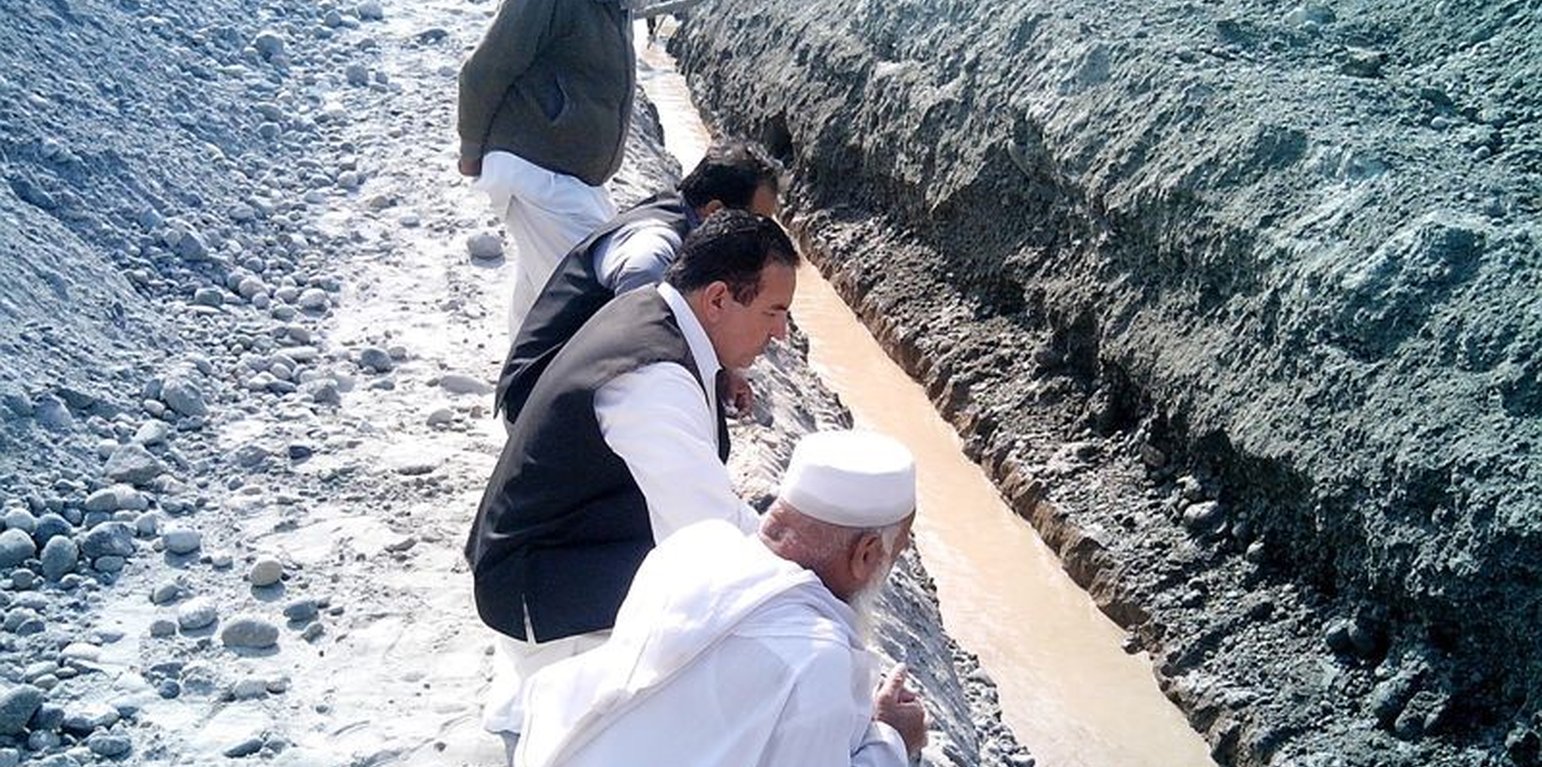




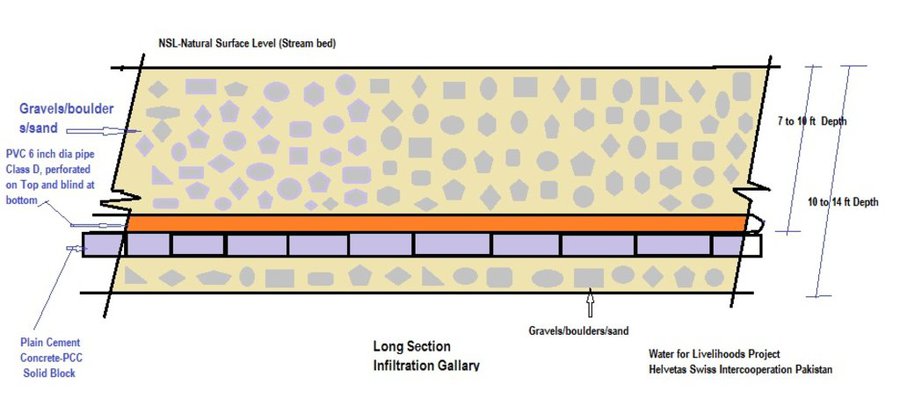
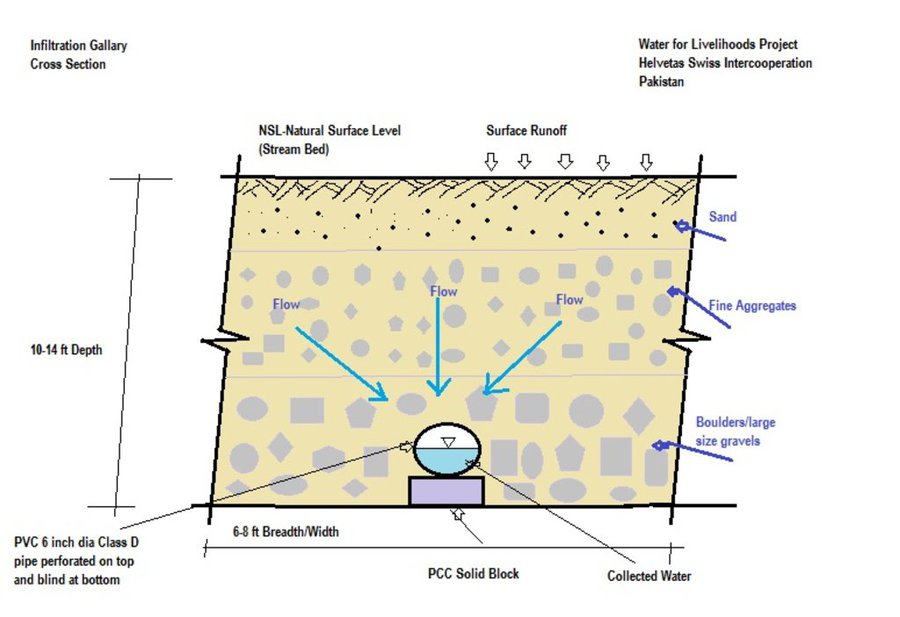
This method is applied in areas with low rainfall, where soils have a sandy-gravelly texture and where the sub-surface water can not percolate deeply, but instead flows laterally in shallow sub-surface channels. The technology consists of the following main elements: filtration materials (sand / gravel), collection chambers, perforated pipes, conveyance lines made from solid blocks, and storage tanks. Construction includes the following main activities and inputs:
• Excavation of rectangular trenches with machinery or by hand
• Construction of a solid base line with PCC (plain cement concrete) blocks on the top of boulders
• Installation of perforated and blind pipes - and storage tanks where necessary
• Coverage of the trench first with boulders and then sand on top.
Once the gallery is constructed there is no further need for intervention; this means that maintenance costs for the user (farmer, households of the local community) are minimal. Traditionally, the technology has been implemented by local farmers for many years. Where improvements are required, support by local technicians is provided. The technology is based on local knowledge, and locally available construction materials. The method is technically simple, cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Farmers and other users consider this technology as very efficient as there is no need for external energy supply, and it can be easily replicated. Furthermore, it requires a minimum of external construction material and the operation costs are minimal. The captured water is filtered through the subsurface layers and - as long as there is no specific external contamination - it is safe and can be used for various purposes as already noted. This extra water supply is particularly effective for irrigation, contributing to increased production and allowing diversification of crop production (potentially also of high value crops), thereby improving the livelihoods of remote rural communities. The primary impact of this technology is to reduce risks related to droughts or water scarcity as natural phenomena or consequences of climate change effects. Additionally infiltration of water into the galleries reduces surface erosion of fertile soil, hence it lessens soil degradation.
地点: Karak, Laki Marwat & Dera Ismail Khan, Southern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, 巴基斯坦
分析的技术场所数量: 2-10个场所
技术传播: 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 2013
介绍类型




| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Skilled Labour | Days | 109.0 | 12.0 | 1308.0 | |
| Un-Skilled Labour | Days | 465.0 | 6.0 | 2790.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Machinary (Excavator) | Hour | 118.0 | 25.0 | 2950.0 | |
| 施工材料 | |||||
| Bricks (Number) | 1000 | 12.5 | 95.0 | 1187.5 | |
| PCC blocks, rough stone (cubic foot) | 100 | 44.5 | 50.0 | 2225.0 | |
| Cement (50 kg bags) | 50 | 275.0 | 5.0 | 1375.0 | |
| sand, crush, boulder, gravel (cubic foot) | 100 | 63.0 | 35.0 | 2205.0 | |
| 其它 | |||||
| PVC pipe perforated (6" diameter filter section class D) (ft) | 1 | 590.0 | 5.0 | 2950.0 | |
| PVC blind pipe (3" diameter class B) (ft) | 1 | 3600.0 | 1.0 | 3600.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 20'590.5 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 20'590.5 | ||||
increased crop production efficiency due to additional and year-round water avalability for irrigation.
with the additional water for irrigation, water is no limiting factor anymore, with allows an improved crop productin in terms of quality and quantity.
SLM之前的数量: -1
SLM之后的数量: 1
SLM之前的数量: -1
SLM之后的数量: 2
with additional water through irrigation, additional crops might be cultivated, which contributes to production and income diversification.
with additional water through irrigation, additional areas can be used for agriculture.
SLM之前的数量: 0
SLM之后的数量: 2
SLM之前的数量: -2
SLM之后的数量: 3
SLM之前的数量: 0
SLM之后的数量: 3
the technology directly contributes to additional water for irrigation
Irrigation allows improved, diversified crop production. Water access for lifestock ensures animals health. Both crucial aspects for the income of local farmers
SLM之前的数量: 0
SLM之后的数量: 1
SLM之前的数量: -1
SLM之后的数量: 2
SLM之前的数量: 0
SLM之后的数量: 2
SLM之前的数量: 0
SLM之后的数量: 2
SLM之前的数量: 0
SLM之后的数量: 1
reduced consequences of droughts/water scarcity, in terms of production failure/lost harvest and reduced production