2.1 该方法的简要说明
Individual farmer seeking information and experimenting with machinery to maintain economic viability
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: Maintenance of economic viability; seeking not to replace employee.
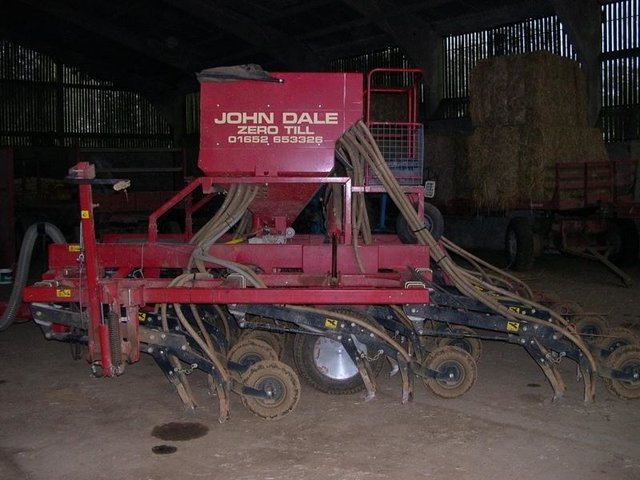
Methods: Seeking information from open days, agricultural shows, machinery manufacturers, demonstrations, other farmers in UK and overseas; experimented with drill on own farm before purchase.
Stages of implementation: Stages of implementation: information seeking over 6 months, trialled drill in one crop, hired drill for following crop on sale and return, purchase of new drill in 2002.
2.3 该方法的照片
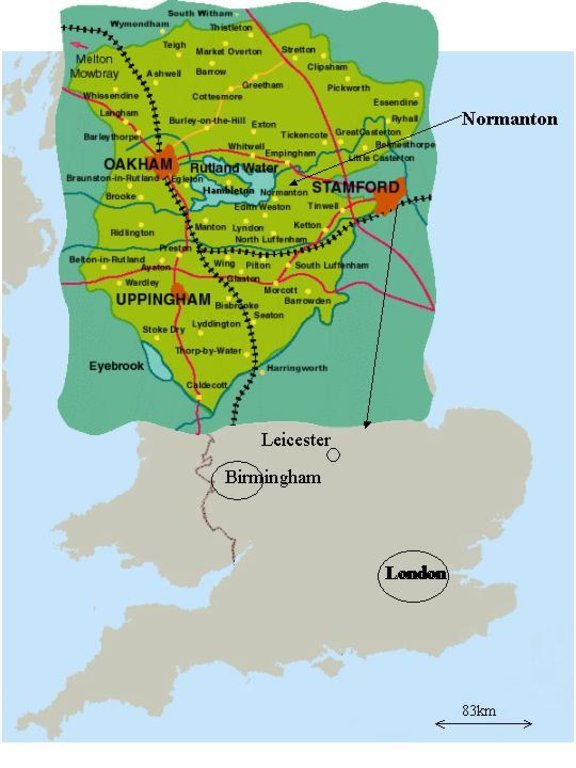
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (economic viability)
To find appropriate machinery to maintain economic viability
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Loss of ploughman and desire not to replace him but retain economic viability.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
farmer conservatism
Treatment through the SLM Approach: seeking knowledge and advice;willingess to take risks; family support
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
machinery costs; desire to to replace lost employee
Treatment through the SLM Approach: preparation of sound financial case
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
Dependent on farmer attitude.
了解SLM,获得技术支持
lack of appropriate expertise
Treatment through the SLM Approach: sought advice from a number of sources