Transport of freshwater from local streams [希腊]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: John Gkiougkis
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Μεταφορά γλυκού από γειτονικά αρδευτικά κανάλια
technologies_1042 - 希腊
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Pechtelidis Alexandros
Democritus University of Thrace
Vasilissis Sofias 12, Xanthi 671 00, Greece
希腊
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Democritus University of Thrace (Democritus University of Thrace) - 希腊1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
10/06/2011
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Combating Soil Salinization [希腊]
Use of freshwater to combat soil salinization.
- 编制者: John Gkiougkis
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
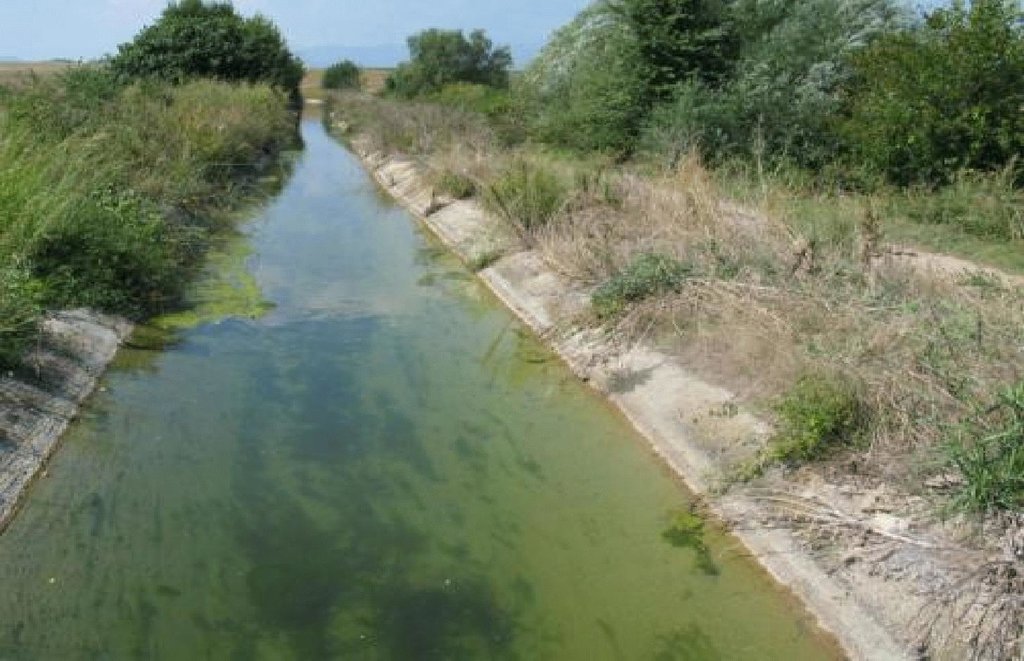
Freshwater transport from local streams for irrigation purposes, in order to replace the traditional form of irrigation (by pumping saline groundwater from wells).
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
In low-lying regions suffering from overuse of the ground water for irrigation and seawater intrusion, pumping groundwater is detrimental and results in soil degradation (salinization) and reduced plant growth.
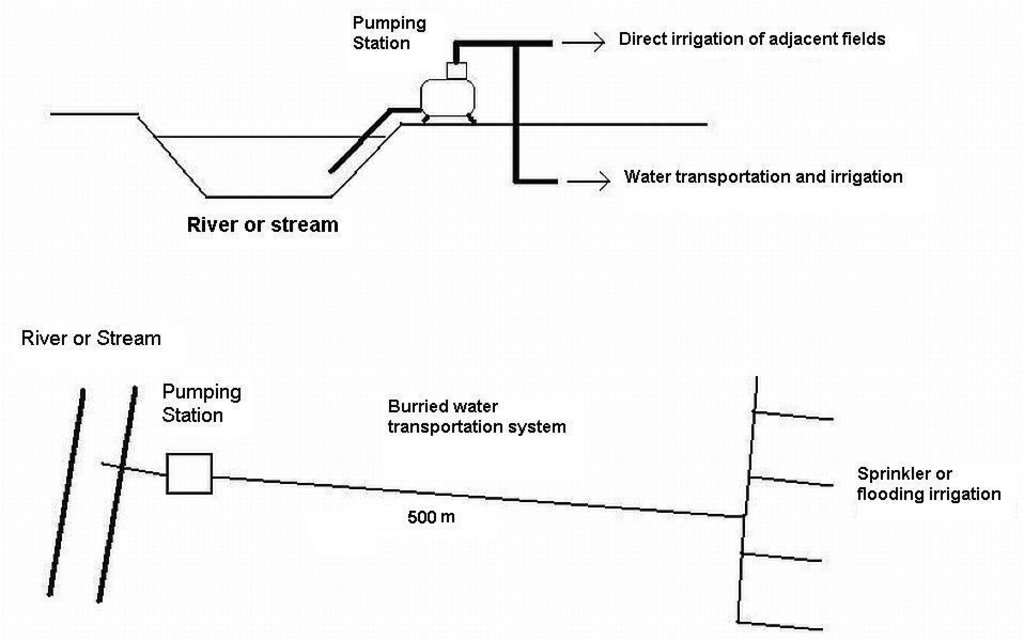
Purpose of the Technology: For this reason, freshwater is transported over distances of up to 500 m (or more) from surface streams, for irrigation using water of better quality. In this way, overexploitation of the aquifer is being reduced.
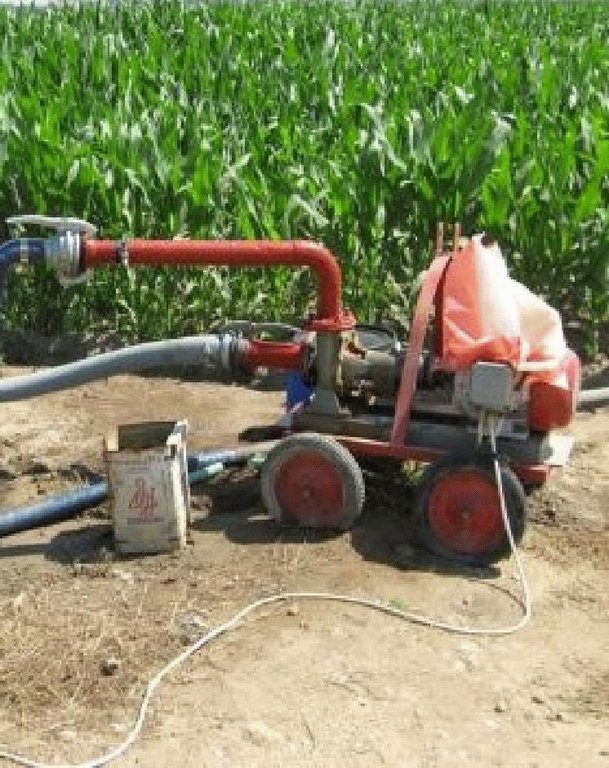
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The pumps transfer water from canals or streams for irrigation purposes. A pumping station (10HP), pipes (PP-R, Ø 1100mm) for water transport and diesel or electricity for pump operation are the major items needed to replace groundwater with freshwater irrigation. However, annual maintenance of the pump and network is necessary.
Natural / human environment: The majority of families living in the research area make their living mostly from agricultural activities but also from livestock. Croplands are dominantly irrigated by wells (groundwater) and only those which are close to streams are irrigated with freshwater. Owing to over-pumping of the aquifer in order to irrigate the crop fields, there has been seawater intrusion over the past years. As a result, irrigation with groundwater led to saline soils. The group affected by this process comprises farmers who are now beginning to understand the extent of the desertification problem in the area. The degradation process significantly affects the quality of life of the local people. Saline soils lead to low productivity and thus to lower incomes (causing poverty) and thus an increase in social unrest. Although the farmers are totally aware of the on-going degradation problem that affects their fields and their livelihoods, they seem to be unwilling to change the way they irrigate their fields (with groundwater) as long as they do not have an alternative source of irrigation such as freshwater from local streams. The lack of information about how the salt-affected fields can be restored also makes the farmers believe that this situation is permanent and will extend over a wider area.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
希腊
区域/州/省:
Prefecture of Xanthi
有关地点的进一步说明:
Eastern Macedonia and Thrace
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop annual cropping: Maize, cotton, wheat
Major food crop annual cropping: Maize, wheat
Major cash crop perennial (non-woody) cropping: Clover
Other crops perennial (non-woody) cropping: Clover
Major cash crop tree/shrub cropping: Olive trees
Major food crop tree/shrub cropping: Olives
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil salinization and sodification.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil salinization.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
注释:
Water supply: mixed rainfed - irrigated, full irrigation
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 100Longest growing period from month to month: April to August
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 9.59 m2.
Areas adjacent to freshwater surface streams.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M7:其它
注释:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cs:盐化/碱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation
Main causes of degradation: disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (overexploitation of groundwater), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.) (overexploitation of groundwater), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers of the area, poor soil drainage), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (lack of freshwater supply network), increased pressure on groundwater for irrigation
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (higher temperature), change of seasonal rainfall (reduced rainfall), droughts (climate change)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Scheme showing the SLM technology application
Location: Eastern Nestos Delta River Basin. Prefecture of Xanthi
Date: 14/03/2010
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water spreading, replacing saline groundwater with surface freshwater, reduce pressure/overexploitation on aquifer
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase of infiltration, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Agronomic measure: soil desalinization
Material/ species: freshwater
Remarks: salinity leaching
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
euro
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
0.7
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | construction of irrigation network | 农业学的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | Irrigation network | 1.0 | 969.0 | 969.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | hire of an ecavator | Irrigation network | 1.0 | 1107.0 | 1107.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Pumping station | Irrigation network | 1.0 | 3460.0 | 3460.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Water transport pipes | Irrigation network | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 其它 | Diesel fuel (1 Lt) | Liter | 1.0 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Electricity (1 Kw) | Liter | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 5537.8 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
Life span of the irrigation network: Lifetime
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Network maintenance | 农业学的 | annualy |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | Irrigation network | 1.0 | 138.0 | 138.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hire of an ecavator | Irrigation network | 1.0 | 275.0 | 275.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Pumpiong station | Irrigation network | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | diesl fuel or erlectricity | Irrigation network | 1.0 | 1512.0 | 1512.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 2125.0 | |||||
注释:
The above costs are calculated on May, 2011.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Diesel or electricity price affects the final cost.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate. Mediterranean type climatic conditions
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (Below 10m (plain costal region))
Landforms: Plateau/plains (Plain costal region)
Slopes on average: Flat (Plain region)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low-medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor/none (hard-pan formation, crusting and water repellency)
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: on surface (near the coastline or/and adjucent to Nestos river), < 5 m (the rest of Nestos river basin)
Water quality (untreated) is for agricultural use only (irrigation) (Occassionaly wastewater discharges from upstrem factories)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Coastal wetlands with high biodiversity
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Animal breeders or/and factories workers.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 1-2 ha, 2-5 ha, 5-15 ha (very few individuals)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
3.4t/ha
SLM之后的数量:
4.2t/ha
注释/具体说明:
Increased, but: Sodic soils may first require gypsoum application
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Less salinity risk
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Due to increased demand for freshwater
灌溉用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
Due to increased demand for freshwater
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
Freshwater for irrigation from streams/river
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Requires funding for implementation
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Better crop quality
其它社会经济效应
Demand for groundwater
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Income increase and thus well-being.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
For sodic soils
土壤
土壤结壳/密封
盐度
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Due to water abstraction from streams/river for irrigation
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
Due to reduced groundwater exploitation
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
注释:
The benefits are obvious from the first year of application of the SLM technology and the maintenance cost is logical.
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
50
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
50 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The remaining area (50 %) is irrigated with groundwater.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Better yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Application of fertilizers |
|
More income due to improved crop quality How can they be sustained / enhanced? Selection of crop type |
|
Better future perspective for the area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Financial motives |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Increased irrigation water quality which result in better soil quality How can they be sustained / enhanced? Construction of more irrigation canals |
|
Remediation of soils How can they be sustained / enhanced? Better drainage systems |
|
Groundwater recharge How can they be sustained / enhanced? Construction of more irrigation canals |
|
Improved quality/quantity of yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Selection of the most suitable crop type |
|
Improved livelihood of the locals How can they be sustained / enhanced? Better local products promotion |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Bureaucratic problems | Promotion of fast track financial programs |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Installation cost | Financial aid from government/EU |
| Applicable only for fields adjacent or very close to a fresh water source | Construction of canals |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Gkiougkis I. et. al. (2010) Proceedings of the 12th International Congress, Geological Society of Greece, Patras, May, 2010
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Combating Soil Salinization [希腊]
Use of freshwater to combat soil salinization.
- 编制者: John Gkiougkis
模块
无模块