



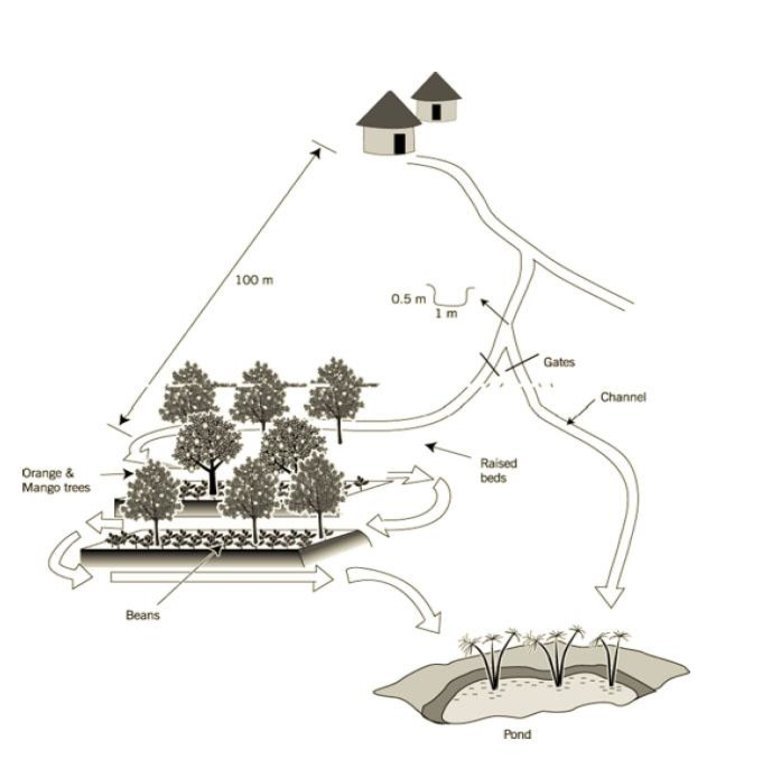
Setting up the infrastructure involves dividing the land in the valley into raised beds of ±10 m x 20 m which are separated by furrows, acting as drainage channels. Below the furrows is a pond. These furrows, however, can also fulfil the opposite role – distributing runoff water from upslope in the valley bottom if required. A diversion channel has been constructed to guide runoff from a track towards the valley. The channel is 0.5 m deep, 1 m wide, over 100 m in length and with a gradient of 0.5% - 1.0%. It is estimated that the ratio of catchment to cultivated area is 10:1. The channel is left open to divert runoff in times of shortage (though, naturally, as with any rainwater harvesting system, there has to be rain locally before it can be harvested). This water then can be held by the furrows whose outlet can be blocked. Citrus fruits (oranges) and mangoes are planted on the beds, and intercropped with annuals.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose is production of cash crops, based on reclamation of land and control of concentrated runoff. The impact is achieved through a flexible method
of drainage/water harvesting, which helps ensure suitable moisture conditions for growth.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The main maintenance aspect is clearing inlets, channels and removing vegetation, using common household hand tools such as spades and hoes.
Natural / human environment: The technology is situated in a valley near a swamp. It consists of growing both annual and perennial crops throught the year. The farm is located in a semi-arid area. The soil is sandy loam and shallow.
地点: Katakwi, Katakwi, 乌干达
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. 1-10 平方千米)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型




| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Uganda shillings) | 每项投入的总成本 (Uganda shillings) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 270.0 | 270.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 23.0 | 23.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | |||||
| Compost manure | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 345.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.34 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (Uganda shillings) | 每项投入的总成本 (Uganda shillings) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 340.0 | 340.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 315.0 | 315.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 71.0 | 71.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 726.0 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.73 | ||||
Negative: Can lead to waterlogging