Joint Wildlife Management in the mountain ecosystem of the Naryn region in Kyrgyzstan [吉尔吉斯斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Nazgul Esengulova
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff
Нарын областында тоолуу экосистемаларынын табигый анчылык ресурстарын жергиликтуу жамааттардын негизинде колдонуу
approaches_2582 - 吉尔吉斯斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - 德国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
11/05/2012
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
Joint Wildlife Management based on economic empowerment and assigning hunting (wildlife) grounds to the Association of local hunters and providing her with user rights for game resources leads to a sustainable use of natural resources and biodiversity and wildlife conservation (in the frame of CACILM).
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: Wildlife in Kyrgyzstan, especially mountain ungulates, is threatened because these resources can be easily accessed due to an inadequate state supervision and regulation as well as due to lack of knowledge among the local population and mechanism for integrated land use (considering different coordinated types of resource use) and resource conservation. Decrease in the natural habitat (caused by the expansion of pasture and arable land) and illegal hunting lead to a decrease in wildlife populations. In Kyrgyzstan, the fauna is exclusively owned by the state. User rights for wildlife are separated from land use ones. The approach aims at the conservation and sustainable use of wildlife based on providing representatives of the local community, organized in an Association of local hunters (ALH), with legal user rights for wildlife resources.
Methods: (1) supporting local hunters in organizing an Association of local hunters (ALH) with the help of facilitators; (2) transferring wildlife management functions from the Wildlife Department to the ALH based on assigning hunting grounds to them and providing them with user rights according to jointly developed management plans; (3) building trust in partnership relations between the ALH and the Wildlife Department of State Agency for Environmental Protection and Forestry (SAEPF) based on joint registration and monitoring and determination of the resource status (see Annex 3); (4) capacity building of the ALH with the help of independent experts and advising activities provided by the Wildlife Department; (5) developing an atmosphere of trust by establishing links between the Wildlife Department, local hunters (ALH), the local community (Aiylokmotu) and rural organizations (Pasture User Association, PUA) based on joint planning and information sharing.
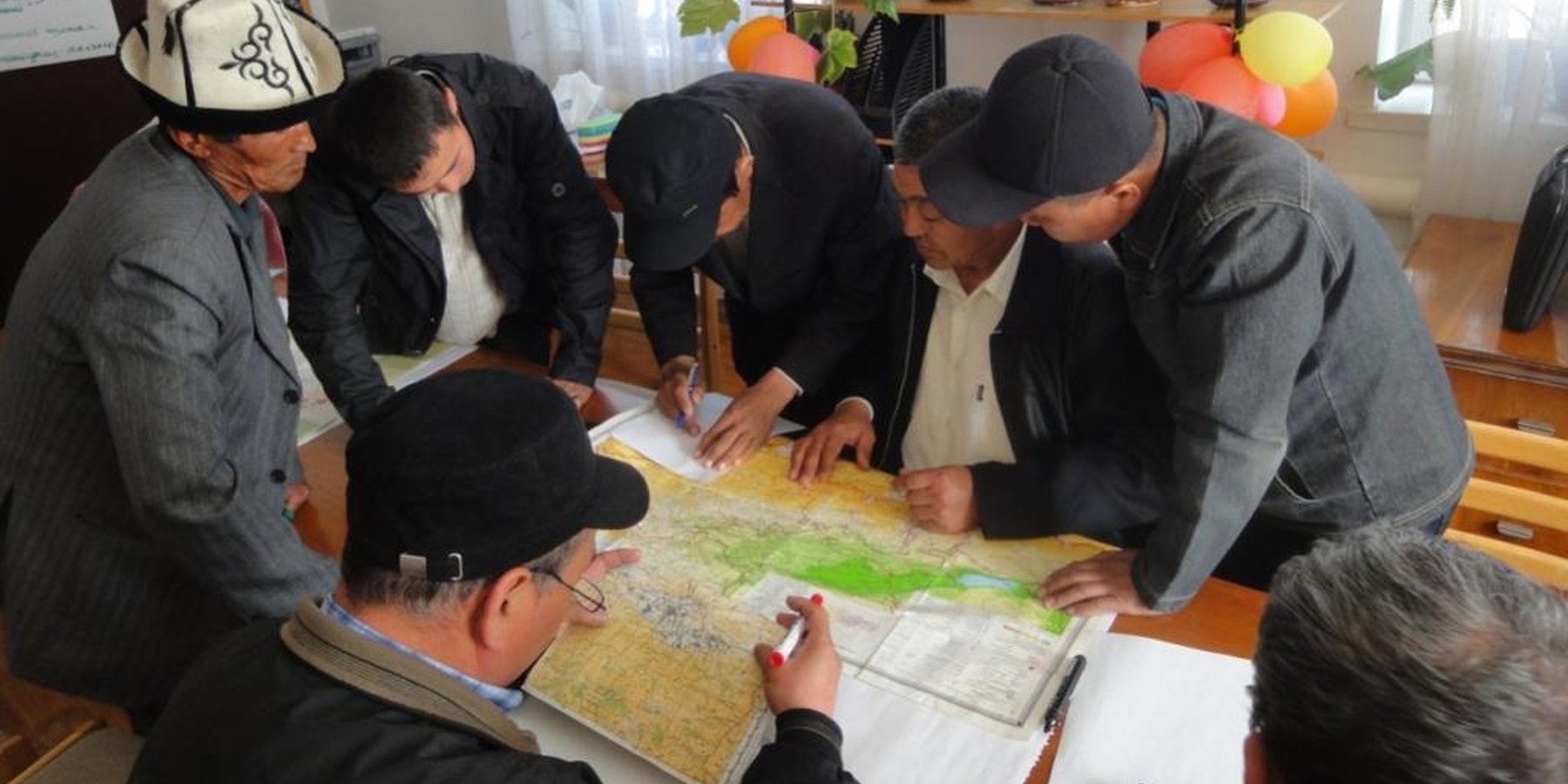
Stages of implementation: (1) setting up groups of well-trained (sensitive) facilitators and training them on the principles of facilitation, conflict management and sustainable management of natural resources; (2) identifying reliable active hunters with the help of facilitators and managers by interviewing neutral people; (3) organizing a meeting at the field level to analyze the situation and identify interests in establishing of the ALH; (4) raising awareness of local hunters on wildlife resources, existing problems and possible solutions offered by sustainable management; (5) establishing an ALH in the pilot area as a legal entity; (6) assigning areas to the ALH and advising activities on methods for wildlife management provided by the Wildlife Department and the specialized NGO 'Ak-Terek'; (7) organizing expeditions with specialists from the Wildlife Department to register and monitor the resource status; (8) developing a management plan with the support of experts from the Wildlife Department and independent experts, plan approval and implementation.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
吉尔吉斯斯坦
区域/州/省:
Kyrgyzstan, Naryn oblast
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kochkor district, Toloksky Aiylokmotu (villages Tolok and Kok-Jar)
注释:
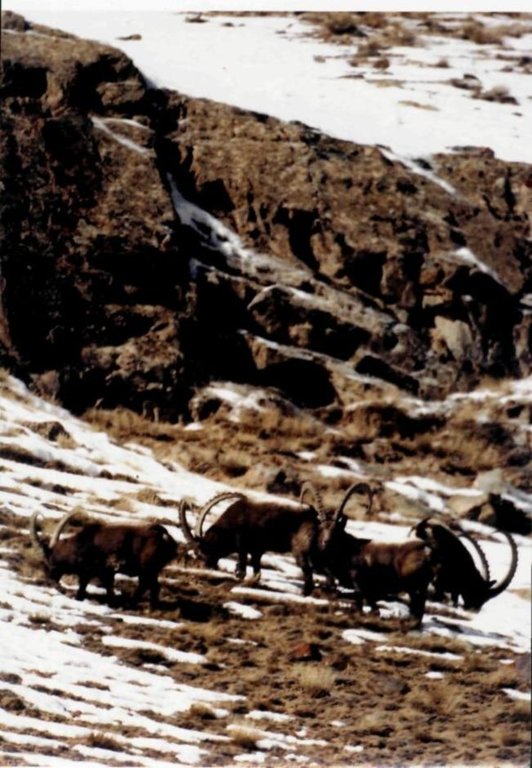
Tolok village is situated at 2343 meters above sea level. Hunting grounds are located in the basin of Tolok river in a narrow gorge in the area of alpine meadows with a middle degree of soil degradation. The area is inhabited by wild mountain goats, deer, wolves, foxes, marmots, hares, partridges.
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2010
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2014
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (Transferring responsibilities of wildlife management to the local population, assigning hunting grounds to the Association of local Hunters and providing her with legal user rights for game resources, sustainable management of wildlife and joint planning)
The approach aims at conservation and sustainable use of wildlife based on economic empowerment and transfer of legal use rights for wildlife resources to representatives of the local community, organized in the Association of local hunters according to jointly developed management plans.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Decrease in wildlife populations due to an unregulated unsustainable use of resources by the local population and due to lack of participatory mechanisms for the population to manage these resources, inadequate state regulation and supervision, aggravated by a conflict of interest among users over other natural resources with different intentions (pasture, forest, mineral resources, tourism).
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
- 阻碍
Hunting is basically illegal. Local hunters do not trust the new approach of wildlife management and have no capacity for self-organization and no experience of joint decision making.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Providing necessary information to the local population by holding meetings and seminars with representatives of the Wildlife Department. Trainings on capacity building for self-organization.
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
There is a need for initial investment to get the ALH started and deferred revenues are expected. The ALH is not expected to extract big financial revenues from wildlife management and wildlife use.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Explanation of financial expectations (exclusive right of first access to game resources and authority of access right distribution, patriotism)
机构设置
- 阻碍
There is a lack of joint organizations at the field level which manage wildlife resources sustainably.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Establishing an Association of local hunters to manage wildlife resources sustainably
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 启动
- 阻碍
There is a lack of policy promoting Joint Wildlife Management
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Order of the Wildlife Department, Concept of Reform for wildlife sector prohibiting state agencies to manage wildlife economically, promoting the assignment of wildlife areas to the ALH
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly hindered the approach implementation Existing legislation does not comply with the principles of sustainable use and wildlife management and does not promote Joint Wildlife Management. There is a lack of regulation and integration of land users.
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
The local population has no necessary capacities (environmental awareness, knowledge of sustainable wildlife management).
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Trainings
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Hunters from the villages Kok-Djar and Tolel in the Naryn region
Hunting is a traditionally male-dominated activity
Pasture user committees
- 社区组织
- NGO
Public Foundation “Ak-Terek”
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
Wildlife Department of SAEPF
- 国际组织
GIZ Regional Program on Sustainable Use of Natural Resources via the Project “Sustainable use of the mountain ungulate species in Kyrgyzstan”
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 互动 | Consulting with the Wildlife Department |
| 计划 | 互动 | Participation at discussing the approach design and determining the form and specifics of self-organization |
| 实施 | 互动 | Local hunters implement the approach through their representatives in the ALH |
| 监测/评估 | 互动 | Monitoring and evaluation are conducted on base of questionnaires and interviews with key actors supported by the Wildlife Department and GIZ Project and on base of annual progress assessment in reports prepared for the Wildlife Department (increase in wildlife population, reducing conflicts among resource users). |
| Research | 无 |
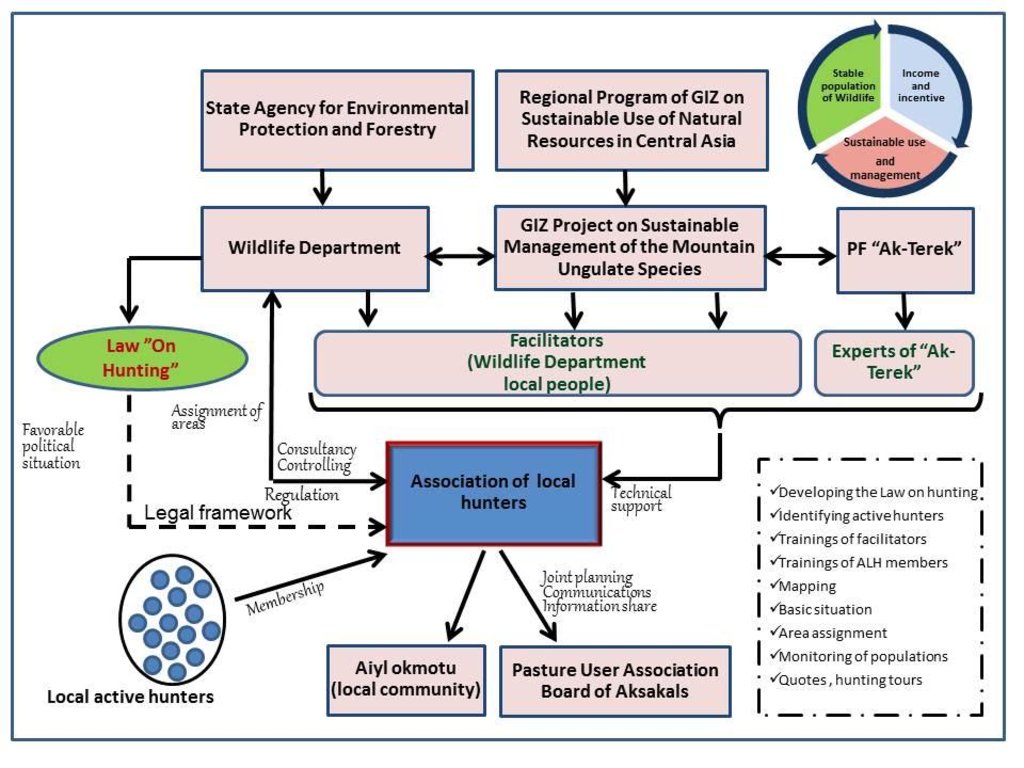
3.3 流程图(如可用)
具体说明:
The approach has been implemented by the GIZ project 'Sustainable management of the mountain ungulate species' under the Regional Program on Sustainable Use of Natural Resources in Central Asia which initiated and implemented establishment of the ALH in conjunction with the Wildlife Department and the NGO 'Ak-Terek'. The Wildlife Department has developed new methods for monitoring and determining wildlife quotas. The NGO 'Ak-Terek' promotes and facilitates self-organization of hunters in the ALH, mitigate possible conflicts arising in the integrated land use. Local hunters are organized into the ALH, defining her structure and principles of organization (legal status, functions, membership), as well as monitoring and developing management plan, etc. The Wildlife Department confirms the legal assignment of wildlife areas to the ALH and provides advice to them on game management.
作者:
Nazgul Esengulova (720001, Logvinenko St., 26а, Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan )
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
是否就技术的选择做出了决定?:
- Experts from the Wildlife Department
解释:
In a seminar involving the local population and project experts and experts from the NGO 'Ak-Terek' as facilitators in order to explain the principles of wildlife management.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. Decisions were made by the village population supported by WLD experts.
In the meeting of key hunters, shepherds and other interested residents of the village with the project staff and the Foundation 'Ak-Terek', there was determined a form of local self-organization of wildlife users.
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
- Wildlife Department
如果相关,请说明性别、年龄、地位、种族等。:
Mainly males at age 40-50
培训形式:
- 在职
- 农民对农民
- 公开会议
培训形式:
- 2 day seminars on the spot
涵盖的主题:
1. Raising awareness of actual problems and possible solutions; joint mapping of resources and discussion of scenarios for development of hunting grounds;
2. Principles of sustainable wildlife use;
3. Methods for monitoring and registering the number of wild animals;
4. Planning economic activities of game management for an assigned area;
5. Professional ethics of game users;
6. Programs for employees of environmental, law enforcement and customs authorities.
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在土地使用者的土地上
说明/注释:
Name of method used for advisory service: situation analysis; Key elements: on-site visit, group consultation during workshop, preparation of resource map
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Department with its local staff and the NGO 'Ak-Terek' are capable to continue providing advisory services after the project finishes.
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 否
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
Bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: expeditions, field researches, surveys
Bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through measurements; indicators: number of wild animals
Economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: benefit from selling hunting tours and ecotourism
No. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Number of hunters and associations
Management of Approach aspects were regular monitored by project staff, government through observations; indicators: annual planning, monitoring of achievement and difficulties, adaptation of the approach if necessary
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
否
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- 10,000-100,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (GIZ, via “Sustainable use of the mountain ungulate species in Kyrgyzstan” ): 95.0%; government (Wildlife Department of SAEPF): 5.0%; national non-government (PF “Ak-Terek” ); local community / land user(s) (local resource users )
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
否
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 设备
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Tools, binoculars, GPS navigators, tents | 部分融资 | |
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
注释:
Voluntary participation in monitoring and registering as well as analyzing wildlife areas for the further assignment of hunting grounds to hunters
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
With establishing the Association of local hunters and involving the latter into wildlife management, stabilization and even an increasing tendency of wildlife populations according to ecosystem's carrying capacity have been made possible. Joint planning and activities in the assigned areas decreased the number of conflicts over resources. Diversification of land use and a better integration of land users are present.
该方法是否有助于社会和经济弱势群体?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Integrating approaches of wildlife management (a relevant order of the Hunting Department) before a new law 'On Hunting' is adopted. Economic empowerment of the LAH and political will for the issue. Increase in sensibility of the main resource users concerning the conservation of biodiversity.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The project is extended over other areas in Kyrgyzstan (Kemin, Ak-Suu and Talas regions) and in Khatlon and Gorno-Badakhshan oblasts of Tajikistan (Shurabad, Darvaz, Rushan, Ishkakshim, Murghab regions).
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Legally ongoing recreational hunting. Revenue increase resulting from the wildlife protection due to legalization of hunting and sustainable resource management.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Since the target group does not refer to very poor people
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 增加利润(能力),提高成本效益比
Additional income from hunting tours
- 规章制度(罚款)/执行
Legalization of hunting
- 声望、社会压力/社会凝聚
Attitude of local people to illegal hunting
- 环境意识
Moral improvement of society
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
Additional income from hunting tours
- Improvement of ecosystem
Wildlife protection improves the ecosystem where local people live
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
若是,请说明如何维持:
5 years later, after the number of wild animals in the assigned area is increased. During this period, members of the Association would realize the obvious long-term benefits resulting from the new approach (increasing wildlife population would lead to an increase in hunting licenses issued) and would become experienced in sustainable game management.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Opportunity to lobby for own interests through Hunters’ Association in the local community (Aiylokmotu). |
| Opportunity to extract revenue from hunting tours. |
| Opportunity to legalize hunting. |
| Opportunity to manage resources in the assigned area and to plan how to use them. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Trainings and expert advice from the Wildlife Department and the Academy of Sciences of KR.) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Users of various natural resources (pasture, beekeepers, hunters) jointly plan their activities and use resources. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Increasing awareness of the local population on degradation of natural resources and the need for their careful use.) |
| Resource use and management are transferred in the hands of resource users. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Adoption of necessary legislation to establish wildlife user associations.) |
| Positive impact on the local ecosystem: stabilization of the wildlife population resulting from of protection of the assigned area and limited shooting. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Trainings for hunters on a new method of registration and monitoring of wild animals in order to determine the status of wildlife populations.) |
| Active and regular participation and support of the Wildlife Department in planning and implementing approach and creating an atmosphere of trust. |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Deferred minor revenue over the first years of implementation related to an increase in wildlife populations. | Development of ecotourism as a primary source of income. In the future, ecotourism can be practiced along with hunting tourism, providing additional income. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Resource users have poor capacities for self-organization and are incapable of coherent collective actions. | Consultancy, meetings, involvement of conflict managers and facilitators. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Final Report for GIZ 'Analysis and Preliminary Results of the Joint Wildlife Management Component of the Project
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Pesch Markus
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块