Homestead Development [Ethiopia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_993 - Ethiopia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Bernahu Kidist
Gamo Gofa Zone Rural Development Department
Ethiopia
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Gamo Gofa Zone Rural Development Department - Ethiopia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
It is an integrated land husbandary practice aimed at improving farm productivity of a household through the sustainable land resources development
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
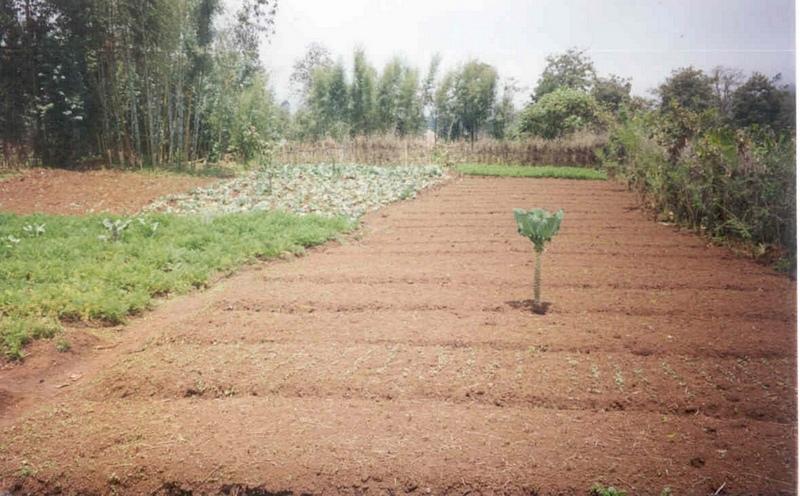
Description:
t involves the practicing of various farming practices in order to increase the productivity of land and improve the livelihoods.
Purpose of the Technology: it is a technology which can improve farm productivity interms of biomass, food, farmers income and prevent the area from land degradation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Constructing of the required SWC measures and undertake vegetative panting
Natural / human environment: increase biomass, productivity increase per unit area, improve soil fertility, reduce soil erosion, improve soil moisture content.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Ethiopia
Region/ State/ Province:
Southern Nation & Nationalitie Peoples Region (SNNPR)
Further specification of location:
Boreda Woreda
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3 km2.
the technology area is increasing from time to time due to its economical benefits has brought the farming community
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Developed in the country
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Silvo-pastoralism

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - barley
- cereals - maize
- legumes and pulses - beans
- root/tuber crops - sweet potatoes, yams, taro/cocoyam, other
- wheat
- enset, Desho, elephant grass
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- coffee, open grown
- pome fruits (apples, pears, quinces, etc.)
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 185 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Dec Second longest growing period in days: 150 Second longest growing period from month to month: Jan - May
Is intercropping practiced?
Yes
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
maize and beans

Grazing land
- free grazing, stall feeding
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): loss of topsoil, reduction of soil fertility, population and livestock pressure, free grazing
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): shortage of farm land and grazing land, low productivity of land
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: wheat-bean-sweet potato-maize-barely-beans
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- home gardens
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
Comments:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, improve feed and fodder source, change feeding habit
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: maize and beans
Remarks: 50,000/60,000
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: maize, with legumes/sweet potato
Remarks: 5-10 meters of strip width
Green manure
Material/ species: lupin and vetch
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: leaves/manure/ash
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1-2m
Grass species: Desho, elephant grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12.00%
Bund/ bank: level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.3 m
Spacing between structures (m): 15
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50
Bund/ bank: graded
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.2 m
Spacing between structures (m): 14
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.7
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 45
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.65
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 45 m
Construction material (earth): excavate from the channel and fill between stone walls
Construction material (stone): stone is collected from the field
Construction material (wood): wood is used for the construction of check dams
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 7%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 5%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Birr
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
0.70
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | seedling raising | on set of rain |
| 2. | transplanting grass | during rainy season |
| 3. | weed and cultivation | during rainy season |
| 4. | surveying | dry season |
| 5. | Digging channel | dry season |
| 6. | bund construction | dry season |
| 7. | bund stablization with grasses | rain season |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 220.0 | 220.0 | 48.0 |
| Equipment | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 50.0 |
| Plant material | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 68.0 | 68.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | |
| Construction material | Sand | ha | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| Construction material | Cement | ha | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | |
| Other | Others | ha | 1.0 | 64.0 | 64.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 414.5 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 51.81 | |||||
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | tillage | dry season / twice |
| 2. | planting | on set of rainfall / once |
| 3. | compost application | during planting / twice |
| 4. | weeding | rainy season / twice |
| 5. | harvest | end of season / once |
| 6. | replanting of grass | mid of the rainy season /once |
| 7. | cleaning the channel | before rains/annual |
| 8. | maintenance of the broken part of the bund | before & after rains/twice a year |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 31.0 | 31.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 31.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 3.88 | |||||
Comments:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, shovel, sickle, axe,
Some of the costs such as seedling planting, transportation and digging of pit is not included. A person can dig 75 pits/day and he can plant 50 seedlings/day
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Market flactuation for industrial product, labour cost, uneven distribution of rainfall
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
LGP is 185 days
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium-high
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
55% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
45% of the land users are poor and own 30% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: land user who work on SWC activities have more income because of the incentive they obtain for participation.
Level of mechanization is manual work (hoe) and animal traction (oxen)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Land use rights:
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
during good time
fodder production
fodder quality
wood production
production area
land management
Income and costs
farm income
Comments/ specify:
during good time
economic disparities
workload
Other socio-economic impacts
Input constraints
Socio-cultural impacts
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Quantity before SLM:
60
Quantity after SLM:
28
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
Can lead to waterlogging
soil cover
soil loss
Quantity before SLM:
43
Quantity after SLM:
2
Climate and disaster risk reduction
wind velocity
Other ecological impacts
Biodiversity
Soil fertility
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
reliable and stable stream flows in dry season
downstream flooding
downstream siltation
groundwater/ river pollution
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
2534
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
362 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
2172 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: the technology has immediate return
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
improved soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? practicing more of fertility enhancing techniques that use locally available material |
|
soil erosion is controlled How can they be sustained / enhanced? biological and physical SWC activities increased and maintained |
|
increased household income How can they be sustained / enhanced? biological and physical SWC activities increased and maintained |
|
availability of animal feed How can they be sustained / enhanced? planting grass and fodder plants |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
it is a practice serving as model showing on how to integrate different options of technologies How can they be sustained / enhanced? focusing on techniques which enhance production |
|
it is implemented on individual household basis How can they be sustained / enhanced? through developing self-help activities |
| interest has been developed on funding agencies |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| labour consuming | group formation and participation of all members of the family |
| physical structures occupied more land | increase the productivity of land per unit area and use vegetative measures |
| high input demand | maximum use of locally available inputs |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| labour and time consuming | participate all family members |
| incentive dependant | give incentives only for the needy |
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules