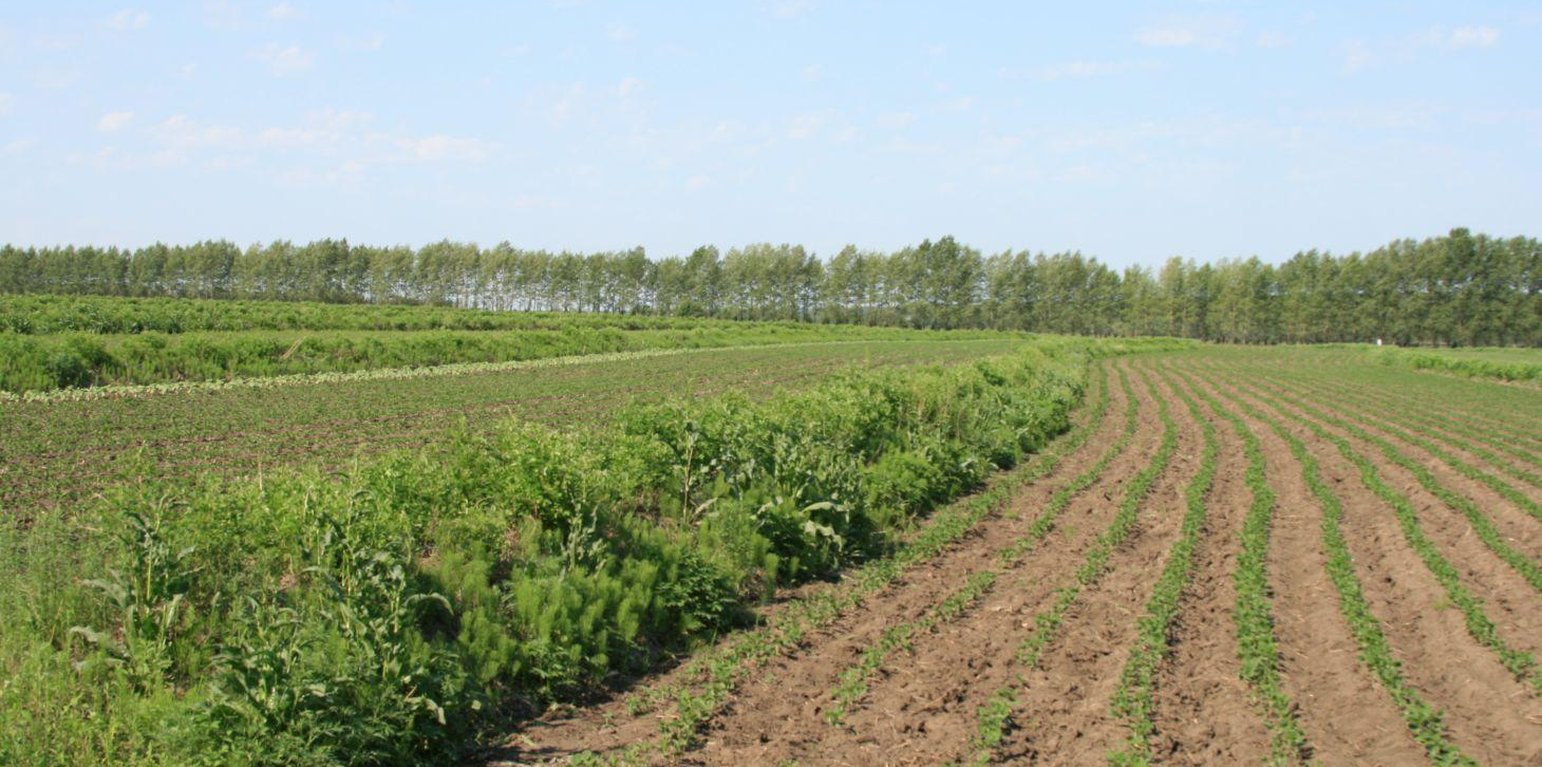




Shrubbery buffer strip with bund(SBSWB) is a traditional technology, it is introduced by the field staff about 60 years ago who worked in the farm in Heilongjiang province.This technology with low-cost, high effectives and easy to construct, which has been widely applied in all black soil region of Northeast China (Heilongjiang,Jilin,Liaoning,North of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region).
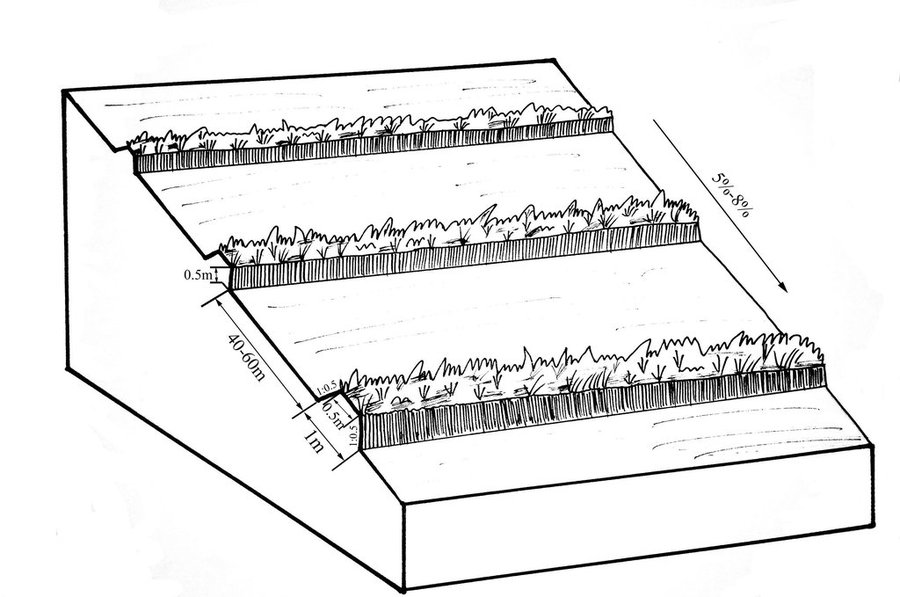
Purpose of the Technology: The final purpose of these buffer strips is increasing crop production by decreasing soil loss. More specific objectives include: 1)protect the land from surface erosion by cutting slope length, increase infiltration and soil moisture; 2)to prevent soil loss of gentle slope farmland by allowing excess runoff to filter through but trapping sediment; 3) through the effect of tillage and water erosion between the strips, level bund lead to the formation of forward slope terraces over time, then developing into terrace final;4) creation of opportunities for additional income by harvesting fodder(grass) production and fruits(shrub).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A construction is generally carried out in autumn of the year; plantation is made in spring of the next year. The construction in a man-machine integration mode is generally carried out step by step and from top to bottom along the contour line(s). The ladder-shaped cross section of a ridge is 0.3-0.5m in width (suitable width on the top), 0.5-0.6m in height, 1:1 or 1:0.5 in inner-side gradient and 1:0.5 in outer-side gradient.
In a construction, peel the surface soil with machine, with the peeling depth generally being 0.3m, which should be subject to soil layer depth; then haul the ridge construction plough (a kind of machine or device) with a tractor to build the ridges, consolidate the ridges through artificial slapping; Finally restore the surface soil to accomplish ridge construction. The tops of the constructed ridges should be maintained to be in a horizontal surface. The distance between two ridges in this region is generally stipulated to be 50 meters. The soil for ridge construction should be free from such sundries as gravels, tree roots and turfs.
Natural / human environment: Shrubbery buffer strip is found mainly in Northeast China, at altitudes between 700 and 1600 m. Climate there is cold in winters and cool in summers, with a monsoon moisture regime. In the area, the annual mean temperatures is from 2 to 8 °C, and the annual mean precipitation is from 500 to 1000 mm. Most of the farmland slopes are less than 7°but slope lengths mainly range from 200 to 1000m in this area.
Northeast China, the grain production base of China, or the bread basket of China, includes three provinces (Hei-long-jiang, Ji-lin, and Liao-ning) and the eastern part of the Inner Mongolian autonomous region. In 2009, 17.1% the China’s total grain production came from this region, which included 33.5%, 55.7% and 9.6% of corn, soybean, and rice, respectively. Approximately 118 million people live in this region. Grain produced per capita is over 1000 kg annually.
地点: Heilongjiang,Jilin,Liaoning,North of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, The black soil region of Northeast China, 中国
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. > 10,000 平方千米)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 50多年前(传统)
介绍类型





| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (RMB) | 每项投入的总成本 (RMB) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Layout of contour | Person/day | 3.0 | 16.0 | 48.0 | |
| Build ridge | Person/day | 36.0 | 9.6 | 345.6 | |
| 设备 | |||||
| Machine use | hours/day | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | |
| tools | day | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Seedling Plant shrubbery | ha | 600.0 | 0.016 | 9.6 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 491.2 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 78.59 | ||||