Rangeland Improvement in Savanah with High Livestocks [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Jasson Rwazo
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Uboreshaji wa Nyanda za malisho katika uoto wa asili wa savana wenye ng'ombe wengi.
technologies_1314 - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Poder Alexander
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Improvement of degraded rangeland in savannah using multiple rangeland improvement techniques that complement each other to optimize livestock production and productivity sustainably.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
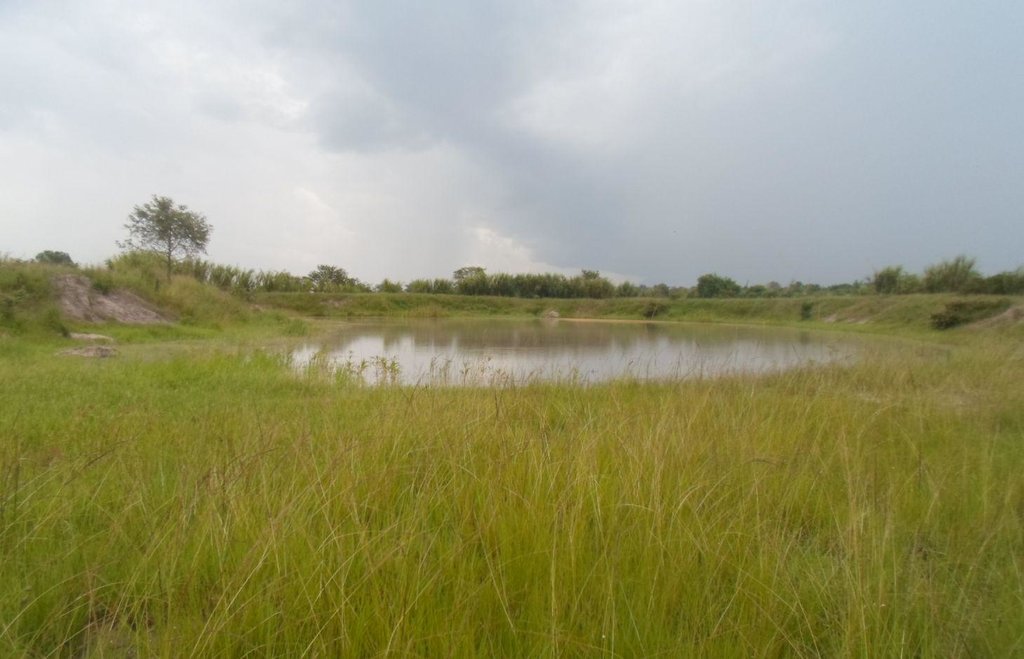
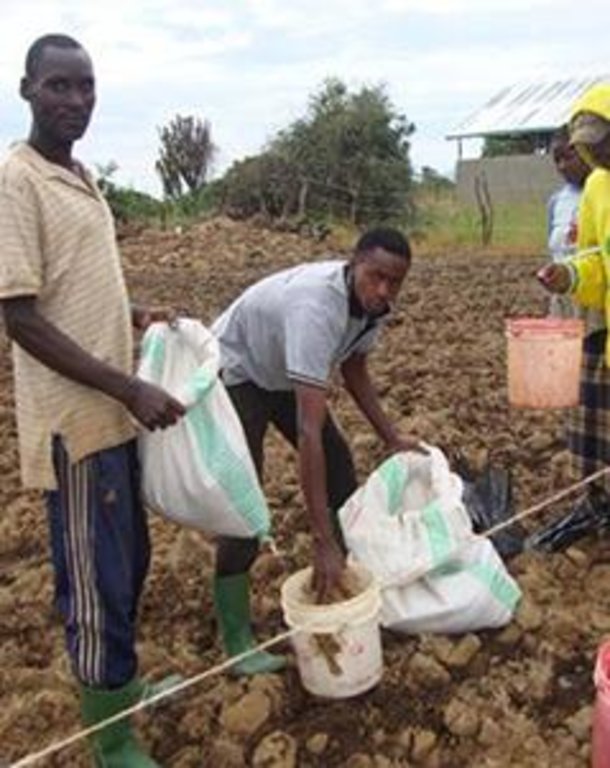
Multiple rangeland and pasture improvement techniques that combines water harvesting, rangeland reseeding and pasture establishment, livestock breeding management techniques to restore degraded rangeland in savannah with high livestock and optimize livestock production and productivity sustainably. These includes; 1. Chaco dam excavation for rain runoff harvesting mainly during the rainy season (February to April and August to December) mostly;(i).To ensure year round availability of water largely for watering livestock and partly for domestic and agriculture use especially during the main dry season when local sources (Ponds, springs or stream) are dry,(ii).To reduce soil erosion by water (lily or gully erosion, (iii).To reduce river bank erosion and silitation due direct watering of livestock in to Kagera river, (iii). To reduce the distance animal has to walk for watering and (iv) to reduce water use conflicts between herders and other land users. 2. Establishment of pasture demonstration plots where farmers are exposed to a basket choice (Low cost technique Vs high cost technique) of pasture and rangeland improvement technique either through ;( a). Tilling the land and broadcasting drought tolerant indigenous degenerated palatable pasture species of high nutritive value and, mainly (i).Grass; Cenchrus cliaris, Chloris gayana and (ii).Legumes; Centrocema puberse, Lablab purpureus, Mucuna Pluriens and Puperaria Phaseilides ) to a manured degraded rangeland; (b).i. Encouraging re-growth of proper pasture species in a degraded area to take place through clearing bushes, shrubs or trees ( leaving edible shrubs and few selected shed trees especially acacia spp which allow pasture re-growth underneath and provide shed against intense sun radiations to livestock especially during the main dry season- July to September); ii. Closing the degraded area by fencing using live indigenous trees or using wooden pole with or without barbed wire for 2 -3 years, removal of anthills and discouraging regeneration of unproductive invasive species and hence returning the rangeland to productivity;3. Genetical improvement of local cattle (Ankole or Zebu) through crossbreeding with introduced improved bull especially boran, Frisian or Mpwapwa bulls to allow farmers to keep few improved offspring of high production and productivity ;4.Farmer training on rangeland improvement and grazing management including hay making and how to estimate carrying capacity 5. Establishment of livestock markets directly on the rangeland to encourage off take and hence control stocking rate and increase carrying capacity.
Purpose:To contribute to the increase of herders’ standard of living through increased livestock production and productivity while conserving the environment
Estblishment activities:1. Community mobilization and formation of project management commetee with 10 members; 2. Identification of project sites; 3. Land clearing; 4. Establishment of pasture demonstration plots; 5. Excavation of chacodam and construction of watering troughs; 6. Fencing of individual owned land using wooden pole with barbed wire or live fencing using euphobia spp; 7. Farmer training on pasture establishment and controll of stocking rate; 8. Procurement of bulls (Boran or Mpwapwa) for cross breeding with ankole females; 9. Construction of livestock market
Maintanence Activities: 1. Repair of livestock infrastructures (Chacodam, watering troughs, livestock fence, livestock markets).
The technology is implemented in extensive grazing land under semi arid condition receiving 600 -1000mm of rains per year. A combination of rangeland improvement measures (Excavation of chacodam for rainwater runoff harvesting, pasture improvement and establishment techniques, fencing and breeding management through cross breeding local cow (Ankole/zebu) with Boran/Mpwapwa bulls) complement each other to restore degraded rangeland and increase livestock production and productivity in savannah. The slope is gentle to moderate; soil depth is shallow and soil texture clay. Heavy tools (Bulldozer) to Simple hand tools are traditional used. Bulldozers are used during chacodam excavation and bush clearing by well-off herder will small hand tools such as hand hoe, bush knife and spade are used smallholder herders for excavation of water pond and construction of indigenous livestock watering points. Land ownership is Communal/village, individual titled and individual not titled. Water use rights is open access (unorganized), communal (organized). Application of this technology determined by high establishment costs.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
区域/州/省:
Kagera
有关地点的进一步说明:
Missenyi, Tanzania
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
动物类型:
- 牛 - 非乳制品工作
- Ankole, Zebu
注释:
Livestock density (if relevant):
> 100 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Major land use problem without conservation includes, overgrazing, soil erosion, siltation of water bodies (Kagera River) and loss of paratable pasture spp.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Shortage of pasture and water for livestock
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
注释:
Grazing land: Extensive grazing land
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Number of growing seasons per year:
2
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A7:其它

植物措施
- V3:植被的清理
- V5:其它

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M5:物种组成的控制/变化
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
注释:
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Overgrazing due overstocking due to illegal migration on livestock), change in temperature (increased average temperature from 20.9o to 21.5oC in the past 20 years), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (decreased average annual rainfall from 1000mm to 870mm in the past 20 years), droughts, land tenure (Lack of village land use plan), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Uncontrolled bush fire set purposely to remove overgrown bushes), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), change of seasonal rainfall, population pressure (In migration of people from neighbourig districts and countries), education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Location: Bubale Village. Missenyi District/Kagera
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, water harvesting / increase water supply, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Legume inter-planting
Remarks: Legumes are inter-planted with grass to increase the nutritive value of the pasture
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Farmyard manure
Quantity/ density: 60t/Ha
In blocks
Vegetative material: G : grass, O : other
Grass species: Cenchrus cliaris, Chloris gayana, elephant grass,
Other species: Legumes:Centrocema puberse, Lablab purpureus, Mucuna Pluriens and Puperaria Phaseilides
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 40
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 80
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 240
Structural measure: Water trough
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 21
Structural measure: Appron
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 27
Construction material (earth): Clay soil
Construction material (concrete): concrete
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Control / change of species composition: Crossbreeding local female cattle(Ankole or Zebu) with boran or mpwapwa bulls
Other type of management: Closing the degraded area by fencing using pole or live indigenous trees with or without barbed wire for 2 -3 years, removal of anthills and discouraging regeneration of unproductive invasive species.
作者:
Jasson Rwazo, P.O.BOX 38, Missenyi Tanzania,email: Wazo12375@yahoo.co.uk
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Tanzanian Shilling
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
2186.41
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
6.86
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Procurement of 6 Boran/Mpwapwa bulls | |
| 2. | Transportation of bulls from Dodoma | |
| 3. | Vaccination against East Cost fever (ECF) | |
| 4. | Fencing | Procument Barbed wire |
| 5. | Excavation of water chaco dam | During the dry season |
| 6. | Fence construction | During the dry season |
| 7. | Construction of livestock market | |
| 8. | Land preparation | Eary June to september |
| 9. | Manure application | Mid september to early november |
| 10. | Planting | Early octobar |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 810.93 | 810.93 | |
| 设备 | tools | ha | 1.0 | 34.0 | 34.0 | |
| 植物材料 | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 1204.0 | 1204.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 274.42 | 274.42 | 20.0 |
| 施工材料 | Chacodam Excavation | ha | 1.0 | 16007.0 | 16007.0 | 20.0 |
| 施工材料 | Const livestock makert | ha | 1.0 | 12577.0 | 12577.0 | 20.0 |
| 其它 | Procument of 6 bulls | ha | 1.0 | 548.84 | 548.84 | 20.0 |
| 其它 | Vaccination | ha | 1.0 | 54.88 | 54.88 | |
| 其它 | Fencing | ha | 1.0 | 1957.7 | 1957.7 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 33468.77 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 15.31 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair of the fence | Once per year |
| 2. | Weeding and bush thinning | 0nce per year |
| 3. | Construction of fire break | Once per year |
| 4. | Harvesting pasture seeds | Once per year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 205.34 | 205.34 | 20.0 |
| 设备 | tools | ha | 1.0 | 34.0 | 34.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 239.34 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.11 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Hand hoe, bush knife, Bulldozer, handhooe, spade, truck, Hand hoe, hamer, nails, woods
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Excavation of chacodam, fencing and procurement of breeding bulls
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
- 非常丰富
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
5% of the land users are very rich and own 50% of the land.
35% of the land users are rich and own 25% of the land.
55% of the land users are average wealthy and own 10% of the land.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,未命名
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
木材生产
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
contribution to human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Grazing management and conservation knowledge
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水的回收/收集
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤压实
减少气候和灾害风险
火灾风险
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
下游淤积
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
注释:
Construction of chaco dam for water harvesting during the wet season to be used during the dry season, planting drought tolerant pasture sp
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
50 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increased livestock production(Milk and Meat) |
| Increased farm income |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increased water availability for livestock and domestic use |
| Increased pasture availability for livestock |
| Increased conservation knowledge |
| Increased livestock production and productivity |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High fire risk | Strengthener fire control bylaw, control burning and use of fire break |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
04/12/2015
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块