Peak flow control structures (leaky woody dams) [匈牙利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Brigitta Szabó
- 编辑者: Piroska Kassai, Zoltan Toth, Klara Kerpely
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Lefolyás-szabályozó létesítmények (szivárgó rönkgátak)
technologies_6201 - 匈牙利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Municipalities as integrators and coordinators in adaptation to climate change (LIFE-MICACC)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Institute for Soil Sciences, Centre for Agricultural Research (ATK TAKI) - 匈牙利有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
World Wide Fund for Nature Hungary Foundation (WWF Hungary) - 匈牙利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Peak flow control structures are designed to reduce flow velocities and quantities running down from catchment areas. Leaky dams are peak flow control structures that are made of wood and allow low flows to pass through, but hold back high flows, thus providing temporary storage and enhanced infiltration of flood water.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Peak flow control structures are designed to reduce flow velocities and quantities of water running down from catchment areas. Leaky dams are peak flow control structures that are made from wood and allow low flows to pass through, but hold back high flows, thus providing temporary storage and enhanced infiltartion of flood water. The structures are elevated 30 cm above streambed level to allow baseflow (and fish) to pass through. The technology is usually applied in hilly areas covered by forest. Woody check dams are made from whole tree trunks sourced locally, placed across the watercourse and secured into place with stakes and wire on both sides of the bank. The purpose is to control sediment and to slow flow velocities and quantities of water running down from catchment areas, in order to reduce flood peaks. The impact of the technology is to retain sediment and water in the upstream part of the catchment to reduce the size of flood peaks, this way avoiding flash floods downstream. The cost of installation and ongoing maintenance is low. However, leaky dams need to be cleared of debris and sediment occasionally so that water can still flow through the gaps. This reduces the likelihood of water flowing over the top of the barrier. The approximate lifetime of a leaky woody dam is about ten years, depending on the tree species used.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
https://youtu.be/1TnzpVUoDUc
6-min video on the application of leaky woody dams and other water retention measures in Püspökszilágy village.
位置:
Püspökszilágy
摄影师的名字:
Filmever Studio
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
匈牙利
区域/州/省:
Pest County
有关地点的进一步说明:
Püspökszilágy
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2020
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 降低灾害风险
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:具体说明管理类型:
- 清除枯木/剪枝
(半)天然林类型:
- 温带大陆森林自然植被
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 落叶植物
产品和服务:
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
- 自然灾害防护

水道、水体、湿地
- 排水管道、水道
- gullies
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
- 减少基于生态系统的灾害风险
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
- S6:墙、障碍物、栅栏、围墙
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
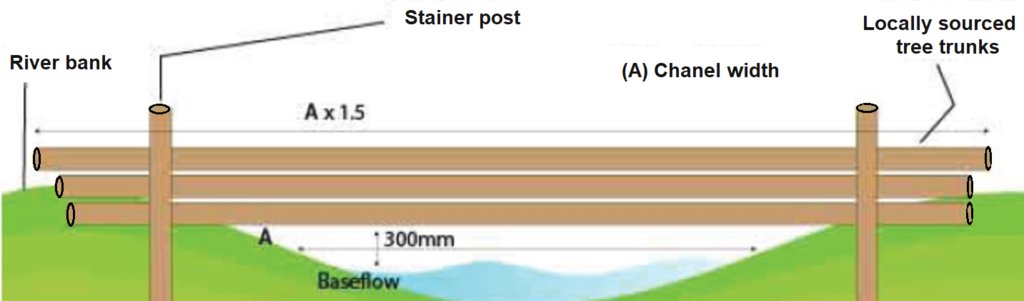
There are a few key rules to follow when installing any leaky dams:
1. They must be installed, as a minimum, in a sequence of 3.
2. The distance between each dam should be 7 times channel width.
3. The width of the dam should be 1.5 times channel width.
4. The structure should be set 300mm above base flow level.
5. Logs should be no more than 400mm in diameter.
6. Where possible, materials should be sourced locally.
7. Structures should be installed 90° to the flow.
Other recommendations for design:
- Use to obstruct flows within watercourses or along runoff pathways, gullies, valleys.
- Use in small watercourses less than 3 m wide.
- Height of a barrier should not exceed 1 m.
作者:
source: https://www.ydrt.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/NFM-Leaky-Dams-guide.pdf and https://www.ciria.org/ItemDetail?iProductCode=C802F&Category=FREEPUBS&WebsiteKey=a054c7b1-c241-4dd4-9ec1-38afd4a55683
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
a single structure at multiple points in a watershed
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installing | Possible in any season. (Logging preferably out of vegetation season.) |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Installing (team work) | person-days | 4.0 | 50.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machinery for installing (e.g. chainsaw, posthole digger, small excavator) rental cost | 1 | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | No explicit cost, locally sourced wood can be used | |||||
| 施工材料 | Fastening device kit (e.g. metal wire, poles, clamps) | 1 | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 600.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 600.0 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Checking conditions of the structure | yearly or after extreme rain events |
| 2. | Cleaning of debris and sediment | if silting up starts |
| 3. | Fixing or replacing logs | if moved by flood |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Checking status and cleaning of debris and sediment | person-days | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Fixing or replacing logs, if necessary | person-days | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machinery rental, if necessary | 1 | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 200.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 200.0 | |||||
注释:
Permit required on permanent watercourses. Average lifetime of a dam is about 10 years
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Width of the water course.
Availability of locally sourced wood logs.
Availablility of equipment.
Labour costs.
Procurement rules applicable to project owner.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
550.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Dry periods are becoming longer and heavy rainevents more frequent due to climate change.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Püspökszilágy
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Temperate climate, four seasons, mean annual temperature: 10 degrees C
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The technology is applied by the municipality (local government).
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
The technology is applied by the municipality (local government).
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
注释/具体说明:
The main purpose of this measure is slowing the movement of water during high flow events, but temporally it collect water as well providing watering place for wild animals.
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
This measure usually takes place in forests (in the upper zone of the watershed), but it has a positive effect on the lower area (agricultural fields) of the watershed by preventing surface runoff and reducing flood events
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
One of the main positive effect of this measure is decreasing flash flood events and its impact both on inhabited area. Since the installation no inundation has happened. However, it may be the result of a combination of different measures.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
One of the main positive effect of this measure is decreasing flash flood events and its impact both on inhabited area. Since the installation no inundation has happened. However, it may be the result of a combination of different measures.
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
The measure is a very effective solution to avoid flood damage.
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
注释/具体说明:
The measure is a very effective solution to avoid flood damage.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 森林火灾 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 滑坡 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
The presented measure (in Püspökszilágy) is one of the study sites of the LIFE-MICACC project
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
The installation costs of the measure was financed by a LIFE grant from the European Union with national co-financing.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Slow release of water into surrounding area (agricultural fileds) |
| Efficient temporary storage of water |
| Prevention of soil erosion |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Prevention of flooding: protection of the infrastructure of the surrouanding settlements |
|
Positive effect on biodiversity: rooting habitat, place of nesting birds, areas of growth for microbes, algae and fungi available water for wildlife |
| Stabilisation of river banks |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| No negative effects are known |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The lifetime of a dam is limited (~10 years) |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
A risk-based network analysis of distributed in-stream leaky barriers for flood risk management. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 20, 2567–2584, 2020
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://nhess.copernicus.org/articles/20/2567/2020/
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Naturally Resilient Natural Flood Management techniques- Level 2
URL:
https://www.ydrt.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/NFM-Leaky-Dams-guide.pdf
标题/说明:
WWF Hungary online news
URL:
https://wwf.hu/hireink/klima-es-energia/ot-hazai-telepules-mutat-peldat-hogyan-vegyuk-fel-a-harcot-a-klimavaltozassal/
标题/说明:
LIFE-MICACC project website
URL:
https://nwrm.bm.hu/
标题/说明:
WWF Hungary online news in English
URL:
https://wwfcee.org/news/five-hungarian-local-municipalities-lead-the-way-in-tackling-climate-change
7.4 一般注释
-
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块