часто используют эту технологию.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
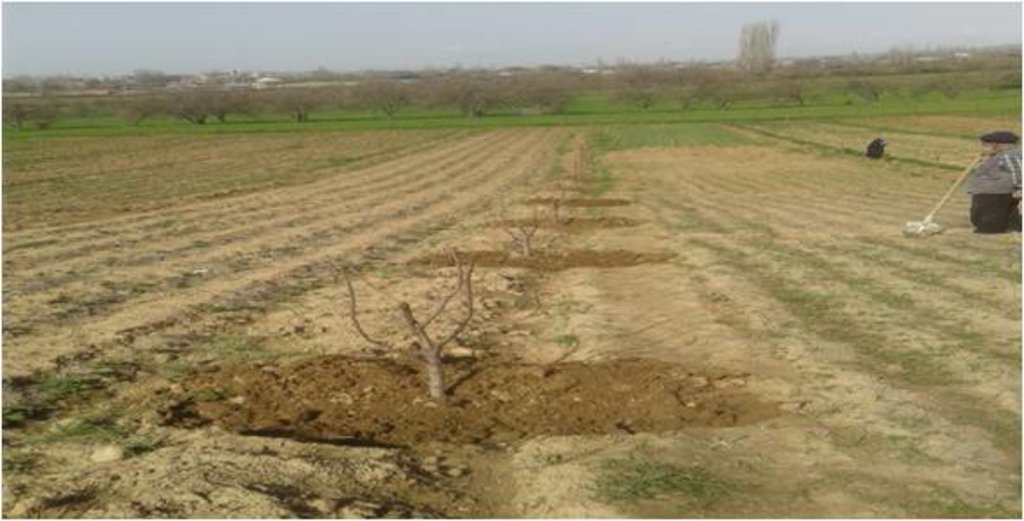
Участок Рохати находится на в восточной части предгорной зоны, около 30 км от столицы. В кишлаке Рохати в частном виноградарском и садоводческом хозяйстве где применяется эта технология, в основном засушливая богара и часть хозяйств условно поливное земледелие. Основная хозяйственная деятельность это садоводства и виноградарство частично скотоводство. Основные работы в садах и виноградниках проводятся в ручную техникой пользуются только во время вспашки междурядий. Так как земельные участки находятся по рельефу на покатых склонах многие работы проводятся в ручную или при помощи мини трактора. Для богарных условий очень приемлема эта технология. При богарных условиях выращивания садов и виноградников успех в основном зависит от осадков, которые выпадают осенью, зимой и весной. Землепользователи каждую осень проводят вспашку для сохранения влаги осадков. Вся жизнедеятельность растений зависит от накопленной влаги для роста, развития и получения качественного урожая. В зонах, где применяется эта технология, осадков в последние годы выпадает мало 450 - 500 мм и накопленной влаги для садов и виноградников недостаточно. Землепользователи проводят вокруг кустов молование почвы мульчирование сеном для того, чтбы влага меньше испарялась. Но влаги не хватает для созревания урожая. После проведения экспериментов в хозяйствах стали использовать черного полиэтиленовую пленку, которой закрывали поверхность почвы вокруг при корневой части куста после молования и внесение органоминеральной подкормки. Поверхность пленки засыпали 4-5 см почвой для поддержки полиэтиленовой пленки. Результаты получили положительные поскольку под кустами и деревьями после покрытия полиэтиленовой пленкой сохраняется влага. Землепользователи испытали эту технологию используя для покрытия поверхности почвы
черную полиэтиленовую пленку вокруг ствола деревья или куста винограда. Перед покрытием пленкой проводили все необходимые подкормки минеральными удобрениями и навозом. При возможности условно поливные участки поливают дают влагозарядку, после всего этого почва покрывается пленкой.
Этот процесс на богарных землях проводят после прекращение осадков в конце весны. Основная функция полиэтиленовой пленки это сохранить накопленную влагу не давая зря ей испаряться. Днем, при нагревание почвы влага поднимается в верх, испаряясь. Вечером накопленный пар превращается на капли воды, и снова поступает в почву и увлажняет её и этот процесс постоянно в обороте. Эта вода является конденсационной. Преимущество в том, что она постоянно в обороте в почве для сохранения жизнедеятельности растения. Эта технология предотвращает эрозию и деградацию почвы, сохраняя почвенную влагу. Фермеры дехкане эту технологию часто используют. Технология новая она только начало распространяться. Технология является природоохранной не приносит ущерб окружающей среде.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
General remarks regarding photos:
Участок с использованием полиэтилена для сохранения влаги.
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Район Рудаки дж. Рохати.
Further specification of location:
Участок Х.Хасан.
Comments:
Технология применяется по карте на восточной част Таджикистана от столици 35 км.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Технология применяется как инновация землепользователя и полевой эксперимент
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- conserve ecosystem
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Tree and shrub cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
Основным культурой является плодовые деревья
Comments:
технология применяется под культурой плодовых деревьев и можно использоват на виноградниках богарных и в условиях маловодия.
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
До применения было богарные земли под плодовым садом.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
Технология применяется в богарных и условно поливных землях.
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Плодовые сад одинраз за вегетацию даёт урожай.
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- integrated soil fertility management
- cross-slope measure
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Comments:
Применяетс технология повсе местно.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
Comments:
Технология является агрономическим с использованием многолетных древестных культур.
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
Comments:
Применяется для сохранения влаги .
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Технология является природоохранным снижения и предотвращения деградации земель. Так как оно связано с удержанием влаг в почве.
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
На схеме приведено рисунки как подкладывать полиэтиленовый пленка покрытия почвой 5 см. под кустами плодовых деревьев в условиях условно поливных и богарных землях.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
На 1га площади
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare:
10000 м квадрат
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
8.9
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
3,0
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Подготовка полиэтиленовый пленки | Agronomic | весной май |
| 2. | Внесение подкормки минеральных удобрения | Agronomic | осень - весной |
| 3. | Покрытие пленкой | Agronomic | Конец весны после прекращения осадки. |
Comments:
Техническая работа не очень трудная основная работа подготовка материалы .
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Ручная работа | день | 40.0 | 4.5 | 180.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Полиэтиленовая пленка | м. квад. | 832.5 | 0.5 | 416.25 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 596.25 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | подготовка полиэтиленовой пленки | Agronomic | весной |
| 2. | Внесение подкормки минеральных удобрение. | Agronomic | осень - весна |
| 3. | Покрытия полиэтилена | Agronomic | конец весны |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Ручная работа | день | 40.0 | 4.5 | 180.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Полиэтиленовый пленка | м.квад. | 832.5 | 0.5 | 416.25 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 596.25 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
Все затраты покрывается землепользователем
Comments:
Частная хозяйства все расходы оплачивантся землепользователем.Расчеты приведены в долларах США.
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Покрытия пленкой.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
Осадка выпадает осенью , зимой и весной предгорях холмистых зонах иногда осадки бывает до 450 мм.
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ГМС. Г. Душанбе
Agro-climatic zone
- arid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Технологию можно принимать в любом рельефе не зависимо от крутизны склона.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Данных нет
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Технология применяется в условиях богары и условно поливной зоне.
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
По биоразнообразию не очень богат встречаются кустарники полукустарничные породы и травянистые растительности.
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- rich
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
- elderly
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Хозяйство является частным иногда используют наёмных рабочих сил.
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
Хозяйство является среднем масштабом.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Comments:
Землепользование является индивидульным пользованием земли.
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
После применение технологии улучшилось
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
Увеличился урожайность
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
Улучшилось
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
Влажность почвы улучшилось
Climate and disaster risk reduction
drought impacts
Comments/ specify:
Засуха по этапно снижается
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
Comments regarding impact assessment:
После применения технологии улучшения идет произвольно.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| seasonal temperature | summer | increase | well |
| annual rainfall | decrease | moderately | |
| seasonal rainfall | winter | decrease | moderately |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local hailstorm | moderately |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| heatwave | well |
| cold wave | moderately |
| extreme winter conditions | well |
| drought | moderately |
Comments:
По климатическим явлениям технология успешно справляется
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
С текушими расходами технология позитивна.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
4 домохозяйств
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
Технологию может применять любой землепользователь
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Затраты уменьши |
| Сорняки вокруг растении нет . Растения хорошо растет и дает урожай. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Затраты уменьши |
| Сорняки вокруг растении нет . Растения хорошо растет и дайт урожай. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Каждый сезон надо снят и менять пленку |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Каждый сезон надо снят и менять пленку |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
число опрощенных 4
- interviews with land users
число 4 землепользователей
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules