Shrubbery buffer strip with bund [中国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Mei Zhao
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Grass Buffer Strip
technologies_1544 - 中国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Belts of shrub or grass, planted on the level bund which constructed along contour line in gentle slope farmland in the black soil region of Northeast China.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
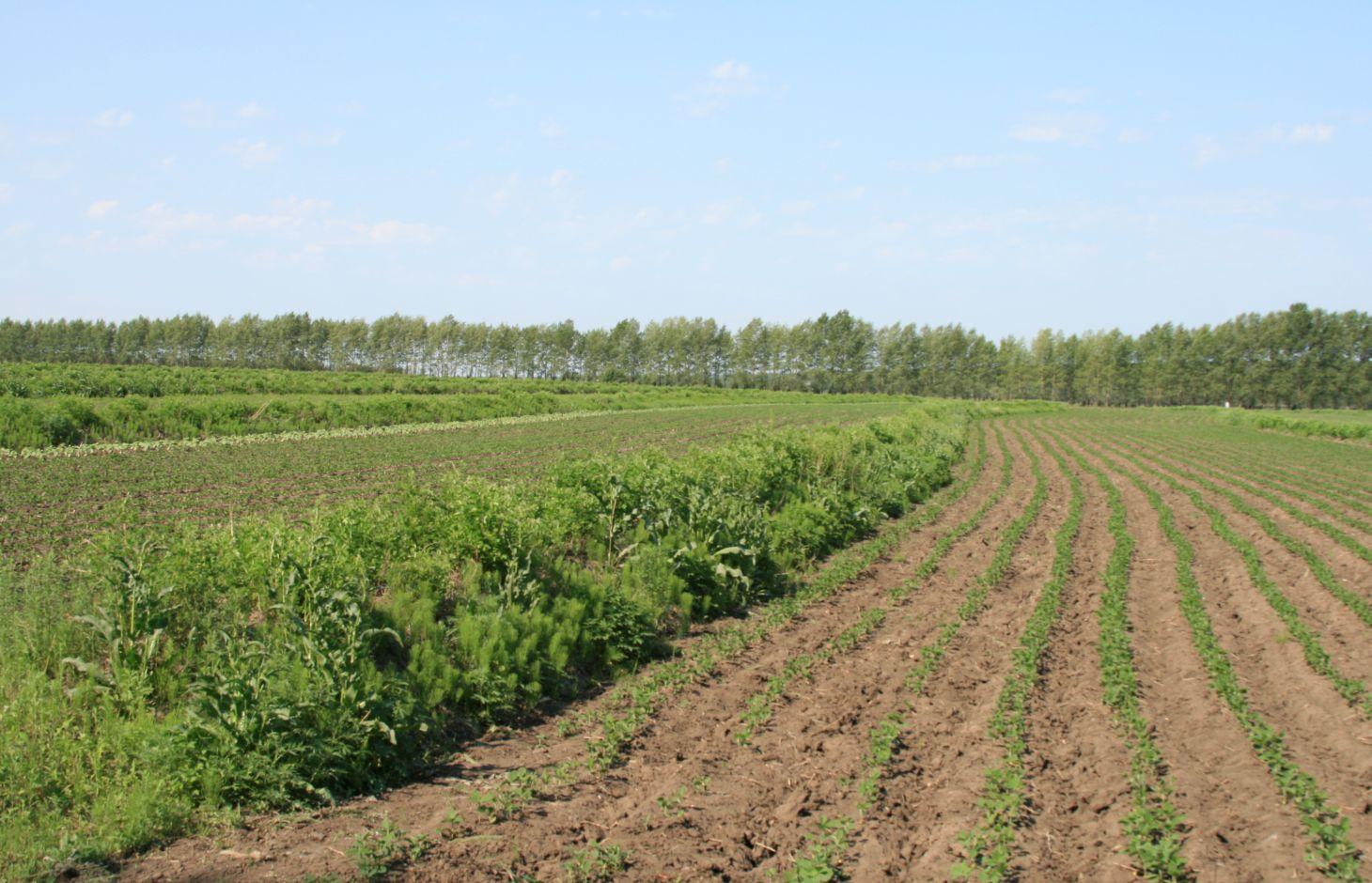
Shrubbery buffer strip with bund(SBSWB) is a traditional technology, it is introduced by the field staff about 60 years ago who worked in the farm in Heilongjiang province.This technology with low-cost, high effectives and easy to construct, which has been widely applied in all black soil region of Northeast China (Heilongjiang,Jilin,Liaoning,North of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region).
Purpose of the Technology: The final purpose of these buffer strips is increasing crop production by decreasing soil loss. More specific objectives include: 1)protect the land from surface erosion by cutting slope length, increase infiltration and soil moisture; 2)to prevent soil loss of gentle slope farmland by allowing excess runoff to filter through but trapping sediment; 3) through the effect of tillage and water erosion between the strips, level bund lead to the formation of forward slope terraces over time, then developing into terrace final;4) creation of opportunities for additional income by harvesting fodder(grass) production and fruits(shrub).
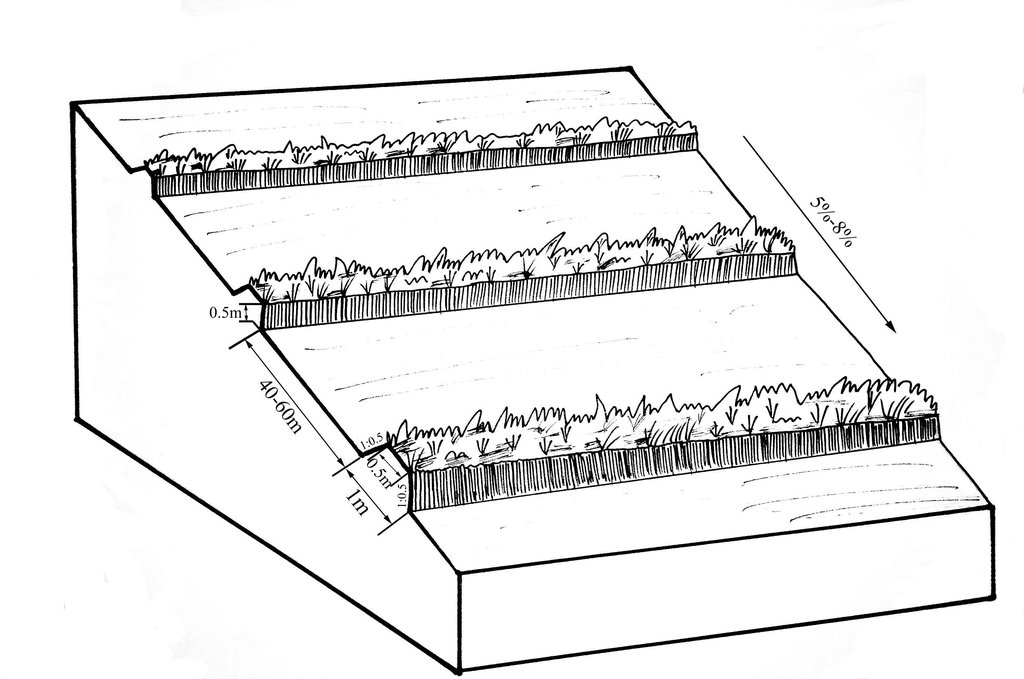
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A construction is generally carried out in autumn of the year; plantation is made in spring of the next year. The construction in a man-machine integration mode is generally carried out step by step and from top to bottom along the contour line(s). The ladder-shaped cross section of a ridge is 0.3-0.5m in width (suitable width on the top), 0.5-0.6m in height, 1:1 or 1:0.5 in inner-side gradient and 1:0.5 in outer-side gradient.
In a construction, peel the surface soil with machine, with the peeling depth generally being 0.3m, which should be subject to soil layer depth; then haul the ridge construction plough (a kind of machine or device) with a tractor to build the ridges, consolidate the ridges through artificial slapping; Finally restore the surface soil to accomplish ridge construction. The tops of the constructed ridges should be maintained to be in a horizontal surface. The distance between two ridges in this region is generally stipulated to be 50 meters. The soil for ridge construction should be free from such sundries as gravels, tree roots and turfs.
Natural / human environment: Shrubbery buffer strip is found mainly in Northeast China, at altitudes between 700 and 1600 m. Climate there is cold in winters and cool in summers, with a monsoon moisture regime. In the area, the annual mean temperatures is from 2 to 8 °C, and the annual mean precipitation is from 500 to 1000 mm. Most of the farmland slopes are less than 7°but slope lengths mainly range from 200 to 1000m in this area.
Northeast China, the grain production base of China, or the bread basket of China, includes three provinces (Hei-long-jiang, Ji-lin, and Liao-ning) and the eastern part of the Inner Mongolian autonomous region. In 2009, 17.1% the China’s total grain production came from this region, which included 33.5%, 55.7% and 9.6% of corn, soybean, and rice, respectively. Approximately 118 million people live in this region. Grain produced per capita is over 1000 kg annually.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
中国
区域/州/省:
The black soil region of Northeast China
有关地点的进一步说明:
Heilongjiang,Jilin,Liaoning,North of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- > 10,000 平方千米
注释:
This technique has been common applied in gentle slope farmland of the black soil region of Northeast China. It is very useful for reduce soil loss and intercept runoff.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
SBSWB appear in the vicinity of Heilongjiang province in the last century 60's
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 大豆
- 根/块茎作物 - 甜菜
- rice
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: April to August
注释:
Main cash crop: soybean, sugarbeet
Main food crop: paddy rice, maize
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Beacuse of long slope, high rainfall intensity, freezing and thawing processes, and intensive cultivation has lead to substantial water runoff, soil erosion, and gully formation. Soil erosion has been the serious problem threatening agriculture sustainability in the region for decades.The flora of the area are very diverse.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil fertility and crop yeild are decreasing year by year.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply also mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S2:堤、岸
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Et: loss of topsoil
Main causes of degradation: soil management (The extensive cultivation and management modes reduce the thickness of black soil layer by 0.5 cm per year.), population pressure (Great population pressure makes the land carrying capacity decline year by year.), education, access to knowledge and support services (The channels for the local peasants with low levels of education to learn knowledge are few, and they will not take initiative to learn knowledge.)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (This area is the most important grain production area in China, there is serious excessive exploitation in this area.), change of seasonal rainfall (The rainy seasons mainly focus on July and August.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (The downpours in summer bring about soil loss.), land tenure (As the lands are owned by country or by peasant communities, the peasants are not strongly aware of the importance of land protection.), poverty / wealth (The serious gap between rich and poor)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
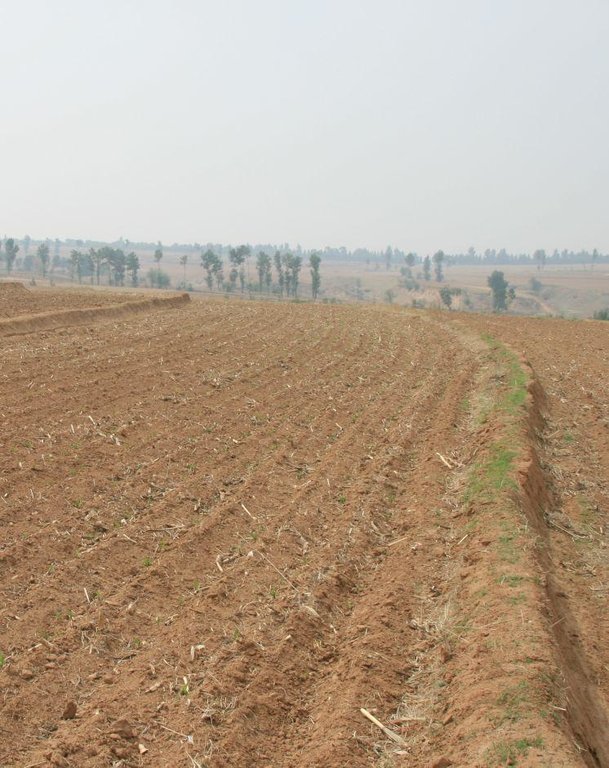
The upper-base width, lower base width, height, slope ratio and spacing of a ridge are 0.5m, 1m, 0.5m, 1:0.5 and 40-60m respectively. A row spacing of the shrubs planted on the ridges should be 0.5m. Generally one row on each ridge is enough. About 80 shrubs are needed for every hectare; if herbaceous plants are planted, no special plantations are required.
Location: Chao Yang City. Liao Ning Province
Date: Nov 12,2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Field staff/agricultural advisor should have intermediate know-how level, because land user should be instructed by them)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (The knowledge level of lander user is not required to be high, who just need(s) to follow the instructions from field staff/agricultural advisor)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200-600
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5.644-8.466
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 40-60
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Fruit trees / shrubs species: caragana, lespedeza, amorpha, daylily, Melilotus
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5-8%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0%
Wall/ barrier
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2.09-5.55
Spacing between structures (m): 40-60
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3-0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): >100
Construction material (earth): The soil should be free from such sundries as gravels, tree roots and turfs.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5-8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
作者:
Zhao Mei, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
RMB
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
6.25
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
9.25
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plant shrubbery | autumn |
| 2. | Layout of contour and the line of SBSWB with the leveling | autumn |
| 3. | Build the ridge | autumn |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Layout of contour | Person/day | 3.0 | 16.0 | 48.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Build ridge | Person/day | 36.0 | 9.6 | 345.6 | |
| 设备 | Machine use | hours/day | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | |
| 设备 | tools | day | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seedling Plant shrubbery | ha | 600.0 | 0.016 | 9.6 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 491.2 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 78.59 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | The farmers will actively protect the Bund in their land. Don't need money. | autumn |
| 2. | The farmers will actively protect the Bund in their land. Don't need money. | autumn |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Spade, Spade
3 people are required to layout contour, daily labor cost for per person is 100 Yuan, so the total labor cost is 300Yuan ($48), tools fee is 50Yuan ($8).
One tractor can built 2.6 ha of ridges per day at a cost of 500 Yuan ($80). The ridges constructed should be artificially tamped, 120 people are needed to tamp the ridges in an area of 2.6ha, about 46 people for each hectare. As the daily labor cost for per person is 60 Yuan, the total expense on each hectare is 2760 Yuan($441.6), and the labor intensity is intermediate.
If shrubs are planted on the ridges, 400 shrubs are required for each 1 hectare management area. In addition, as the price of caragana microphylla in 2012 is 0.1 Yuan per one, the total cost of the caragana microphyllas per hectare should be 40Yuan($6.4).
Therefore, the total construction cost per hectare is 3650Yuan($584).
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most determinate fators affecting the cost is labour
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
Thermal climate class: boreal
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: high
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
Soil water storage capacity: low - medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
5% of the land users are very rich.
45% of the land users are rich.
35% of the land users are average wealthy.
15% of the land users are poor.
5% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
木材生产
产品多样性
生产区域
土地管理
能源生产
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
经济差异
工作量
社会文化影响
文化机会
娱乐机会
社区机构
国家机构
冲突缓解
Livelihoods and human well-being
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
盐度
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
动物多样性
有益物种
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Although Certain quantity of land will be occupied and grain output will be affected in SBSWS during the early period of a construction, in the long run, SBSWS can prevent the loss of the most fertile surface soil, in addition, with the ever increased quantity of the sediment intercepted by SBSWS and as the heights of the vegetational belts increase year by year, the slope croplands will become bench terraces, and the grain output will be increased.
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
NA
注释:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Large-area popularization of SBSWB has been achieved in the locality.
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The implementation of this measure was accomplished under the encouragement and support of the government. There are relatively few peasant households who initially take this measure. The main reason for the peasant reluctance to adopt this measure is that the ridges will occupy land and reduce arable area. They are unconscious of and do not care about soil loss, and unable to realize in the long run the harm brought about by soil loss.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The trend depands on government support
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Convenient for construction How can they be sustained / enhanced? Popularization carried on |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Gradual formation of the slope-type terraces, which can be developed into bench terraces many years later How can they be sustained / enhanced? Increase of ridge height year by year |
|
Intercepting the sediments carried by runoffs, preventing water and soil loss of the arable lands on the gentle slopes How can they be sustained / enhanced? In combination with other water and soil conservation measures during operation, such as no-tillage and drainage ditches; |
|
increase of infiltration How can they be sustained / enhanced? Chopping down branches at regular intervals to guarantee that the plants on the ridges will not enter into rivary with the crops over water and sunlight; |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The ridges occupy land and reduce arable area | government support |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Reduction of arable lands brings about low enthusiasm of the peasants | Conflict between the arable lands and the immediate interests of the peasants. Popularization of water and soil preservation knowledge should be strangthened to make the presants realize that although the immediate interests will be hurt, the long-term interests will increase. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Title:Techniques standard for comprehensive control of soil erosion in the black soil region Author:Shen bo; Meng lingqinYears:2009
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
internal materials
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块