double dug beds - Busia experience [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
technologies_1095 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
05/07/1999
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
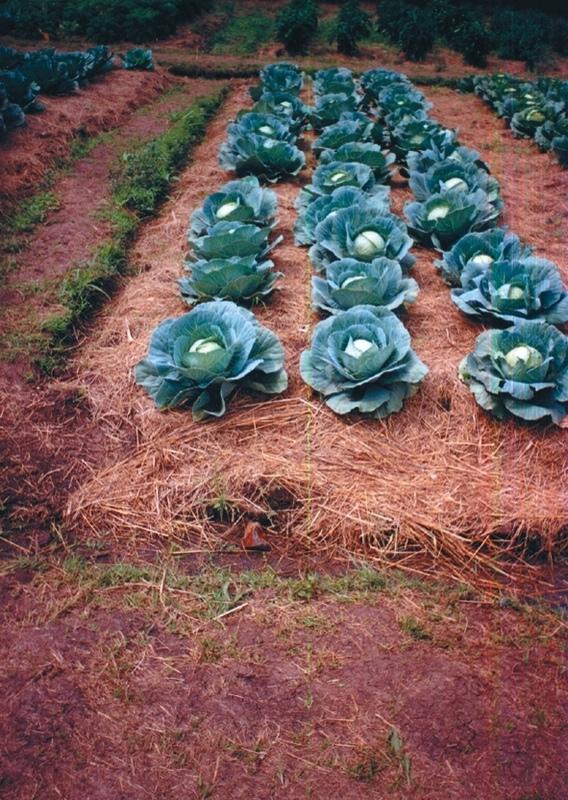
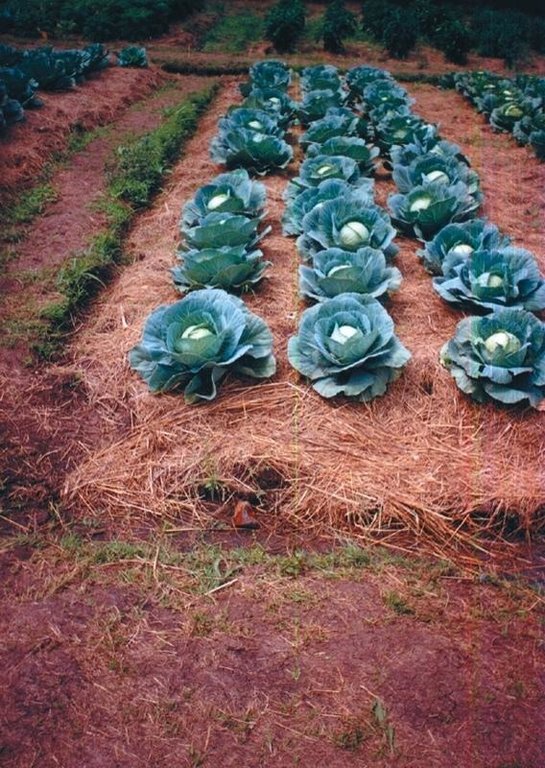
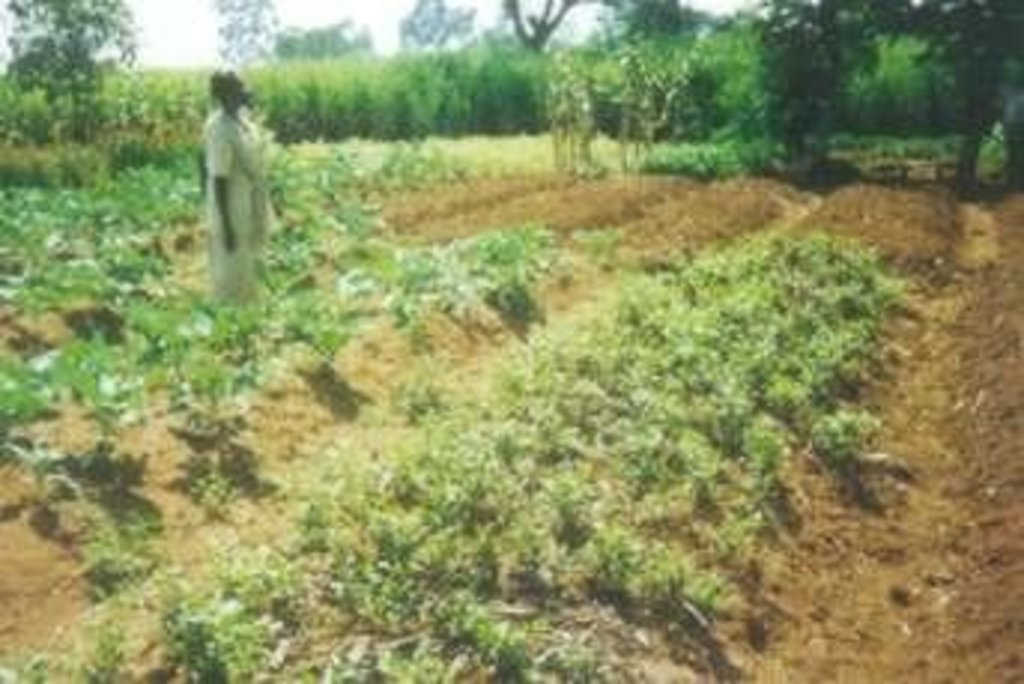
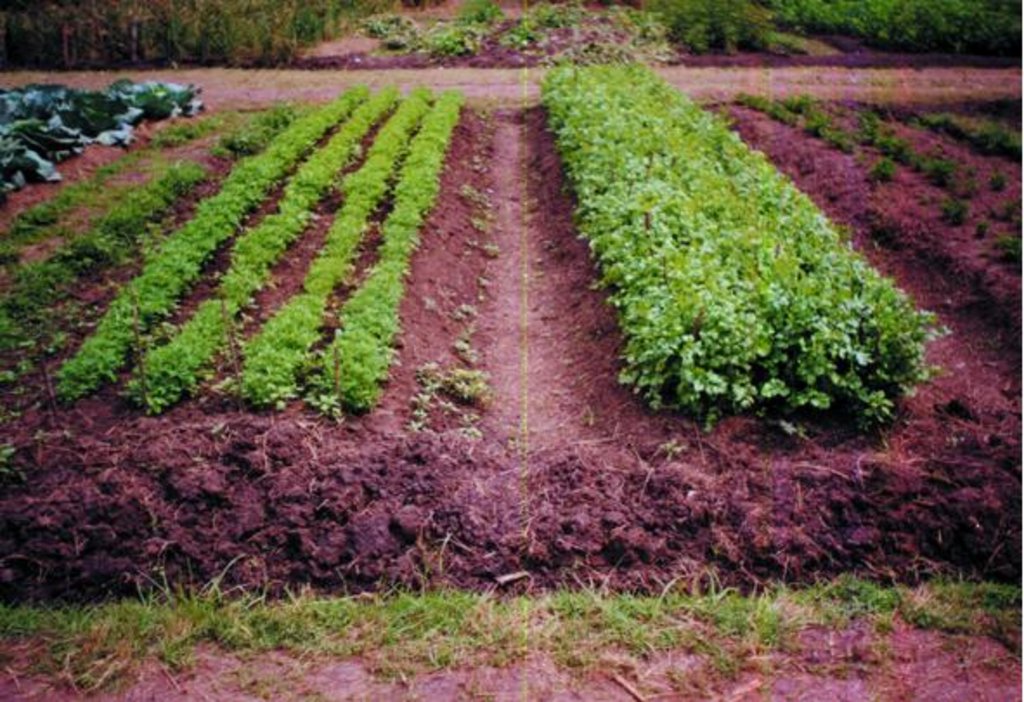
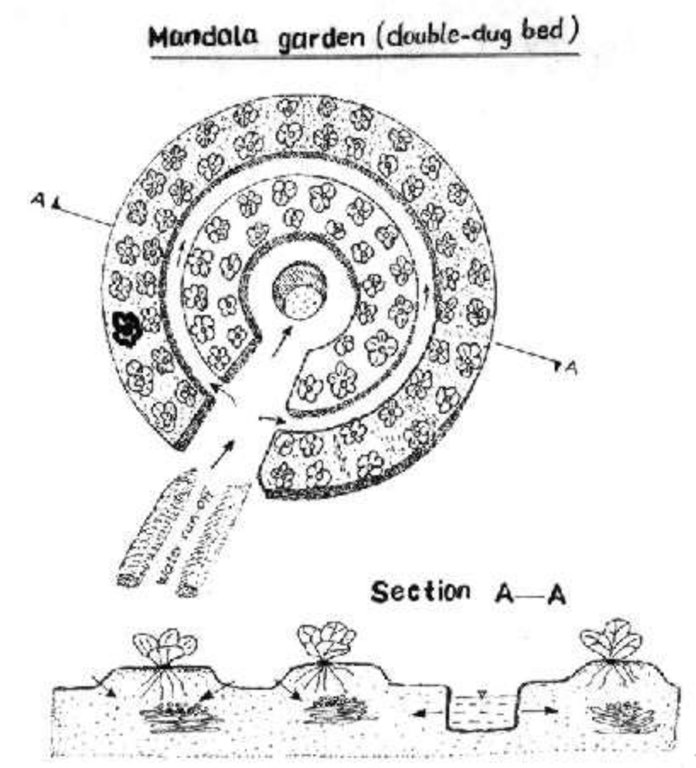
Digging of planting beds to increase soil depth for higher moisture retention in the rootzone.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
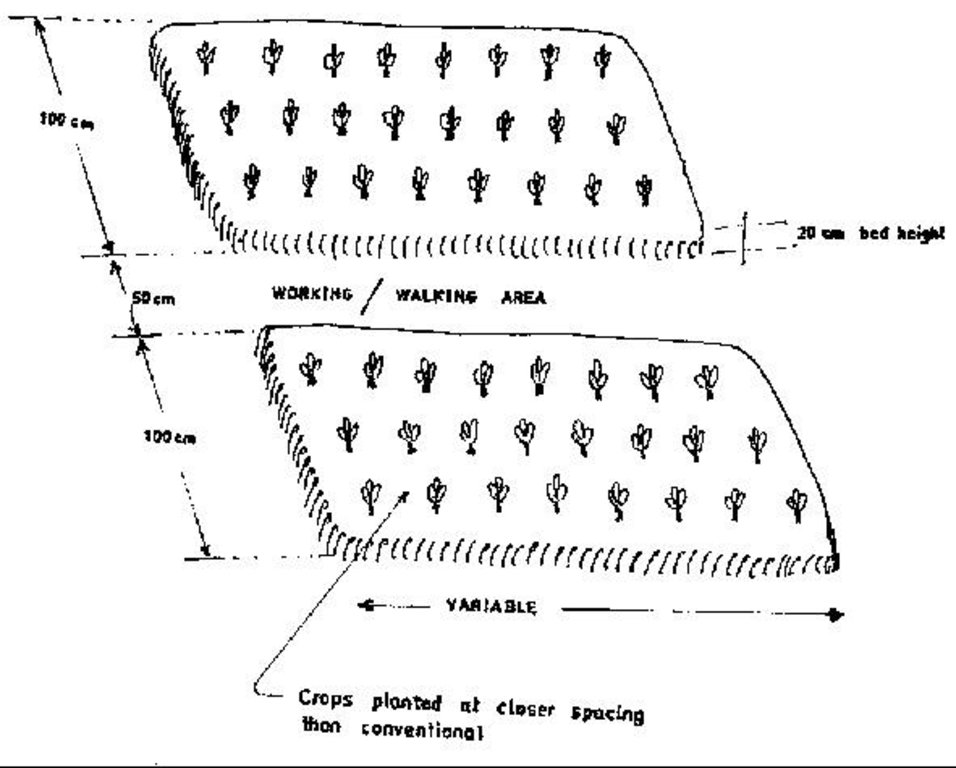
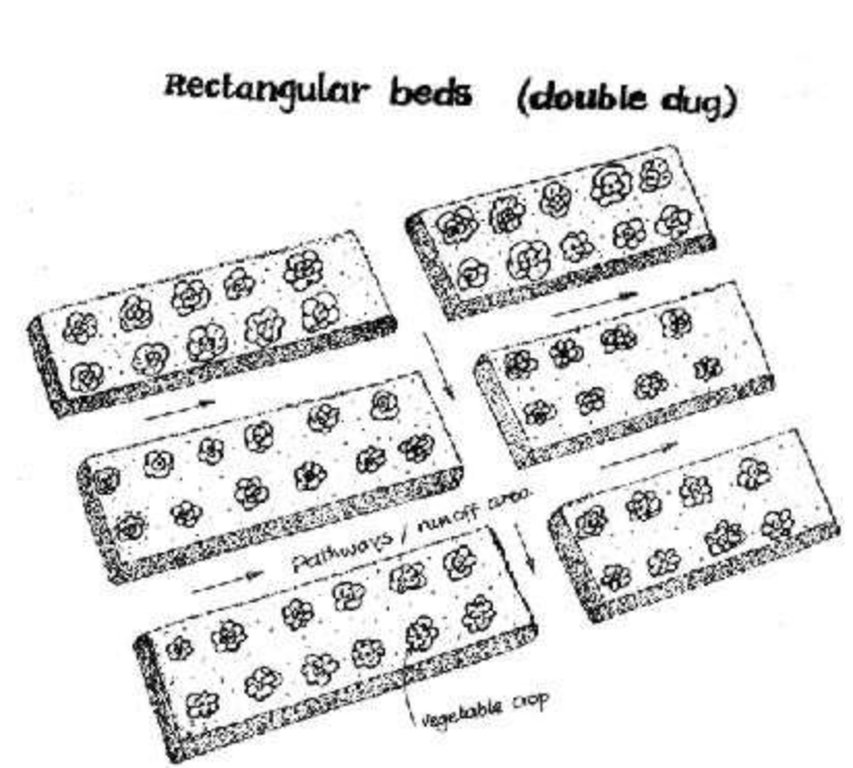
Description: Excavating the planting bed to remove the infertile sub-soil and separate the top soil. The top soi is later mixed with farm yard manure and returned into the excauated are to form the planting bed. Purpose: Improvement of water retention and root zone storage through increased depth of soil. Helps to increase the yields of crops. Maintenance: Involves repairing the shoulders of the raised beds and addition of organic manures to improve fertility. Environment: Suitable for vegetable gardens around the dweling areas but can be adopted for field crops with high value. Areas with rock outcrops and shallow underlying rocks are not suitable due to limited depth.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Western/ Busia
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Kenya Institute of Organic Farming - Kabete, Nairobi
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - Poor soil fertility, Shallow soil depth limiting penetration, Striga weed problem.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Poor soil moisture availability - Unavailability of production inputs.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Shifting cultivation: major food crop = maize, cotton
fallow cultivation: major food crop = maize / cassava
continuous cropping: major cash crop = cotton, major food crop = sorghum, other = maize / cassava
ley farming: major cash crop = sugarcane
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also full irrigation
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - JulSecond longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Nov
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1.5 m2.
the technology is being practiced in the district. The practice is spatially scattered within the divisions where other technologies are also being practiced.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: deep tillage / double digging
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (soils with poor moisture retention leading to erratic cropping pattern), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge)
Secondary causes of degradation: poverty / wealth (Lack of captial - quite a high number of people are poor.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: The bed width need to be narrowto allow ease of operations by attendant
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Kenya shilling
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
65.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
0.80
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | layout of seedbeds | 结构性的 | |
| 2. | Excavation to remove the top soil | 结构性的 | Dry season |
| 3. | Excavation to remove the subsoil | 结构性的 | Dry season |
| 4. | mixing top soil with manure | 结构性的 | Dry season |
| 5. | returning the mixture to the excavated bed | 结构性的 | Dry season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | .Layout of planting beds | 农业学的 | Dry season / Whenever necessary |
| 2. | Excavation to remove top soil | 农业学的 | Dry season / |
| 3. | Excavation to remove subsoil | 农业学的 | Dry season / once for all |
| 4. | Mixing top soil with manure | 农业学的 | Dry season / As necessary |
| 5. | returning the mixture to the excavated bed | 农业学的 | Dry season / once for all |
| 6. | repairing raised edges of tillage beds | 结构性的 | dry season/every season |
| 7. | digging in manure | 结构性的 | dry season/on demand |
| 8. | mulch application | 结构性的 | all year/during cropping |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
area of land affected by the technology (beds)
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour is the most important and is abudant, at a cost of KES 50 or U$ 0.8 per man day. Opportunities of group work can be employed to reduce total cost of technology establishment.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Annual rainfall: Also 1,501-2,000 mm
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: gentle
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil texture: sandy, clay, loam
Soil fertility is low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - good
Soil water storage capacity is low - medium
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
5% of the land users are rich and own 5% of the land (dwell in towns).
35% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land (rely on land /off farm employment).
60% of the land users are poor and own 55% of the land (have no other form of income except land).
Off-farm income specification: due to poor soils and low moisture availability for crop production most people rely on off farm employment for survival
Level of mechanization: tsefly problem has reduced oxen population and there are availability and affordability problems for many years for mechanised cultivation.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
15
SLM之后的数量:
5
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 10-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
190 households
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: for projects and groups as for women, seeking income generating activities
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Water Conservation and harvesting - A minor Field Study.. 2001.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
SWCB, MOARD Nairobi, Kenya
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块