Shrubbery buffer strip with bund [China]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Mei Zhao
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Grass Buffer Strip
technologies_1544 - China
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
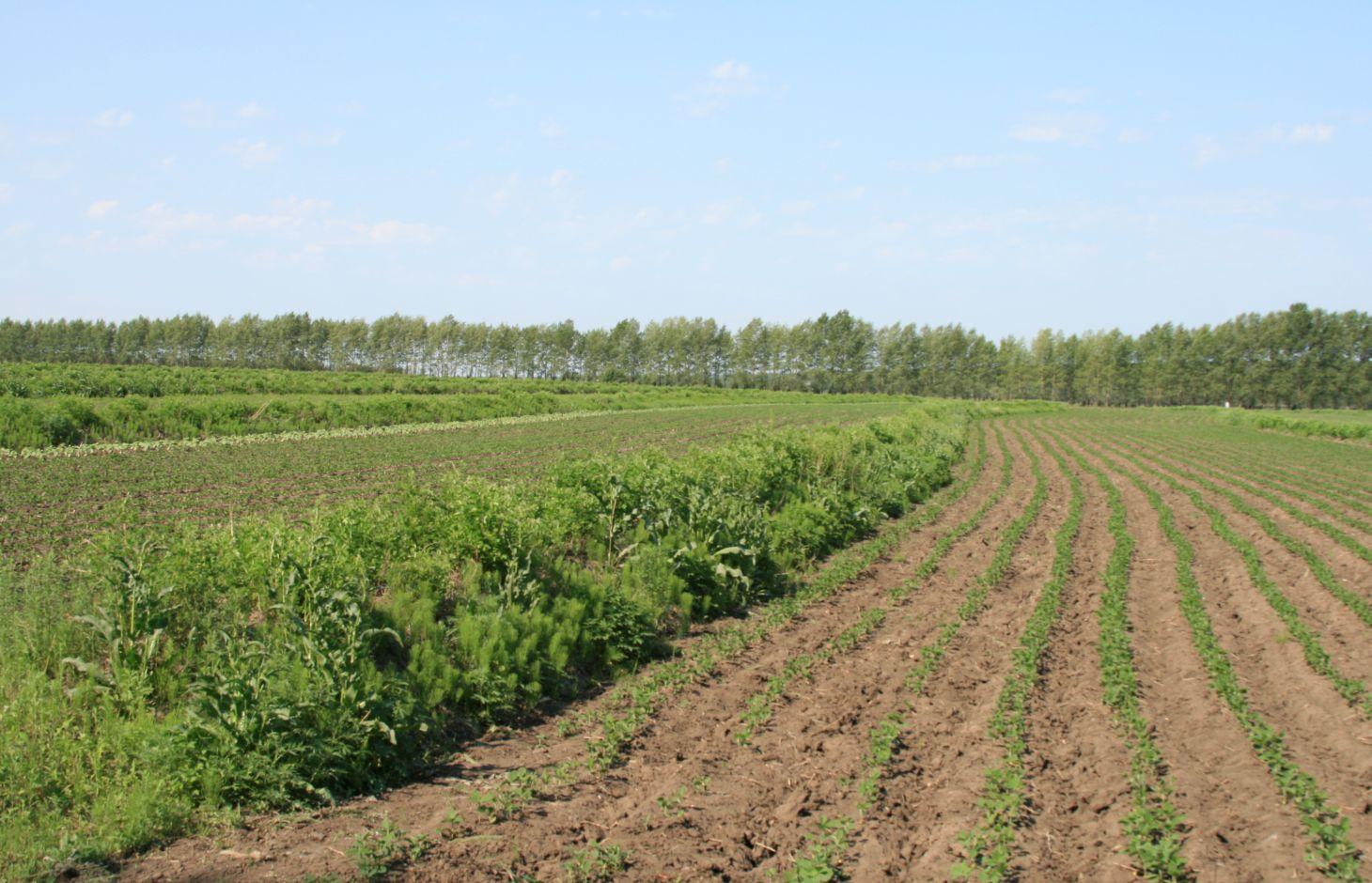
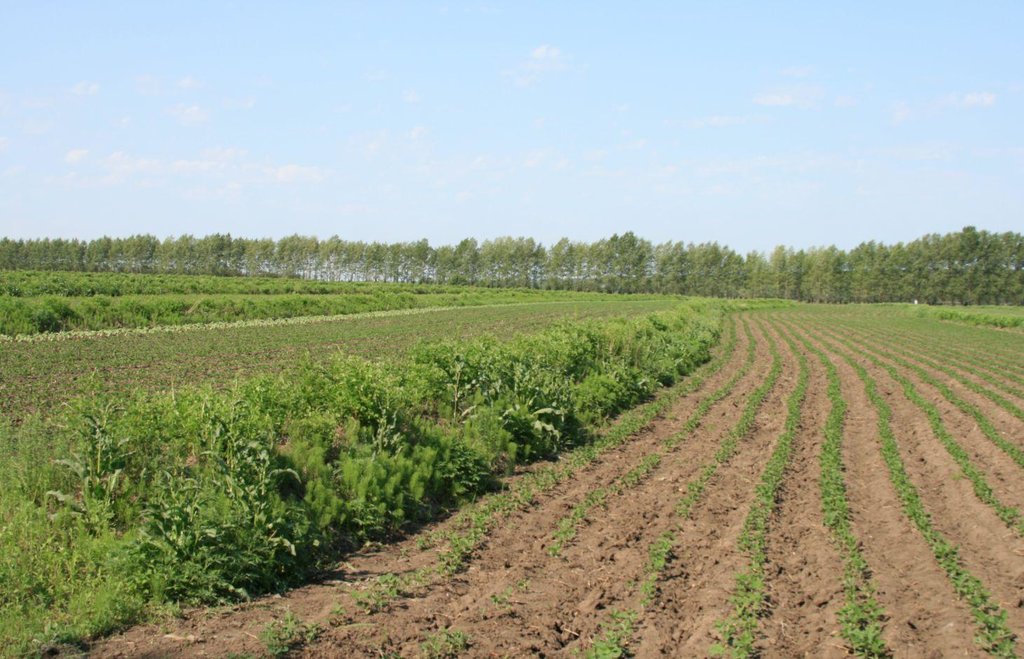
Belts of shrub or grass, planted on the level bund which constructed along contour line in gentle slope farmland in the black soil region of Northeast China.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Shrubbery buffer strip with bund(SBSWB) is a traditional technology, it is introduced by the field staff about 60 years ago who worked in the farm in Heilongjiang province.This technology with low-cost, high effectives and easy to construct, which has been widely applied in all black soil region of Northeast China (Heilongjiang,Jilin,Liaoning,North of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region).
Purpose of the Technology: The final purpose of these buffer strips is increasing crop production by decreasing soil loss. More specific objectives include: 1)protect the land from surface erosion by cutting slope length, increase infiltration and soil moisture; 2)to prevent soil loss of gentle slope farmland by allowing excess runoff to filter through but trapping sediment; 3) through the effect of tillage and water erosion between the strips, level bund lead to the formation of forward slope terraces over time, then developing into terrace final;4) creation of opportunities for additional income by harvesting fodder(grass) production and fruits(shrub).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A construction is generally carried out in autumn of the year; plantation is made in spring of the next year. The construction in a man-machine integration mode is generally carried out step by step and from top to bottom along the contour line(s). The ladder-shaped cross section of a ridge is 0.3-0.5m in width (suitable width on the top), 0.5-0.6m in height, 1:1 or 1:0.5 in inner-side gradient and 1:0.5 in outer-side gradient.
In a construction, peel the surface soil with machine, with the peeling depth generally being 0.3m, which should be subject to soil layer depth; then haul the ridge construction plough (a kind of machine or device) with a tractor to build the ridges, consolidate the ridges through artificial slapping; Finally restore the surface soil to accomplish ridge construction. The tops of the constructed ridges should be maintained to be in a horizontal surface. The distance between two ridges in this region is generally stipulated to be 50 meters. The soil for ridge construction should be free from such sundries as gravels, tree roots and turfs.
Natural / human environment: Shrubbery buffer strip is found mainly in Northeast China, at altitudes between 700 and 1600 m. Climate there is cold in winters and cool in summers, with a monsoon moisture regime. In the area, the annual mean temperatures is from 2 to 8 °C, and the annual mean precipitation is from 500 to 1000 mm. Most of the farmland slopes are less than 7°but slope lengths mainly range from 200 to 1000m in this area.
Northeast China, the grain production base of China, or the bread basket of China, includes three provinces (Hei-long-jiang, Ji-lin, and Liao-ning) and the eastern part of the Inner Mongolian autonomous region. In 2009, 17.1% the China’s total grain production came from this region, which included 33.5%, 55.7% and 9.6% of corn, soybean, and rice, respectively. Approximately 118 million people live in this region. Grain produced per capita is over 1000 kg annually.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
China
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
The black soil region of Northeast China
Especifique más el lugar :
Heilongjiang,Jilin,Liaoning,North of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si se desconoce el área precisa, indique el área aproximada cubierta:
- > 10,000 km2
Comentarios:
This technique has been common applied in gentle slope farmland of the black soil region of Northeast China. It is very useful for reduce soil loss and intercept runoff.
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace más de 50 años atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
SBSWB appear in the vicinity of Heilongjiang province in the last century 60's
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas anuales - Especifique cultivos:
- cereales - maíz
- leguminosas y legumbres - soya
- cultivos de raíces/ tubérculos - remolacha
- rice
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: April to August
Comentarios:
Main cash crop: soybean, sugarbeet
Main food crop: paddy rice, maize
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Beacuse of long slope, high rainfall intensity, freezing and thawing processes, and intensive cultivation has lead to substantial water runoff, soil erosion, and gully formation. Soil erosion has been the serious problem threatening agriculture sustainability in the region for decades.The flora of the area are very diverse.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil fertility and crop yeild are decreasing year by year.
3.4 Provisión de agua
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Water supply also mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- medida de pendiente transversal
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas estructurales
- S2: Taludes, bancos
Comentarios:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación del suelo encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wo: efectos de degradación fuera del sitio

erosión de suelos por viento
- Et: pérdida de capa arable
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Et: loss of topsoil
Main causes of degradation: soil management (The extensive cultivation and management modes reduce the thickness of black soil layer by 0.5 cm per year.), population pressure (Great population pressure makes the land carrying capacity decline year by year.), education, access to knowledge and support services (The channels for the local peasants with low levels of education to learn knowledge are few, and they will not take initiative to learn knowledge.)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (This area is the most important grain production area in China, there is serious excessive exploitation in this area.), change of seasonal rainfall (The rainy seasons mainly focus on July and August.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (The downpours in summer bring about soil loss.), land tenure (As the lands are owned by country or by peasant communities, the peasants are not strongly aware of the importance of land protection.), poverty / wealth (The serious gap between rich and poor)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación del suelo
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación del suelo
- reducir la degradación del suelo
Comentarios:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
Especificaciones técnicas (relacionadas al dibujo técnico):
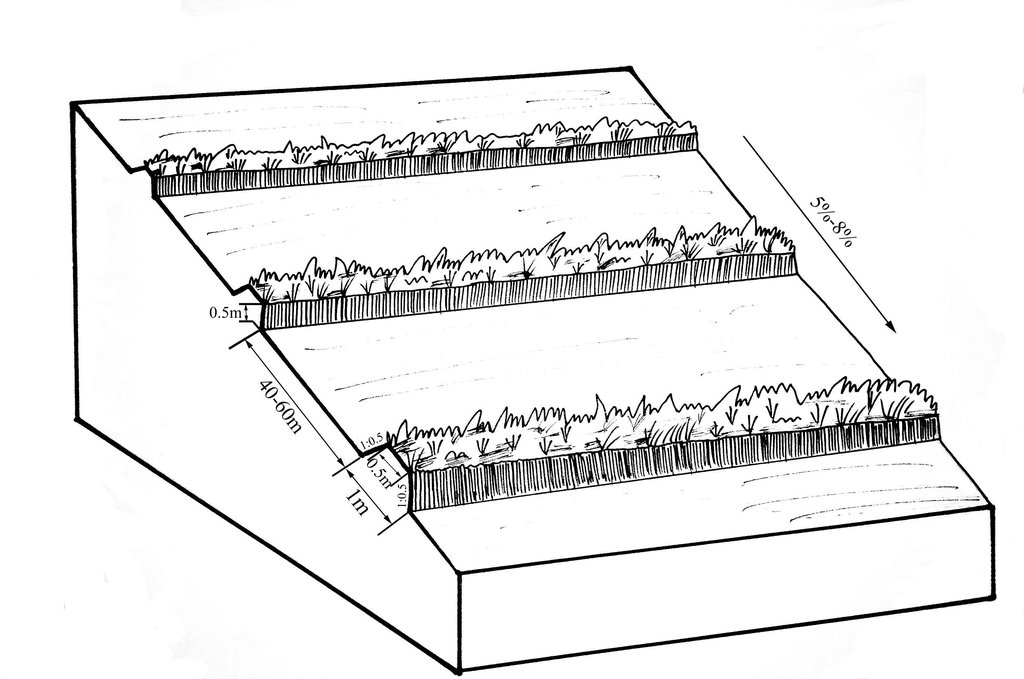
The upper-base width, lower base width, height, slope ratio and spacing of a ridge are 0.5m, 1m, 0.5m, 1:0.5 and 40-60m respectively. A row spacing of the shrubs planted on the ridges should be 0.5m. Generally one row on each ridge is enough. About 80 shrubs are needed for every hectare; if herbaceous plants are planted, no special plantations are required.
Location: Chao Yang City. Liao Ning Province
Date: Nov 12,2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Field staff/agricultural advisor should have intermediate know-how level, because land user should be instructed by them)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (The knowledge level of lander user is not required to be high, who just need(s) to follow the instructions from field staff/agricultural advisor)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200-600
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5.644-8.466
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 40-60
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Fruit trees / shrubs species: caragana, lespedeza, amorpha, daylily, Melilotus
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5-8%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0%
Wall/ barrier
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2.09-5.55
Spacing between structures (m): 40-60
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3-0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): >100
Construction material (earth): The soil should be free from such sundries as gravels, tree roots and turfs.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5-8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Autor:
Zhao Mei, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China
4.2 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
RMB
Si fuera relevante, indique la tasa de cambio de dólares americanos a la moneda local (ej. 1 U$ = 79.9 Reales Brasileros): 1 U$ =:
6,25
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
9.25
4.3 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Momento (estación) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plant shrubbery | autumn |
| 2. | Layout of contour and the line of SBSWB with the leveling | autumn |
| 3. | Build the ridge | autumn |
4.4 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Layout of contour | Person/day | 3,0 | 16,0 | 48,0 | |
| Mano de obra | Build ridge | Person/day | 36,0 | 9,6 | 345,6 | |
| Equipo | Machine use | hours/day | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | |
| Equipo | tools | day | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Seedling Plant shrubbery | ha | 600,0 | 0,016 | 9,6 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 491,2 | |||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 78,59 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | The farmers will actively protect the Bund in their land. Don't need money. | autumn |
| 2. | The farmers will actively protect the Bund in their land. Don't need money. | autumn |
4.6 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: Spade, Spade
3 people are required to layout contour, daily labor cost for per person is 100 Yuan, so the total labor cost is 300Yuan ($48), tools fee is 50Yuan ($8).
One tractor can built 2.6 ha of ridges per day at a cost of 500 Yuan ($80). The ridges constructed should be artificially tamped, 120 people are needed to tamp the ridges in an area of 2.6ha, about 46 people for each hectare. As the daily labor cost for per person is 60 Yuan, the total expense on each hectare is 2760 Yuan($441.6), and the labor intensity is intermediate.
If shrubs are planted on the ridges, 400 shrubs are required for each 1 hectare management area. In addition, as the price of caragana microphylla in 2012 is 0.1 Yuan per one, the total cost of the caragana microphyllas per hectare should be 40Yuan($6.4).
Therefore, the total construction cost per hectare is 3650Yuan($584).
4.7 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The most determinate fators affecting the cost is labour
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: temperate
Thermal climate class: boreal
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility: high
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
Soil water storage capacity: low - medium
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
- rico
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
5% of the land users are very rich.
45% of the land users are rich.
35% of the land users are average wealthy.
15% of the land users are poor.
5% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra usada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- escala mediana
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
producción de forraje
calidad de forraje
producción animal
producción de madera
diversidad de producto
área de producción
manejo de tierras
generación de energía
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
calidad de agua para ganado
disponibilidad de agua para irrigar
calidad de agua para irrigar
demanda de agua para irrigar
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
ingreso agrario
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
disparidades económicas
carga de trabajo
Impactos socioculturales
oportunidades culturales
oportunidades recreativas
instituciones comunitarias
instituciones nacionales
mitigación de conflicto
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
calidad de agua
cosecha/ recolección de agua
escurrimiento superficial
drenaje de agua en exceso
nivel freático/ acuífero
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
salinidad
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
diversidad animal
especies benéficas
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
velocidad de viento
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
inundaciones río abajo
colmatación río abajo
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
sedimentos transportados por el viento
daño a campos de vecinos
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | Incremento o reducción | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Although Certain quantity of land will be occupied and grain output will be affected in SBSWS during the early period of a construction, in the long run, SBSWS can prevent the loss of the most fertile surface soil, in addition, with the ever increased quantity of the sediment intercepted by SBSWS and as the heights of the vegetational belts increase year by year, the slope croplands will become bench terraces, and the grain output will be increased.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
NA
Comentarios:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Large-area popularization of SBSWB has been achieved in the locality.
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The implementation of this measure was accomplished under the encouragement and support of the government. There are relatively few peasant households who initially take this measure. The main reason for the peasant reluctance to adopt this measure is that the ridges will occupy land and reduce arable area. They are unconscious of and do not care about soil loss, and unable to realize in the long run the harm brought about by soil loss.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The trend depands on government support
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Convenient for construction How can they be sustained / enhanced? Popularization carried on |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Gradual formation of the slope-type terraces, which can be developed into bench terraces many years later How can they be sustained / enhanced? Increase of ridge height year by year |
|
Intercepting the sediments carried by runoffs, preventing water and soil loss of the arable lands on the gentle slopes How can they be sustained / enhanced? In combination with other water and soil conservation measures during operation, such as no-tillage and drainage ditches; |
|
increase of infiltration How can they be sustained / enhanced? Chopping down branches at regular intervals to guarantee that the plants on the ridges will not enter into rivary with the crops over water and sunlight; |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The ridges occupy land and reduce arable area | government support |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Reduction of arable lands brings about low enthusiasm of the peasants | Conflict between the arable lands and the immediate interests of the peasants. Popularization of water and soil preservation knowledge should be strangthened to make the presants realize that although the immediate interests will be hurt, the long-term interests will increase. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Title:Techniques standard for comprehensive control of soil erosion in the black soil region Author:Shen bo; Meng lingqinYears:2009
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
internal materials
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos