Sustainable livestock and pasture management [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Kamolidin Abdulloev
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Farrukh Nazarmavloev, William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
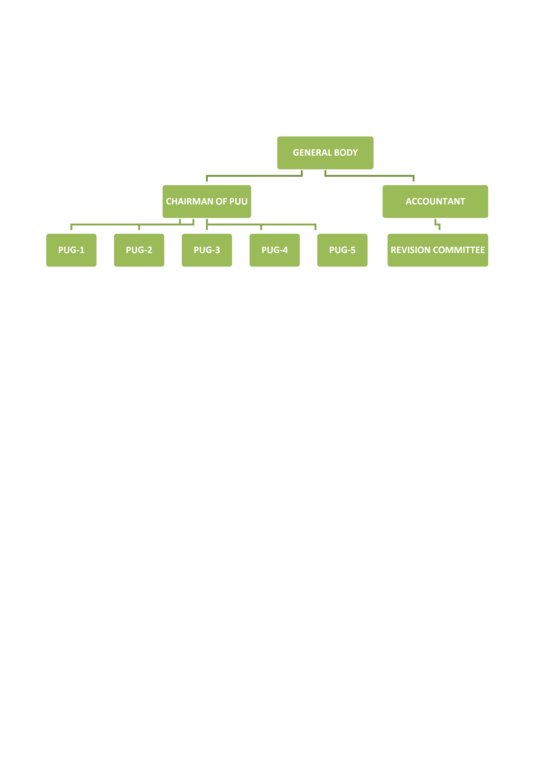
Pasture Users Unions
approaches_3713 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Environmental Land Management and Rural Livelihood Project有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Committee for Environment Protection of Tajikistan (Committee for Environment Protection of Tajikistan) - 塔吉克斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
02/04/2018
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考

Meadows and pastures [匈牙利]
Permanent meadows or pastures are more effective in controlling land degradation than arable cropping. They are especially appropriate in hilly regions on sloping land where the risk of water erosion is high.
- 编制者: Brigitta Szabó
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
Sustainable livestock and pasture management is implemented through creating Pasture Users Unions (PUU) which design and implement pasture and livestock management plans.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
The Government of Tajikistan is implementing a project, funded by the Pilot Program for Climate Resilience (PPCR) and the Global Environment Facility (GEF), with the objective of enabling rural people to build up their productive assets in ways that sustainably improve natural resource management, and build resilience to climate change in selected climate-vulnerable sites. Livestock are an integral part of the agriculture sector, although there has been a shift to more extensive livestock grazing from the intensive livestock farming system practiced before independence. Today, more than 90% of livestock are held in household farms, indicating the importance of livestock to rural livelihoods, and the system is based primarily on grazing, supplemented by limited cultivated fodder crops and minimal use of concentrates.
Pastures comprise about 35% of Tajikistan’s total land area and 80% of its agricultural land - however substantial degradation is taking place. Pasture degradation may be exacerbated by climate change, which is likely to increase variability in water availability and temperature, and may result in local droughts and floods. Properly managed pasture helps control water flows in ways which contribute to mitigating floods and droughts, maintaining soil conservation and fertility, and providing habitats for wild plants and animals. The aim of the activity is to introduce sustainable community-managed pasture/fodder-based livestock production systems in villages in the Faizobod district of jamoat Dustmurod Aliev, situated in the mid-hills of Tajikistan. Approximate membership of the Pasture Users Unions (PUU) is between 50 and 200 households per village depending on size, with between 6 and 10 villages per jamoat. Comprehensive pasture and fodder assessments and evaluation of the feed/fodder balances are carried out, followed by the development of Pasture and Livestock Management Plans (PLMP) for various interventions including; improvement of pasture productivity through rotational grazing, protecting areas for regeneration, pasture rehabilitation, improving access to remote pastures, and supplementary fodder production; animal health requirements and breed improvement measures; infrastructure to access and use remote pastures, such as spot road improvements, and stock watering points. By virtue of the fact that users will welcome this approach in their jamoats, they will be able to manage the broad issues of pasture degradation, animal health and fodder production. Above all it will help farmers to control the balance between livestock and fodder.
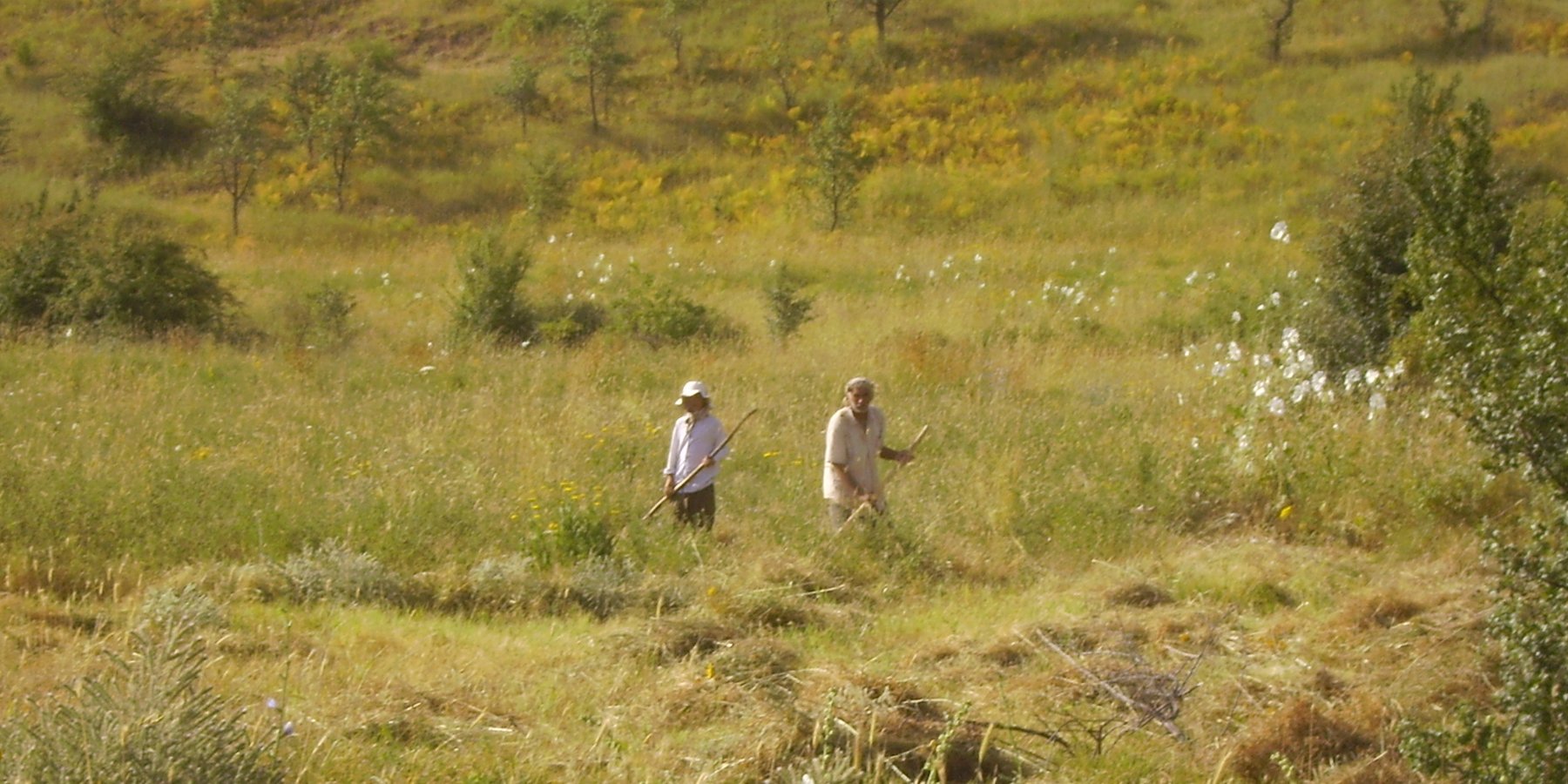
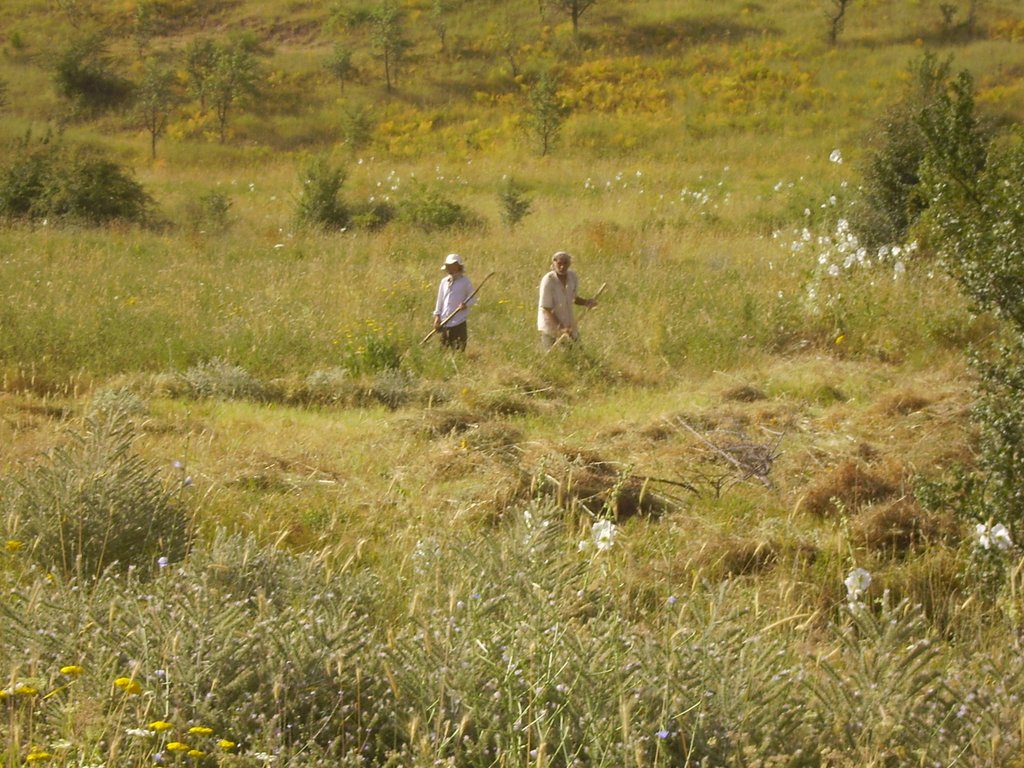
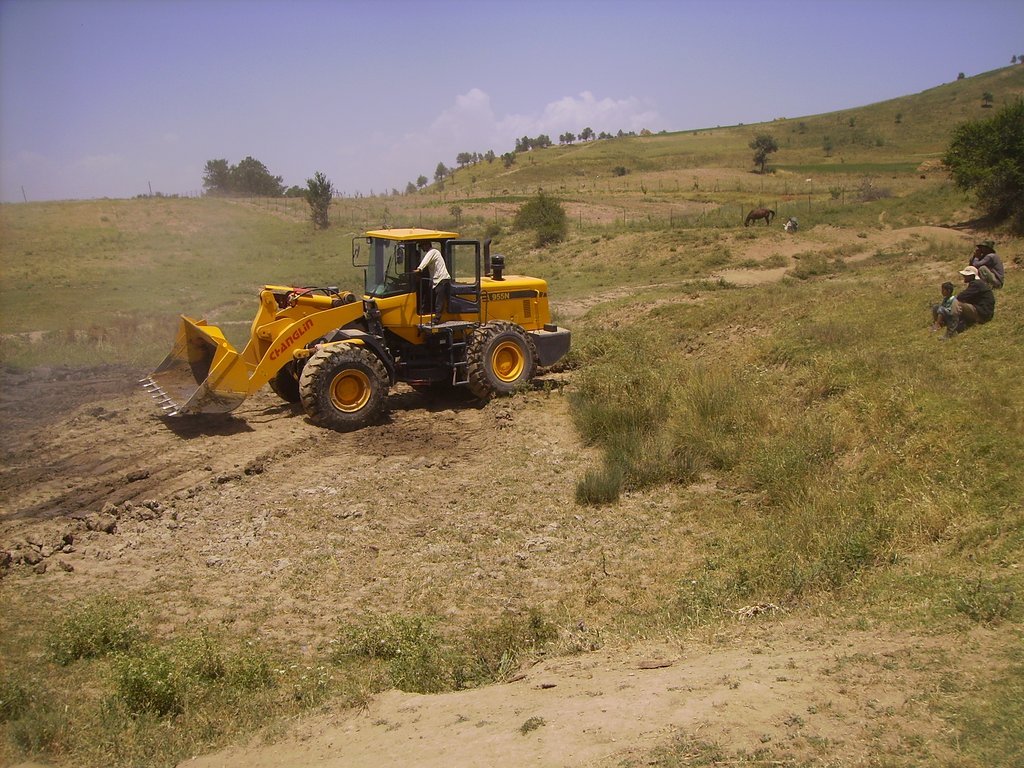
2.3 该方法的照片
关于照片的一般说明:
Photos shows how the Pasture User Union maintains infrastructure in the pastures, giving them the opportunity to collect enough fodder for the winter time and keeping access open to the most distant pasture lands
2.4 该方法的视频
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Faizobod district
有关地点的进一步说明:
Jamoat Dustmurod Aliev
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2017
若不知道准确的年份,请注明该方法的大致开始日期。:
不到10年前(最近)
注释:
The project created 8 PUUs (4 in 2015 and 4 in 2016), and facilitated them to prepare Pasture and Livestock Management Plans. Institutions finished the project financed activities but they still continue their work
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
To help mitigate the effects of climate change on the rural population and slow pasture degradation processes through introducing and demonstrating sustainable pasture/fodder-based livestock production systems;
To support the development of a Pasture and Livestock Management Plan (PLMP) for Pasture User Unions (PUU), in a participatory, inclusive and gender sensitive way: to
- Serve as tool to organize the management of community managed pastures in such a way that it will
increase pasture yields in quantity and quality, without causing land degradation & erosion;
- Serve as a tool to improve livestock management, and;
- Bring the number of livestock in balance with the available fodder;
- Increase animal off-take through better yielding pastures, adoption of improved
feeding practices & improved animal management and through better animal health;
- Increase the income of the rural population from livestock keeping, and;
- Reduce downstream flood risk in mountain areas, due to improved land management.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
- 启动
The land users are livestock keepers thus all the approaches are welcome as it will directly affect them
- 阻碍
Pasture User Unions do not have their own certificated lands under their control
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 启动
As the Pasture Users Unions are equipped with the agriculture tractors and excavators, they process the lands and rehabilitate pasture roads and also bank stabilization works and from all of these activities earn money. The other sources is their membership fees that collect every month from the members.
机构设置
- 启动
A Pasture Law was passed on 19 March 2013 (Law No 951) that will enable the formation of Pasture User Unions for the joint use and management of pasture resources.
参与者的的协作/协调
- 启动
The Pasture User Unions collaborate with the local district hukumat and all its departments, non-governmental and donor organisations in the process of implementation of Pasture and Livestock Management Plans. PUU also have very good cooperation with the land users and livestock keepers.
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 启动
Pasture User Union of "Sorkho" is established in Faizobod district, registered at jamoat level, and has their charter, stamp and other office equipment and an office.
政策
- 启动
Pasture laws are passed that supports pasture managament activities.
土地治理(决策、实施和执行)
- 阻碍
The main issue that is PUUs haven't ownership of the pasture land.
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 启动
The project also includes training and technical support of the PUUs on budgeting, SLM approaches, and administration
市场(购买投入,销售产品)和价格
- 启动
Materials are broadly available at an affordable price
工作量、人力资源可用性
- 启动
Local people understand the importance of the activity and are ready to contribute cash and power for its implementation.
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 社区组织
The head of each PUU has been involved in the process of preparation
The Pasture User Union of "Sorkho" that was established by the project ELMARL. Support with the photos and information
- SLM专家/农业顾问
- NGO
Mountain Societies Development Support Programme (MSDSP)
They was partner organisation that did facilitation during the establishment and implementing Pasture User Unions plans
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 互动 | Awareness raising and introductory meetings, training, seminars and other with the local livestock keepers |
| 计划 | 互动 | Local land users participated in the process of the preparation of plan (PLMP) |
| 实施 | 自我动员 | Local land users and livestock keepers contributing in cash or as labor during the implementation of their plan |
| 监测/评估 | 自我动员 | Assessments, field observations, monitoring and controlling of the process of implementation |
| 自我动员 | Fully involved during the operation and maintenance of the pasture infrastructures, and research |
3.3 流程图(如可用)
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是SLM专家,咨询土地使用者之后
解释:
The approach has been developed, tested and adapted by the consultants and specialists of the project with the involvement of pasture users according to the Pasture Law that was passed on 19 March 2013 (Law No 951)
明确做出决策的依据:
- 对充分记录的SLM知识进行评估(基于证据的决策)
- 研究结果
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
- 现场工作人员/顾问
培训形式:
- 在职
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
涵盖的主题:
ToT on environmental management of pasture lands, accounting, planning
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
否
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,非常
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
说明机构、角色和职责、成员等。:
Pasture Users Unions
Local hukumat departments:
Ministry of Agriculture, Committee for Environmental Protection and Committee of Women Affairs
具体说明支持类型:
- 能力建设/培训
- 设备
提供进一步细节:
The representatives of mentioned departments participated in the trainings, conferences and meetings during project implementation and helps participants with the recommendations and guides
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
The main tasks of monitoring relative to the livestock and pasture improvement activities; (a) Activities required to improve livestock
management (animal health, housing, feeding, breeding), (b) activities required to improve pasture
production (rotational grazing, protecting pastures, pasture rehabilitation through spot planting with
legumes, improving access to remote pastures, supplementary fodder production, set stocking
rates), (c) investment needs1 & sources of funding, (d)an implementation plan showing
responsibilities/targets/indicators
若是,该文件是否用于监测和评估?:
是
注释:
As the approach supports project and land users to define
(a) measures to improve pasture productivity and sustainability, such as rotational grazing, protecting areas for regeneration, pasture rehabilitation, improving access to remote pastures, and needs for supplementary fodder production;
(b) grazing utilization levels;
(c) animal health requirements and breed improvement measures;
(d) investment needs; and (e) implementation responsibilities, targets and indicators in their plans
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
否
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
说明该方法中SLM部分的年度预算,单位为美元:
100000.00
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
The project funded by the Pilot Program for Climate Resilience (PPCR) and the Global Environment Facility (GEF) with the objective of enabling rural people to build their productive assets in ways that sustainably improve natural resource management and build resilience to climate change in selected climate vulnerable sites
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
如果是,请具体说明支持的类型、条件和提供者:
The grant amount would average US$ 100,000 for each of the 8 PUUs with the specific amount depending on pasture area and existing number of livestock units (to be finalized during implementation)
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 劳动力
| 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|
| Beneficiaries would contribute at least an additional 25% match of the grant amount (partly in cash and/or in kind as labour or equipment costs). |
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
注释:
Investments could include: a) infrastructure to access and use remote pastures, such as spot road improvements, stock watering points, shelters and stock-pens, and milk cooling equipment; b) machinery to produce and harvest fodder; c) costs of rehabilitation measures for degraded areas such as fencing, weed and shrub control, and re-seeding; d) inputs for supplementary fodder production such as seeds; e) vaccinations and parasite control; and f) artificial insemination. Funds could also be used for additional training above that provided by the contracted NGO and for provision of office equipment and furnishings for PUUs.
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
5.5 其它激励或手段
是否有其他激励措施或工具用于促进SLM技术的实施?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
The Pasture User Unions have equipped with the high volume machines to improve the pasture roads and riverbanks
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否有助于当地土地使用者,提高利益相关者的参与度?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The ELMARL project used this approach in 4 pilot districts and established 8 PUUs that improve and rehabilitated 12600 hectares of pasture lands. Results showed that PUUs have made significant progress in implementing their activities. As a result of the use of machinery, more than 120 km of roads for livestock and hazardous areas were repaired and rehabilitated, and conditions of pastures improved over an area of 6,750 hectares. As a result of construction of watering points for livestock, PUUs were given the opportunity to graze livestock in summer pastures for more than one month and conditions for 1050 hectares of pastures were improved. As a result of the use of bridges for livestock, the PUU members obtained an access to 470 hectares of pastureland, construction of kashars provided the opportunity for pasture users to use 3900 ha of pasture lands, 1.86 ha of area was rehabilitated by establishing demonstration plots, the area of 75 hectares of land was processed and improved through the use of small agricultural tractors, 250 hectares of pastureland have been improved through sowing grasses as fodder, 100 hectares of pasture lands have been improved through the installation of irrigation pump.
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Of course, establishing PUUs and designing Pasture and Livestock Management Plans that directly adopted to the SLM will help land users to manage their lands. Some of examples from the PUUs activities contribute to the SLM; construction of 'kashars' (Animal and herder shelters) Implementing these activities has made great profit to PUUs. Cattle breeders were able to extend period for cattle grazing in summer pastures and reduce the burden of livestock in pastures around the village; Improvement of cattle breeding leads to increased productivity and reduce degradation; Improvement of the roads condition – situation of roads for livestock is being improved due to the fact that PUUs in Faizobod district have purchased technique, which guarantees the safe keeping of livestock and also lands that are around the road; sowing perennial grasses was the only activity, which occupied 250 hectares of pasturelands for fodder, and not all PUUs pay attention to these problems. The activity can provide livestock with fodder and prevent lands from erosion as well.
该方法是否提高了SLM的协调性和成本效益?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Using of machinery is the one of activities that was supported by PUUs to rehabilitate roads for livestock and hazardous areas. If PUUs rent this machinery it will be too expensive and organisations does not have such kind opportunity, but machinery helps them to repair their lands in regularly base.
该方法是否调动/改善了使用财务资源实施SLM的途径?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The PUUs equiped with the needed machinery and office where they could organise meetings, so they can construct, rehabilitate and generally support their members(livestock keepers, land users). Presently the PUUs in a very good relationship with their members and collect membership fees regularly, also they have another source of money from the mashinary services. PUU regularly maitaining systems.
该方法是否提高了其他利益相关者的知识和能力?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The PUUs are the member of the GIZ 'Pasture Management Networking Platform' and participated in the meetings regularly. The main task of the meetings is to exchange information and experience on SLM and pasture management projects among various implementing partners.
该方法是否改善了性别平等并赋予女性权力?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
PUUs appraised for gender and their inclusion of women and the poor, and possible actions identified to address inequities. Where inequitable arrangements are found that exclude or marginalize vulnerable groups, opportunities will be sought where possible to address these inequities, e.g., targeting a proportion of certain types of production investments to groups of vulnerable households (wool processing, poultry development). Gender and social issues to be addressed during capacity building will mainly relate to an identified need to increase awareness and strengthen capacity of peer-to-peer learning and community mobilization, particularly focusing on increasing the level of participation of nondirect beneficiaries and members of marginalized groups.
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The regulation of land allocation, lease and management is under the jurisdiction of the local level authorities together with the district representation of the Land Committee, but also needs to be approved by the provincial and central authorities. Most PUUs quoted that provision of land certificates for Dekhkan Farms on pastureland and PUUs have made attempts to acquire land use right on pastureland and some became successful.
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 减少土地退化
Pasture degradation, due in part to overgrazing and poor stocking practices, is an
important threat and all above mentioned activities contributed to the land degradation
- 降低灾害风险
Regular road and bridge rehabilitation via machinery and controlling grazing pasturelands contribute to the reduction of disasters
- 环境意识
The environmental impact of the approach is largely positive with its planned activities
- 提高SLM知识和技能
The PUUs are members of the GIZ 'Pasture Management Networking Platform' and participated in the meetings regularly. The main task of the meetings is to exchange information and experience on SLM and pasture management projects among various implementing partners.
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
若是,请说明如何维持:
The approach is a sustainable mechanism itself as it has almost all needed resources and capacity to continue their activity. As an example PUU has found a new sources of income today one of the PUUs, “Sorkho” participated in the district competition to implement the program “Prevention of Land Refinement by using biosynthic methods” conducted by the MSDSP Aga Khan Foundation in Surkhdara area of D. Aliev jamoat in Fayzobod district and succeeded in that so in further that will be a lesson to be learnt by other PUUs. The PUU has now established cooperation with this organization on the basis of mutual agreement and is trying to improve the state of pastures at the jamoat level, and nowadays its work is already in progress.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Office and all needed equipments for the operation of PUU Membership fees |
|
Machinery for land and infrastructure Income from the machinery |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Confidence between the PUU and its members Availability of Pasture and Livestock Management Strategy (includes planned activities for the 3 to 5 years) Availability of needed pasture and livestock Infrastructure; veterinary infrastructure, machinery to improve pasture roads and bridges, livestock watering points. |
| Needed knowledge and capacity to improve pasture production (rotational grazing, protecting pastures, pasture rehabilitation through spot planting with legumes, improving access to remote pastures, supplementary fodder production, set stocking rates |
|
Mechanism of controling to improve livestock management (animal health, housing, feeding, breeding) Livestock and pasture management; feeding practices, housing, breeding, disease control,marketing of products, usage of the different type of pastures |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Sufficient source of funding |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| As it is new the approach needs more support and collaboration on behalf of other government and nongovernment organisation |
Government needs to support them to be more capable Non governmental organisation need to design project to train them |
| PUUs does not have their own certificated lands in their balance |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
15
- 与土地使用者的访谈
20
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
ELMARL Project
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Faizobod district, PUU "Sorkho"
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
ELMARL Annual Report 2017
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Meadows and pastures [匈牙利]
Permanent meadows or pastures are more effective in controlling land degradation than arable cropping. They are especially appropriate in hilly regions on sloping land where the risk of water erosion is high.
- 编制者: Brigitta Szabó
模块
无模块