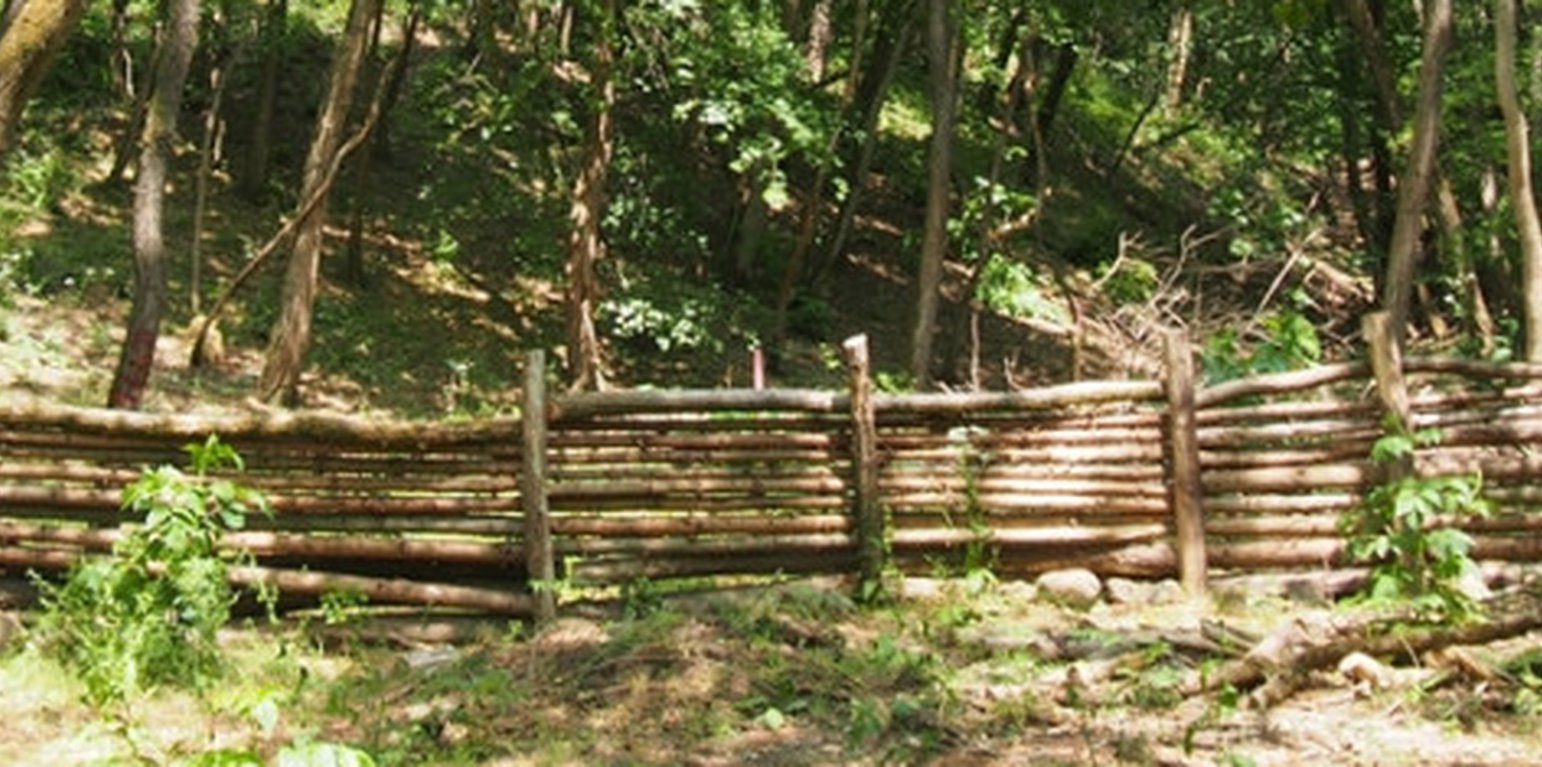




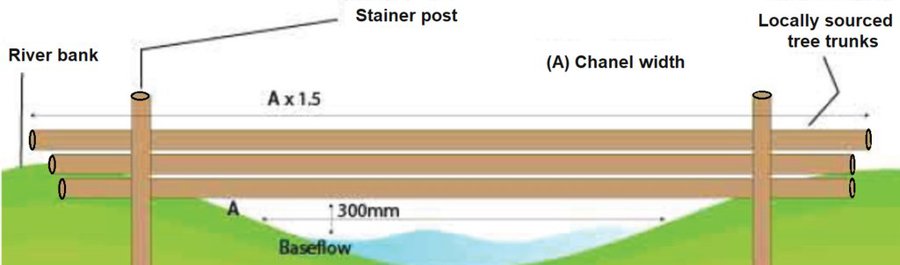
Peak flow control structures are designed to reduce flow velocities and quantities of water running down from catchment areas. Leaky dams are peak flow control structures that are made from wood and allow low flows to pass through, but hold back high flows, thus providing temporary storage and enhanced infiltartion of flood water. The structures are elevated 30 cm above streambed level to allow baseflow (and fish) to pass through. The technology is usually applied in hilly areas covered by forest. Woody check dams are made from whole tree trunks sourced locally, placed across the watercourse and secured into place with stakes and wire on both sides of the bank. The purpose is to control sediment and to slow flow velocities and quantities of water running down from catchment areas, in order to reduce flood peaks. The impact of the technology is to retain sediment and water in the upstream part of the catchment to reduce the size of flood peaks, this way avoiding flash floods downstream. The cost of installation and ongoing maintenance is low. However, leaky dams need to be cleared of debris and sediment occasionally so that water can still flow through the gaps. This reduces the likelihood of water flowing over the top of the barrier. The approximate lifetime of a leaky woody dam is about ten years, depending on the tree species used.
地点: Püspökszilágy, Pest County, 匈牙利
分析的技术场所数量: 单一场所
技术传播: 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
在永久保护区?: 否
实施日期: 2020
介绍类型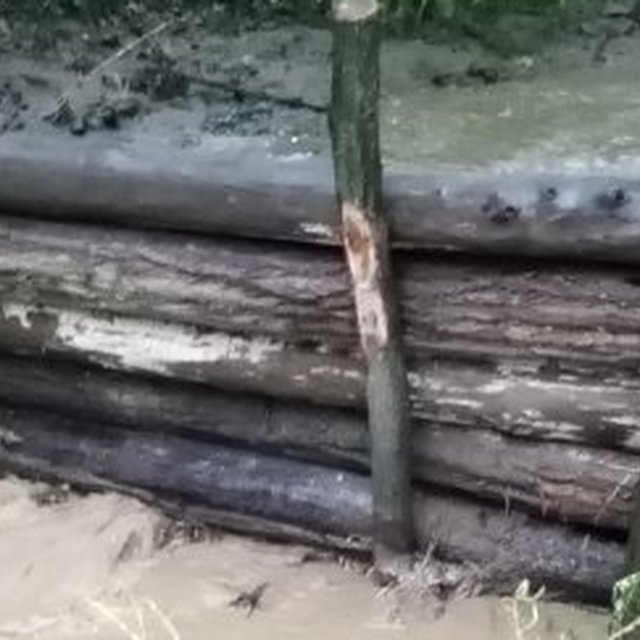




| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Installing (team work) | person-days | 4.0 | 50.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Machinery for installing (e.g. chainsaw, posthole digger, small excavator) rental cost | 1 | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| No explicit cost, locally sourced wood can be used | |||||
| 施工材料 | |||||
| Fastening device kit (e.g. metal wire, poles, clamps) | 1 | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 600.0 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 600.0 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Checking status and cleaning of debris and sediment | person-days | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Fixing or replacing logs, if necessary | person-days | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Machinery rental, if necessary | 1 | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 200.0 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 200.0 | ||||
The main purpose of this measure is slowing the movement of water during high flow events, but temporally it collect water as well providing watering place for wild animals.
This measure usually takes place in forests (in the upper zone of the watershed), but it has a positive effect on the lower area (agricultural fields) of the watershed by preventing surface runoff and reducing flood events
One of the main positive effect of this measure is decreasing flash flood events and its impact both on inhabited area. Since the installation no inundation has happened. However, it may be the result of a combination of different measures.
One of the main positive effect of this measure is decreasing flash flood events and its impact both on inhabited area. Since the installation no inundation has happened. However, it may be the result of a combination of different measures.
The measure is a very effective solution to avoid flood damage.
The measure is a very effective solution to avoid flood damage.