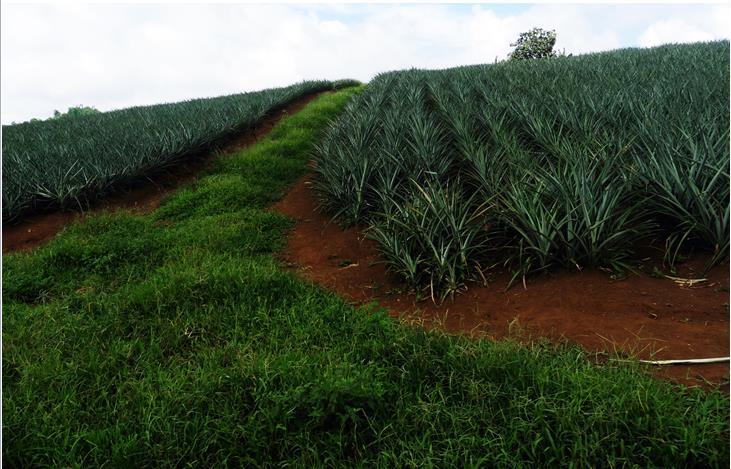
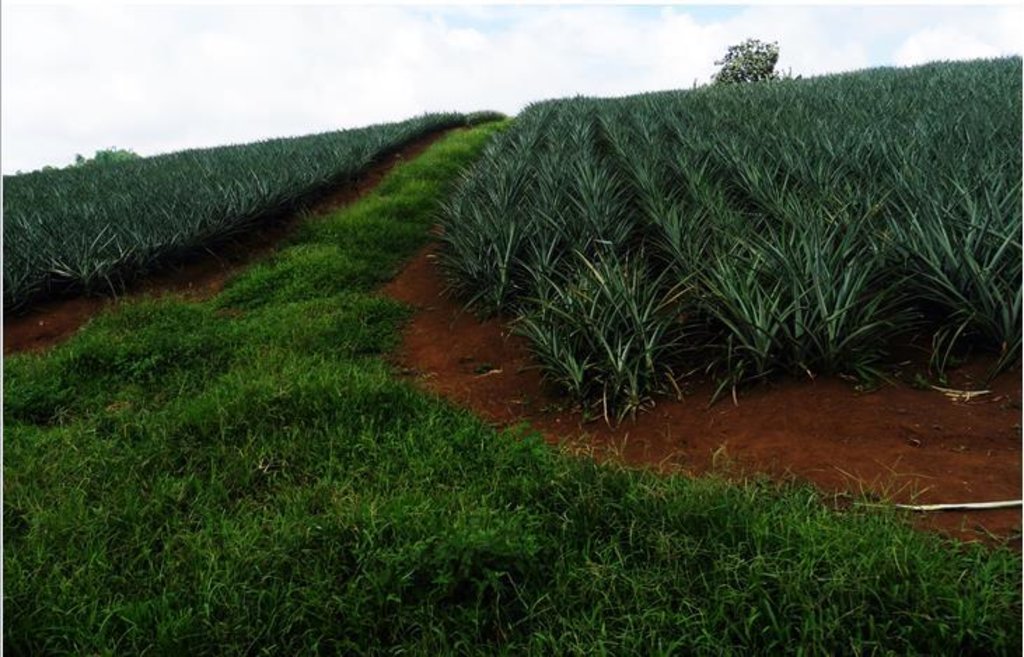
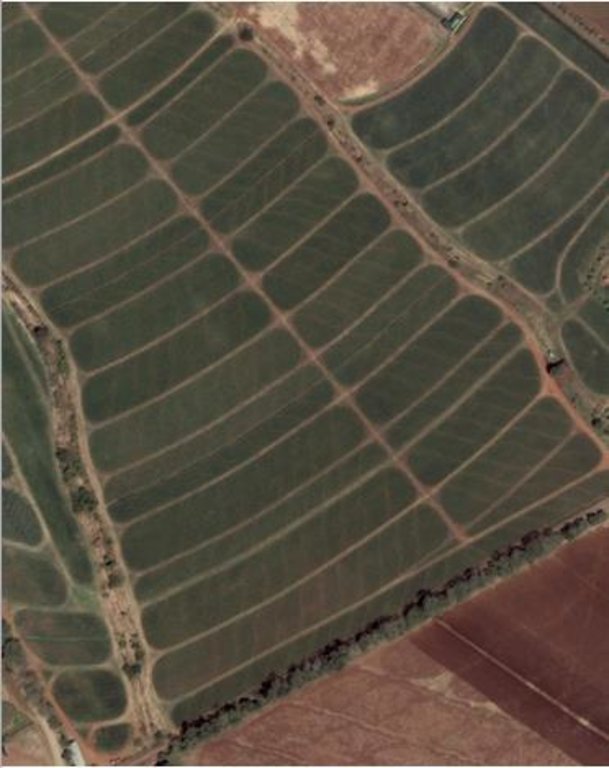
Contour Straight Block Layout [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: Baldwin Pine
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1308 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Manubag Jerry
(088) 221 4302
manubagjerry@gmail.com
Mt. Kitanglad and Agri Development Corporation
Brgy. Lurugan, Valencia City,
菲律宾
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Mt. Kitanglad and Agri Development Corporation (MKADC) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
15/07/2015
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Approach in Improving … [菲律宾]
Integration of soil and water conservation technologies primarily aim to protect the area from loss of biodiversity and land degradation.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
It is a package of soil and water conservation technology that integrates contouring, bedding, and blocking.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The main commodity used in the area is pineapple planted in each bed within blocks. Each block contains around 23-25 beds. Spaces between blocks with a dimension of 2-3 meters (width) served as vegetative strips where grass is being utilized and maintained. Grass as natural vegetative strips served as control for soil erosion by water. Vegetative strips are used as roads for accessibility purposes in times of planting and harvesting season. Pineapple production would last for 18-20 months for normal season and these requires massive land preparation. Plowing is done through a modified moldboard plow.
Purpose of the Technology: Pineapple were planted in beds within blocks, which is efficient and effective in water-induced soil erosion control.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Deep plowing,around one meter deep is a normal practice in the area. This practice would ensure proper root development of pineapple which is crucial for their growth; also it ensures re-introduction of pineapple trashes from the previous cropping as organic matter. Next activity is harrowing, which is usually done twice to pulverize the soil. Plastic mulching is a also a practice after bedding to suppress weeds and conserve water. Weeding is done manually. Foliar fertilizer spraying is done to induce flowering.
Natural / human environment: The area is under humid agro-climate condition with a topography ranging from 1-10% slope. It receives an annual average rainfall of approximately 3072 mm/year. The elevation ranges from 370-890 meter above sea level.
Mt. Kitanglad and Agri Development Corporation (MKADC) operates the area where the technology are being practiced. The technology has been introduced through experiments and adoption from neighboring farms. Farmers living within the area are the laborers of the company, they do all needed activities during preparation of the land, planting and harvesting.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Valencia City, Bukidnon
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
The company through its own initiative, they made a trial and error experiments in designing the layout of the pineapple plantation, including how the vegetative strips will be laid out. In addition, they obtained designs from other farms that practiced soil and water conservation practice and they try to modify it.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop: pineapple
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Presence of hardpan which causes water logging, this has an adverse effect on the growth and harvest rate of pineapple.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
具体说明:
Longest growing period from month to month: growing period is 18 monthsSecond longest growing period from month to month: ratooning would last for 24 months
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Approximately 6-7 square kilometer
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: relay cropping, contour planting / strip cropping, mulching, rotations / fallows, breaking crust / sealed surface
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: soil management, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), land tenure
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), change of seasonal rainfall, labour availability
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
作者:
Patricio Yambot
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Each bed is within blocks. Vegetative strips width is approximately 2-3 meters. Contour lines with an approximate 0.5 meters width served as diversion ditches.
Location: Luguran, Valencia City Bukidnon
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Technical knowledge required for farmer level: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Relay cropping
Material/ species: pineapple
Remarks: in beds within contoured blocks
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: pineapple
Mulching
Material/ species: plastic mulching
Remarks: in each bed
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: grassland
Breaking crust / sealed surface
Material/ species: modified molboard plow
Remarks: plowed accross the slope
In blocks
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 2000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Perennial crops species: pineapple
Layout change according to natural and human environment: the technology follows a fallow period.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Philippine peso
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
46.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
6.50
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of vegetative strips. Vegetative strips has been prepared and laid out during land preparation ( agronomic measures) and is part of the paid labor . | 植物性的 | |
| 2. | Plowing, also included the preparation of vegetative strips. | 植物性的 | |
| 3. | Harrowing | 农业学的 | |
| 4. | Bedding | 农业学的 | |
| 5. | Mulching | 农业学的 | |
| 6. | Planting | 农业学的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labourer | ha | 1.0 | 143.0 | 143.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 225.0 | 225.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Pineapple strings | ha | 217.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 368.0 | |||||
注释:
Equipement needed for plowing, harrowing and bedding
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ratooning | 农业学的 | 1 |
| 2. | Spraying | 农业学的 | As needs arise |
| 3. | Weeding | 农业学的 | As needs arise |
| 4. | Fertilizer Application | 农业学的 | As needs arise but normally one to three times per cropping season |
| 5. | Harvesting | 农业学的 | Once or twice per cropping season |
| 6. | Trimming of grasses | 植物性的 | As needs arise |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labourer | ha | 1.0 | 279.0 | 279.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 279.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Mouldboard plough
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Planting materials and labour
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
3072 (Annual Average Rainfall)
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes: gentle to moderate (The area ranges from 1-10% slope, 5-8 % Slope is dominant in the area.)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Level of mechanization: Mechanized/motorized (Mechanized land preparation (through the use of mouldboard plough) is mostly done in the area.)
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Market Orientation: Mixed (subsistence/commercial) Products were both marketed and consumed by land owners, some products that did not qualify quality standards were served as feeds for animals.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
冲突缓解
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
yes, greatly
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 不好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Mt. Kitanglad and Agri Development Corporation (MKADC) operates the area where the technology are being practiced. The technology has been introduced through experiments and adoption from neighboring farms.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Good for erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continued practice of the technology |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Ease of establishing the technology. How can they be sustained / enhanced? More scientific research |
| Transferrability/ Acceptability |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| More researches should be done to prove the effectiveness and efficiency of the technology as soil and water conservation technology. | Allow research authorities to conduct researches in their farm. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Somehow labor intensive | Mechanization but should be regulated, productivity of the soil should not be compromised. |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Approach in Improving … [菲律宾]
Integration of soil and water conservation technologies primarily aim to protect the area from loss of biodiversity and land degradation.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
模块
无模块