Infilling of gullies with vegetative structures [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Daler Domullojonov
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
Пуркунии селрохахо
technologies_1450 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Barotov Bahrom
Welthungerhilfe
塔吉克斯坦
SLM专业人员:
Ashurov Bakhtiyor
Welthungerhilfe
塔吉克斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe e. V. (Welthungerhilfe) - 塔吉克斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/05/2011
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Reclamation and infilling of eroded gullies using barriers of willow branches and live mulberry cuttings to trap loess soil from surface water runoff.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
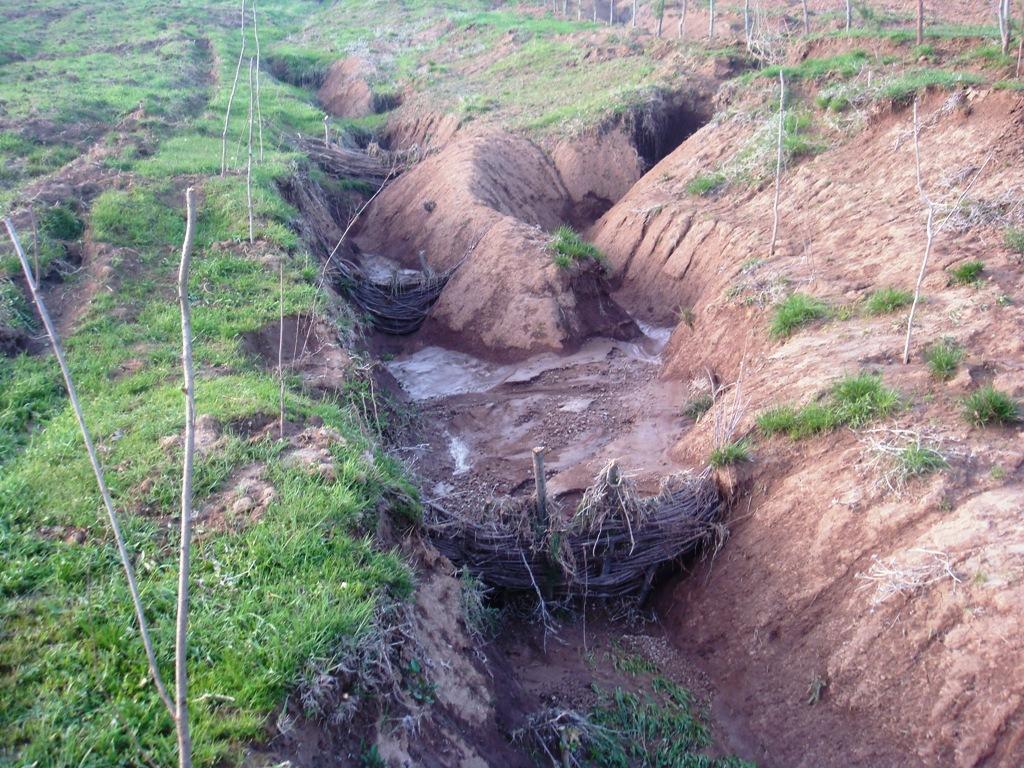
Due to many different factors and mechanisms, soil erosion is at an advanced stage in many of the hilly and mountainous parts of Tajikistan. After disrupting the soil cover in steep areas, starting the process of soil detachment and transportation water runoff gets concentrated into specific areas. As a result, rills develop on the steep areas, and eventually enlarge into gullies.
Purpose of the Technology: To address this problem, low cost barriers are constructed from flexible living branches of a sprouting variety of tree, such as willow. These branches are placed along the gulley at intervals of 3-10 metres, so that they slow down the flow of surface water and trap the sediment, thus eventually filling in the gulley over a period of several years.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The barriers are designed to slowly help infill eroded gullies by trapping the sediment from muddy surface water runoff. This helps prevent further erosion, increases the amount of land available for pasture, and reduces the risk of mud flows or floods further down the slope.
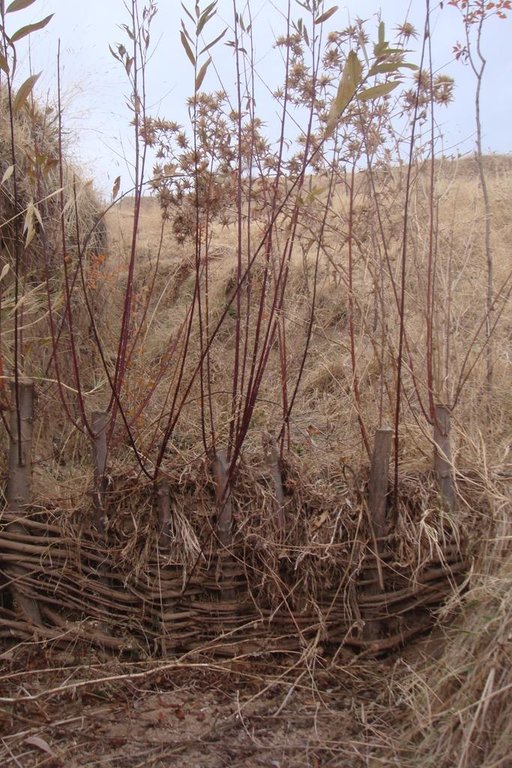
In gullies no wider than 1-2m, live cuttings from local tree varieties with a diameter of 3-5cm and 1 metre in length can be used to establish horizontal woven barriers across the gulley. The barriers are placed at 3-5m intervals along the gulley, starting at the base.
These barriers are constructed from cuttings that are woven in narrow sections with 5-6cm intervals between them. Enforcement and strengthening of these plugs can be achieved through the use of long branches of locally available mulberry. The height of the plug should not exceed 0.5m. The construction activities start in the spring and within several weeks some of the cuttings begin to sprout and grow. To avoid erosion at the sides of the structure, the cut offs are embedded into the sides of the gulley.
Natural / human environment: Gulley plugging is used in pasture land that suffers from overgrazing, deforestation and trampling, which has resulted in the degradation of the soil. Subsequently, the soil has become more vulnerable to the impact of heavy rain in the spring and autumn months, and is prone to erosion from surface water runoff.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Tajikistan / Khatlon
有关地点的进一步说明:
Khovaling / Dorobi
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology was developed and promoted using the framework of EC TACIS funded Welthungerhilfe project in Khatlon
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧场:
- 半游牧/游牧
主要动物种类及产品:
cows, goats, sheep
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing on pasture lands, that leads to reduced vegetation cover and deforestation, contributes greatly to the causes of top soil erosion and gulley formation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gullies are formed after intensive rainfall events. There is nothing in place to stop this erosion.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: cows, goats. sheep
Grazingland comments: There is local grazing on this land, but some areas are subjected to nomadic grazing during the migration of livestock between the winter and summer pastures.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of grazing system comments: There is local grazing on this land, but some areas are subjected to nomadic grazing during the migration of livestock between the winter and summer pastures.
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 160Longest growing period from month to month: March - June
牲畜密度(如相关):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.017 m2.
Approximately an 800 m long eroded gully was reclaimed.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S6:墙、障碍物、栅栏、围墙
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Trees were cut from a steep slope on the side of the hillside.), overgrazing (Freely grazed area, carrying capacity less than animal numbers grazing.)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (More intensive rainfall.), land tenure (Lack of control of livestock grazing activities.), poverty / wealth, war and conflicts (Gullies appeared after civil war.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
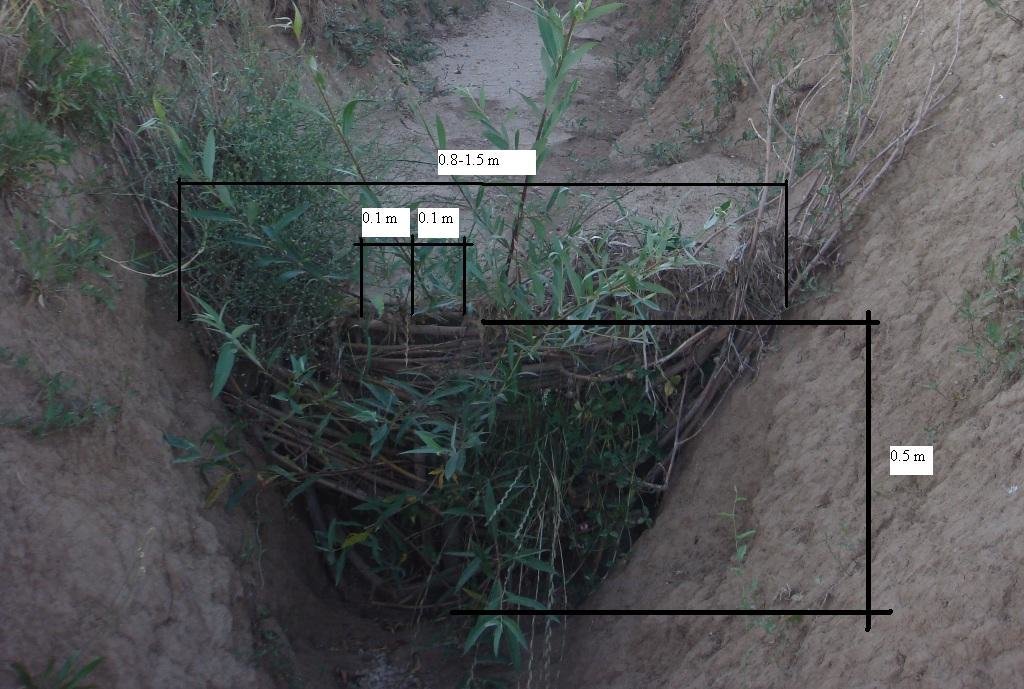
For the plugging of the gully, a low cost and simple barrier was made from locally available fast sprouting species of trees; in this case live willow cuttings were used. In the gully a narrow section was selected, and cuttings (3-5 cm diameter, 1 m length) were placed in a line with 10 cm intervals in between. One third of the cuttings were planted in the gulley, and the rest were used to create a 'wave' wall of flexible branches, which was planted with local mulberry trees (1-1.5 cm diameter). The weaved branches have to be pushed down from the top to make the barrier suitably dense. The ends of the mulberry branches have to be stuck securely to the soil inside the gulley.
Location: Dorobi village. Khovaling / Khatlon / Tajikistan
Date: 2nd July, 2010
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Trees/ shrubs species: mulberry
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3-5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Construction material (wood): Willow and mulberry branches
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Tajik Somoni
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
4.5
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.50 $
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | planting mulberry in willow wave structure | 植物性的 | spring |
| 2. | establishment of barriers in gully bed | 结构性的 | once in the beginning |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Planting mulberry | Persons/day | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Establishment of barriers in gully | Persons/day | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Mulberry seedlings | Pieces | 20.0 | 1.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Willow cuttings | Pieces | 20.0 | 1.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 90.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Reinforce structure with additional seedlings when needed | 植物性的 | annually |
| 2. | establishment of additional barriers after filling existing barriers with sediments | 结构性的 | once per year in beginning of rainy season |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Reinforce structure | Persons/day | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Establishment of additional barriers | Persons/day | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Mulberry seedlings | Pieces | 20.0 | 1.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Willow cuttings | Pieces | 20.0 | 1.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 90.0 | |||||
注释:
The unit cost is for a gulley plug, 1.5 metre wide and around 1m in height.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The materials used to construct the gulley plug are locally available, and are therefore free of charge to the land user. The labour (or time in labour) is the most substantial cost, and this is directly proportional to the number of gulley plugs required to infill the entire eroded gulley. If there is a big sediment load in the surface water runoff it will back fill behind the gulley plugs rapidly and additional barriers will need to be established.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Precipitation is concentrated during the autumn and spring, averaging 1100-1200mm
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate. 3 months below 5 degrees, 7 months above 10 degrees
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 1257 m a.s.l.
Slopes on average: Average slope 12.6%, max slope 17.2%
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil texture = loess soil
Soil fertility is low due to over use and lack of fallow time.
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water: In the area around the gulley the land is compacted.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 2%
20% of the land users are average wealthy.
80% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 租赁
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
The trees can be harvested once the gulley is full of sediment.
生产区域
SLM之前的数量:
1.5
SLM之后的数量:
1.6
注释/具体说明:
Gully filling can help create new areas of arable land.
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
Livelihood and human well-being
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Sediments are trapped
减少气候和灾害风险
滑坡/泥石流
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
缓冲/过滤能力
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
注释:
As a living barrier it needs to grow, and therefore it is sensitive to drought conditions.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 大于 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
10 households in an area of 1.7 ha
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is little trend towards (growing) spontaneous adoption of the technology.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
No training and additional skills are required. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Broad promotion to other communities with similar climatic conditions and similar issues. |
| It is low cost option. |
| Easy to establish, with a low workload. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Gulley plugs are relatively easy to construct and have a low initial outlay. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It could be further supported by the strong involvement of local authorities, through the organisation of cross visits, and disseminating ideas between farmers. |
| It is flexible as various varieties of local sprouting trees can be used to build the gulley plug. |
| It can prevent further erosion and expansion of the gulley. It can also increase the amount of land available for pasture activities. |
| Environmentally friendly |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The gulley plug is weak in the beginning as the mulberry trees become more established. It is more susceptible to the impact of heavy rainfall events and concentrated run off down the gulley. | High levels of maintenance in the first initial few seasons. |
| The gulley plug becomes less effective as the gullies become wider and deeper. | Fencing around the gulley. |
| The gulley plug has to be protected from livestock who will eat the vegetation. |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Welthungerhilfe project final narrative report (144-912) - 2010
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Welthungerhilfe projects in Khatlon region, Temurmalik district
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块