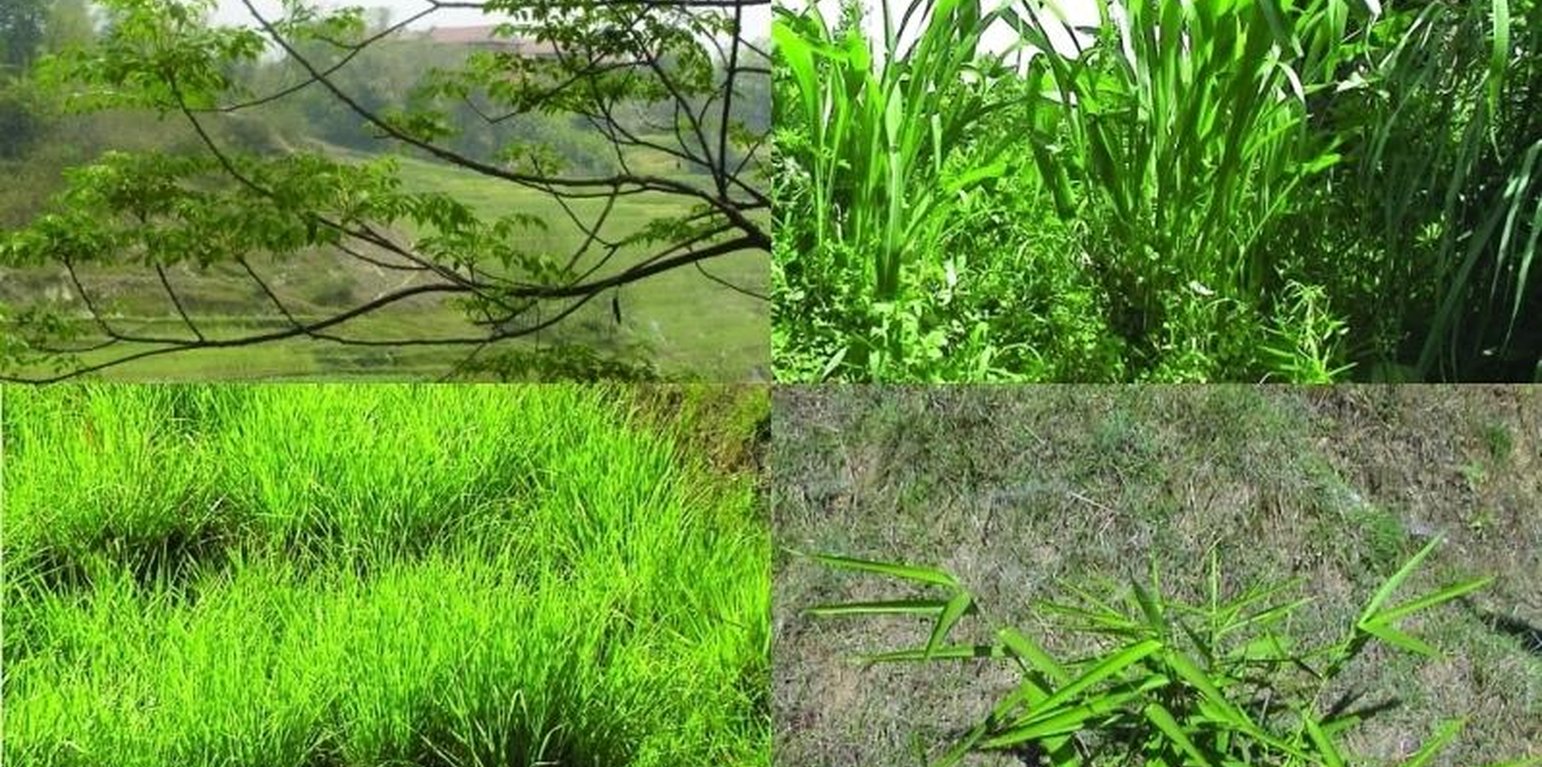




Fodder plays a major role in the crop-livestock-manure-soil nutrient cycle on farms in the middle mountains of the Himalayas. Livestock convert fodder shrubs and grasses from the forest, crop residues, and other fodder into manure through digestion. However, in the middle hills of Nepal the lack of availability of good quality fodder often limits not only, the productivity of livestock, but also reduces the nitrogen content of animal dung if, for example, only cereal crop residues, are fed to the animals.
In earlier times, livestock were left to graze in the forests and on community lands. The animals sought out their own food and were only assembled for milking and to protect them from wild animals. With the introduction of stall-feeding, the demand for fodder has increased greatly with a subsequent large increase in women’s workload as it is they who are responsible for collecting the fodder.
Most fodder is collected in forest areas, and most livestock manure is applied to arable land, in particular to rainfed fields. This results in a net transfer of nutrients from forest areas to arable lands. It is estimated that, in this way, about 3 to 7 ha of forest land is needed to maintain 1 ha of arable land without degrading the state of the forest. In addition to reducing the availability of forest resources, the widespread closure of community forests has diminished access to fodder during certain times of the year. All this is putting serious pressure on the remaining unprotected forest resources.
Marginal lands and terrace risers offer an opportunity to reduce this pressure. The planting of grasses and shrubs suitable for fodder on these areas not only increases fodder availability but also reduces erosion and landslides that originate in these areas. If leguminous fodder species are planted, they increase soil fertility by increasing the nitrogen content in soils.
地点: 尼泊尔
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域
在永久保护区?:
实施日期:
介绍类型



| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Nursing seedling | Persons/day | 3.0 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Seedlings | unit | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 10.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 10.0 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Replace dead plants | Persons/day | 3.0 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 6.0 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 6.0 | ||||
due to shading effect
mainly for women
some of the new species provide inputs for organic pest management