Disaster risk reduction and sustainable land-use by integrated rehabilitation of flashflood/debris flow affected site [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Stefan Michel
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Umed Vahobov
Снижение риска стихийных бедствий и устойчивое землепользование через интегрированное восстановление местности разрушенного селевым потоком
approaches_4320 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人员
SLM专业人员:
Muhidinov Nodir
nodir.sfl@gmail.com
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
塔吉克斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Negmatov Negmatjon
negmatdzhon.negmatov@giz.de
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
塔吉克斯坦
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Strengthening of Livelihoods through Climate Change Adaptation in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit - Tajikistan (GIZ Tajikistan) - 塔吉克斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考

Applying drip irrigation for efficient irrigation water use … [塔吉克斯坦]
Drip irrigation substantially saves water compared to conventional furrow irrigation. Here the technology is applied for different perennial and annual crops and with use of different sources of water.
- 编制者: Stefan Michel

Cultivation of local juniper species for rehabilitation of … [塔吉克斯坦]
The local species of juniper trees (Juniperus seravschanica, Juniperus turkestanica and Juniperus semiglobosa) are rarely rejuvenating under conditions of intensive grazing and are difficult to propagate in nurseries. The technology describes the propagation of these important trees from locally collected seeds and their cultivation.
- 编制者: Stefan Michel
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
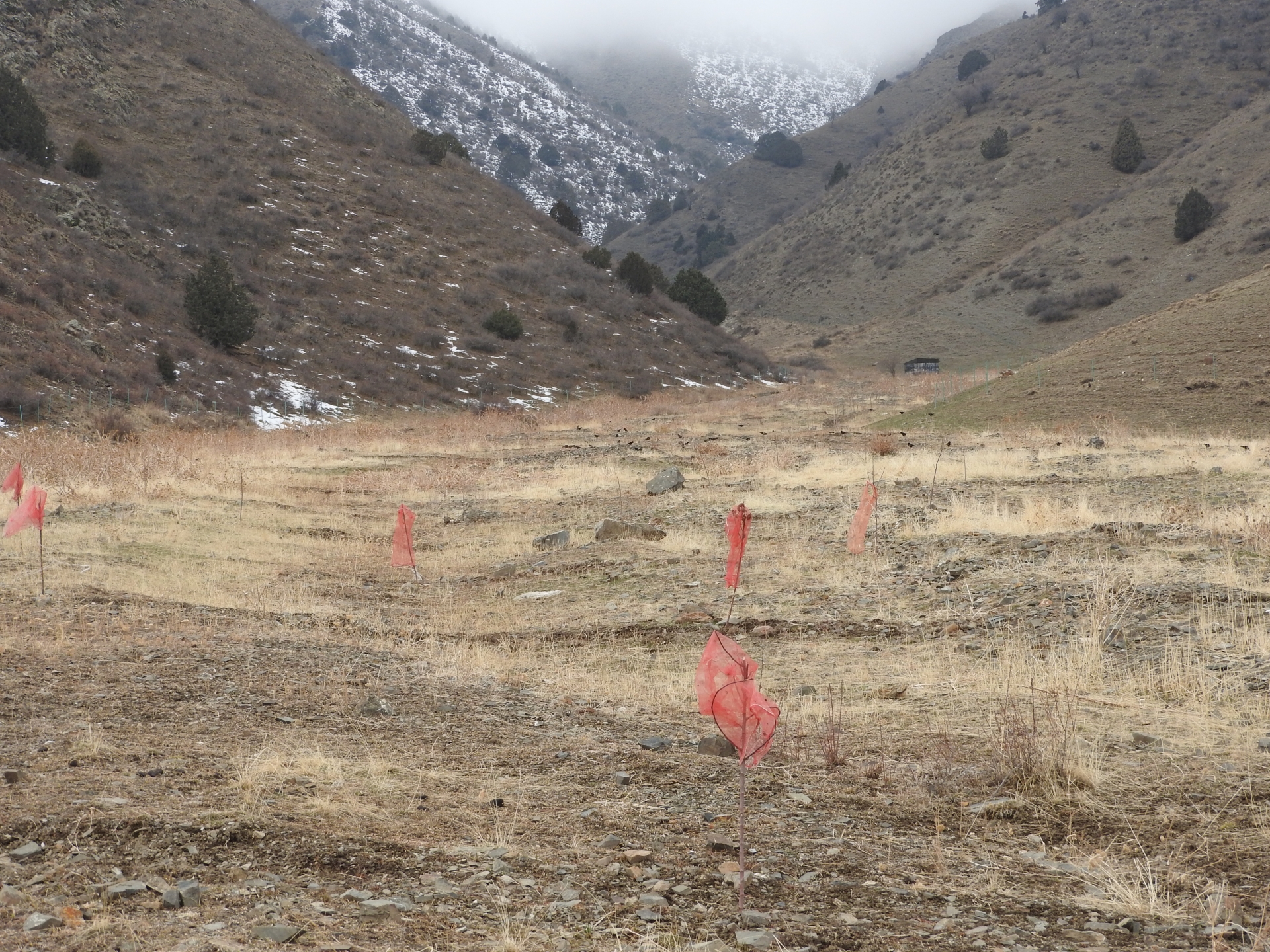
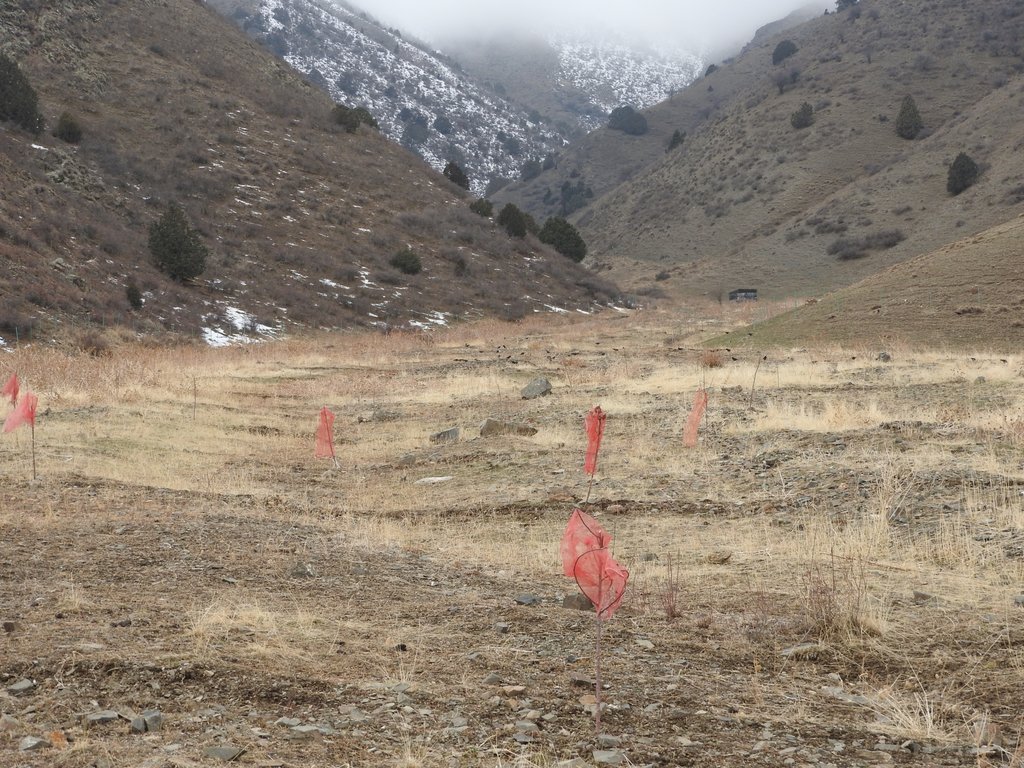
A site affected by a debris flow was rehabilitated by joint communal work and integrated preventive measures addressing the upper catchment as well as the valley and the debris conus were implemented in collaboration of community, individual farmers, Committee of Emergency Situations and forestry enterprise.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Local people in many parts of Tajikistan, among these the project region at the northern main slope of the Turkestan range, report about formerly unknown flashfloods and debris flows, even in areas where such events are not remembered. Also relief, soil and vegetation often confirm that such sites for long times had not been transformed by these forces. The occurrence of flashfloods and debris flows in formerly not affected areas, unusual seasons or an increase in frequency and destructiveness of such events can be attributed to land degradation in upper catchment areas in combination with climate change impact.
The degradation of the vegetation in upper catchments has contributed to reduced infiltration of water and high and fast surface runoff. Important elements of this degradation are overgrazing and deforestation. Overgrazing and out of season grazing cause the reduction of the protective plant cover and the multiple trails of livestock with compressed soil reduce infiltration and increase the surface runoff. Deforestation is typically related to intensive livestock grazing, in particular by goats, as intensive browsing prevents the regeneration of shrub and tree vegetation. In upper catchments affected by these processes during heavy rainfall and snow melt large amounts of water concentrate in small valleys and take with them large amounts of soil and gravel. The deforestation in valleys contributes to the intensity of such flashfloods and debris flows.
The frequency and intensity of these events is increasingly exacerbated by the impact of climate change. The already visible trends and predictions show higher levels of aridity, higher temperatures during the vegetation season, reduced overall precipitation in catchment areas – all affecting the retention potential of upper catchment areas – and more irregular rainfall patterns, reduced snow packs and accelerated snow melt as well as the loss of glaciers as buffers of water flow. These factors all contribute to a higher frequency and intensity of flashflood and debris flows and their occurrence in previously not or less affected areas.
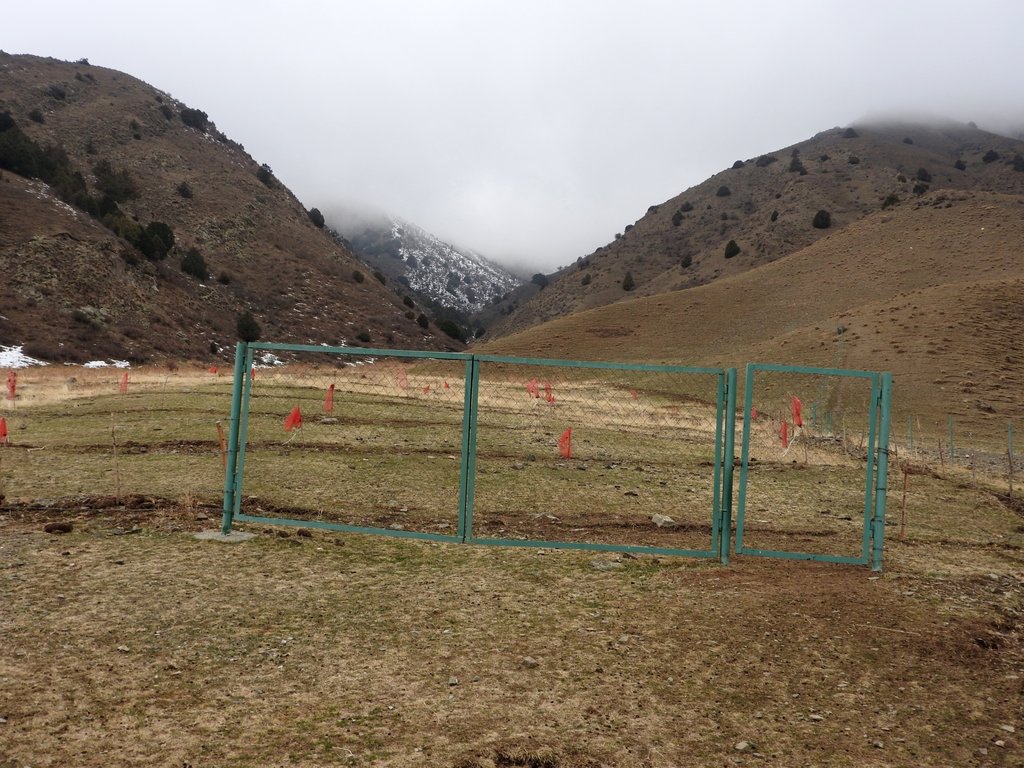
Near the village Shamoli in Shakhriston district, as in many other locations, such a debris flow made a road impassable and has destroyed pasture lands and five hectares of arable lands belonging to several farmers with another 10 ha being at risk in case such events occur again. Local people assisted by the Committee of Emergency Situations opened and cleaned the road. The developed in collaboration with experts an integrated approach for rehabilitating the affected lands and reducing the disaster risk. The approach included the following elements:
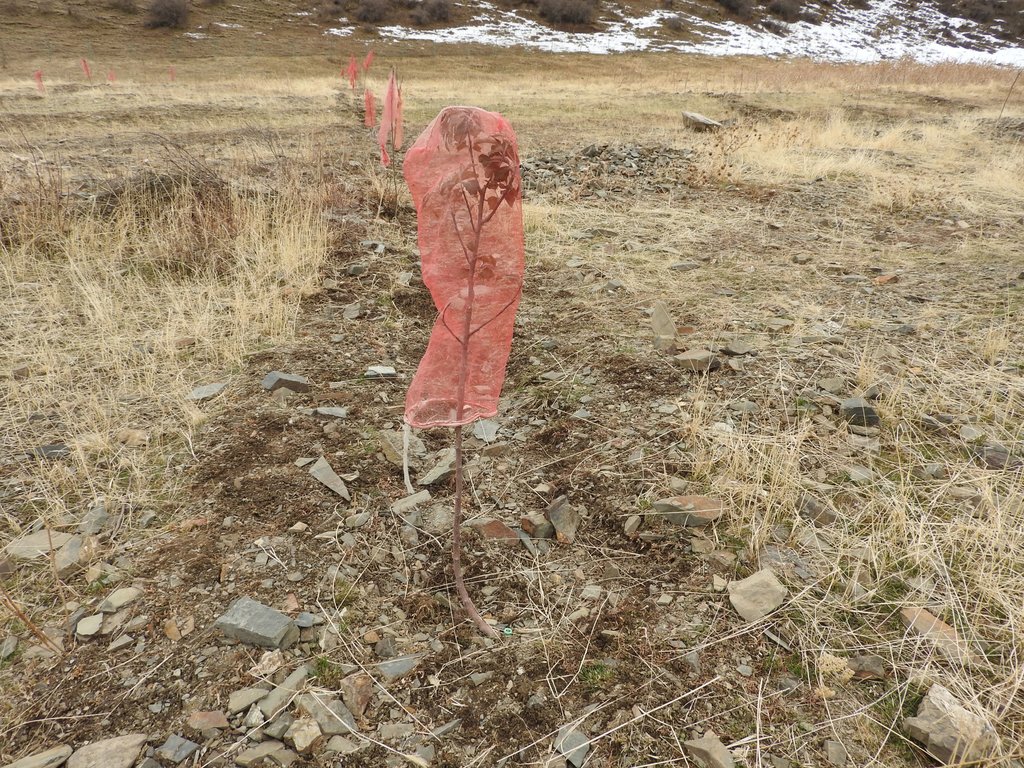
•Blocking of gullies with planting of willows for reducing sediment load in case of future flashfloods;
•Agreement with the forestry enterprise about general regulation of grazing and tree planting (specifics to be decided by the forestry enterprise);
•Joint communal work (hashar) for cleaning affected arable lands from debris;
•Fencing of 4 ha lands in the valley leased by one farmer from the forestry enterprise for rehabilitation of protective vegetation and sustainable land use (orchard and hay making);
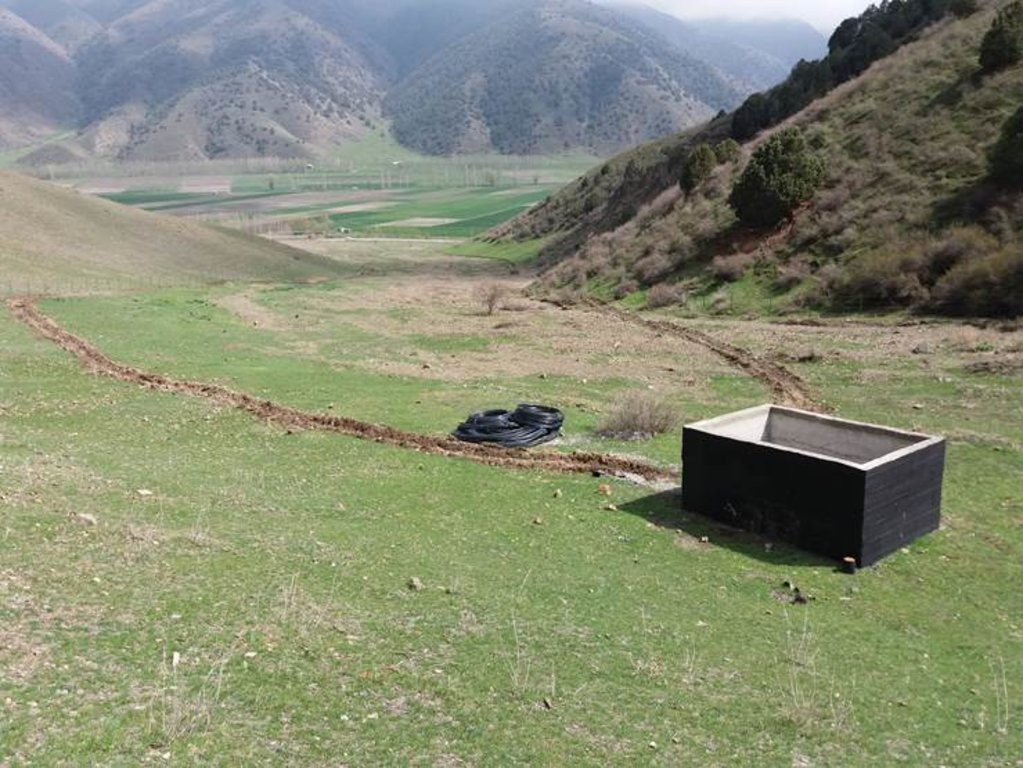
•Construction of reservoir for water collection from spring and use for drip irrigation of trees planted at the debris conus in the opening of the valley.
The approach brought together the Committee of Emergency Situations, the administrative communities, affected local people and the forestry enterprise. Assisted by experts provided by the project, the situation was jointly analyzed; risks identified and the integrated intervention planned. The project assisted with technical planning, construction supervision, purchase and transportation of construction materials. The community contributed about 30% of the overall costs, mainly in form of voluntary communal work, the so called hashar. One farmer leased the most critical area at the opening of the valley and took the responsibility for the maintenance of the area in exchange for the opportunity to use hay and fruits from the planted trees.
The approach is generally replicable. But in most such sites the upper catchment areas belong to different communities, often to different districts and substantial parts are located in neighboring Kyrgyzstan. Therefore addressing the degradation of these areas and a reduction of disaster risk through integrated watershed management in the entire catchments will require more collaboration across administrative boundaries and even national borders.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Sughd region
有关地点的进一步说明:
Shahriston district; Shahriston sub-district, Shamoli site
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2017
若不知道准确的年份,请注明该方法的大致开始日期。:
不到10年前(最近)
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
Rehabilitation of land affected by debris flow and reduction of risk of future events.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
For complex measures the financial assistance by the project was needed.
机构设置
- 启动
Communal work for addressing issues affecting the entire community or individual members.
参与者的的协作/协调
- 启动
Collaboration between community members, community leadership, Committee for Emergency Situations and forestry enterprise.
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
Understanding of SLM issues insufficient, involvement of external experts needed.
工作量、人力资源可用性
- 启动
Communal work for addressing issues affecting the entire community or individual members.
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Individual farmers and local community
Discussion of rehabilitation and prevention measures;
Implementation of works;
Maintencance of site with protection plantation.
- SLM专家/农业顾问
Experts provided by GIZ
Advise on disaster risk reduction, blocking of gullies, planting of trees, drip irrigation.
- 地方政府
Community administration, Committee of Emergency Situations, forestry enterprise
Identification of risk sites;
Design, planning and supervision of interventions;
Lease of intervention site;
Regulation of grazing and tree planting in upper catchment.
- 国际组织
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
Overall project implementation;
Technical planning and oversight;
Procurement of construction materials via competitive bidding process
如果涉及多个利益相关者,请注明领导机构:
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 互动 | Local community members, asking community leadership and GIZ staff for assistance to address impact of debris flow |
| 计划 | 互动 | Involvement of community members in planning |
| 实施 | Local community members carrying out works through traditional voluntary community work ("hashar"). | |
| 监测/评估 | Local farmer maintaining the planted area controls condition of irrigation system and trees. | |
| maintenance | Local farmer maintaining the planted area. |
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 所有相关参与者,作为参与式方法的一部分
明确做出决策的依据:
- 对充分记录的SLM知识进行评估(基于证据的决策)
- 个人经验和意见(无记录)
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
否
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
说明/注释:
Not of specific relevance for this approach.
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,少许
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
说明机构、角色和职责、成员等。:
Existing community institutions have been strengthened through joint successful implementation of the works and the need for further collaboration.
具体说明支持类型:
- 财务
- 能力建设/培训
- 设备
提供进一步细节:
Fencing, materials of irrigation system, technical advice.
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
若是,该文件是否用于监测和评估?:
否
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
否
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- 2,000-10,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Government of Germany, implemented via Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ). The approach has been implemented in the frame of a much larger program and the specific budget for the SLM component of the Approach cannot be determined.
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
如果是,请具体说明支持的类型、条件和提供者:
Technical planning and supervision, procurement of materials and transportation funded by GIZ.
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 无
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
5.5 其它激励或手段
是否有其他激励措施或工具用于促进SLM技术的实施?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
The farmer managing the site in the valley, where trees have been planted, can use the fruits and the hay produced from the site. This is the key incentive for him to carry out all maintenance.
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否有助于当地土地使用者,提高利益相关者的参与度?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Mobilization for joint work to address problems affecting all farmers/community members
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Integration of different technologies to rehabilitate lands and reduce future disaster risk.
该方法是否提高了SLM的协调性和成本效益?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Collaboration between land users, community leadership, Committee of Emergency Situations and forestry enterprise.
该方法是否调动/改善了使用财务资源实施SLM的途径?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Mobilization of financial resources from GIZ.
该方法是否提高了土地使用者实施土地管理的知识和能力?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Knowledge of and skills to implement several technologies for land rehabilitation, sustainable land use and disaster risk reduction.
该方法是否建立/加强了机构、利益相关者之间的合作?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Collaboration between land users, community leadership, Committee of Emergency Situations and forestry enterprise.
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Lease of critical site to motivated farmer by forestry enterprise.
该方法是否改善了粮食安全/改善了营养?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Rehabilitation of affected farmlands and reduced disaster risk.
该方法是否提高了土地使用者适应气候变化/极端情况和减轻气候相关灾害的能力?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Reduced risk of disasters, which increase due to climate change.
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 增加生产
Fruits and hay from rehabilitated critical site.
- 降低灾害风险
Reduced risk of disasters, which increase due to climate change and threaten productive lands and property.
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Rehabilitated lands and reduced risk. |
| Use of products from critical site, which was planted with fruit trees. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Same as land users' view. |
| Mobilization of collaboration and joint communal work. |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High costs of fencing | External funding. |
| High costs of irrigation system | External funding. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High costs of fencing |
External funding; Cheaper temporary electric fencing; Approaches without fencing, based on agreement in the community to prevent livestock damage through herding. |
| High costs of irrigation system |
External funding; Planting of drought resistant trees. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Applying drip irrigation for efficient irrigation water use … [塔吉克斯坦]
Drip irrigation substantially saves water compared to conventional furrow irrigation. Here the technology is applied for different perennial and annual crops and with use of different sources of water.
- 编制者: Stefan Michel

Cultivation of local juniper species for rehabilitation of … [塔吉克斯坦]
The local species of juniper trees (Juniperus seravschanica, Juniperus turkestanica and Juniperus semiglobosa) are rarely rejuvenating under conditions of intensive grazing and are difficult to propagate in nurseries. The technology describes the propagation of these important trees from locally collected seeds and their cultivation.
- 编制者: Stefan Michel
模块
无模块