Silvi Pasture [印度]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Nursery
technologies_1470 - 印度
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Mewara Ramesh
印度
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
27/09/2002
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Comprehensive watershed development [印度]
Participatory approach that includes a package of measures leading to empowerment of communities to implement and sustain watershed development.
- 编制者: David Gandhi
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
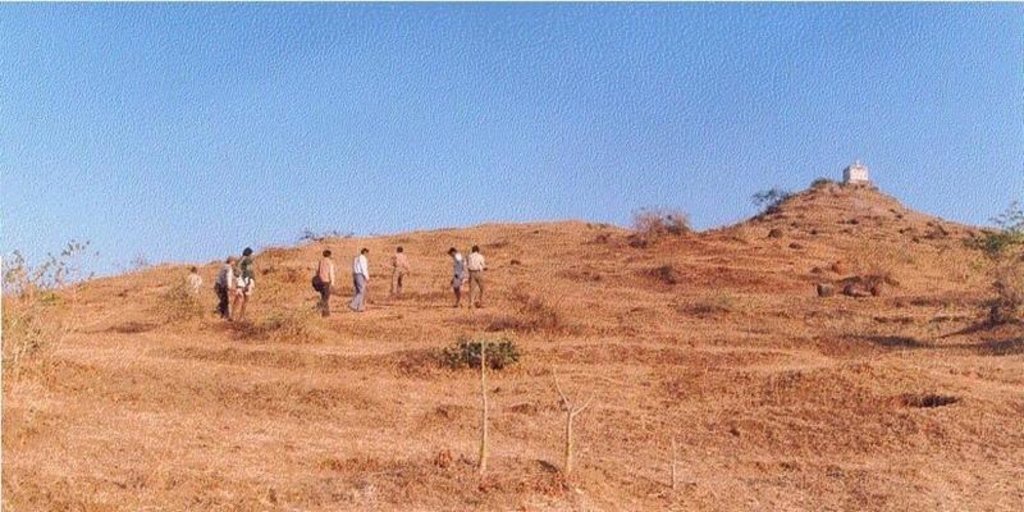
Regeneration of degraded hill side using structural, vegetative & managerial measures.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
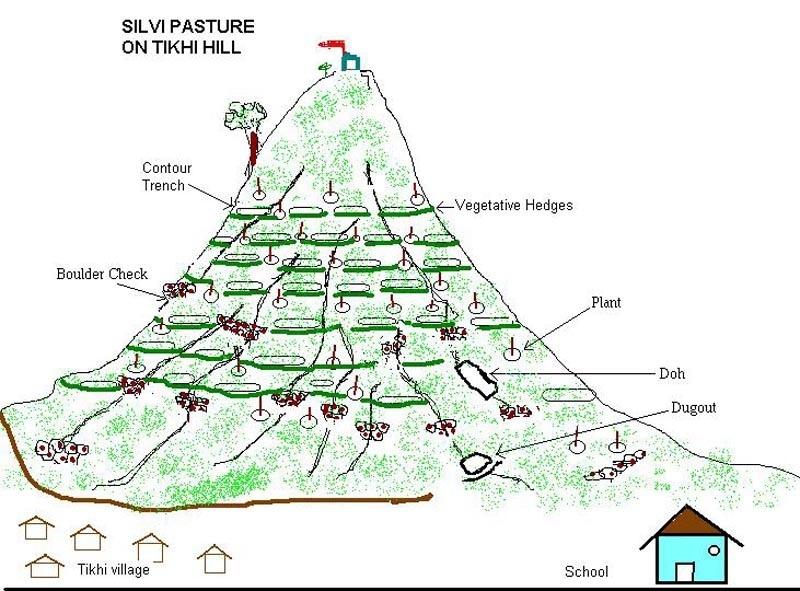
Managerial Measures : awareness generation amongst community, users groups, area closure, cut & carry system; Structural Measures :- contour trenches, gully plugs, sunken structure for run off and erosion control; Vegetative Measures :- seeding of grasses and shrubs, plantation of dryland fruit & forest tree species, vegetative barriers across slopes & gullies.
Purpose of the Technology: Short term benefits :- increased fodder availability, increase in well water levels, increased soil moisture in foot hill crop lands; Long term benefits :- environmental regeneration leading to increased production from non-arable & surrounding arable lands.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
印度
区域/州/省:
Madhya Pradesh
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Learning from visits to successful watershed development projects.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Grass land :- Degradation due to over grazing; Crop Land :- Low yeilds due to erosion, low soil moisture, improper cultivation practices on sloping lands.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low yields of grass and crops
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Mar
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 区域封闭(停止使用,支持恢复)
- 横坡措施
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 79.33 m2.
The project area comprises 26 villages (2286 HH) mainly tribal. A significant portion of the area is uncultivable waste which is used for open grazing. The technology "Silvi-Pasture" was implemented in few villages to demonstrate an integrated system of SWC and production.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Social causes - Lack of awareness and mobilisation amongst the communities.), Top down approach (Macro planning rather than micro (village level) planning.)
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
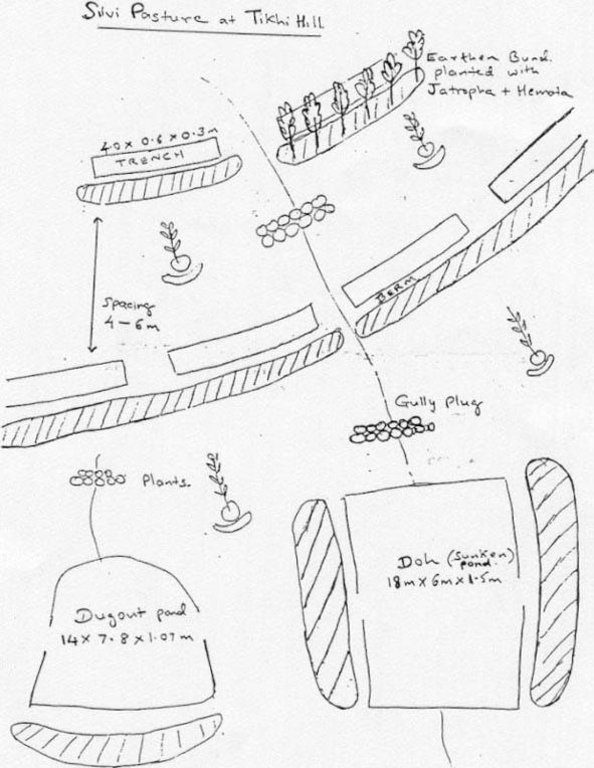
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical Drawing of SWC technology area, Tikhipada
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard
Trees/ shrubs species: Jatropha, Salai, Neem, Lantana
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Awla (goose berry)
Grass species: Stylo Hemata, Dicanthus(Dinanath)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 35.00%
Construction material (earth): Excavation of earth for trenches/ditchs/pans
Construction material (stone): Stone plugs in gullies
Construction material (other): Vegetative support to stone plugs & ditches
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 35%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: land use planning - Silvi Pasture
Change of land use practices / intensity level: land use change - Area Closure
Control / change of species composition: livestock management - Cut & carry system
Other type of management: Management by community( User Group)
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rupees
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
48.85
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of plantation pit | 植物性的 | Summer |
| 2. | Procurement of seeds, plants | 植物性的 | Before rainy sesion |
| 3. | Sowing of grass & shrub seeds | 植物性的 | Before Ist shower |
| 4. | Planting of saplings | 植物性的 | After Ist heavy shawer |
| 5. | Survey/Layout | 结构性的 | April (summer) |
| 6. | Excavation of ditches | 结构性的 | May |
| 7. | Transportation of stones to site | 结构性的 | May |
| 8. | Construction of sediment/sand trap | 结构性的 | May |
| 9. | Excavation of Pan(Doh) | 结构性的 | May 2nd year |
| 10. | Discussion with community & exposure visit | 管理 | Feb |
| 11. | Formation of users group, meeting, preparation of action plan | 管理 | March |
| 12. | Establishment of structural measures & training of users group | 管理 | April-Jun |
| 13. | Establishment of vegetative meassures | 管理 | July-Sep. |
| 14. | Area Closure | 管理 | April-Oct. |
| 15. | Harvesting & distribution of grass by users group | 管理 | Oct.-Nov. |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding , mulching | 植物性的 | 2-3 month after planting /Twice in year for Ist 2 year |
| 2. | Watering | 植物性的 | Dry season /During prolonged dry spells |
| 3. | Reseeding of grass/shrubs | 植物性的 | Before Ist shower /Upto 2 years |
| 4. | Casualty replacement | 植物性的 | After Ist heavy shower /Year 1 & II |
| 5. | Repair of breaches in ditches/traps | 结构性的 | July-Sep. during mansoon/As required |
| 6. | Construction of additional traps | 结构性的 | July-Sep. during mansoon/As required |
| 7. | Desilting of Ditches/traps/Pans | 结构性的 | Oct.-Nov. after mansoon/Annually |
| 8. | Refresher training of users group | 管理 | Seasonally / |
| 9. | Regular meeting of users group | 管理 | / 3 times/year |
| 10. | "Shramdan" ( Voluntary labour by usersfor maintenance) | 管理 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
The treatment covered an area of aroung 10 ha. 1- Contour Trenches - 6000 Rmt. 2- Large Boulder Check - 58 3- Small Boulder Check - 55 4- Dugout - 1 No. 5- Doh - 1 No. Seeding with jatropha, stylo and dinanath. Planting of saplings.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
1- Slope : - Due to steep slope , interval between contour trench lines was less; 2- Soil Depth : - Due to stony strata, excavation cost was high; 3- Material : - Boulders were transported from outside. 4- Lead/Lift : - Due to steep slope, labour output was less 5- Drought :- Replantation costs were high
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
800.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
However during 1999 to 2002 below average
农业气候带
- 半干旱
- 干旱
Semi arid (ranked1)
Arid (ranked 2, due to 3 years of below avg. rainfall, signs of desertification eg. thorny species, lowering of water levels in wells are apparent)
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1) and ridges (ranked 2, isolated hillcock)
Slopes on average: Steep (ranked 1, conical Shaped hillock - upper slope > 30%) and hilly (ranked 2, conical Shaped hillock - lower slope < 30%)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (highly eroded surface, exposed parent rock)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (weathered fragments(Kopra))
Soil fertility: Very low (absence of soil)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (absence of vegetation)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor (high runoff from stony surface)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low (high runoff from stony surface)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
18% of the land users are average wealthy (4 H.H.).
59% of the land users are poor (13 H.H.).
23% of the land users are poor (5 H.H.).
Off-farm income specification: Around 10% of the total income is from paid labour/migration
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
340 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Elemets of the technology have been adopted by land users eg. SWC, grass improvement. There is tremendous pressure on grass land due to large number of local cattle & goats, migratory herds of camel & sheeps. Hence spontaneous adoption is not observed since community mobilisation is essential as also efforts for user rights.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Comprehensive watershed development [印度]
Participatory approach that includes a package of measures leading to empowerment of communities to implement and sustain watershed development.
- 编制者: David Gandhi
模块
无模块