Vallerani system [布基纳法索]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sabina Galli Vallerani
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli
technologies_1528 - 布基纳法索
- Vallerani System: July 16, 2018 (inactive)
- Vallerani System: July 16, 2018 (inactive)
- Vallerani System: July 12, 2018 (inactive)
- Vallerani System: Aug. 15, 2018 (inactive)
- Vallerani system: April 4, 2018 (inactive)
- Vallerani system: Jan. 4, 2017 (inactive)
- Vallerani System: Sept. 30, 2020 (public)
- Vallerani System: March 8, 2019 (inactive)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
03/05/2012
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
A special tractor-pulled plough that automatically constructs water-harvesting catchments, ideally suited for large-scale reclamation work.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
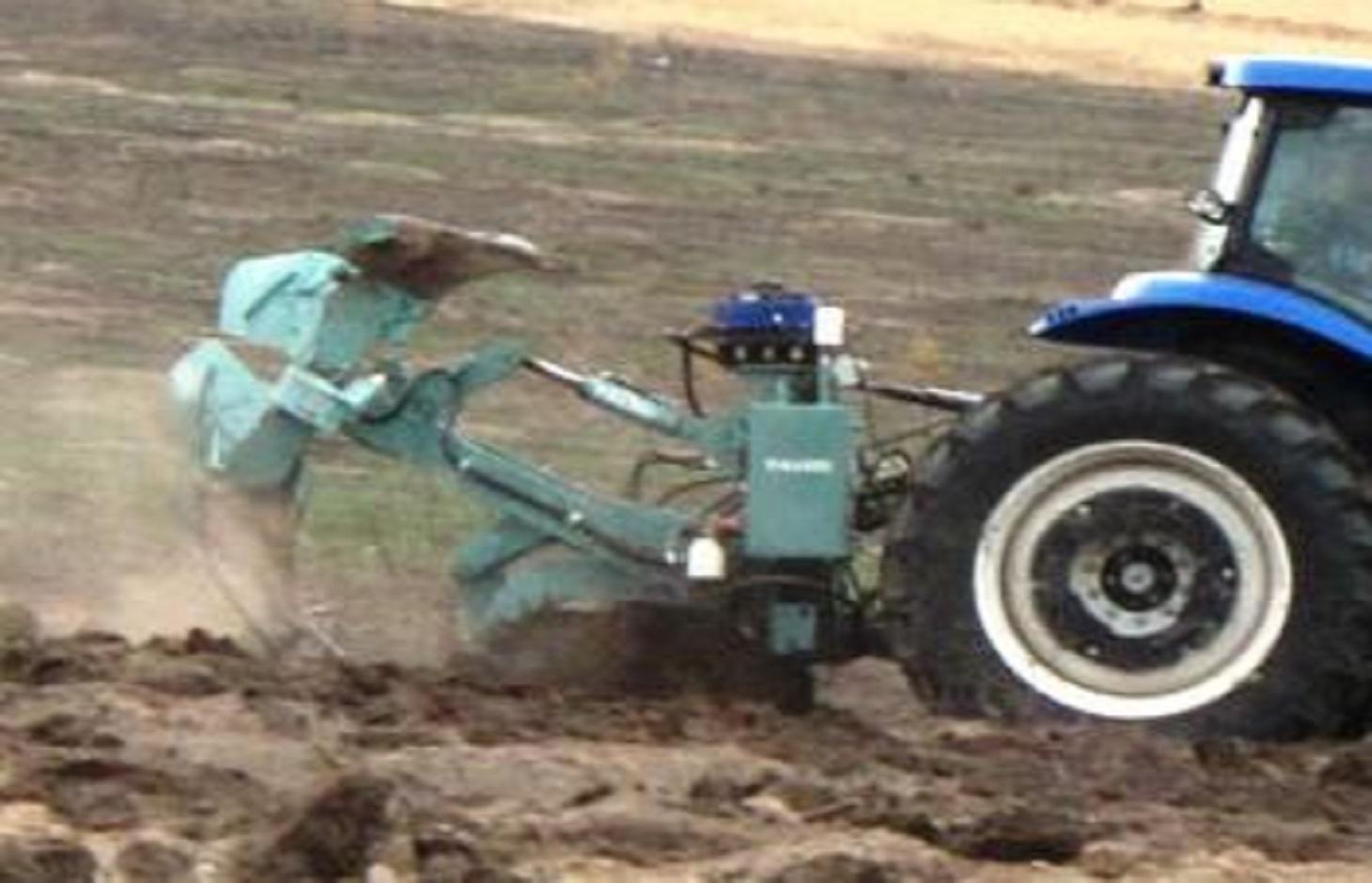
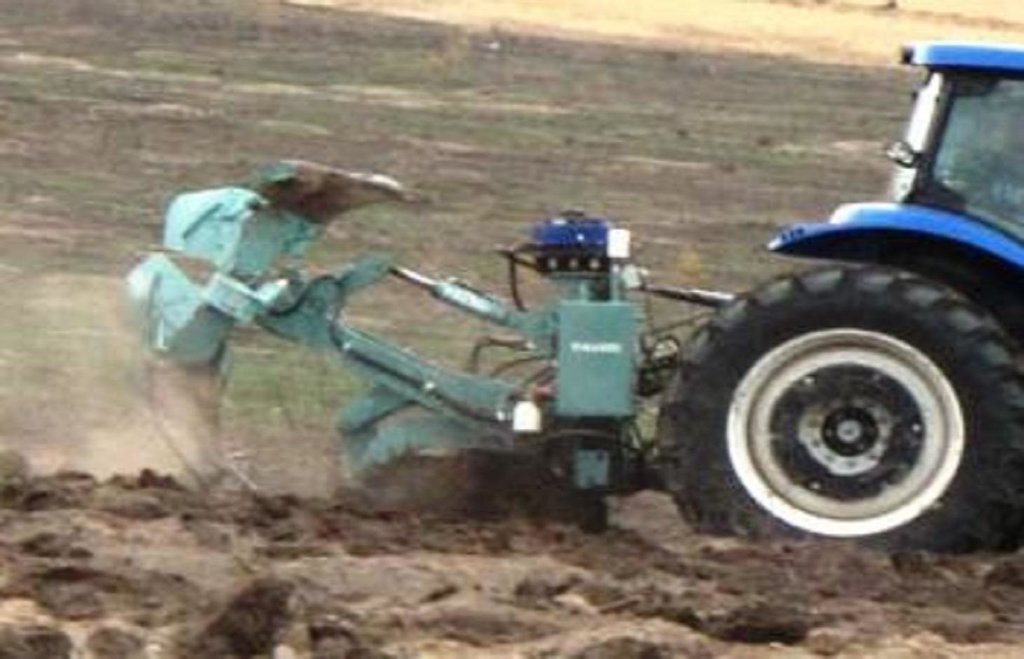
The Vallerani implement is a modified plow named Delfino3, pulled by a heavy-duty tractor. A normal plow on flat land excavates a symmetrical furrow, and earth piles up equally on both sides of the furrow. The Delfino3 plow has a single reversible plowshare that creates an angled furrow and piles up the excavated soil only on the lower (downhill) side. This soil forms a ridge that stops or slows down runoff water as it flows downhill. The plow’s blade moves up and down (i.e. in and out of the soil), creating micro basins about 5 meters long, 50 cm deep and spaced about 2 m, each with a ridge. Two ripper placed before the plow work the soil to a depth of 70 cm, rise at the basin and descend between the basins. Thus to attain, in the stretch of land between the crescent, a collection bag which receives water from the crescents itself. Even with very low rainfall (150-500 mm/year) each micro-basin/storage bag can collect 1500 litres of water, including runoff. This water is protected against evaporation and remains available to plant roots and groundwater.
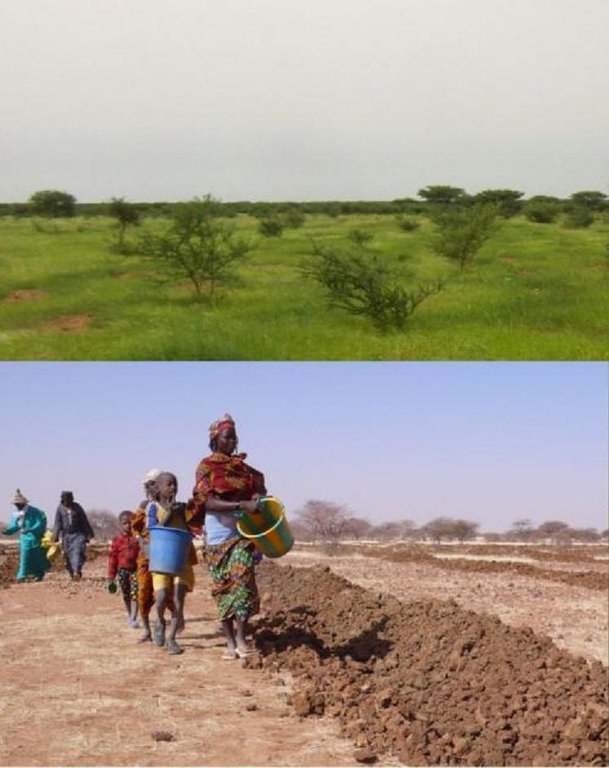
The Vallerani System is based on direct sowing of seeds of shrubs and trees of locally available, indigenous species. They are sown along the ridges of the basins and in the wake of the ripper. In the case study area Acacia tortilis, Ziziphus mauritania, Balanites aegyptiaca, Acacia senegal, Acacia seyal and Faidherbia albida have been sown. While for most species seeds can be collected by the local population, for species rarely present in the region, the seeds have to be purchased from tree nurseries. The use of goat excrements containing seeds has also proven successful (about 95% of all micro basin have at least one tree growing after 3 years) when directly sown. With more moisture available for a long time trees grow rapidly and the herbaceous cover improves in quality and in quantity - providing 20-30 times more livestock fodder (1000-2000kg dry herbaceous biomass ha/year), also helping to conserve the soil. The plowed and sown area is not protected by fences, grazing of animals shall be allowed so that villagers can benefit from the forage and reduce the accumulation of biomass fuel that would further the risk of fires in the dry season.
The Vallerani plow can ‘treat’ up to 20 ha, digging 5.720 micro basins, in a single day. The speed and effectiveness of the Delfino3 plow are its major advantages in the fight against desertification, but can also be its major limitation as to be able to make the best of it, it is necessary to find great availability of land to be reforested or cultivate. This is mainly possible related to a large public or business initiative. The spreading "like wildfire" that has characterized the case study was made possible by the presence on the territory of an NGO already active and rooted in the territory for many years and by perseverance, respect and competence of partner "of the North". Once the project has invested in the tractor and the plow (tractor ~ 70,000 EUR, plough ~ 40,000 EUR), the remaining cost of implementation – labour costs for local workers and drivers, fuel etc. amount to around EUR 125 / ha / year.
The case study area in the north east of Burkina Faso receives about 300-500 mm of annual rainfall. The soils of this agropastoral land are heavily degraded with a low tree density and an almost entirely absent herbaceous cover.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
布基纳法索
区域/州/省:
Oudalan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Gorom-Gorom
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧场:
- 半游牧/游牧

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Land degradation-desertification with reduction of vegetation cover in terms of plant density and species diversity is the main problem: disappearance of grasses and trees, reduction of the size of the plants that are resistant and of the biological activity of the soil. Runoff, water and wind erosion increase. Drought and irregular precipitation have heavy consequences on soil fertility, availability of water for humans and livestock, and recharging groundwater.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 90
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 50 m2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
注释:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, change of seasonal rainfall, droughts
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Above:
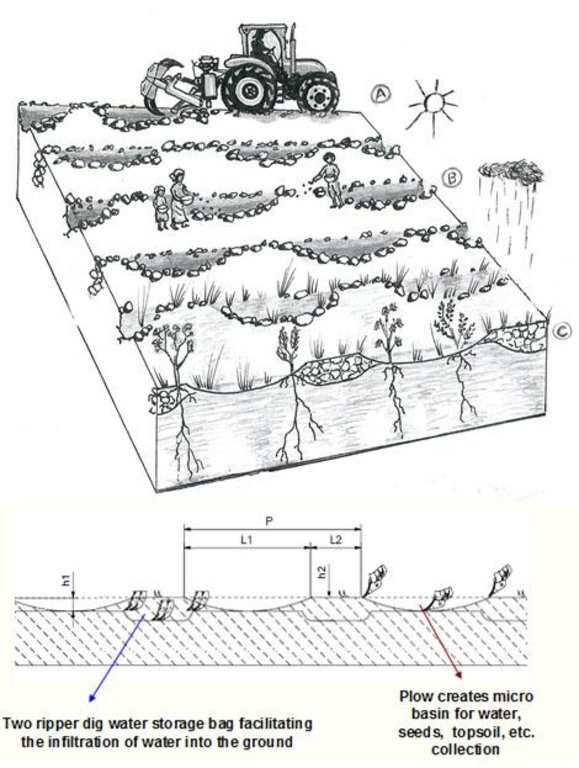
A. The land chosen together with the local population is plowed with the special Delfino3 plow. B. Local people sow seeds (collected from local trees or bought if species are rare) or goat dung containing seeds (collected in the night enclosures after feeding the goats shaking trees with ripe seeds). C. The micro basins collect the rain that falls into the crescents and 50% of the runoff water. The water easily penetrates into the soil, fills the storage bags, remains available to plant roots and drains into the groundwater without risk of evaporation. Each micro basin/storage bag can collect up to 1.500 l of water.
Below
h1-Depth of the ploughshares work: =40/50 cm
Width of the micro basin: 40/50 cm
L1-Length of the micro basin, programmable: =3,5/5 m
h2 Depth of the rippers work: =50/80 cm
P-Total length of work: 4/8 m
Tractors horsepower 210/250 (150-198 Kw)
Working speed: 4/7 Km/h
Weight : 2000 Kg
Location: Oudalan, Gorom Gorom province. Burkina Faso
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), water harvesting / increase water supply, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Spacing between structures (m): 0.5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 5
Change of land use practices / intensity level
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Project planning, consulting and training by VS and national experts | 结构性的 | |
| 2. | Plowing with the Delfino special plow pulled by a 210hp tractor | 结构性的 | Dry season |
| 3. | Seed harvesting can be done by local people either collecting them directly from plants or by shaking the plants at the appropriate time, to feed the goats and sheep with the fallen seeds and collect their dung in the night enclosure | 结构性的 | |
| 4. | Missing seeds can be purchased in local markets or, if trees are too rare or if the species is no longer present, seeds must be purchased at a nursery | 结构性的 | When seeds are ripe |
| 5. | Direct sowing | 结构性的 | Dry season |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 50.0 |
| 设备 | machine use | ha | 1.0 | 23.4 | 23.4 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 95.4 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | No maintenance activities are required | 结构性的 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
All data presented in the table refer to an ideal project which lasts 5 years with 3000 hectares plowed each year. All works are carried for economic retribution. Item number 1 refers to the planning, training and consulting engineers that has a strong impact on the cost per ha ($47). This voice would remain the same if 3 MTU (Mechanized Technical Unit) were used in the same area reducing its impact to $ 15,6 per ha.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Upfront costs for the aquisition of the required materials are around 40,000 EUR for the plough and 70,000 EUR for the tractor.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
400-600 mm
农业气候带
- 干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The project involves the reforestation and reconstruction of the herbaceous layer for the grazing of livestock that are male dominated activities. Since 2010 women have sown special plants for medical use, domestic use and as raw material for crafts and protected them from grazing.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
Off-farm income specification: The only activity people of the region are engaged in is goat and cattle breading. Crop production is practiced only for subsistence use.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
up to 30% more than before implementation
饲料质量
木材生产
SLM之前的数量:
50 trees/ha
SLM之后的数量:
350 trees/ha
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
The technology can be applied for agriculture producing 2 to 4 times more than with traditional systems
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
No more malnutrition=better health!
文化机会
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
More wood, fodder and water available= more time available
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Old, young and woman work together for common benefits
国家机构
注释/具体说明:
Were applied on large scale
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Environment education in theory and practice, is part of the system
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
More fodder and water highly reduces conflict motivations
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
Women have collected, sown and protected medicinal plants and plants for raw materials for handcrafts to sell at the market
Training of skilled labour in disadvantaged regions
注释/具体说明:
Chance to find good jobs
contribution to human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Thanks to the enormous increase of trees, pasture and crop production, the quality of life and health of men and animals have improved considerably.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤水分
土壤流失
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
减少气候和灾害风险
火灾风险
注释/具体说明:
Through the high soil cover with trees and grass fire risk increase, this is avoided through open access to grazing.
其它生态影响
Increased threat from wild animals
注释/具体说明:
Biodiversity highly increases, local people might be afraid of some animals coming back like jackal or snakes
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 大于 50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The system includes the use of a heavy duty tractor and a special plow whose costs are high though difficult to sustain by the local population. All correlated activities are done (or can be done) without external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The system includes the use of a heavy duty tractor and a special plow whose cost is high though difficult to sustain by the local population. All other activities part of the system are practicable from the population under an initial guidance of someone with specific training. Where the technology is known there is active participation of local people and a strong demand for new interventions
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| This practice allows for the rapid and efficient treatment of large degraded areas within a short time |
| The tree and shrub species planted are mainly indigenous and locally adapted species |
| Through its tillage process the Vallerani system offers the highest degree of efficiency in the first years from processing. Its effects last for a long time so it does not need to be repeated on the same site |
| The VS does not use any water (except rain) in countries where water is rare and precious. It further avoids the risk of soil salinisation. |
| The delfino3 can plow strongly degraded land, this makes that local people often ask to work their worse land |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The investment costs for the machinery are extremely high and cannot be covered by single land users or even communities | projects must be financed externally |
| The speed and effectiveness of the Delfino3 plow are its major advantages in the fight against desertification, but can also be its major limitation as to be able to make the best of it, it is necessary to find great availability of land to be reforested or cultivate | This is mainly possible related to a large public or business initiative. The spreading "like wildfire" that has characterized the case study was made possible by the presence on the territory of an NGO already active and rooted in the territory for many years and by perseverance, respect and competence of the partner "of the North" |
| Since great extentions will be processed, a big organisation is needed for all activities (awareness raising, collecting seeds, personnel training, logistics, etc), | this must be well organized and should operate already before starting plowing |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Conedera, M., N. Bomio-Pacciorini, et al. 2010. Reconstitution des écosystèmes dégradés sahéliens. Bois et Forêts des Tropiques 304(2).
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.vallerani.com/images/Reconstitution.pdf
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Akhtar Ali, Theib Oweis, Atef Abdul Aal, Mohamed Mudabbar, Khaled Zubaidi, and Adriana Bruggeman. 2006. The Vallerani Water Harvesting System. ICARDA Caravan No. 23.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.vallerani.com/images/Caravan-23.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块