Equitable Payments for Watershed Services [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2567 - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Dosteus Lopa
dosteus.lopa@co.care.org
CARE International in Tanzania
Morogoro
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - 瑞士有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CARE International (CARE) - 美国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
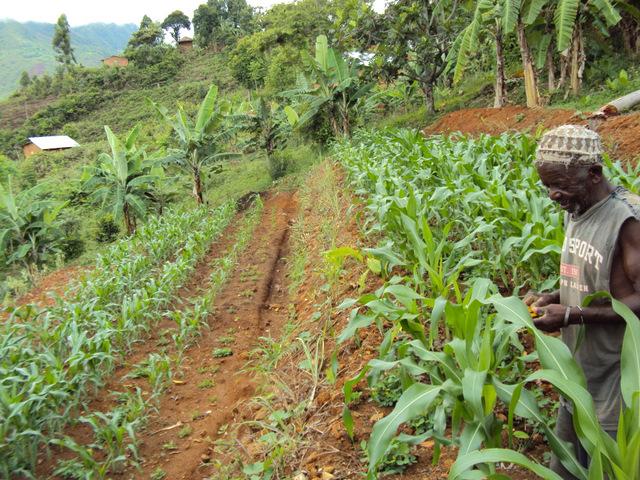
Equitable Payments for Watershed Services (EPWS) is a programme using Payments for Ecosystem Services (PES) to improve rural livelihoods.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: Incentive mechanisms are used to reward upstream landowners for maintaining a beneficial land use or for adapting a particular land use practice which affects the availability and/or quality of downstream water resources. The EPWS approach has enormous potential to advance a new conservation revolution based on a compensation mechanism encouraging and financing conservation efforts as well as improving the livelihoods of the rural poor. EPWS aims to spread SLM technologies to communities, to raise awareness of the benefits of SLM and to improve land productivity. Farmer groups are formed to lead the implementation of SLM.
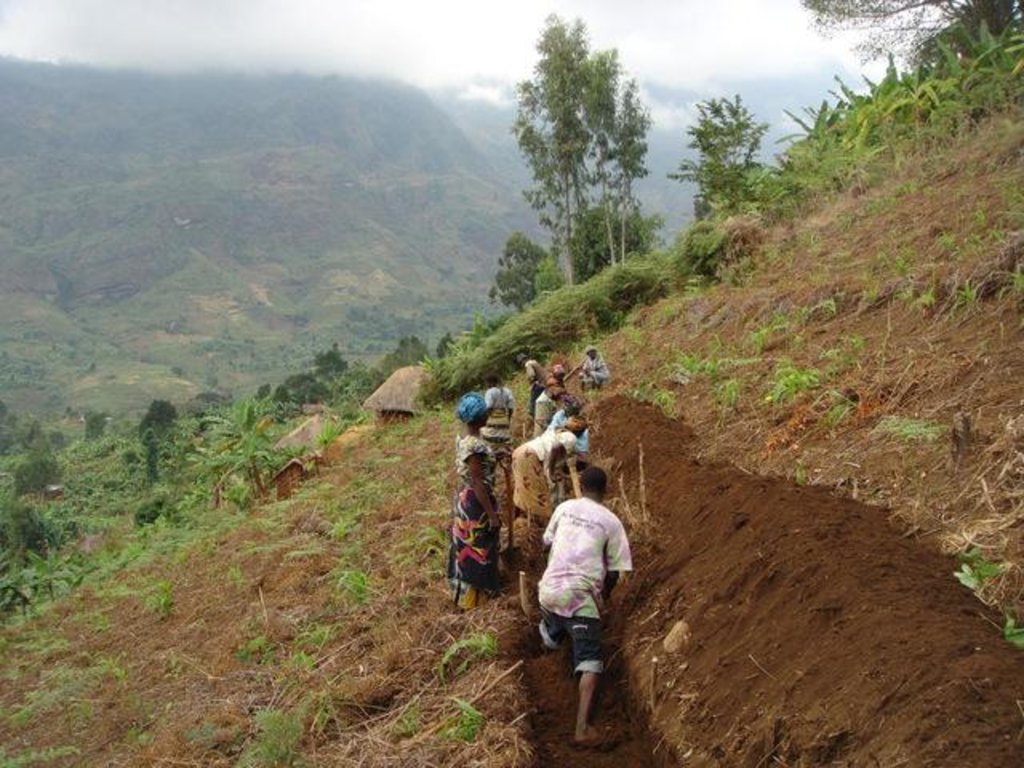
Methods: The approach includes supervision, support and training of farmers to ensure appropriate implementation of SLM and efficient soil erosion control. Methods include demonstration plots and farmer-to-farmer extension. Capacity building to farmers (on gender mainstreaming, good governance and relevant laws and policies) and monitoring of hydrological and livelihood status are important components of the approach. Efforts to ensure good women integration resulted in a relatively high proportion within the farmer groups (>35%). A payment mechanism has been established to compensate farmers for delivering watershed services (in form of freshwater) through implementation of SLM. Compensation payments – paid in cash and through material support – are made first to establish land use changes, and thereafter for service delivery and maintenance. They are mainly covered through international donors (DANIDA) and ‘buyers’ from the private sector, investing in watershed management.
Role of stakeholders: The EPWS team consisting of CARE International, WWF staffs and short-term workers (such as students) is always involving government staff in various activities to induce them to knowledge on EPWS in particular and the PES concept at large.
Other important information: This PES approach is very new in the country and there is little expertise within the government -which therefore needs to take deliberate efforts to groom experts through seminars and courses on PES mechanisms and its operationalisation
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
有关地点的进一步说明:
Morogoro
Map
×2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Improvement of livelihoods, improvement of hydrological system)
Improve livelihoods through SLM / Improvement of hydrological system / Mechanism to ensure effectiveness, growth and sustainability of EPWS / Enhance quality of program implementation
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Land cover changes due to extensive cultivations / Deforestation and forest degradation / Soil erosion, loss of soil fertility / Low storage capacity of the Uluguru Mountains due to land cover change / Declining amount of available water in the river coming from Uluguru Mts / Increased run-off and sediment load in water system due to bare lands
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Efforts to ensure good women integration resulted in a relatively high proportion within the farmer groups (>35%).
- SLM专家/农业顾问
experts on hydrology, GIS, SWC, economics, forests, etc.
- NGO
DAWASCO
- 私营部门
Coca Cola KLtd
- 地方政府
Morogoro district council
district commissioners, ward councillors
- 国际组织
DANIDA, CARE International Tanzania, WWF Tanzania
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 无 | |
| 计划 | 互动 | |
| 实施 | 外部支持 | Farmers are being compensated (paid in cash) for labour and area provided for the implementation of SLM (opportunity costs). Material support through manure, seeds and working tools is given as well. |
| 监测/评估 | 无 | |
| Research | 无 |
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是SLM专家,咨询土地使用者之后
解释:
Interactive implementation and decision making; participatory feasibility studies to identify the core problems; PRA to identify and agree on SLM technologies; government staff was involved in various activities e.g. planning, training, data collection and analysis, extension, etc.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
培训形式:
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
涵盖的主题:
practical skills on SLM measures, leadership skills, governance, gender mainstreaming, policies and laws to ensure their understanding on the implementation of the EPWS project in their locality
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在土地使用者的土地上
说明/注释:
Key elements: technical support on monitoring, provision of extension services for improved land use, situation analysis, awareness creation, capacity building on legal issues and mapping of interventions; People involved: University, foresters, hydrologists, Ministry of agriculture, land use planners
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 否
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were monitored through measurements
socio-cultural aspects were monitored through observations
economic / production aspects were monitored through observations
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 社会学
- 经济/市场营销
- 生态学
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
Research is a main part of PES as an approach to facilitate SLM adoption and has been very effective in guiding programme design; it included SLM assessment, hydrological analysis, economic analysis, social and livelihoods assessment, etc. All interventions applied were proposed by research conducted before and during implementation.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- 100,000-1,000,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (DANIDA): 60.0%; private sector ('buyers' of ecosystem service): 9.0%; local community / land user(s) (through labour power): 31.0%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 农业
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 种子 | 部分融资 | |
| 化肥 | 部分融资 | |
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 以现金支付
注释:
Farmers are being compensated (paid in cash) for labour and area provided for the implementation of SLM (opportunity costs). Material support through manure, seeds and working tools is given as well.
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
increased production
该方法是否有助于社会和经济弱势群体?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
women have gained training in improving land use practices
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Upscaling to neighbouring villages will be facilitated by the establishment of networks of farmers groups to receive training by local extension services. A steering committee, with representatives of the farmers, investors and government offices will facilitate replication in other parts of the country.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
through change of crop production
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 支付/补贴
- 加入运动/项目/团体/网络
- 环境意识
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
若是,请说明如何维持:
Participant land users can continue the activity without additional support- maintenance costs are low and the technologies will improve productivity and resilience of farming system. Upscaling to neighbouring villages will be facilitated by the establishment of networks of farmers groups to receive training by local extension services. A steering committee, with representatives of the farmers, investors and government offices will facilitate replication in other parts of the country.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| PES as an additional argument for supporting property claims |
| To ensure services are delivered and payments are made and a reliable monitoring mechanism has been put in place |
| Poor people are in the centre of the objectives |
| Approach rewards land users for providing watershed services |
| PES as an incentive for conservation, helping to change land users’ vision towards improved land management |
| Once measures are applied they are simple and cheap to maintain |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| May reduce the effectiveness of non-incentive based approaches as people will now demand rewards/payments | awareness creation is important to all players including government and local communities |
| Payments / rewards are realised before service delivery | ensure integration of PES with other approaches to ensure effectives short and long term benefits. Paying labour cost upfront while waiting for the service delivery rewards |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块