Sub-surface water harvesting for an efficient use of water resources [巴基斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Eveline Studer
- 编辑者: Munawar Khan
- 审查者: Hanspeter Liniger, Nicole Harari, Alexandra Gavilano
Infiltration gallery
technologies_540 - 巴基斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
Engineer-Water conservation:
Muhammad Khan
Water for Livelihoods Project-Intercooperation Pakistan
巴基斯坦
Water Management specilist:
Rehman Nasib-ur
On-Farm water managment, department of Agriculture
巴基斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
The technology promoted sunstainable water conservation. It is cost effective and requires no external energy supply as it is based on gravity flow.
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Water Use Management Plan (WUMP) [巴基斯坦]
The overall purpose of WUMP is to compile an inventory of available water ressources in a particular geographical or administrative area, to identify communities' priorities in order to achieve an effective, equitable and efficient use of water resources at local level. This approach promotes a participatory and inclusive analysis and …
- 编制者: Eveline Studer
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
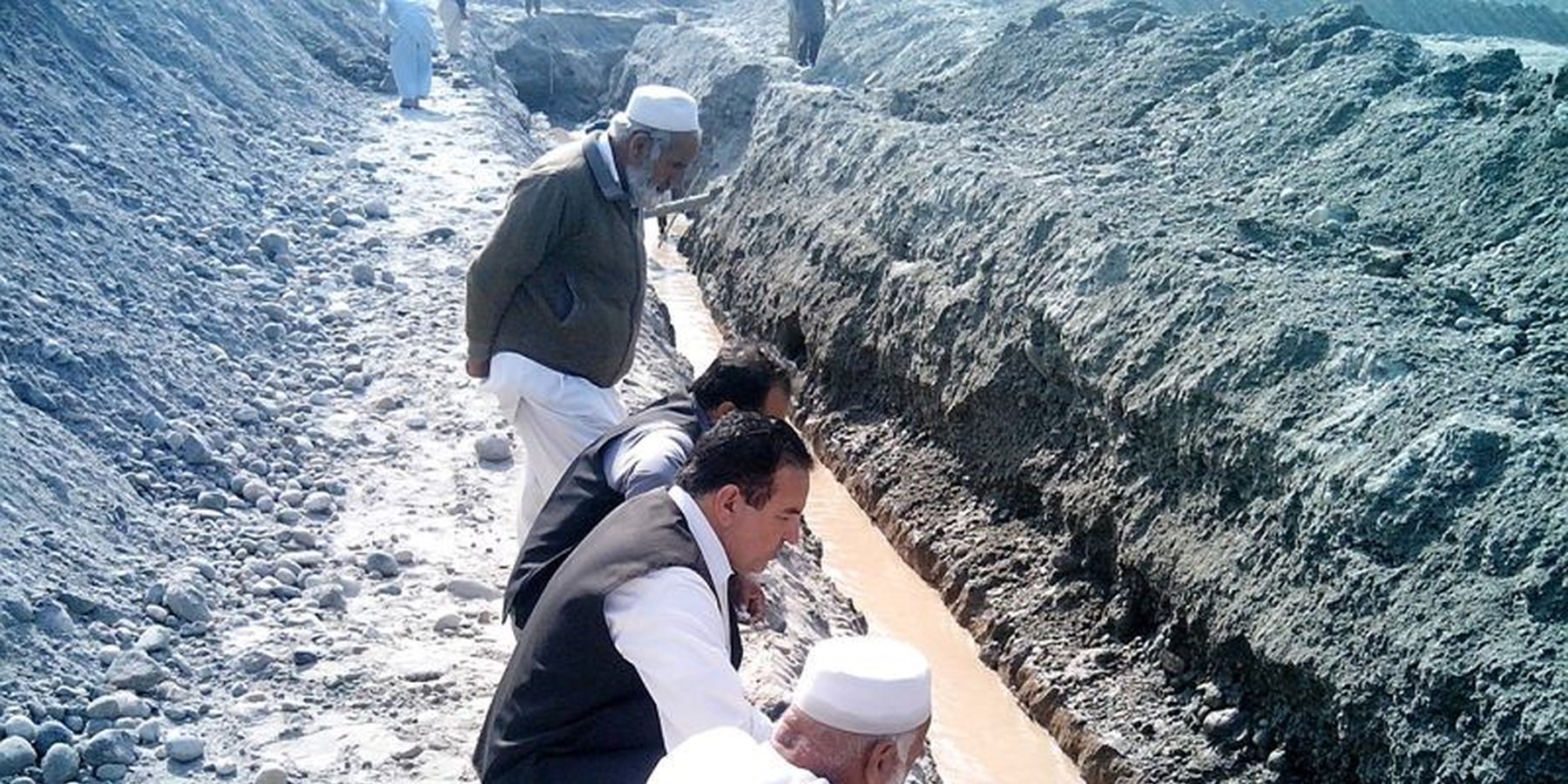
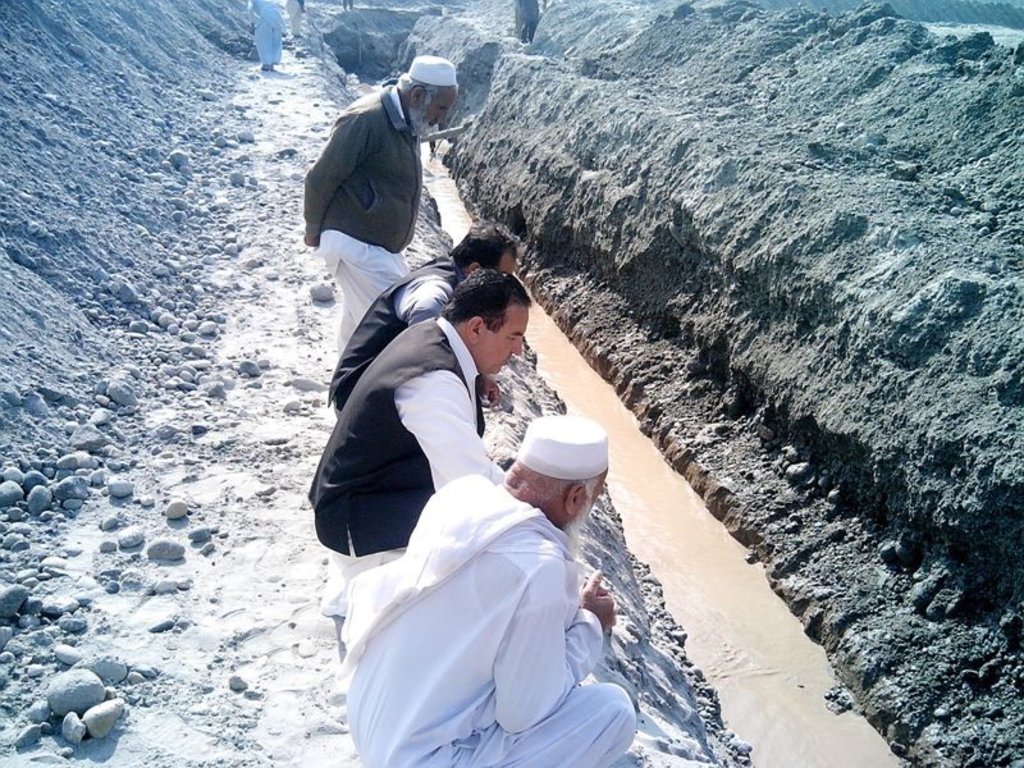
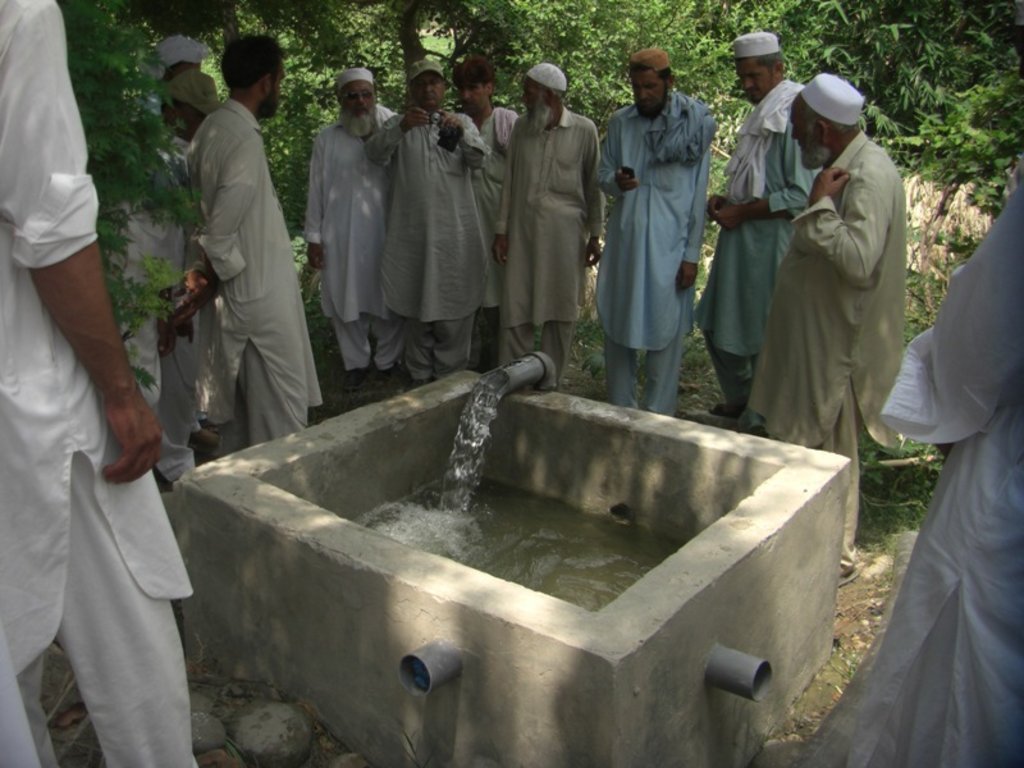
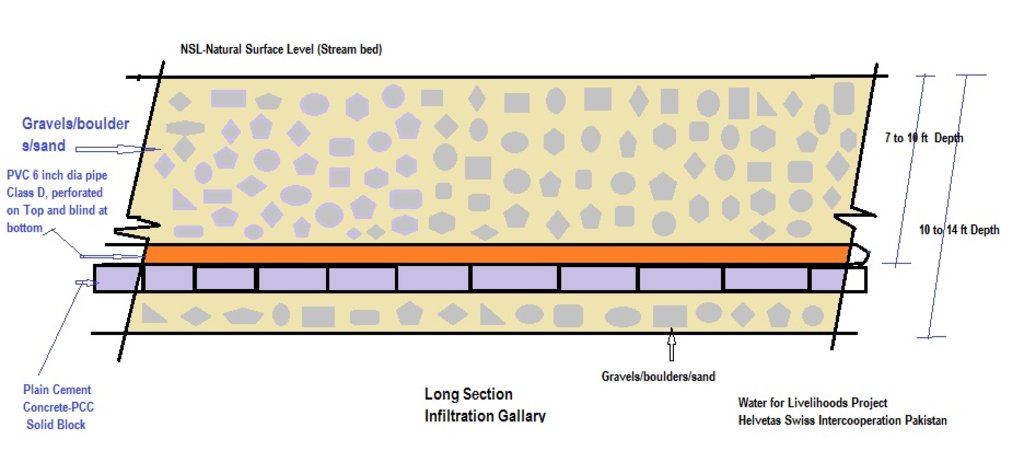
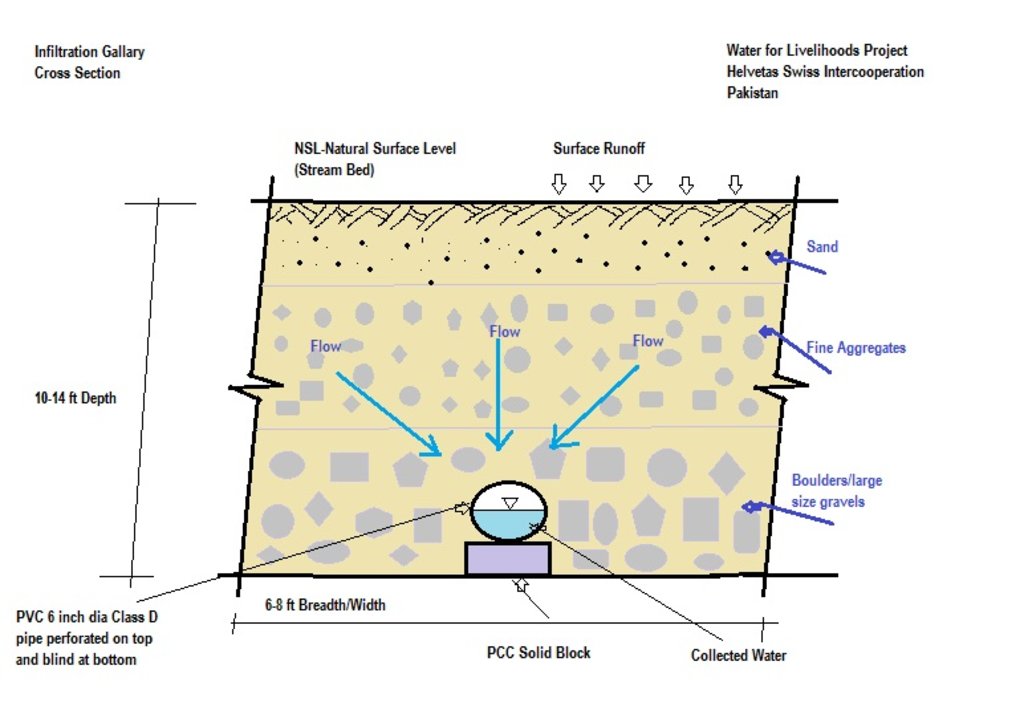
The purpose of this water harvesting technology is to capture, collect and distribute sub-surface water. First, an infiltration gallery is developed, which allows the percolation and collection of sub-surface water through perforated pipes at a depth of approximately 3-4.5 metres. Sub-surface water is filtered by gravel/sand underground and infiltrates into the gallery. The harvested water is used for household needs as well as for livestock and irrigation through gravity flow.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
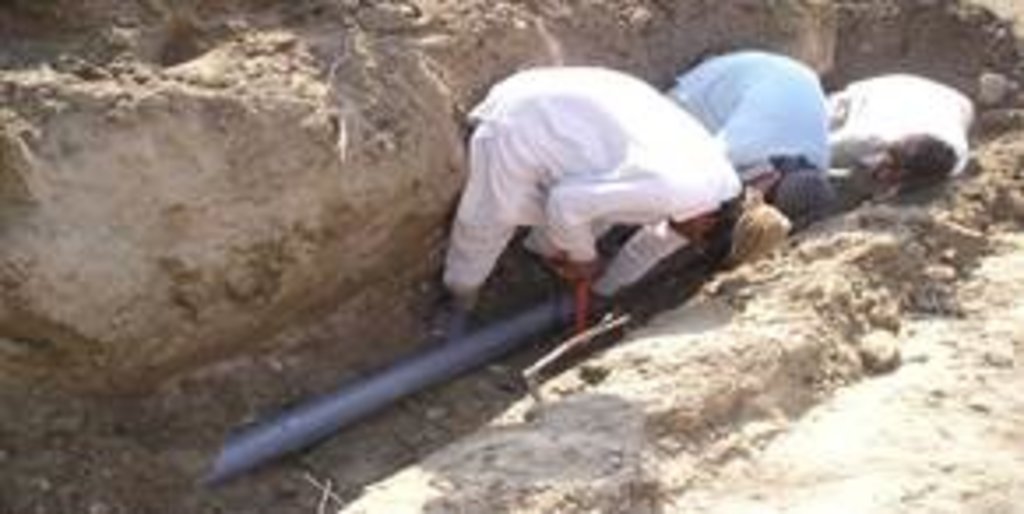
This method is applied in areas with low rainfall, where soils have a sandy-gravelly texture and where the sub-surface water can not percolate deeply, but instead flows laterally in shallow sub-surface channels. The technology consists of the following main elements: filtration materials (sand / gravel), collection chambers, perforated pipes, conveyance lines made from solid blocks, and storage tanks. Construction includes the following main activities and inputs:
• Excavation of rectangular trenches with machinery or by hand
• Construction of a solid base line with PCC (plain cement concrete) blocks on the top of boulders
• Installation of perforated and blind pipes - and storage tanks where necessary
• Coverage of the trench first with boulders and then sand on top.
Once the gallery is constructed there is no further need for intervention; this means that maintenance costs for the user (farmer, households of the local community) are minimal. Traditionally, the technology has been implemented by local farmers for many years. Where improvements are required, support by local technicians is provided. The technology is based on local knowledge, and locally available construction materials. The method is technically simple, cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Farmers and other users consider this technology as very efficient as there is no need for external energy supply, and it can be easily replicated. Furthermore, it requires a minimum of external construction material and the operation costs are minimal. The captured water is filtered through the subsurface layers and - as long as there is no specific external contamination - it is safe and can be used for various purposes as already noted. This extra water supply is particularly effective for irrigation, contributing to increased production and allowing diversification of crop production (potentially also of high value crops), thereby improving the livelihoods of remote rural communities. The primary impact of this technology is to reduce risks related to droughts or water scarcity as natural phenomena or consequences of climate change effects. Additionally infiltration of water into the galleries reduces surface erosion of fertile soil, hence it lessens soil degradation.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
巴基斯坦
区域/州/省:
Southern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
有关地点的进一步说明:
Karak, Laki Marwat & Dera Ismail Khan
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
This technology is suitable for area with little slope to retain a maximum amount of water. when the stream bed has a higher gravel content, it provides more water. The technology is suitable for strata with no/ low vertical percolation, such as underlying hard rocks.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2013
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
Water for Livelihoods Project (rural development project)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 降低灾害风险
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小米
- 蔬菜 - 其他
- wheat, tomatoes
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Rabi (October to March) & Kharif (April to September) season
注释:
Main crops (cash and food crops):
- Wheat, maize/corn, millet
- Tomato and other vegetables
- Fruit trees: guava etc.
As a result of the introdued technology, farmers can now produce multiple crops and have increased the cropping efficiency.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Prior to the establishment of the infiltration gallery, cropland was mainly rain-fed and only a single crop was produced with 50 % cropping efficiency.
The cropping efficiency increased up to 150 % (growing 3 crops instead of 1 crop in a year).
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
- The technology is simple and not costly to establish.
- It further contributes to adapt to climate change, especially in areas where water becomes increasingly scarce.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 地下水管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备
- S10:节能措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 适应土地退化
注释:
Further the technology contributes to reduce risks and losses linked to droughts as natural hazard and/or the effect of climate change.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Dimensions of the cross section:
- Depth: 10 to 15 feet, width: 6 to 8 feet, length: 300 to 1000 feet
- Slope: 3% on 200 feet
- Volume of storage tank: 30 x 30 x 4 feet
作者:
Munawar Khan & Khan Muhammad
日期:
2013
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Infiltration gallery: conveyance, collection chamber and tank
指定单位面积(如相关):
600 feet gallery (including 3600 feet conveyance lineconveyance line to the tank/water user's end point (adduction section without wholes for infiltration))
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
Skilled labour: 12 USD/day, unskilled labour: 6 USD /day
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation | 2 weeks |
| 2. | Dry stone packing | 1 week |
| 3. | Laying of PCC block (plain cement concrete) | 2-3 days |
| 4. | Installation & fixing of perforated pipes (6" diameter) | 2-3 days |
| 5. | Establishement of filtration media (boulder, gravel, sand packing)at gallery's end point/ water user's access point (if required) material: concrete | 2 weeks |
| 6. | Construction of water collecting chamber | 1 week |
| 7. | Convayance line (3" diameter) | 3 weeks |
| 8. | construction of storage tank (if required) | 4 weeks as parallel activity |
注释:
Totally, it takes 3 months to complete the construction of the infiltration gallery unit (600 feet) including the conveyance line and storage tank. Some of the activities can be carried out in parallel.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Skilled Labour | Days | 109.0 | 12.0 | 1308.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Un-Skilled Labour | Days | 465.0 | 6.0 | 2790.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machinary (Excavator) | Hour | 118.0 | 25.0 | 2950.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Bricks (Number) | 1000 | 12.5 | 95.0 | 1187.5 | |
| 施工材料 | PCC blocks, rough stone (cubic foot) | 100 | 44.5 | 50.0 | 2225.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Cement (50 kg bags) | 50 | 275.0 | 5.0 | 1375.0 | |
| 施工材料 | sand, crush, boulder, gravel (cubic foot) | 100 | 63.0 | 35.0 | 2205.0 | |
| 其它 | PVC pipe perforated (6" diameter filter section class D) (ft) | 1 | 590.0 | 5.0 | 2950.0 | |
| 其它 | PVC blind pipe (3" diameter class B) (ft) | 1 | 3600.0 | 1.0 | 3600.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 20590.5 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 20590.5 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Project / Government partner - i.e. on Farm Water Management department & public Health engineering Department, shared the cost at the ratio of 80 % : 20 %.
注释:
Total cost of the technology is basically proportional to the length of gallery and futher dependson the size of the storage tank.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
注释:
This technology is based on a single cost investment. Except minor repairs of storage tank, there are no relevant maintanance costs.
The filter function of the boulder layer and the perforated pipes reduce sedimentation problems. Minor amounts of silt and fine sediments in the storage tank can be removed with minor effort by the user (unskilled labo no tools required),
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
- Length of the infiltration gallery
- Length of the conveyance line
- Size of storage tank (not alway included)
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
300.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
rains in both season (monsoon & winter)
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Kohat & Bannu & DIKhan Met Department Automatic Weather Station
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Min. /max. temperatures: 9°C / 42°C
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Due to floods in monsoon season, the discharge capacity increases.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
increased crop production efficiency due to additional and year-round water avalability for irrigation.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
with the additional water for irrigation, water is no limiting factor anymore, with allows an improved crop productin in terms of quality and quantity.
饲料生产
SLM之前的数量:
-1
SLM之后的数量:
1
产品多样性
SLM之前的数量:
-1
SLM之后的数量:
2
注释/具体说明:
with additional water through irrigation, additional crops might be cultivated, which contributes to production and income diversification.
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
with additional water through irrigation, additional areas can be used for agriculture.
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
饮用水的质量
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
2
家畜用水的可用性
灌溉用水的可用性
SLM之前的数量:
-2
SLM之后的数量:
3
灌溉用水的质量
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
3
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
the technology directly contributes to additional water for irrigation
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Irrigation allows improved, diversified crop production. Water access for lifestock ensures animals health. Both crucial aspects for the income of local farmers
收入来源的多样性
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
1
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM之前的数量:
-1
SLM之后的数量:
2
土地使用权/用水权
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
2
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
2
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
1
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
注释/具体说明:
reduced consequences of droughts/water scarcity, in terms of production failure/lost harvest and reduced production
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 夏季 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 气候变化/极端气候
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
Design of infiltration galleries (diameter of pipes, size of perforation, slope etc.) was adjusted to local conditions including the consideration of local rainfall / amount of water.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Low cost measure, which requires only a one-time investment, low/no repair or maintenance costs are required. |
| Well assimilated and replicated by local farmers of the area since it is a simple and traditional technology. |
| No requirement of external energy (no pumping). |
| Allows harvest of sub-surface water for different purposes (domestic use, irrigation, livestock). |
| Environmentally friendly, making use as much as possible of local construction material (gravel, sand). |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology can be replicated in areas of similar conditions, as well as up-scaled with little efforts in other areas with a similar environment. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| If the land, where the sub-surface water is harvested is communal property, the distribution of water rights may be an issue. | Involvement of farmer organizations, distribution of water rights based on land holdings have to according check water rights. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Filtration media might clogge in the long run in case silt content is high. | Filtration media should be prepared with graded materials (sand, gravel, boulder). |
| Considering the initial investment cost, the measure cannot be done by an individual alone. | It requires an organized (group of) community. Though this pre-condition can also be interpreted as a strength for a coordinated and efficient use of water. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
5-10
- 与土地使用者的访谈
20-30
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
2-3
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
31/12/2015
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Water Use Management Plan (WUMP) [巴基斯坦]
The overall purpose of WUMP is to compile an inventory of available water ressources in a particular geographical or administrative area, to identify communities' priorities in order to achieve an effective, equitable and efficient use of water resources at local level. This approach promotes a participatory and inclusive analysis and …
- 编制者: Eveline Studer
模块
无模块