Farmer-led experimentation [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Richard Allen
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Laura Ebneter
Krishak ko aguwai ma garine parikshan (Nepali)
approaches_2559 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Soil Management Directorate
+977 1 5520314
Department of Agriculture
Harihar Bhawan, Lalitpur
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Team Leader Sustainable Sustainable Soil Management Programme (SSMP)
+977 1 5543591
ssmp@helvetas.org.np
Sustainable Soil Management Programme (SSMP)
GPO Box 688, Kathmandu
尼泊尔
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考
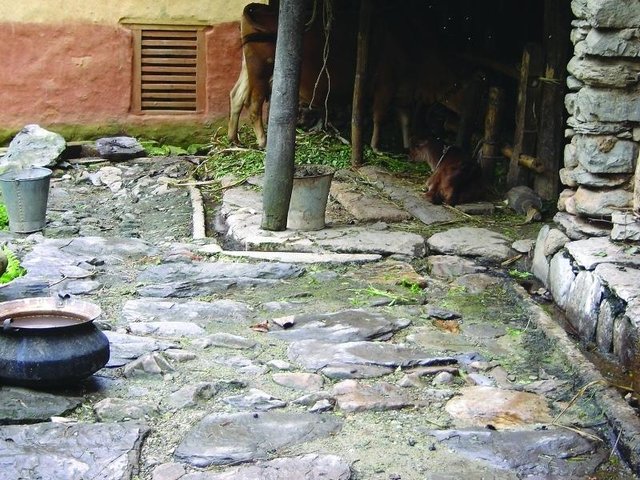

Improved cattleshed for urine collection [尼泊尔]
Collection of cattle urine in improved cattle sheds for use as liquid manure and organic pesticide
- 编制者: Richard Allen
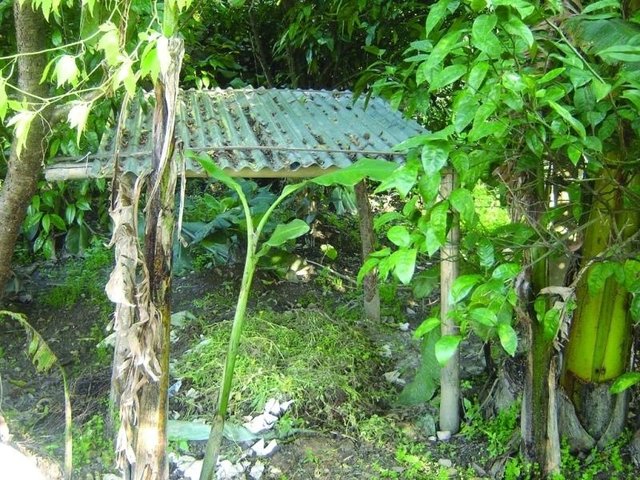

Improved compost preparation [尼泊尔]
Improved compost preparation using a range of biomass and waste to produce high value fertiliser
- 编制者: Richard Allen
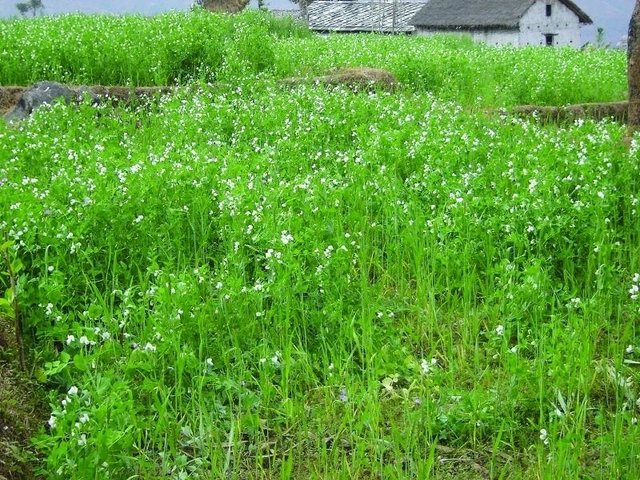

Legume integration [尼泊尔]
Integration of leguminous crops as intercrops on terrace risers or as relay crops
- 编制者: Richard Allen

Organic pest management [尼泊尔]
Promotion of botanical pesticides for organic pest management and liquid manure
- 编制者: Richard Allen
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
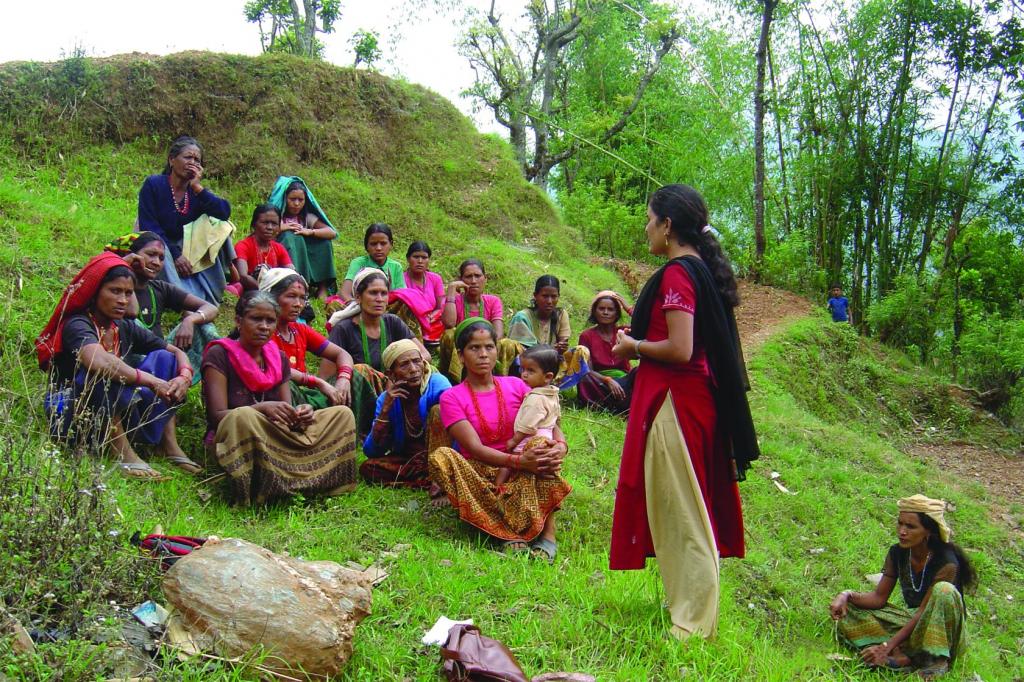
Farmer-led experimentation is a type of action research initiated and carried out by farmers in their own fields. This approach enables farmers to identify technological options suited to local agroecological and socioeconomic conditions. The farmer-led experimentation process is taken up within existing farmer groups. This approach is closely related to the 'participatory innovation development' and the 'participatory technology development' approaches as discussed in Kolff et al. (2005). Simple experiments are usually replicated in five to ten farmers' fields per group. Generally, the whole of each experimental plot from each field is harvested and the yield recorded. Field implementation, group visits, and observations are carried out by the farmers themselves. The processing of results is done in groups together with the support staff from the facilitating organisation. These farmers are very likely to adopt tested technologies that are shown to be better for meeting their needs. The results are also used by support staff and shared with other organisations, and provide input for dissemination through farmer-to-farmer diffusion.
Farmers play a leading role in all steps of the process, starting from problem identification to planning, implementation, and evaluation of the experiments. This ensures that farmers are the driving force in the research process and not mere recipients of research findings that have been generated elsewhere. The detailed implementation plan is discussed within the groups and individual and collective responsibilities are assigned. The experimental site, individual implementing farmers, group visits, and results-sharing meetings are decided on by group consensus. Some observations are recorded by the implementing farmers. Promising innovations are then identified based on the collective evaluation of the tested treatments. Technical and other facilitation support is provided by organisations active in the area.
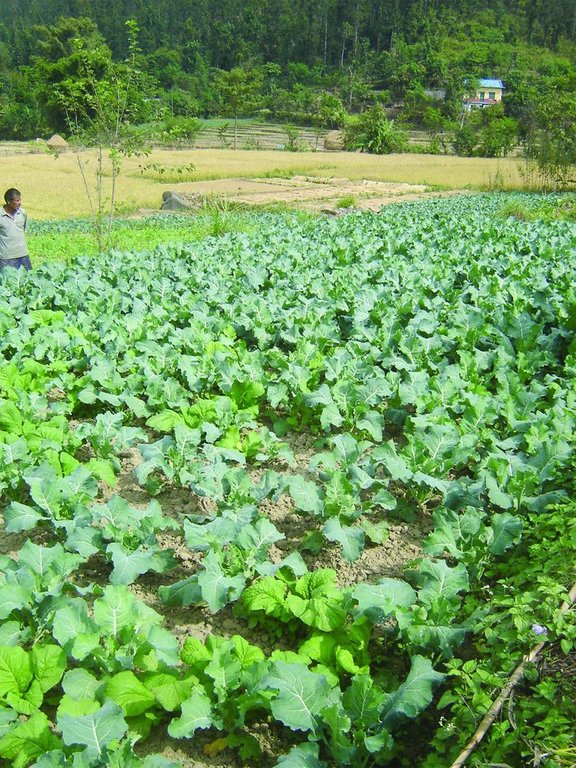
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
区域/州/省:
Midhills
Map
×2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
Local farmers collectively solving problems by identifying and using the most appropriate local solutions. Local farmers designing, testing and disseminating alternative technologies adapted to local conditions. Strengthening joint learning by farmers and development actors.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The common issues concerning farmers in growing crops include pests and diseases, yield decline, inappropriate crop varieties, and the introduction of new varieties. Rather than technicians providing farmers with ready-made solutions to their problems (that may or may not work), farmer-led experimentation allows farmers to carry out their own trials to try and solve specific problems.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
Lack of money for technical support
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Collaborative approach amongst farmers from the same settlements
机构设置
- 阻碍
Dysfunctional government extension system
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Reliance on local human resources and farmer to farmer collaboration
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
Problems related to agricultural production and soil fertility
Treatment through the SLM Approach: esting and adaptation of technologies to local conditions using local human and natural resources
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 互动 | participatory discussions and exercises, field visits, farm maps, farming and labour calendar, Activities: Identification of topics for experiment based on needs and priority, Identification of technological options (indigenous and external), Farmers developing simple and appropriate experiments, De |
| 计划 | 无 | |
| 实施 | 互动 | follow-up visits, discussions, Activities: Farmers implement according to the design for comparison with a control (= existing practice), Farmers note relevant observations on recording sheet. Farmers note other important observations based on their needs and interests, Technical support and discuss |
| 监测/评估 | 互动 | field visit to experimental site by other farmers, participatory discussion and evaluation Activities: Experimenting farmers and other farmers jointly discuss and evaluate based on direct observations of the trial and from the record sheet, Discussion on the lessons learned and identifying possible |
| Research | 无 |
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 仅限土地使用者(自主)
解释:
Made collectively by farmers in group facilitated by organisation working with them.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up). Made by farmers in group
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,适度
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
提供进一步细节:
Technical support provided by project
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were monitored by land users through observations
technical aspects were monitored by land users through observations
economic / production aspects were monitored by land users through observations
area treated aspects were monitored by land users through observations
land users involved aspects were monitored by land users through observations
management of Approach aspects were monitored by land users through observations
There were several changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The adoption of certain technologies has occurred as a result of farmer-led experimentation. For example, a farmer-led trial of two varieties of groundnut (local and B4), in Ghadgaon, Surkhet, led to farmers starting to grow the B4 variety in an area where previously only local varieties had been growing
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local community / land user(s) (local resources, labour, land): 50.0%; other (Dev. project(inputs, external resources)): 50.0%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
如果是,请具体说明支持的类型、条件和提供者:
Provided by the project for testing purposes
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Great impacts on soil fertility and yields have been reported after the adoption of sustainable soil management tested through farmer-led experimentation.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Several farmers in the project area have started to do farmer-led experiments on their own, including on intercropping different vegetables and spices, and on urine application through drip irrigation
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
若是,请说明如何维持:
Some farmers are implementing the approach on their own initiative. This is possible because of the low costs and limited technical requirements of the approach. Farmers exposed to the approach will be able to apply the approach again to problems that arise in their fields without the need to consult outside agencies.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The approach serves both as a local test for suitability and adaptation potential as well as for demonstrating an already tested technology. |
| Once farmers are exposed to the approach, they can apply it on their own initiative. This is possible because of the low costs and technical requirements of the approach. |
| Experiments are conducted on the basis of farmers' priorities and according to local conditions. This means that farmers develop ownership of the experiments and the derived results. |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Experiments are not carried out in a scientifically rigorous way and therefore only have limited scientific value for evaluating technologies. | if scientific proof is required, farmer-led experiments should be closely supported by technicians (per se not a farmer-led experiment anymore!) |
| Documentation of the activities and results for wider sharing is often poor and inadequate | clear guidelines are needed for documentation with clear instructions on what, when, and how to record important information. This is necessary so that the results can be more widely used. |
| In some cases a lack of research equipment for better documentation and observation inhibits better understanding. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
SSMP (2001) Implementation Guideline on Farmer Led Experimentation (in Nepali). Kathmandu: Sustainable Soil Management Programme
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
SSMP
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Paudel, C.L.; Regmi, B.D.; Schulz, S. (2005) - Participatory Innovation Development - Experiences of the Sustainable Soil Management Programme
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
..In Kolff, A.; van Veldhuizen, L.; Wettasinha, C. (eds) Farmer-centred Innovation Development - Experiences and Challenges from South Asia, pp. 109-126. Bern:
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
SSMP
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Improved cattleshed for urine collection [尼泊尔]
Collection of cattle urine in improved cattle sheds for use as liquid manure and organic pesticide
- 编制者: Richard Allen

Improved compost preparation [尼泊尔]
Improved compost preparation using a range of biomass and waste to produce high value fertiliser
- 编制者: Richard Allen

Legume integration [尼泊尔]
Integration of leguminous crops as intercrops on terrace risers or as relay crops
- 编制者: Richard Allen

Organic pest management [尼泊尔]
Promotion of botanical pesticides for organic pest management and liquid manure
- 编制者: Richard Allen
模块
无模块