In "situ" Decomposition of Banana Stalk [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
"Palata System"
technologies_1020 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Rondal Jose
-6329230459
joserondal@yahoo.com
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Elliptical Road, Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
18/10/2006
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
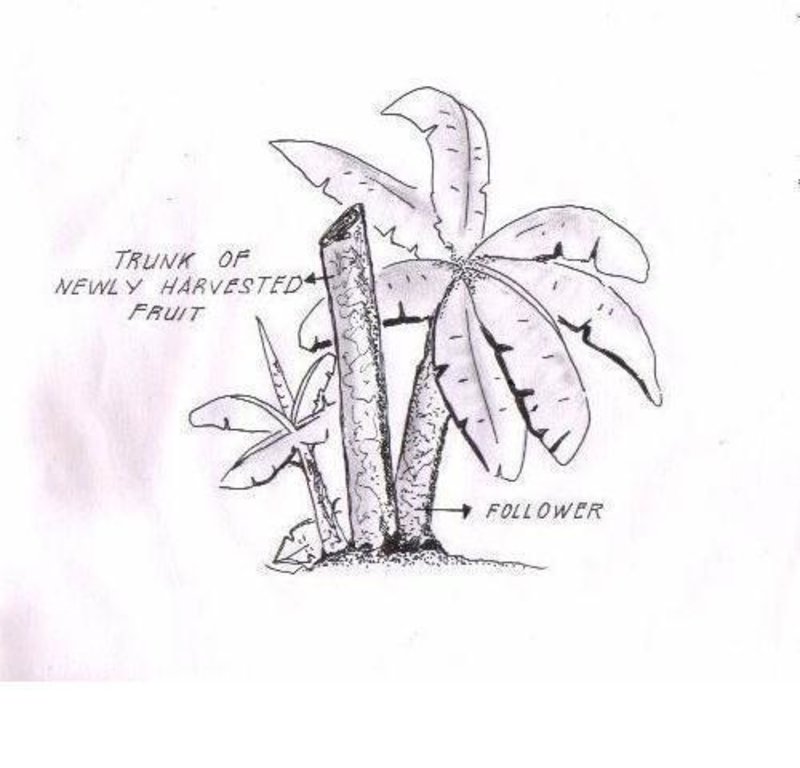
技术定义:
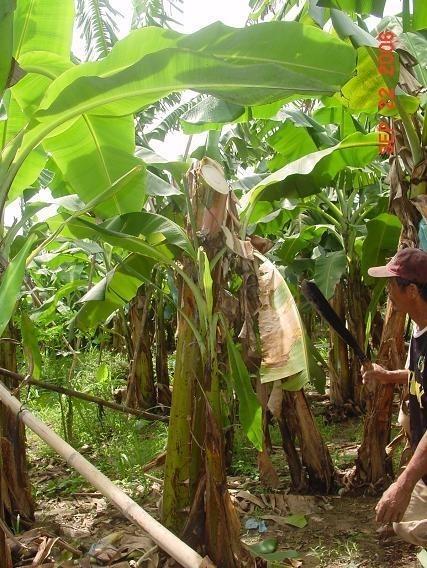
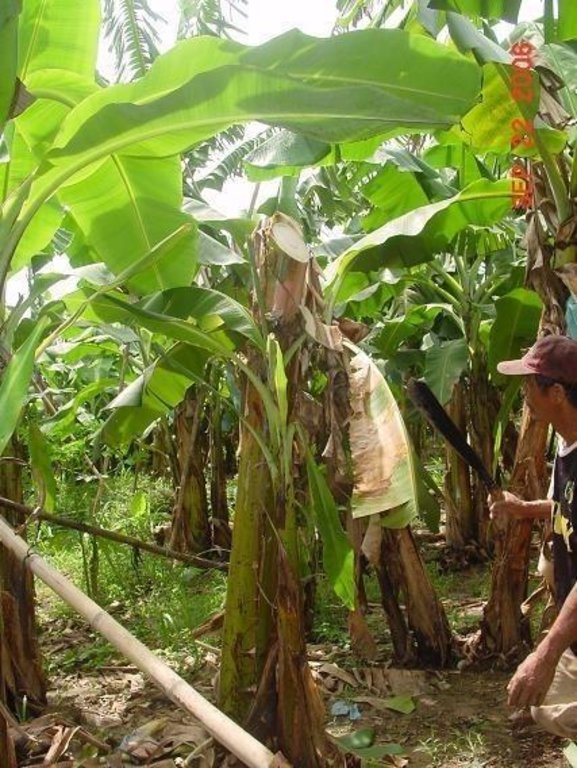
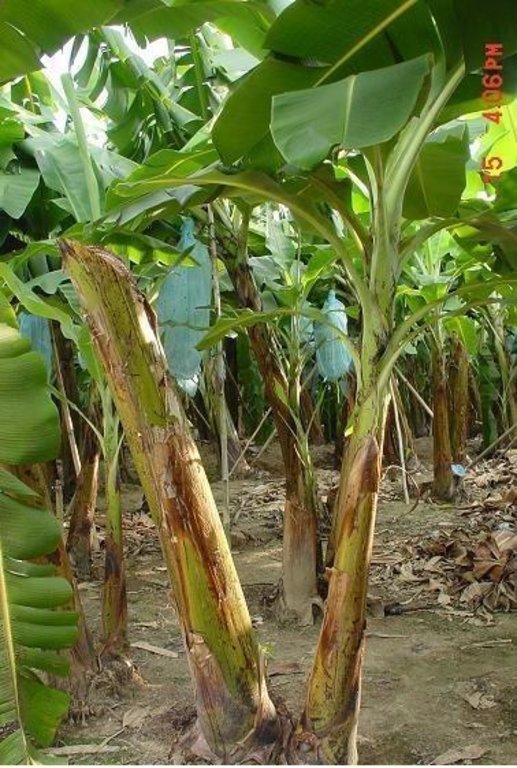
Leaving the trunk of a newly harvested banana standing beside a follower plant to provide nutrients and moisture especially during period of drought.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Traditionally, banana is cut at the base (ground level) during harvesting and the stem is used as mulch. This has been the practice of the banana plantations for many years. Lately however, it was found out by research that by leaving the trunk standing beside a follower plant, yield could be improved because the trunk contains nutrients and moisture which could be used by the succeeding plants. The banana crown is cut just below the fruit and the leaves used as mulch. After a few months the trunk disintegrates and decomposes and the follower plants grow unimpeded utilizing the nutrients and moisture contained in the decomposing trunk..
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
有关地点的进一步说明:
Davao del Norte, Maguindanao, Comval Province
Map
×2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop: Banana
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Large requirement of banana for nutrients and moisture which is insufficient during period of drought.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Decreasing yield due to nutrient depletion and the frequent occurrence of drought
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
注释:
Water supply: mixed rainfed - irrigated, full irrigation
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 270 Longest growing period from month to month: May - Feb
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 集水
- Improoving yield by leaving the trunk of a harvested plant stand beside a follower plant
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 14 m2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Date: 9-15-2006
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase in soil fertility
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: trunk of harvested banana
Quantity/ density: 2,200 plan
Remarks: In rows
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.00
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting of crown of newly harvested plant | 农业学的 | harvest time / annual |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | person-days | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 | |
| 设备 | Tools | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 60.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: 5 big knives
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Based on the plant population per hectare.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
2500.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
When El Nino occurs (abnormally low rainfall from 1001-1500mm)
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (Banana plantations are in the lowland)
Landforms: plateau/plains (Mostly coastal and alluvial plains)
Slopes: flat and gentle (All commercial banana plantations are on level land)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth: very deep >120cm ( Soils are alluvium-derived, hence, very deep )
Soil texture: medium (loamy, silty) and fine/heavy (clay) (loamy because of the influence of river alluvium )
Soil fertility is low: Natural fertility is depleted due to continuous cropping
Topsoil organic matter: medium (1-3%) and high (>3%) (Depleted due to long period of intensive use )
Soil drainage/ infiltration is good to medium (Loamy soils with good permeability)
Soil water storage is medium to low (Not much clay and organic matter)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
60% of the land users are rich and own 60% of the land (Multi-national company).
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land (Land owners/growers).
Off-farm income specification: For small time growers, they work in the banana processing plant. For some, their children have other employment, either locally or abroad.
Level of mechanization: Land preparation
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Size of cropland for households: 2-5ha
Size of cropland for companies 500-100ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 公司
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
little (5-20%) - Practice is just a few years old
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
medium (20-50%) - Due to decrease in fertilizer input
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
just at the base of the follower plant
其它生态影响
increase in soil fertility
注释/具体说明:
little (5-20%) - Just at the base of the follower plant
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
- 大于 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
100 land user families/households
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 50-90%
注释:
70% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
100 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The beneficial effect has been proven in increasing yield and in input cost reduction.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Easy to apply and practically no added cost How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sustained IEC |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Easy to apply How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sustained IEC |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Perpetuation of disease for affected plants. | Plant eradication. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| It could be a way by which pests and diseases multipl. | Burning or proper disposal of plants affected by disease. |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块