Rehabilitation of ancient terraces [秘鲁]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Andenes / Anchacas / Patapatas
technologies_1506 - 秘鲁
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Marquina Rodolfo
descolca@terra.com.pe;
Centro de Estudios y Promoción del Desarrollo – DESCO
Calle Málaga Grenet No. 678 Umacollo, Arequipa, Perú
秘鲁
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Centro de Estudios y Promoción del Desarrollo (DESCO) - 秘鲁1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/07/2002
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Participatory catchment rehabilitation (Participación comunitaria para la rehabilitación … [秘鲁]
Promoting the rehabilitation of ancient terrace systems based on a systematic watershed management approach.
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
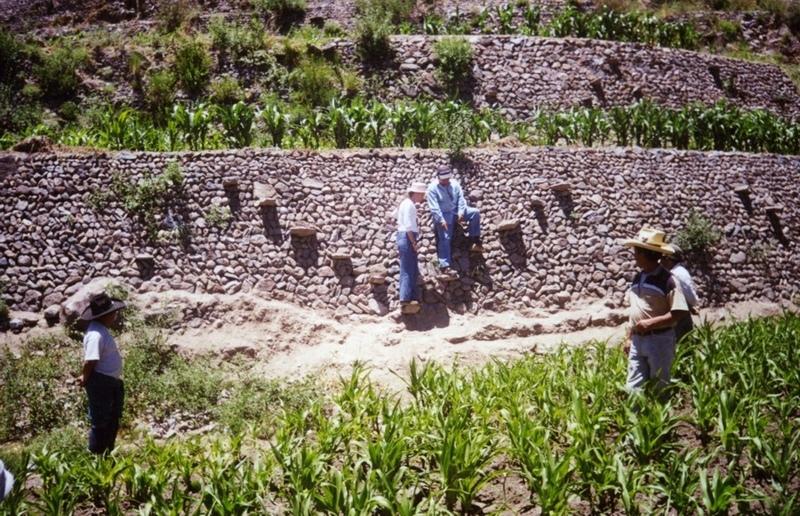
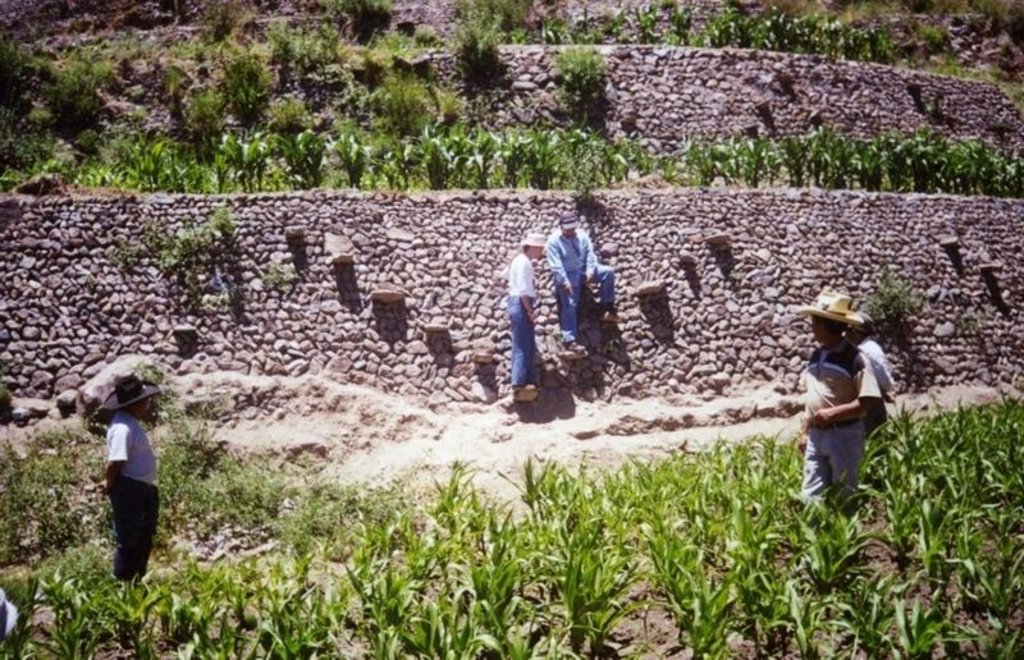
Repair of ancient stone wall bench terraces, and of an associated irrigation and drainage system.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
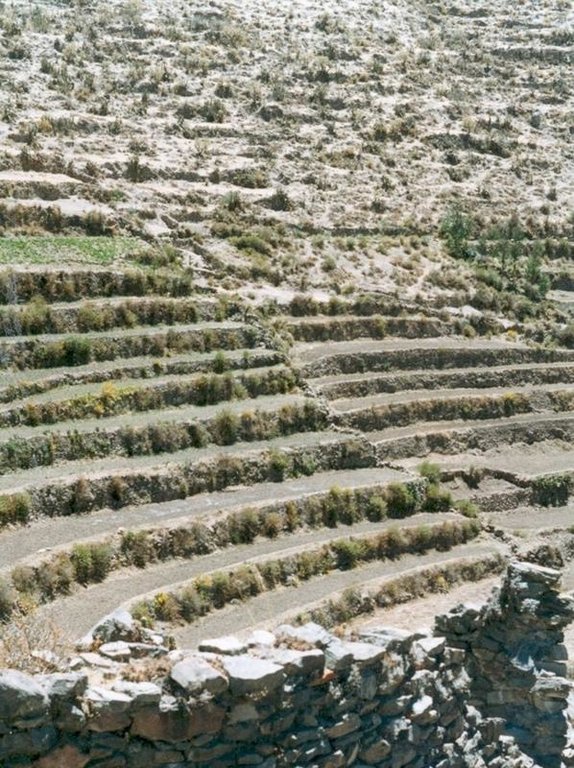
The level bench terrace system in the Colca valley of Peru dates back to 600 years AD. Since then the terraces have been continuously used for crop production, but due to lack of maintenance they have deteriorated, and the population has lost its traditional knowledge of repair.
The rehabilitation of the terraces recreates their original structural design. Broken sections are cleared and the various materials - stones, topsoil, subsoil and weeds - are removed and separated. The foundation is re-established, followed by construction of the stone wall (the ‘riser’). Backfilling with subsoil then takes place; this is consolidated and finally covered with topsoil. Simultaneously the complementary irrigation and drainage systems are reconstructed.
The rehabilitated terraces efficiently conserve soil and water on steep slopes, and they create a favourable microclimate for crops, reducing loss of stored heat at night by minimising air movement (preventing frosts) and mitigating dry conditions through moisture conservation. The main economic benefits are from increased yields and crop diversification.
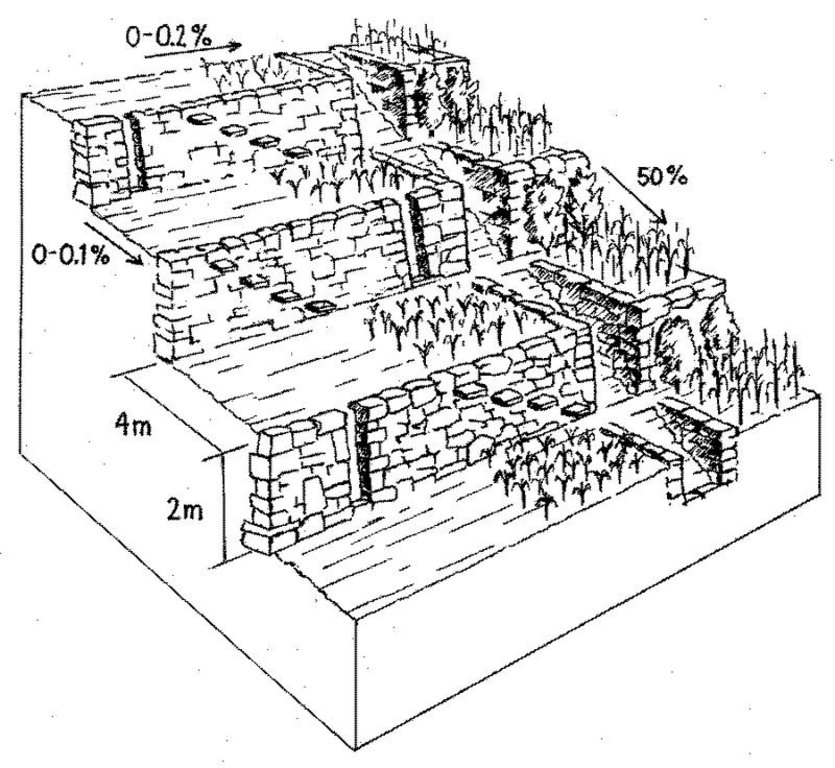
Terraces are spaced and sized according to slope, eg on a 50% slope, terraces are 4 m wide with a 2 m high riser between terrace beds. Stones of ancient terraces had been widely used to build walls for boundary marking after privatisation of land, therefore a large amount of stone had to be provided by splitting rocks and transporting from other locations.
The area is characterised by steep slopes with loamy-sandy, moderately deep soils (on the terrace beds). Most of the annual precipitation (ca. 350 mm) falls within a period of 3 months, which makes irrigation necessary. The farmers in the area own, on average, 1.2 hectares of arable land, divided into around six plots in different agro-ecological zones. Production is mainly for subsistence. Important supportive technologies include agronomic measures such as improved fallow, early tillage, ridging, and intercropping. Tree and shrub planting at the base of terrace walls is an optional measure with the aim of stabilising the walls, diversifying production and again ensuring a good microclimate. On average
250 trees/ha are planted; these are mainly native species such as c’olle (Buddleia spp.), mutuy (Cassia sp.), molle (Schinus molle: the ‘pepper tree’) and various fruit trees including capulí (Prunus salicifolia).
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
秘鲁
区域/州/省:
Río Colca,Caylloma, Arequipa
Map
×2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major food crop: Potatoes, maize,beans, etc

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
主要动物种类及产品:
Alfalfa (cut and carry)
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - Loss of productive capacity: 30% of the agricultural land lost due to degraded terraces, severe deforestation (through
cutting for fuelwood), overgrazing and burning of grazing areas.
- Inefficient irrigation practices (flooding) due to poor maintenance of irrigation system (and drainage system in poor
condition), flood irrigation leads to deterioration of terraces.
- Loss of traditional knowledge of ancestral crop management practices (abandonment of appropriate rotation practices, lack of residue incorporation/recycling, unsystematic crop layout).
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: alfalfa (cut and carry)
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
注释:
Water supply: mixed rainfed - irrigated and rainfed
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Dec - Apr
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 引水和排水
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 100 m2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S1:阶地
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Rehabilitated ancient terraces with high stone risers. Two options for irrigation and drainage of excess water are shown: outlets in the risers (left) and a broad water channel cutting perpendicularly through the terraces (right).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of microclimate
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, improvement of soil structure
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Separation of materials of collapsed wall: subsoil, topsoil, stone, weeds. | 结构性的 | dry period. |
| 2. | Cleaning and re-establishment of the foundation according to originalstructure. | 结构性的 | dry period. |
| 3. | Cutting stones from rocks (blasting and splitting); transporting. | 结构性的 | dry period. |
| 4. | Reconstruction of the stone wall, building on the basis of remainingintact structures of ancient terraces; simultaneous reconstructionof irrigation channels and complementary structures. | 结构性的 | dry period. |
| 5. | Backfilling with subsoil, moistening soil and consolidation with motor | 结构性的 | dry period. |
| 6. | Covering with fertile topsoil. | 结构性的 | dry period. |
| 7. | Levelling of terrace bed and completion of riser edge (lip). | 结构性的 | dry period. |
| 8. | Planting of trees below terrace walls (optional). | 结构性的 | dry period. |
| 9. | Improved fallow, early tillage, ridging, and intercropping (supportivemeasures). | 结构性的 | dry period. |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 560.0 | 560.0 | 40.0 |
| 劳动力 | Construction supervisor (days) | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 180.0 | 180.0 | 40.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 40.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 40.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1400.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Irrigation system cleaning. | 结构性的 | |
| 2. | Clearing weeds from stone wall | 结构性的 | (dry season)./ |
| 3. | Inspection of the stone walls’ stability | 结构性的 | (before sowing)./ |
| 4. | Repair structures | 结构性的 | (rainy season)./ |
| 5. | Tree and root pruning. | 结构性的 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 125.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: A-frame,tape measure,motor drill,wheelbarrow,shovel,pick,steel bar,sledgehammer,hoe,hand compressor.
Person days needed for rehabilitation of 1 ha of ancient terrace system depend on degree of deterioration, the
dimensions of the wall, slope angle (the steeper the more terraces) and availability of stones. In the case of the project, under a typical situation, for physical rehabilitation of 1 ha with 6 terraces, each ca 600 m long, 3–4 m wide and 2 m high, with one third of the main structures in disrepair, 18 men and 7 women work for 5 days; shrub planting is extra. Land users bear 35% of the overall costs: they also provide food for the group during work. The programme pays the rest. 450 m3 of additional stones are required to repair the broken parts, the cost includes blasting/splitting rocks and transport to the construction site.
Supportive agronomic measures and agricultural inputs (seeds and manure) are not included. Maintenance costs vary considerably, depending on the specific situation: an average is taken here.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Also hill slopes (ranked 2) and footslopes (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Also hilly (ranked 2) and rolling (ranked 3)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1, used for maize) and low (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (low recycling of organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Off-farm income specification: main source is wage labour in the valleys
Market orientation of grazing land production system: Subsistence (ranked 1) and mixed (ranked 2, 30% for market)
Market orientation of grazing land production system: Subsistence (ranked 1, complementary to crop production) and commercial/market (ranked 2, income generation to meet basic needs)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 2-5 ha (ranked 3)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Average 30%
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Careful management required (water and livestock)
收入和成本
农业收入
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Easier crop management (level bench, alignment of crops). On the other hand increased labour constraints: heavy work, const. Maintenance. Heavy work by establishment
其它社会经济效应
Efficiency
注释/具体说明:
Efficient use of irrigation water and fertilizers
Input constraints
注释/具体说明:
Tools
Ccarcity of stones (in some places)
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
养分循环/补给
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
动物多样性
栖息地多样性
其它生态影响
Regular crop growth and development
Improved microclimate
注释/具体说明:
Reduced wind; conserving heat
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
240
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 10-50%
注释:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2160 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
240 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption.
40% of terraces have been rehabilitated in 7 districts (8 micro-watersheds) of the Colca valley.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Facilitation of crop management activities (crop alignment, easier tillage with oxen plough, efficiency of pest control, etc) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Appropriate crop management (see measures mentioned in description). |
|
Improved microclimate facilitates crop growth and crop diversification How can they be sustained / enhanced? Complete with improved agronomic practices and agroforestry. |
|
Increased yields and food security How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conserve crop diversity and genetic variety. |
|
Cultural heritage How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conservation of traditional practices |
| Facilitation of crop management activities (crop alignment, easier tillage with oxen plough, efficiency of pest control, etc)-->Appropriate crop management (see measures mentioned in description). - Improved microclimate facilitates crop growth and crop diversification-->Complete with improved agronomic practices and agroforestry. - Increased yields and food security-->Conserve crop diversity and genetic variety Cultural heritage-->Conservation of traditional practices. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Traditional technology is of great value and adapted to local conditions How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness raising of the local population on maintenance of terraces. |
|
Successful implementation is product of evaluation, analysis and documentation of experiences How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further appraisal of the technology. |
|
Soil maintained on steep slopes, no soil loss due to water erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continuous maintenance and appropriate management through training. |
|
More efficient use of irrigation/rain water, longer storage of soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Permanent maintenance of structure. |
|
Maintenance of soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Recycling of organic matter. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Vulnerability of terraces to damage by grazing animals | Do not allow grazing on short terraces with high stone walls. |
| Land users are not skilled in repair of broken sections in the terrace system | More training on maintenance and conservation. |
| Vulnerability of terraces to damage by grazing animals-->Do not allow grazing on short terraces with high stone walls. - Land users are not skilled in repair of broken sections in the terrace system-->More training on maintenance and conservation. Editors’ comments: Terracing systems on hillsides date back to the beginning of agriculture. Often these feature walls (‘risers’) built of stone, and sometimes they are used for irrigation – as in this case from Peru. While many ancient systems have fallen into disrepair with out-migration of rural populations, this is an example of project-based rehabilitation. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
|
Specialised work, not easy to carry out – complex system of different structures |
Promote applied research and extension. |
|
High rehabilitation costs; increased by loss of traditional forms of reciprocal work, and a trend towards individualism |
Reactivate and strengthen traditional labour systems based on reciprocity and mutual help. |
| Limited availability of stones impedes the rehabilitation process |
Carry stones from adjacent or remote places, give training in rock splitting. |
| Not appropriate for use of agricultural machines | Awareness creation. |
| Private properties, but not titled |
Promote the legalisation of titles to facilitate the access to credit and technical assistance. |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Mejia Marcacuzco AP Folleto de divulgación: Andenes, construcción y mantenimiento. (undated).
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Treacy, JM (undated) Las
Chacras de Coporaque: Andenes y riego en el valle del Colca. Instituto de Estudios Peruanos. DESCO
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Participatory catchment rehabilitation (Participación comunitaria para la rehabilitación … [秘鲁]
Promoting the rehabilitation of ancient terrace systems based on a systematic watershed management approach.
- 编制者: Philippe Zahner
模块
无模块