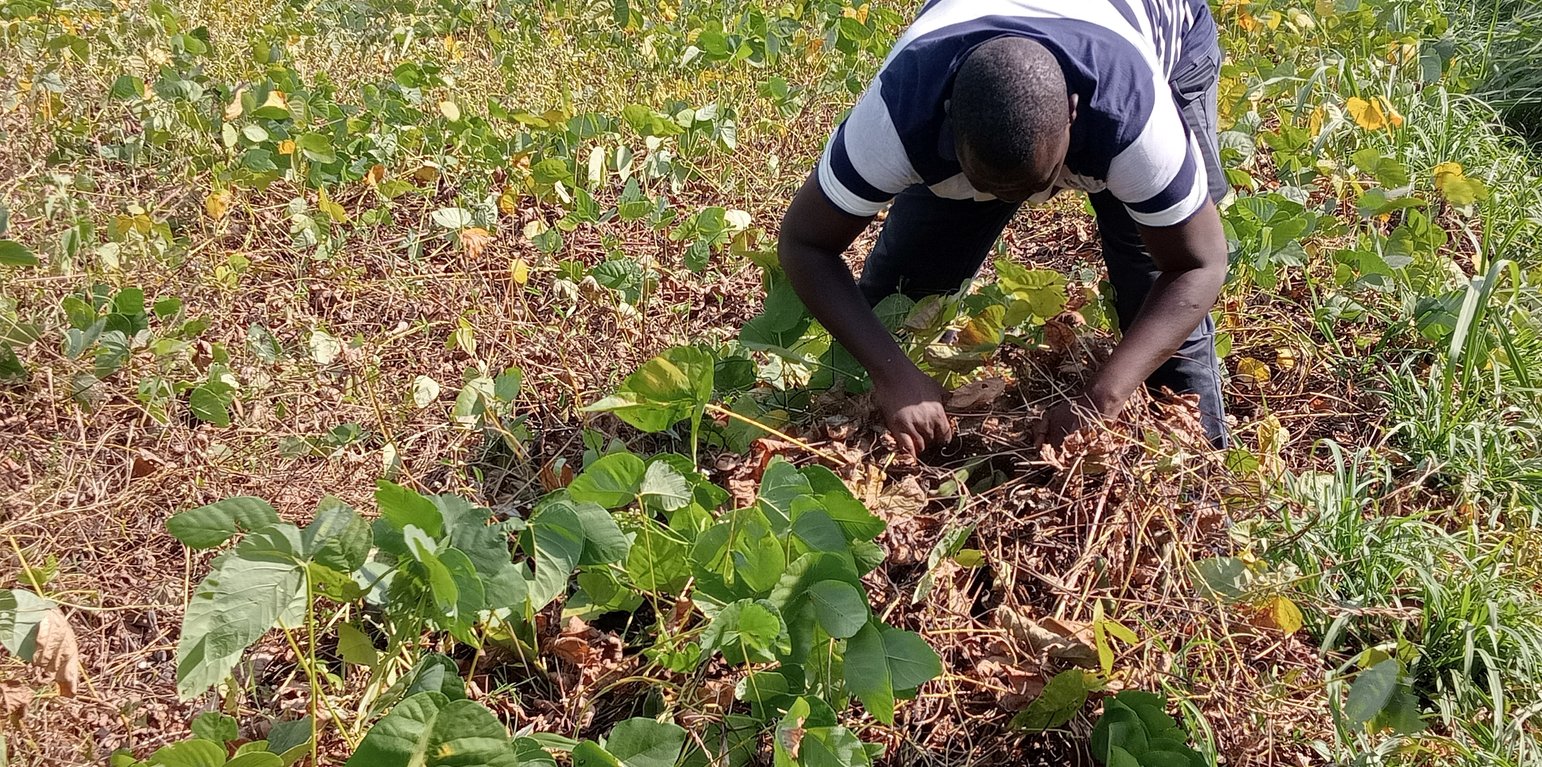




Permanent soil cover is having all-year-round cover on the soil. This can be either in the form of cover crops which are either planted with other crops at the same time, or relay planted later in the season after the main crops have established, or in the form of crop residues (mulch) which is naturally decomposed by microbes. Permanent soil cover provides a shield or umbrella to the soil protecting it from the heat of the sun and the impact of rain. It makes up a fundamental component of conservation agriculture where minimum tillage reduces soil disturbance.
Some of the crops used for permanent soil cover [those promoted by the ProSoil project] include Mucuna pruriens (velvet bean), Canavalia ensiformis, Dolichos lablab, and Desmodium intortum. All of these are legumes, which fix nitrogen from the atmosphere, thus improving soil fertility. In choosing a cover crop, farmers prefer those that fit into their normal cropping systems, and which have multiple purposes, including those that produce edible seeds and vegetables, those that improve soil fertility, those that can be used as animal fodder, and those that can suppress weeds. Some farmers prefer crops that can provide firewood or fencing material and those that can be used for medicinal purposes. Another important factor that farmers consider when choosing a cover crop is the amount and type of work that the cover crop will need, for example for land preparation before planting, weeding, and producing and harvesting the seeds. The crops most preferred are those that cover the soil quickly and completely, and which can also be used for food and fodder, including mucuna. Farmers also like mucuna because of its big pods and grains that are easier to deal with. Farmers can easily multiply mucuna seeds since they do not require complicated treatments; hence, do not need to continue spending money on the seeds.
In establishing a permanent soil cover using cover crops, farmers first intercrop seasonal crops (e.g., maize and beans) and later introduce a green manure cover crop (e.g., mucuna) after about 6 weeks (or at the time when the beans start to produce pods) to ensure that the green manure cover crop does not suppress the main crop(s). The maize is planted at 75 cm row spacing and 25 cm between plants in the same row. However, within each row, the third hole/ space is left for the cover crop (i.e., mucuna). Thus, mucuna is planted after every three maize plants in the same row. The bean intercrop is planted between the maize rows at the spacing of 37.5 cm from the maize row and 20 cm between bean plants in the same row. This spacing requires about 5 kg of cover crop (mucuna) seeds per acre. The crops continue to grow together and upon harvesting the main crops, the cover crop continues to grow on the farm covering the soil until the following cropping season.
Permanent soil cover is beneficial in the farm in various ways including, enhancing soil water infiltration, protecting soil from agents of erosion, increasing soil organic matter, suppressing weeds, aiding in nutrient cycling, and improving the habitat of soil micro- and macro-organisms. Maintaining permanent soil cover through mulching faces some limitations, including competing uses of crop residues e.g., as animal feeds and fuel. Similarly, drought may be a major limitation to maintaining permanent soil cover using cover crops, especially in areas that receive very low rainfall and where the farmer has not invested in irrigation.
地点: Kisa Central Ward in Khwisero Sub-county; and Koyonzo and Khalaba wards in Matungu Sub-county, Kakamega County in western Kenya, 肯尼亚
分析的技术场所数量: 2-10个场所
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域
在永久保护区?: 否
实施日期: 2021
介绍类型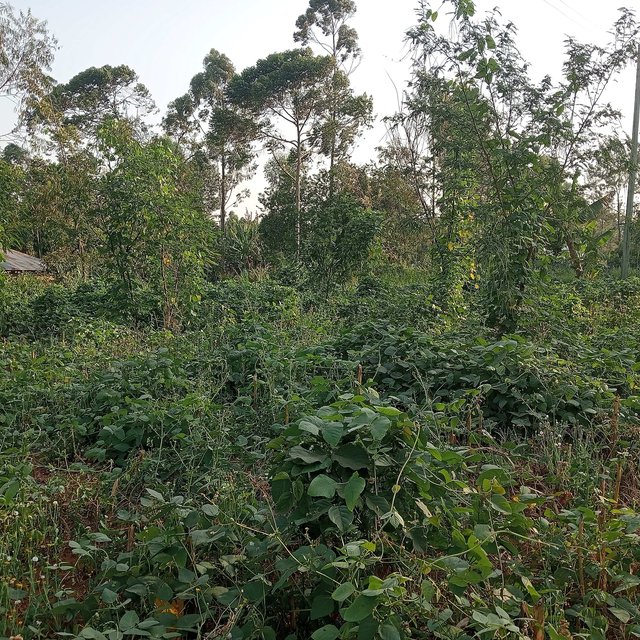



| 品种 | 计数 |
| 牛 - 奶制品 | 1 |
| cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu) | 2 |
| 家禽 | 20 |







| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (KES) | 每项投入的总成本 (KES) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Slashing | Man-days | 5.0 | 250.0 | 1250.0 | 100.0 |
| Sub-soiling | Man-days | 10.0 | 250.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| Planting | Man-days | 4.0 | 250.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| Shallow weeding and uncoiling (e.g., mucuna from the main crop) | Man-days | 9.0 | 250.0 | 2250.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Slasher | No. | 1.0 | 70.0 | 70.0 | |
| Hand-held sub-soiler | No. | 1.0 | 70.0 | 70.0 | |
| Jab planter | No. | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | |
| Shallow weeder | No. | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Cover crop seeds | Kgs | 5.0 | 150.0 | 750.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 8'970.0 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 72.22 | ||||
The above rating varies from one village to the other.
SLM之前的数量: Less than 3
SLM之后的数量: More than 7
Quantity refers to the number of 90 Kg bags of maize produced per acre. Based on the farmer's estimate.
Not easy to quantify. The crops do better compared to how they could do in the past, yet he does not use inorganic fertilizers. Based on the farmer's estimate.
SLM之前的数量: 2
SLM之后的数量: 5
Quantity refers to harvesting cycles per year for nappier grass from the same farm. Based on the farmer's estimate.
Not easy to quantify. Fodder does better compared to how it was before the technology. Based on the farmer's estimate.
SLM之前的数量: 2
SLM之后的数量: 5
Quantity refers to the amount of milk in litres from one cow. Based on the farmer's estimate.
SLM之前的数量: 70
SLM之后的数量: 40
Quantity refers to the percentage probability of the crop failing to do well. Based on the farmer's estimate.
Not easy to quantify but it is easier to prepare land through no tillage than to plough.
SLM之前的数量: 10,000
SLM之后的数量: 0
Quantity refers to the amount of money in Kenya shillings spend on inorganic fertilizers in a season. The farmer no longer buys money inorganic fertilizers. Based on the farmer's experience.
SLM之前的数量: 2
SLM之后的数量: 3
Quantity refers to the number of household income sources.
Not easy to quantify but it is easier to prepare land through no tillage than to plough.
SLM之前的数量: 3
SLM之后的数量: 1
Quantity refers to the number of months in a year when there is total lack of food in the house, and the farmer has to buy all the food required in the house. Based on the farmer's estimate.
Refers to the estimated percentage of knowledge in SLM/ land management. Based on the farmer's estimate. His knowledge in SLM has greatly increased.
Refers to the farmer's estimated soil moisture content during the dry season when soil moisture challenges are expected to be high.
SLM之前的数量: 40
SLM之后的数量: 60
Quantity refers to the farmer's estimated percentage soil cover at the farm.
Not easy for the farmer to quantify. According to him, soil erosion has reduced.
Not easy for the farmer to quantify. Based on the farmer's estimate.
Not easy for the farmer to quantify. Based on the farmer's estimate.
Not easy to quantify as there is no data. Based on the farmer's estimate.
SLM之前的数量: 30
SLM之后的数量: 60
Quantity refers to the farmer's estimated percentage vegetation cover at the farm.
Not easy for the farmer to quantify. Based on the farmer's estimate.
SLM之前的数量: 4
SLM之后的数量: 11
Quantity refers to the number of plants (crops) that the farmer establishes at the farm. Based on the farmer's estimate.
SLM之前的数量: 6
SLM之后的数量: 4
Quality refers to the number of species of weeds and invasive plants at the farm. Based on the farmer's estimate.
Not easy for the farmer to quantify. Based on the farmer's estimate.
No recorded data is available for reference. All are estimates based on the farmer's explanation or as given by him.