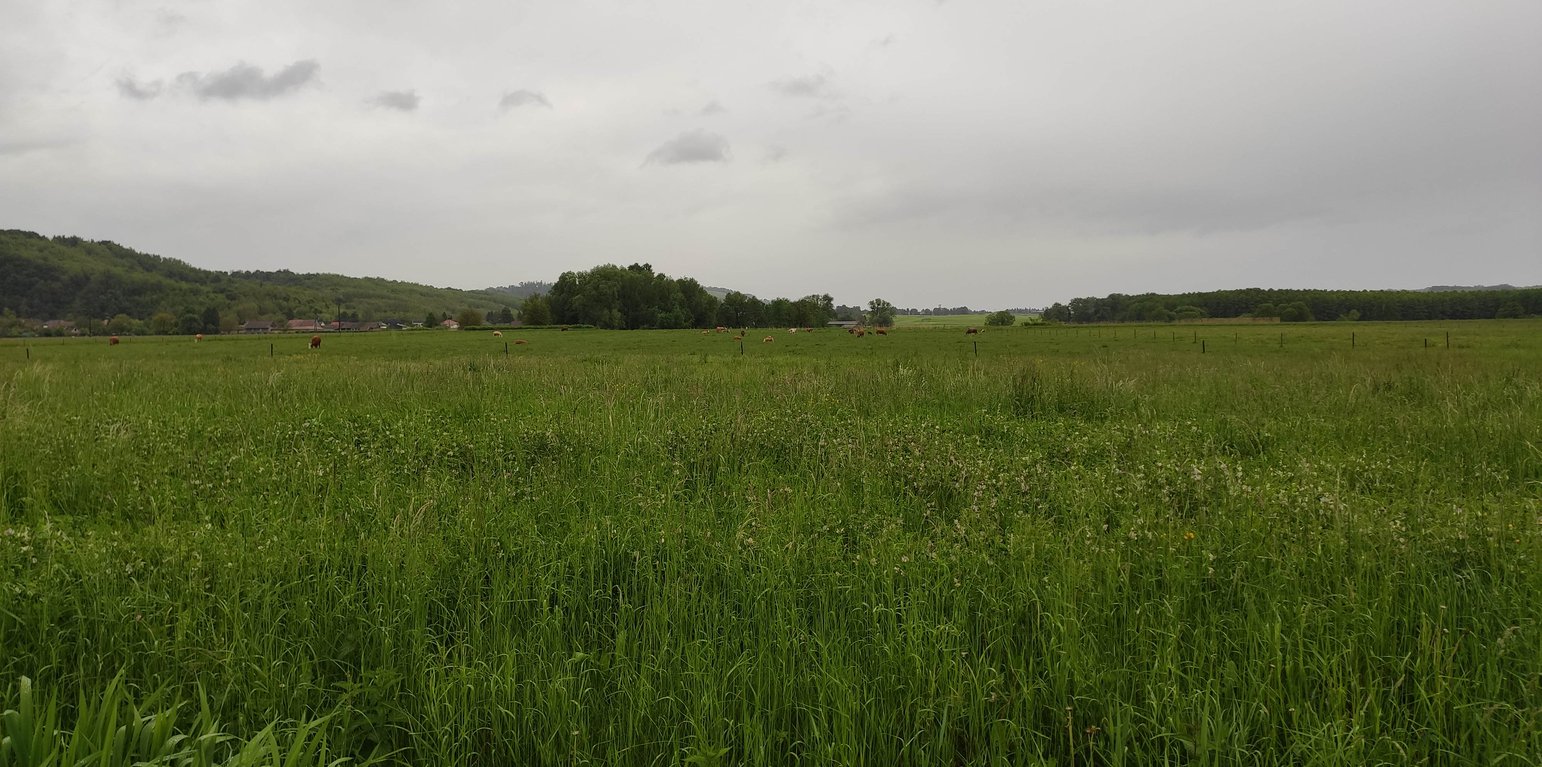




Permanent meadows and pastures are more effective in controlling land degradation than arable cropping. They are especially appropriate in hilly regions on sloping land where the risk of water erosion is high. This is a relevant technology also for valley floors where there is a regular inflow of water – resulting in sediment accumulation. Such grass cover has relevance also in plantations on sloping land.
There are some differences between pastures and meadows especially in their vegetation and land use. In general, meadows have a variety of natural growing plant species while pastures are often planted with specific types of grasses. Pastures are generally used for grazing animals while meadows are often mowed or harvested for hay (that is also often used for animal feed). Meadows may also be situated along streams or rivers on lowland areas, while pastures are typically situated on hilly regions.
Some of the most common grass species in Hungarian meadows are: meadow fescue (Festuca pratensis), smooth meadow-grass (Poa pratensis), and meadow foxtail (Alopecurus pratensis). Wildflowers (e.g Oxeye daisy, Field scabious) are also often growing on natural meadows in Hungary. On pastures the most common grass species are: ryegrass (Lolium perenne), tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea), and meadow fescue (Festuca pratensis). Hungarian pastures may also include legumes, such as red clover (Trifolium pratense) or white clover (Trifolium repens), which can help fix nitrogen in the soil and improve forage quality for grazing animals.
In the case of pastures farmers generally use a rotational grazing system, where the pasture is divided into sections and animals are periodically moved between them. Properly timed resting periods and regular rotation of pastures are essential for protecting the soil from erosion, promoting plant growth and nutrient uptake, and ensuring the long-term health and productivity of the pastures.
The main purpose of the technology (meadow and pasture land use) is to provide feed for livestock while reducing soil erosion and improving trafficability. The main conservation benefits are protection of the soil surface against transportation of particles by water or wind, thus avoiding soil loss and sedimentation. Due to lower velocity of surface runoff, more time is provided for infiltration of water into the soil, resulting in better water retention. In terms of production, meadows and pastures are predominantly used for providing hay or grazing land for ruminants. Different animals graze land differently, so the risk of soil degradation is lower in the case of cattle (which leave taller grass) and higher in case of sheep (which graze down to the soil surface), while in case of goats or pigs, the soil surface is easily damaged. In some special cases the main purpose of grass cover is simply soil conservation (very steep slopes, gully, etc.).
A significant proportion of grasslands (meadows and pastures) in Hungary are permanent, and they play an important role in agricultural production and the preservation of rural landscapes in the country. The common rules regarding the temporary or permanent use of agricultural land for this purposes (pasture or meadow) are contained in the Act CXXIX of 2007. The request for a land use change can be submitted at the local land offices. The most important requirement for land use change is that it must not result in a decrease in the total area of arable land below the minimum threshold set by the authorities and must not result in a decrease in the ecological value of the land. The conversion must be approved by the authorities and the appropriate land use permit must be obtained.
The application trend of this technology/solution is significantly depends on the situation of livestock production of a country. In Hungary, animal husbandry can be mentioned as the driving force of agriculture in the 1980s, with a share of 55-60% of its production value. However, by the end of the 1990s, this proportion had reversed and crop production had predominated. As there is no need for further pastures due to the decrease in livestock population, in recent times this type of land use change is not very common in Hungary.
地点: The case study area is situated within the Balaton Catchment Area in the western Hungary. The climate is moderately warm, moderately humid, the number of sunshine hours per year are high. Mean annual temperature of the region of the Lake Balaton is about 10 ˚C. The average amount of rainfall (600-700 mm / year) nationally means a medium rainfall zone. The Balaton Catchment area is 5765 km2. The main environmental purpose is to reduce pollutant (phosphorus and other plant nutrients) loads of Lake Balaton, where anthropogenic eutrophication is the main issue of environmental concern. Lake Balaton, with its nearly 600 sqkm area, is the largest shallow lake in Middle Europe. The lake as well as the surrounding area form very important natural (ecological, water and landscape) resources and are one of the major target areas of water related recreational tourism in Europe as a whole. 37% of the total catchment area is arable land which is much lower than the national average, 27% is forest, which exceeds the national average. 15% of the land suitable for grassland management, 5% is horticulture, 3% is pomiculture, 2% is viticulture, 1% is reed management and fish farming. The „Kis-Balaton” nature conservation area situated within the Balaton Catchment area. The „Kis-Balaton” wetland is under protection of the Ramsar Convention habitat., Zala County, 匈牙利
分析的技术场所数量: 2-10个场所
技术传播: 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
在永久保护区?: 否
实施日期: 10-50年前
介绍类型




| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 设备 | |||||
| stubble tillage | ha | 1.0 | 33.0 | 33.0 | 100.0 |
| weed control | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| fertilization | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| primary tillage (ploughing 25-30 cm) | ha | 1.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 100.0 |
| secoundary tillage (harrow+packer) | ha | 1.0 | 31.0 | 31.0 | 100.0 |
| seedbed preparation | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| sowing | ha | 1.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| seed (55 kg/ha) | ha | 1.0 | 262.0 | 262.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | |||||
| fertilizers | ha | 1.0 | 380.0 | 380.0 | 100.0 |
| herbicide | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 892.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 892.0 | ||||
Later it may still be possible to continue with crop production on the area.
Arable land use was turned into pasture
In this example beef cattle production was started as a new business
As soil surface is covered permanently in a meadow or pasture, surface runoff decreases significantly.
The most important benefit of meadows and pastures is that soil is covered permanently, that helps in the prevention of soil loss by erosion.
Using mowed grass as mulch can increase the carbon content of the soil.
There are more plant species present simultaneously in meadows and pastures than in cultivated fields, which is beneficial for soil health
Especially naturally managed meadows attract wildlife and therefore increase biodiversity
Water retention is better
As the grass binds the soil particles, the wind cannot pick them up and carry them away even during dry periods.