

Cut-off drains dug to avoid excessive runoff in a field (Turkelboom)


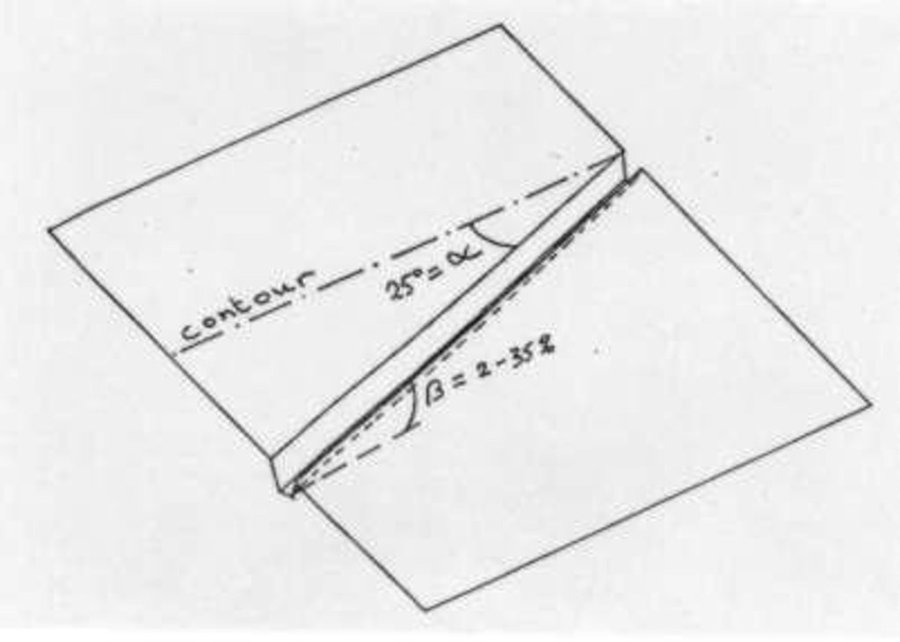
The cut-off drain is the same thing described as 'diversion' or 'diversion ditch'. It is dug by hand-hoe, only one hoe wide in the first year and may expand wider in the second and third year. It is dug with gradient from 15-50% to facilitate drainaing of runoff, not to scour the soil. Note: 1. The width of one hoe is approx. 21 cm , 2. The dimension of the ditch may become 30-40 cm wide and deep after 3 years.
地点: Amphur Mae Fa Luang, Chiang Rai, 泰国
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. 10-100 平方千米)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 50多年前(传统)
介绍类型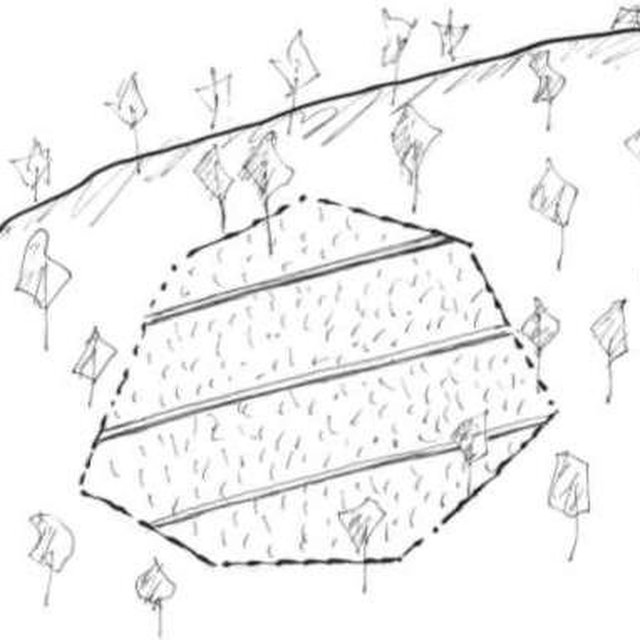



| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Baht) | 每项投入的总成本 (Baht) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 4.32 | 4.32 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 4.32 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.12 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Baht) | 每项投入的总成本 (Baht) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 4.32 | 4.32 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 4.32 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.12 | ||||
Production is not decreased.
Farmers don't mind
Drainage can function as a farm path
SLM之前的数量: 20
SLM之后的数量: 15
SLM之前的数量: 50
SLM之后的数量: 10