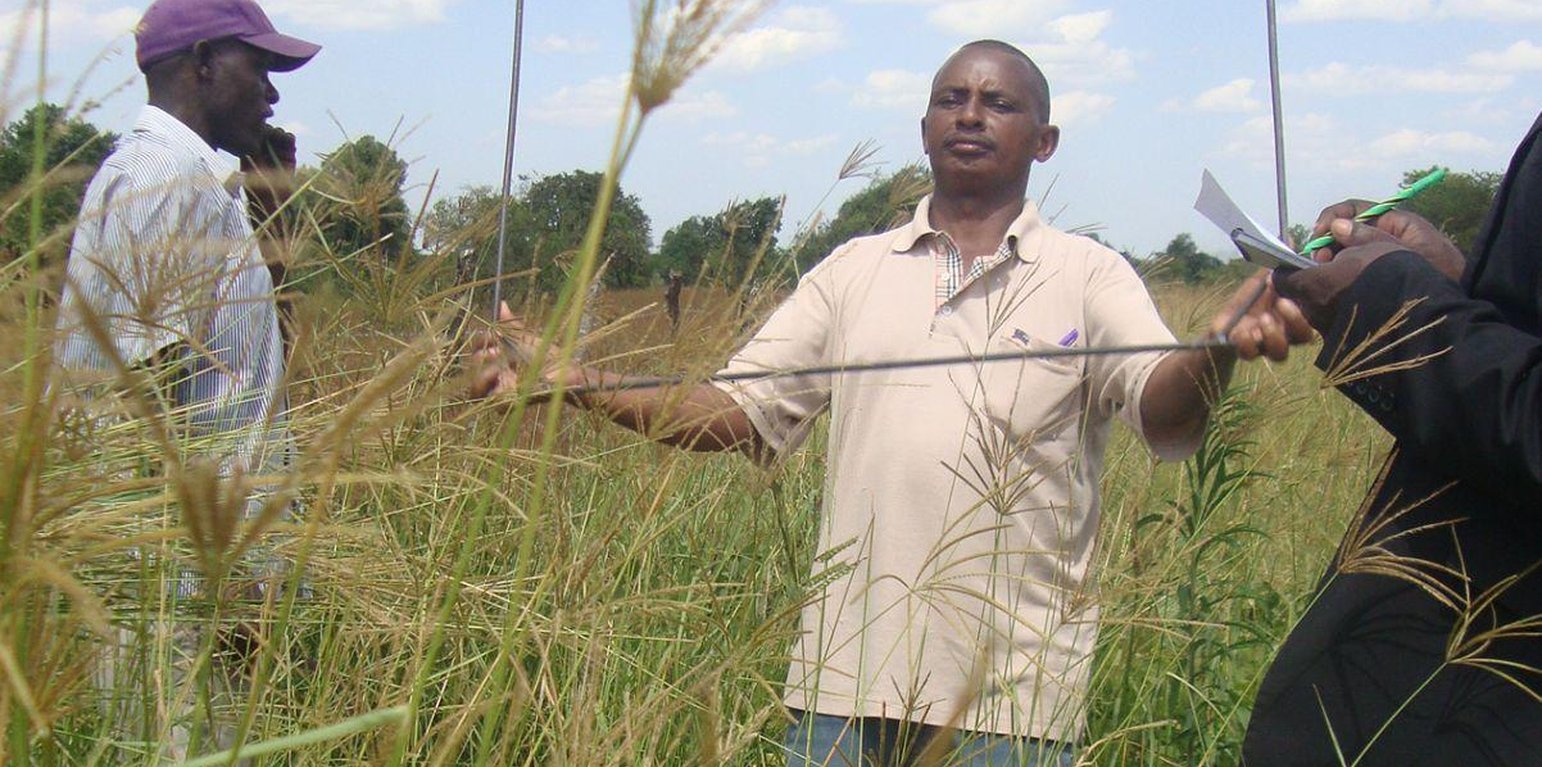




Multiple rangeland and pasture improvement techniques that combines water harvesting, rangeland reseeding and pasture establishment, livestock breeding management techniques to restore degraded rangeland in savannah with high livestock and optimize livestock production and productivity sustainably. These includes; 1. Chaco dam excavation for rain runoff harvesting mainly during the rainy season (February to April and August to December) mostly;(i).To ensure year round availability of water largely for watering livestock and partly for domestic and agriculture use especially during the main dry season when local sources (Ponds, springs or stream) are dry,(ii).To reduce soil erosion by water (lily or gully erosion, (iii).To reduce river bank erosion and silitation due direct watering of livestock in to Kagera river, (iii). To reduce the distance animal has to walk for watering and (iv) to reduce water use conflicts between herders and other land users. 2. Establishment of pasture demonstration plots where farmers are exposed to a basket choice (Low cost technique Vs high cost technique) of pasture and rangeland improvement technique either through ;( a). Tilling the land and broadcasting drought tolerant indigenous degenerated palatable pasture species of high nutritive value and, mainly (i).Grass; Cenchrus cliaris, Chloris gayana and (ii).Legumes; Centrocema puberse, Lablab purpureus, Mucuna Pluriens and Puperaria Phaseilides ) to a manured degraded rangeland; (b).i. Encouraging re-growth of proper pasture species in a degraded area to take place through clearing bushes, shrubs or trees ( leaving edible shrubs and few selected shed trees especially acacia spp which allow pasture re-growth underneath and provide shed against intense sun radiations to livestock especially during the main dry season- July to September); ii. Closing the degraded area by fencing using live indigenous trees or using wooden pole with or without barbed wire for 2 -3 years, removal of anthills and discouraging regeneration of unproductive invasive species and hence returning the rangeland to productivity;3. Genetical improvement of local cattle (Ankole or Zebu) through crossbreeding with introduced improved bull especially boran, Frisian or Mpwapwa bulls to allow farmers to keep few improved offspring of high production and productivity ;4.Farmer training on rangeland improvement and grazing management including hay making and how to estimate carrying capacity 5. Establishment of livestock markets directly on the rangeland to encourage off take and hence control stocking rate and increase carrying capacity.
Purpose:To contribute to the increase of herders’ standard of living through increased livestock production and productivity while conserving the environment
Estblishment activities:1. Community mobilization and formation of project management commetee with 10 members; 2. Identification of project sites; 3. Land clearing; 4. Establishment of pasture demonstration plots; 5. Excavation of chacodam and construction of watering troughs; 6. Fencing of individual owned land using wooden pole with barbed wire or live fencing using euphobia spp; 7. Farmer training on pasture establishment and controll of stocking rate; 8. Procurement of bulls (Boran or Mpwapwa) for cross breeding with ankole females; 9. Construction of livestock market
Maintanence Activities: 1. Repair of livestock infrastructures (Chacodam, watering troughs, livestock fence, livestock markets).
The technology is implemented in extensive grazing land under semi arid condition receiving 600 -1000mm of rains per year. A combination of rangeland improvement measures (Excavation of chacodam for rainwater runoff harvesting, pasture improvement and establishment techniques, fencing and breeding management through cross breeding local cow (Ankole/zebu) with Boran/Mpwapwa bulls) complement each other to restore degraded rangeland and increase livestock production and productivity in savannah. The slope is gentle to moderate; soil depth is shallow and soil texture clay. Heavy tools (Bulldozer) to Simple hand tools are traditional used. Bulldozers are used during chacodam excavation and bush clearing by well-off herder will small hand tools such as hand hoe, bush knife and spade are used smallholder herders for excavation of water pond and construction of indigenous livestock watering points. Land ownership is Communal/village, individual titled and individual not titled. Water use rights is open access (unorganized), communal (organized). Application of this technology determined by high establishment costs.
地点: Missenyi, Tanzania, Kagera, 坦桑尼亚联合共和国
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. 1-10 平方千米)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型











| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Tanzanian Shilling) | 每项投入的总成本 (Tanzanian Shilling) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| labour | ha | 1.0 | 810.93 | 810.93 | |
| 设备 | |||||
| tools | ha | 1.0 | 34.0 | 34.0 | |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| seeds | ha | 1.0 | 1204.0 | 1204.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | |||||
| compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 274.42 | 274.42 | 20.0 |
| 施工材料 | |||||
| Chacodam Excavation | ha | 1.0 | 16007.0 | 16007.0 | 20.0 |
| Const livestock makert | ha | 1.0 | 12577.0 | 12577.0 | 20.0 |
| 其它 | |||||
| Procument of 6 bulls | ha | 1.0 | 548.84 | 548.84 | 20.0 |
| Vaccination | ha | 1.0 | 54.88 | 54.88 | |
| Fencing | ha | 1.0 | 1957.7 | 1957.7 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 33'468.77 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 15.31 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Tanzanian Shilling) | 每项投入的总成本 (Tanzanian Shilling) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| labour | ha | 1.0 | 205.34 | 205.34 | 20.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| tools | ha | 1.0 | 34.0 | 34.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 239.34 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.11 | ||||