Development and promotion of Ecograze [澳大利亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Andrew Ash
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2333 - 澳大利亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CSIRO (CSIRO) - 澳大利亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考

Ecograze [澳大利亚]
An ecologically sound and practical grazing management system, based on rotation and wet season resting.
- 编制者: Andrew Ash
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
Research-based development and promotion of Ecograze principles and practices through on-farm testing and demonstration.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: In 1992, Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), a producer-owned company that provides services to the entire Australian red meat industry, initiated the Ecograze project. Ecograze was intended to provide innovative management options for the pastures in the eucalyptus woodlands of north-east Queensland. It was an eight-year collaborative research project undertaken by staff of the CSIRO (Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation) Sustainable Ecosystems and Queensland Department of Primary Industries with input from Queensland Department of Natural Resources and Mines. It formally concluded in 2001. However, many of the analyses and extension activities have been ongoing since then.
Methods: Ecograze was conducted on five commercial grazing properties that spanned different conditions and consequently allowed extrapolation of results to a much wider area across northern Australia. Practical grazing management strategies have been developed. The Ecograze team assessed the economic implications of managing land in various states by linking a pasture production model, to a model of farm economics. Research teams are currently testing the grazing management technology in commercial situations to understand the real costs and implications of implementing the research-derived Ecograze recommendations. The on-farm tests are supported by a number of new initiatives. These include a MLA funded project to specifically implement the Ecograze principles on farms as a means of reducing sediment and nutrients pollution of waterbodies. The National Action Plan for Salinity and Water Quality, through incentives, supports land management practices to reduce erosion, increase ground cover and minimise runoff. Funding is also provided by the Natural Heritage Trust to fence and sub-divide paddocks. All of these initiatives are supported by State Government agencies, who have extension staff based in the regions to assist farmers with implementing new practices. In the case of Ecograze, there are extension officers in the NE Queensland region who are actively promoting its management principles and are assisting producers in planning new strategies. Many of the Ecograze principles are also included in a new Grazing Land Management (GLM) Education package, developed by MLA and research and development agencies. The GLM package, which is delivered via a three-day workshop, is being extended to producers across northern Australia.
This approach highlights the importance of active collaboration between researchers, farmers, the beef industry and the government - in this case to develop a system to improve the condition of grazing lands. Through the central involvement of research, management options have been identified to suit different land users' needs, climates, grazing pressures and pasture conditions
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
澳大利亚
区域/州/省:
Northern Australia
有关地点的进一步说明:
Queensland
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
1992
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2001
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused on SLM only
Development and promotion of Ecograze principles leading to adoption and thereby enhancing pasture productivity, soil condition and improved livelihoods for pastoralists.
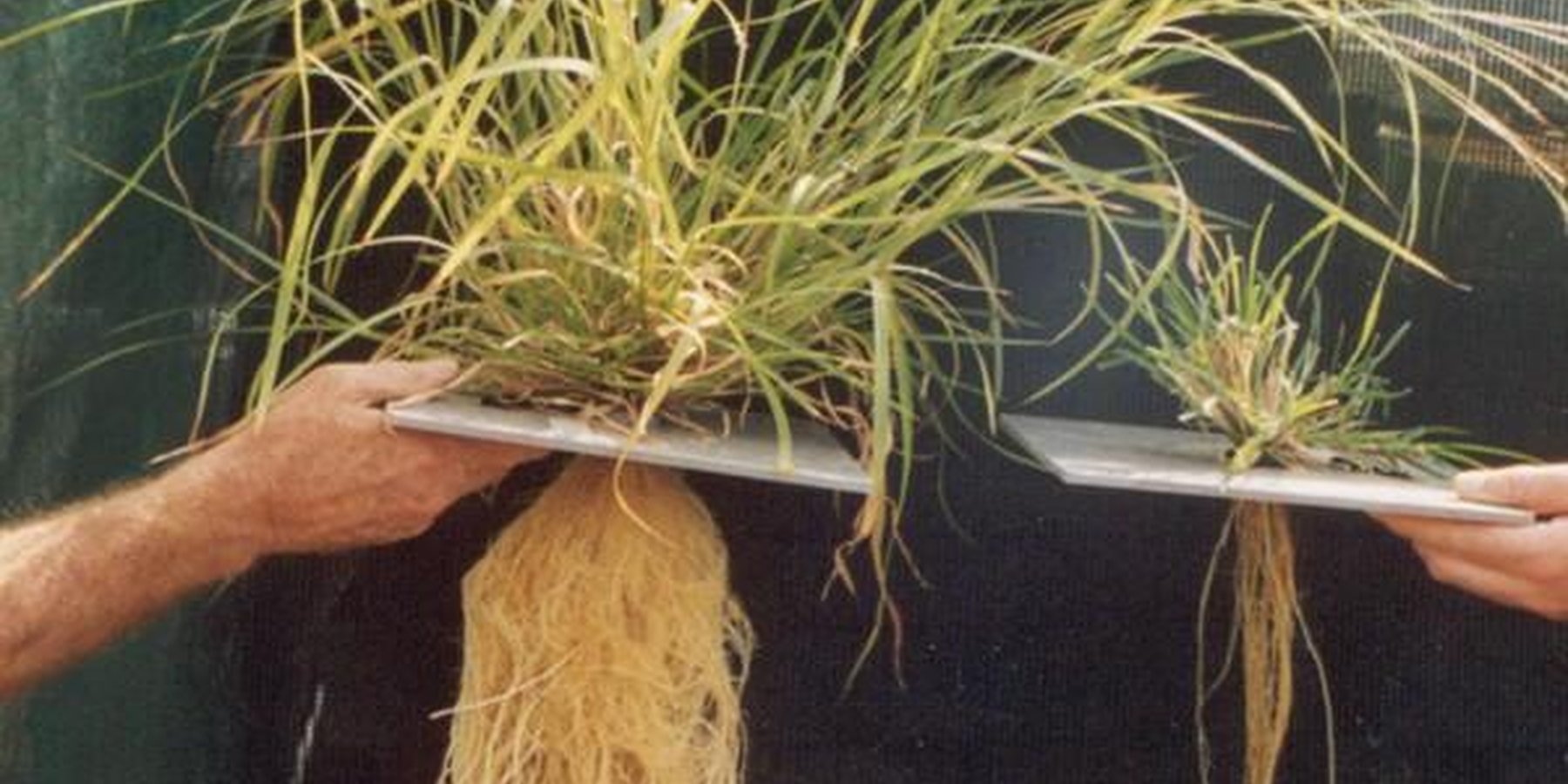
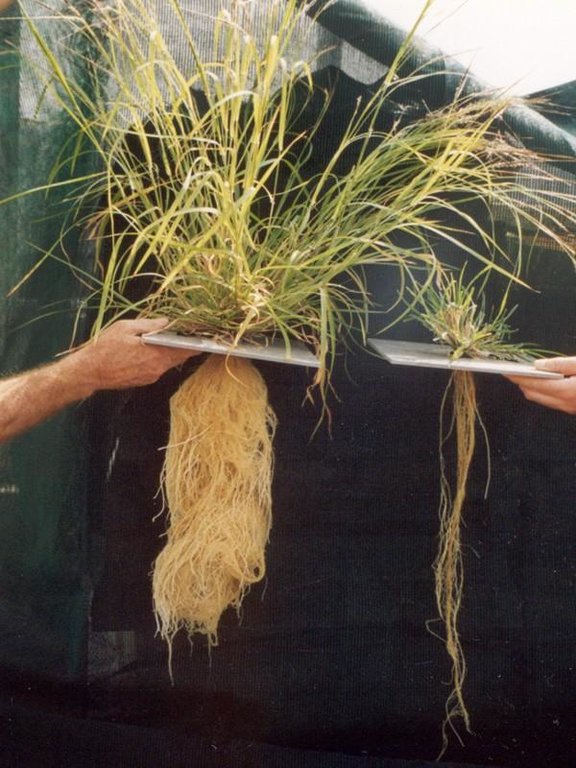
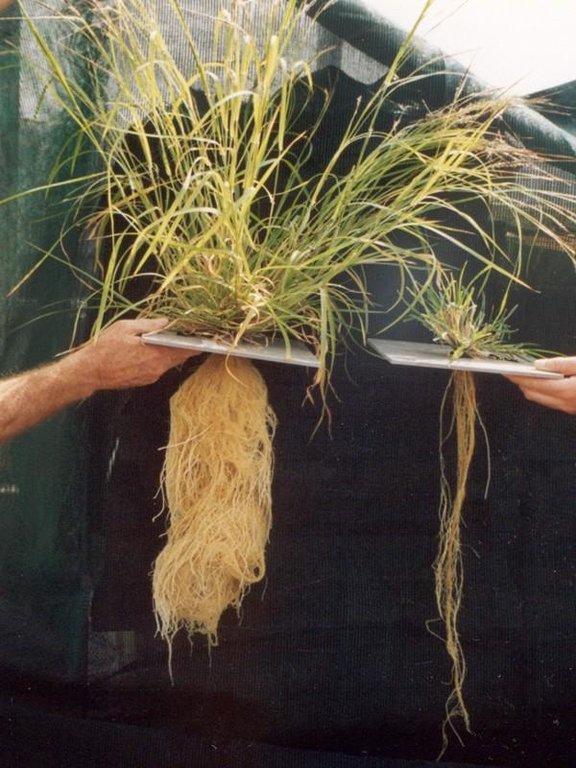
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: (1) Poor rangeland management leading to loss of productive palatable perennial grasses (3 P grasses) resulting in reduced ground cover, soil erosion, profit loss and in some cases irreversible land degradation. (2) Lack of understanding of underlying problems regarding mismatch of animal numbers to forage supply (pressure on grazing land) in a highly variable climate. (3) No clear technical recommendations regarding resting and rotation of rangeland
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
- 阻碍
Many pastoralists are conservative and change their systems only slowly.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: There are ongoing education programmes and demonstrations on target properties.
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
Investment costs for fencing and water points can be burden on individual land holders.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: There are various possible subsidies available (see 'Inputs', under 'Incentives').
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 启动
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights helped a little the approach implementation: In general, implementation of Ecograze principles is undertaken by an individual on private leasehold land. Ecograze is well suited to this individualised system.
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Traditionally, men undertake on-farm planning, implementation of activities and provide labour. Women play an important role in planning and management of finances, and tend to take a more strategic view on NRM issues than the men.
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
- Govt. agencies/extensionistes
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 被动 | workshops/seminars, field days |
| 计划 | 自我动员 | consultation with specialists |
| 实施 | 自我动员 | fencing and water points |
| 监测/评估 | 自我动员 | field observations; field observations of pasture composition; economic assessments |
| Research | 互动 | on-farm; on-farm field trials and demonstration areas |
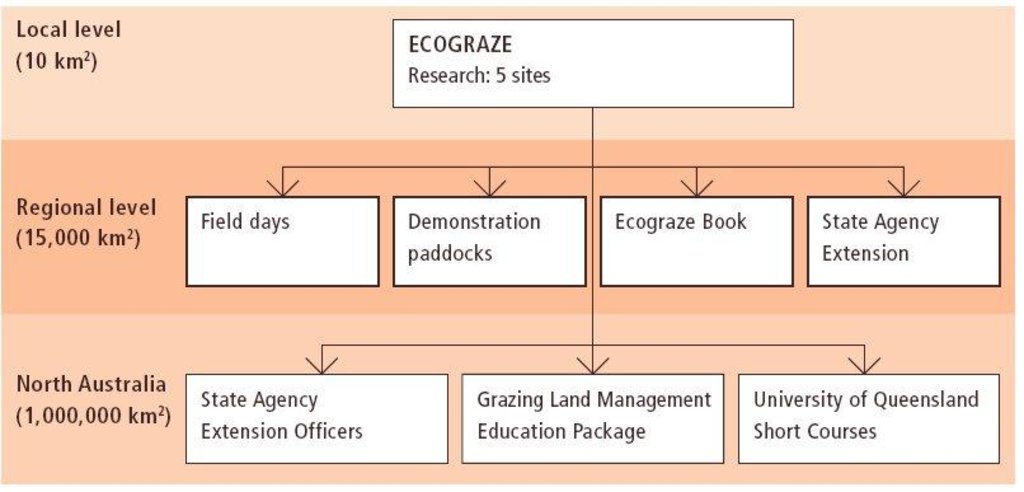
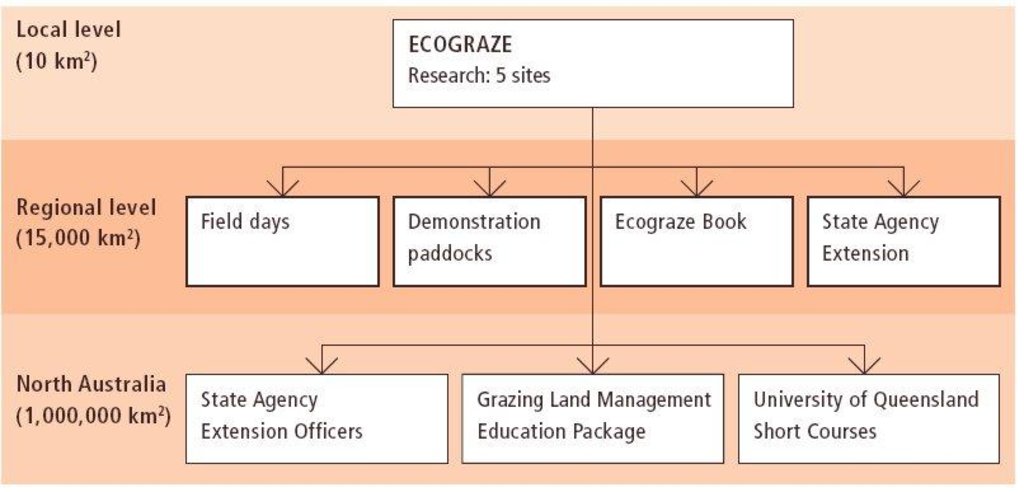
3.3 流程图(如可用)
具体说明:
Programme organization: Components and activities at different levels of the Ecograze programme.
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是土地使用者,由SLM专家提供支持
解释:
Mainly made by land users in consultation with technology experts and government agencies; recognition that Ecograze principles can benefit land users and the environment due to research results of field trials.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up). Mainly made by land users.
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
培训形式:
- 课程
涵盖的主题:
The Ecograze principles and findings have been incorporated into a training course entitled 'Grazing Land Management (GLM) Education Package'. To date (2005) over 100 farmers have participated in the course and it is anticipated that in the next three years this number will reach over 1,000 producers.
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在土地使用者的土地上
- 在固定中心
说明/注释:
Key elements: In on-going research trials in cooperation with land-users, government officers build up their knowledge and capacity to support farmers . Field days form part of the extension and education process. , Government assistance with extension and training through free advice provided by extension officers is helpful, Subsidies to attend training courses like GLM Education also assist with the uptake and adoption of Ecograze. ; There is also a significant interaction between neighbouring properties in sharing of ideas and successes and failures. Commonly, these neighbouring properties are linked through catchment or a Landcare groups.
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,少许
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
具体说明支持类型:
- 财务
提供进一步细节:
financial (see Annex A3)
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
Bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through measurements
Socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations
Economic / production aspects were regular monitored by 0 through measurements;
Area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through measurements
No. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through measurements
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Further research and testing, on-going monitoring and evaluation is underway after the initial project. It is too early to state what changes are likely other than obviously needing to adapt to individual land-users resources and available finances.
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 经济/市场营销
- 技术
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
The impact of the ongoing research on understanding and implementing the technology through the Ecograze project is significant, and continues to be so. Research into various technical aspects of grazing management has been recently supplemented by economic analyses of costs and benefits.
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national government): 40.0%; local community / land user(s) (community / local): 60.0%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
如果是,请具体说明支持的类型、条件和提供者:
Local Landcare groups often request assistance, and this is provided either from the research agencies or from extension officers or through grant applications to the Natural Heritage Trust.
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 无
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
5.5 其它激励或手段
是否有其他激励措施或工具用于促进SLM技术的实施?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
During the research phase of Ecograze, incentives were not available. However, since then, newly established Government initiatives such as the Natural Heritage Trust and the National Action Plan for Salinity and Water Quality, which commenced in 2003, have increased the number of incentives (eg support for on-ground works such as fencing, relocation of water points etc) available to implement management practices such as those recommended in Ecograze.
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Ecograze leads to retention of 3P grasses ('perennial, productive and palatable' grasses), and therefore better pasture coverage, soil retention and greater water use efficiency.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Ecograze principles have been included in the new Grazing Land Management Education package - which is being used across northern Australia by Meat and Livestock Australia and other agencies also. It has also now been incorporated into university courses on grazing management.
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
若是,请说明如何维持:
Progress is continuing with further field trials and participation from land users. Those land users who have begun with the Ecograze system can continue without external support.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Adoption of the technology should result in financial reward. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue ongoing economic analysis as an indication of technology success.) |
| The system has been very well documented and adapted to the land users conditions through the involvement of research, the land users, primary industry, and extension. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continued support for applied/on-farm research to adapt the system to the needs of the land users and the environment. Support for long-term monitoring.) |
| State government extension agencies have also readily accepted Ecograze and are actively promoting its principles with landholders. |
| The approach is focussed on changing attitudes to management in the long term. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue with training and education programmes.) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| One-off training programs such as the Grazing Land Management Education package (a 3-day course) may not be enough to sustain initial commitment to testing new management options. | Create support network and supply follow-up training and/or support. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Ash A, Corfield J and Taoufik T (undated) The ECOGRAZE Project: developing guidelines to better manage grazing country. CSIRO, Meat and Livestock Commission and Queensland Government
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Ecograze [澳大利亚]
An ecologically sound and practical grazing management system, based on rotation and wet season resting.
- 编制者: Andrew Ash
模块
无模块