Improved pasture under citrus [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Pastulan sa ilalim ng dalanghitaan (Filipino)
technologies_1321 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Rojales Jose
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Calonge Arsenio
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Millare Kirby
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Quinto Jasmin
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Gultiano Wilfredo
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
Cornes Jennelyn Mae
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
菲律宾
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
29/06/2016
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Soil Conservation Guided Farm System [菲律宾]
Soil Conservation Guided Farming System (SCGFS) is a land use management approach that integrates technologies: terracing, agro-pastoral technology, multi-storey cropping, and contouring within the socio-economic and bio-physical limitations of upland areas for optimum development of soil and water resource in a sustainable manner.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
It is a farming system that integrates the growing of fodder crops under plantation crops.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
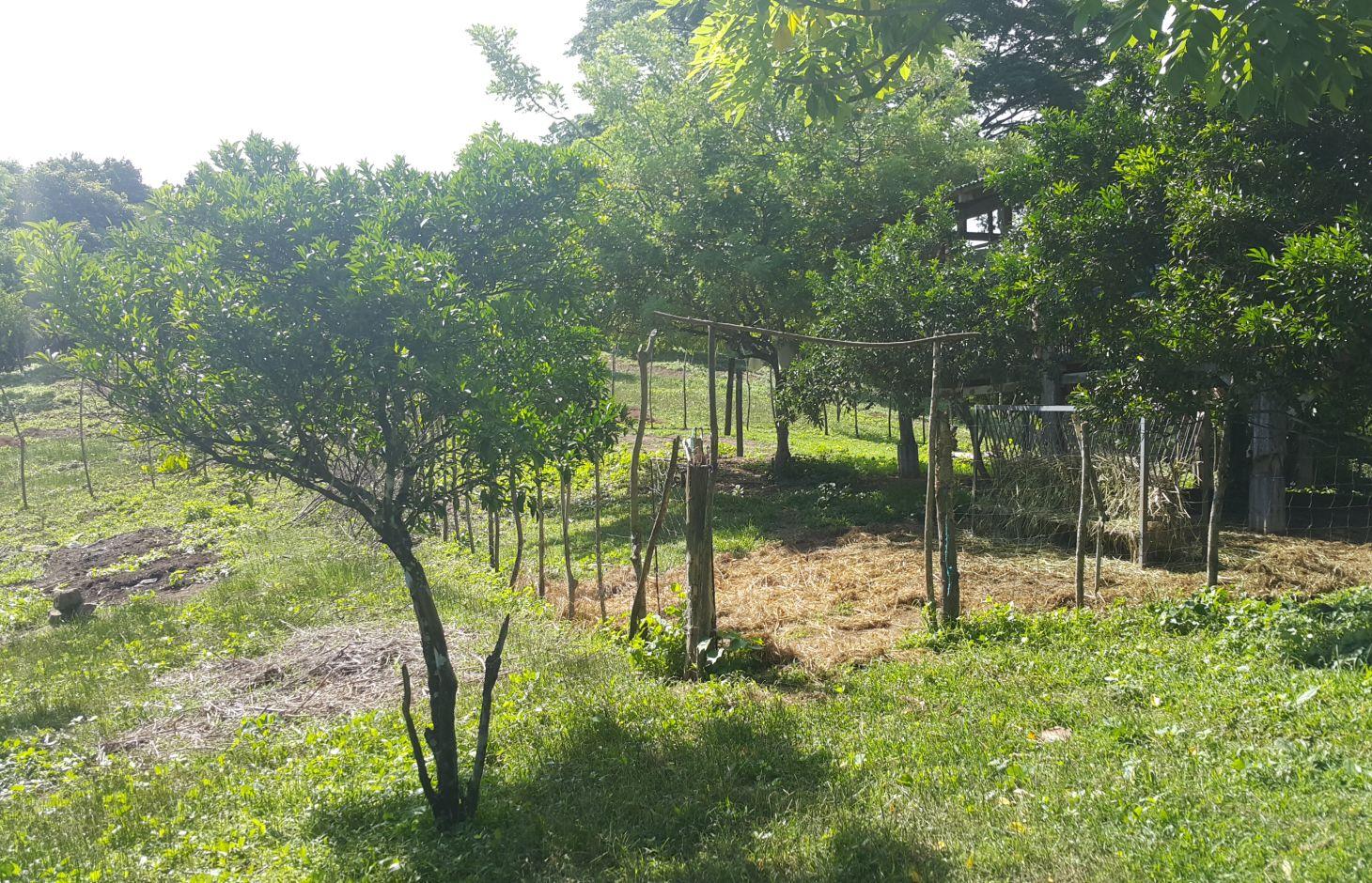
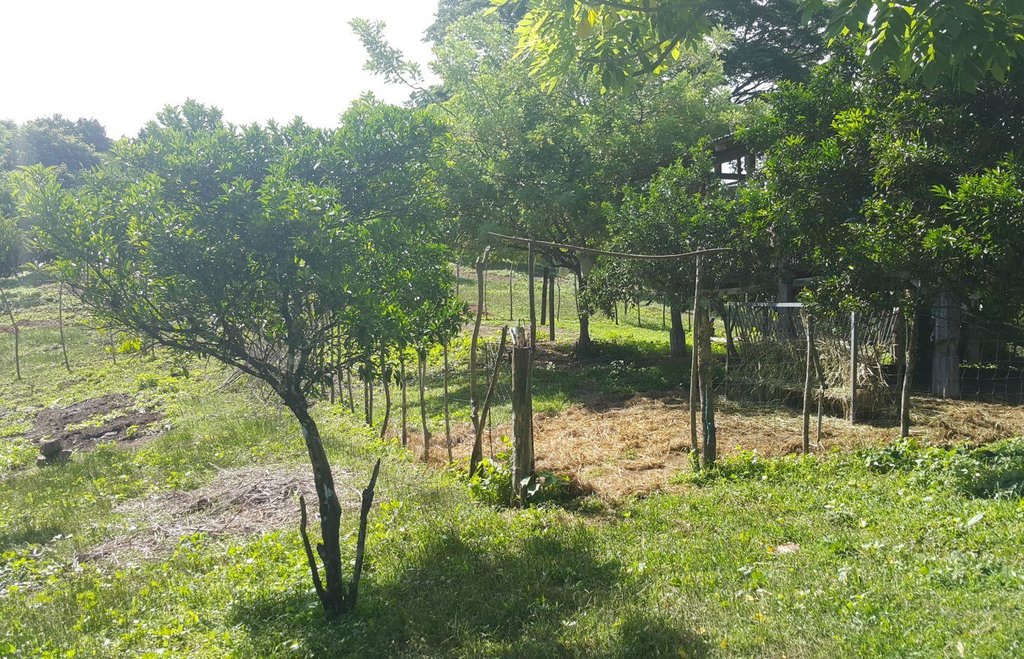
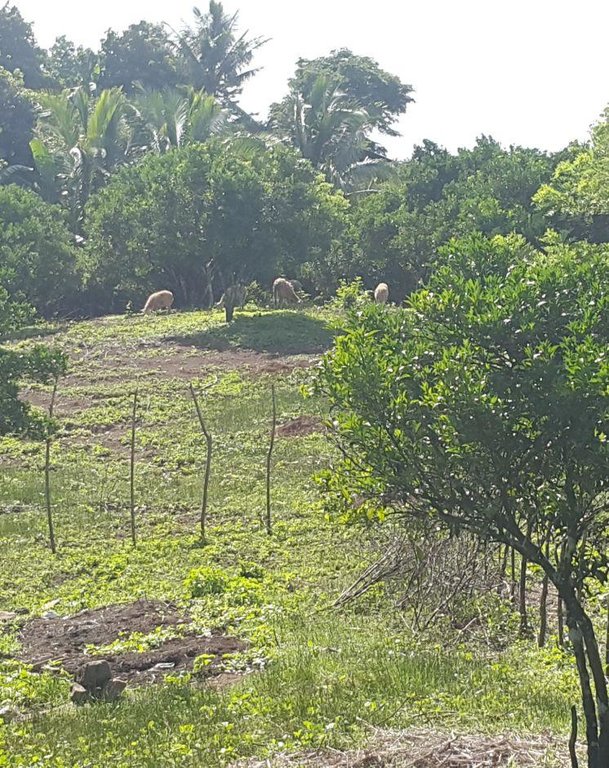
It is an integration of livestock and agronomic crop production of incorporating small ruminants in an existing citrus plantation. This technology was based on the private initiative of the farmer where he adapted it from other land users. He further improved it through study of reading materials and ad hoc monitoring of his environment.
Purpose of the Technology: After the adaption of the technology, the land user observed a decrease in the infestation of aphids. The land user observed and concluded that the decline in the aphids infestation was due to the presence of the small ruminants in the area. The small ruminants forage on grasses that were continuously growing, year-round, in the plantation area. The foraging of grasses improved the micro-environment of the plantation crop, which contributed to the decline and almost total eradication of aphids in the area, as observed by the land user. This promoted natural farming and improved the biodiversity.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The area was first established as a citrus plantation inter-cropped with Vigna unguiculata, Cucurbita maxima, and Ipomoea batatas, as cash crop during the vegetative stage of the citrus crop. As the small ruminants increased in number, the land user decided to do “controlled grazing” by dividing the area into 3 paddocks. During lean days of forage grasses, the land user practices “cut-and-carry” system of feeding. In addition, the manure of the small ruminants serves as a source of organic fertilizer for the citrus and other crops grown by the land user.
Natural / human environment: Aside from the eradication of the aphids on the citrus crop, the technology aided in the financial needs of the land user. It increased the land user’s income by an increase in the fruits bore by the crop and the increase in the number of the small ruminants. The land user sells or sometimes suppliers of citrus fruit and goat meat would go to the area to do wholesale buying. As for the community near the area, they to benefit from the area, by wholesale buying the citrus fruit and be the one selling it to the market. The technology does not only contribute to the livelihood improvement of the land user but also to the community.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Bulacan
有关地点的进一步说明:
City of San Jose Del Monte
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- experience from other farm land user
注释(项目类型等):
8 years
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop:
Citrus

牧场
- Silvo-pastoralism
主要动物种类及产品:
Goat and sheep grazing in combination
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Possibility of pollution in the area. The land user might have applied pesticide to the citrus crops to control the pest, but the land user did not mention of it. Application of herbicide to control the growth of grasses within and outside the area.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Without land conservation, there was an occurrence of pest in the citrus plants.
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): silvo-pastoralism, goat and sheep grazing in combination
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Ms: Silvo-pastoralism
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: July to November
牲畜密度(如相关):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农畜综合管理
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.08 m2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

生物性退化
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (intercropping planting), droughts (time frame of drought)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (grazing of small ruminants), overgrazing (no. of small ruminants), change in temperature (dry season time frame)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Third goal: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
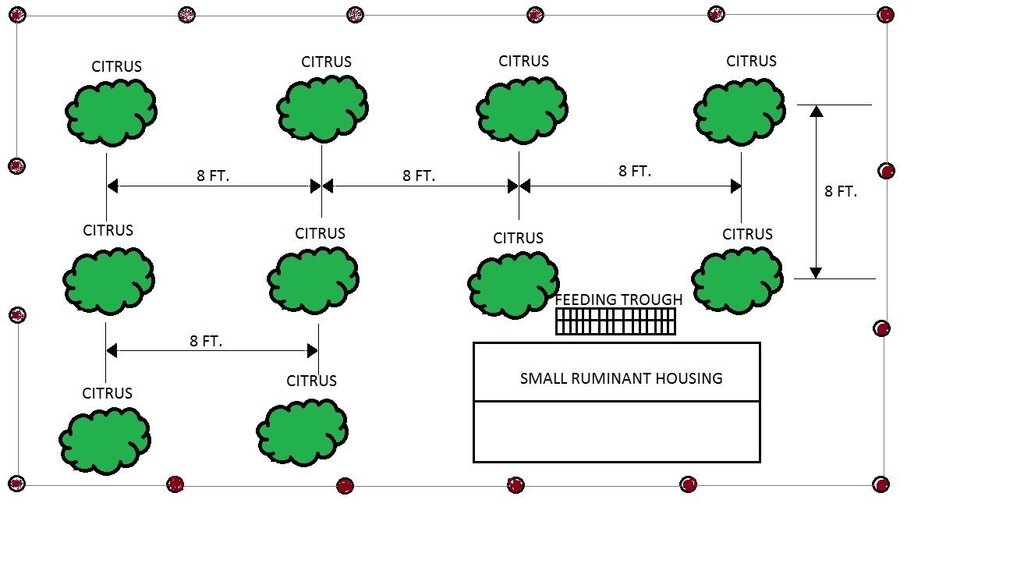
Citrus plants are evenly distributed in the area, with a planting distance of 8 feet by 8 feet. The ground cover are forage grasses for the small ruminants.
Location: Barangay San Roque. San Jose Del Monte, Bulacan
Date: 06/29/2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (technical assistance from agricultural advisory from other aspect in land degradation)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (land user is open minded with the technology introduced)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, increase of surface roughness, increase of infiltration, reduction in wind speed, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: pole sitao-squash-sweet potato/citrus
Agronomic measure: intercropping (1st Year)
Material/ species: pole sitao/citrus
Quantity/ density: 2,000/188
Agronomic measure: intercropping (2nd year)
Material/ species: squash/ citrus
Quantity/ density: 2,000/188
Agronomic measure: intercropping (3rd year)
Material/ species: sweet potato/ citrus
Quantity/ density: 8,800/188
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: goat manure
Quantity/ density: 5,000 kg
Remarks: .5 per square meter
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Philippine Peso
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
47.5
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.26
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | rotational grazing | 植物性的 | rainy season |
| 2. | cut-and-carry feeding system | 植物性的 | dry season |
| 3. | Buying pole sitao | 农业学的 | |
| 4. | Buying sqaush | 农业学的 | |
| 5. | Buying citrus | 农业学的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 10.52 | 10.52 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 3160.0 | 3160.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 48.0 | 48.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Hog wire | ha | 1.0 | 397.89 | 397.89 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 3616.41 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
Life span of products:
Pole Sitao - 1 year
Squash - 1 year
Citrus - 50 years
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 10.52 | 10.52 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 10.52 | |||||
注释:
The above costs usually occurs during the dry season when forage grasses are scarce. Lean months of availability of forages grasses are from the months April to June. This is the time the cut-and-carry method is applied and the start of the maintenance/recurrent cost.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Cut-and-carry method of feeding the small ruminants during lean months of forage grasses.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
2382.00
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Ridges (concave)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is: Good
Soil water storage is: High
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: It is the countries socio-cultural model, where men is the one working and the women stay at home. According to the land user it is the women who is record keeper.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
10% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: off-farm income provides additional income to the land user during the dry season.
Market orientation: Subsistence (small ruminants are bought by the land user)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
3,000 kilograms
SLM之后的数量:
8,000 kilograms
畜牧生产
SLM之前的数量:
5
SLM之后的数量:
5
产品多样性
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
30,000
SLM之后的数量:
80,000
收入来源的多样性
工作量
其它社会经济效应
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
It gave an opportunity to the neighbors of the land user to work at the field, with pay. Thus, an added income to the neighbor of the land user. According to the land user, he was able to send his children to a decent school for a quality education. It also gave the land user another source of income by purchasing a jeepney used as a public transportation through the increased income from the SLM technogy he adapted.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
The increased in the income of the land user contributes to the food security of the family
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
Daily chores of herding the small ruminants contributes to the good over health of the land user
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Rotational grazing and "cut-and-carry" style of feeding contributed to the possible overgrazing which is contributor to erosion
冲突缓解
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
The land user allows the member of his community to harvest some fruits and sell them to the market without the land user asking for something in return.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Rotational grazing and "cut-and carry" style of feeding contributes to the reduction in surface runoff, grasses are maintained on the soil surface
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface reduced soil in any form
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Manure of the small ruminants contributes to nutrient recycling
盐度
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Manure of the small ruminants contributes to the increased in soil organic matter content
生物多样性:植被、动物
外来入侵物种
注释/具体说明:
Incorporation of small ruminants in the farming system which aid in the maintenance of grasses within the plantation area, helps improve the microclimatic condition inside the plantation area that further reduced alien species invasion
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Incorporation of small ruminants in the farming system which aid in the maintenance of grasses within the plantation area, helps improve the microclimatic condition inside the plantation area that further increased biological pest/disease control
减少气候和灾害风险
火灾风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface improves soil tilth which further improves infiltration capacity
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
Manure of the small ruminants improves the soil tilth, an improved soil tilth improves the buffering/filtering capacity of the soil
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface reduces erosion due to wind
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 未知 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Decreased in occurrence of pest |
| Increased land user's income |
| Helped the land user's neighbor by profit sharing during harvest of the citrus fruits |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Less labor input How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the varietal species of the forage grass |
|
Decreased in occurrence of pest How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain the existing micro environment |
| Rotational grazing |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| There was an inbreeding of the small ruminants | Putting another small ruminants of good genetic quality |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Variety of forage grass is of low quality in terms of crude protein content | Planting of improved variety with a high crude protein content |
| Species of small ruminants are not of good genetic quality in terms of meat quality | Putting of species with a good genetic quality in terms of meat produce |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Soil Conservation Guided Farm System [菲律宾]
Soil Conservation Guided Farming System (SCGFS) is a land use management approach that integrates technologies: terracing, agro-pastoral technology, multi-storey cropping, and contouring within the socio-economic and bio-physical limitations of upland areas for optimum development of soil and water resource in a sustainable manner.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
模块
无模块