Vallerani System [布基纳法索]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sabina Galli Vallerani
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Donia Mühlematter
technologies_1528 - 布基纳法索
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
土地使用者:
Long Allain
Reach Afrique, NGO
布基纳法索
SLM专业人员:
Lindo Grandi
Deserto Verde Burkinabé, NGO
瑞士
土地使用者:
Boureima Amadou
Reach Afrique
布基纳法索
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: Water Harvesting – Guidelines to Good Practice (Water Harvesting)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Reach Africa (Reach Africa)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Reach Italia (Reach Italia) - 意大利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
2012/2018
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
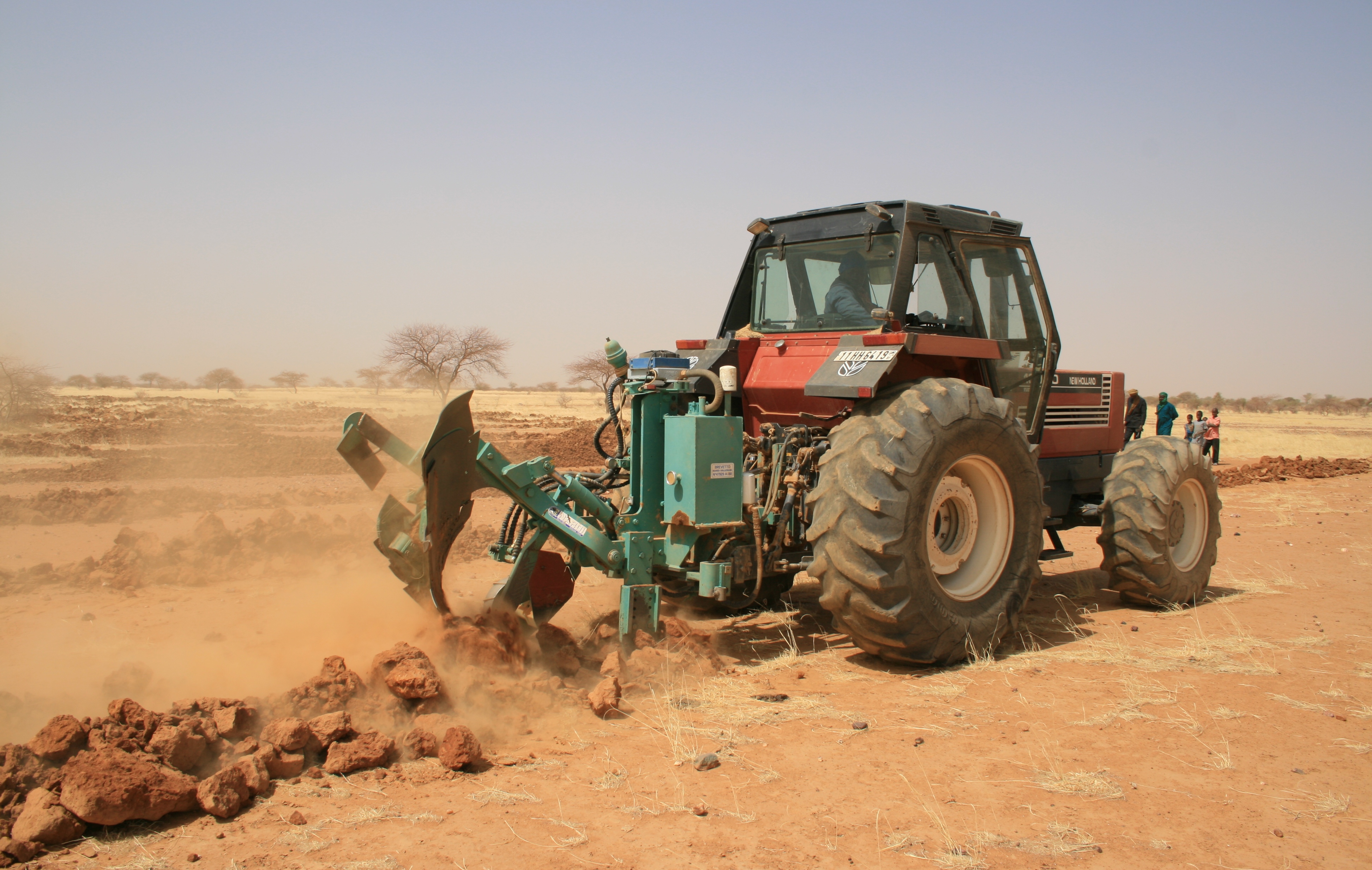
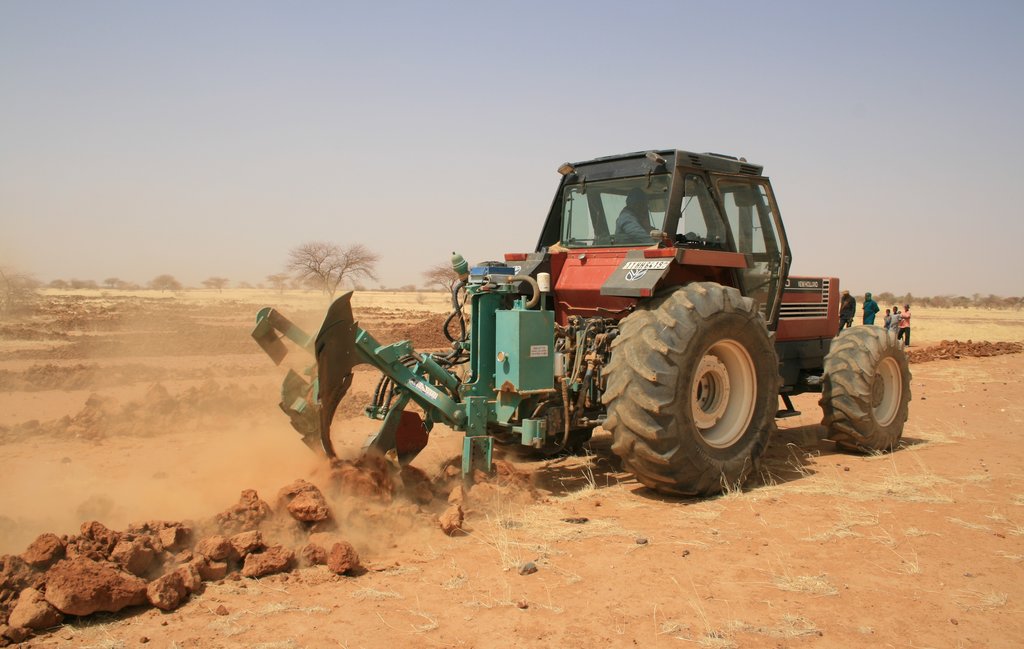
A special tractor-pulled plow that constructs micro-catchments. It combines the traditional techniques of rainwater harvesting with mechanization for large scale land rehabilitation.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
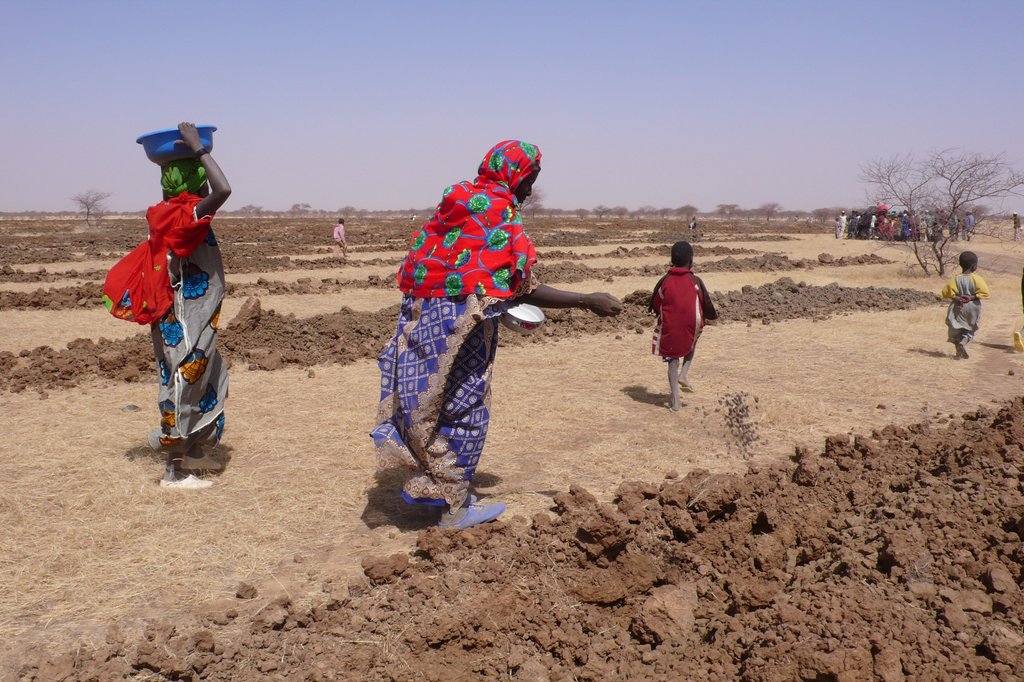
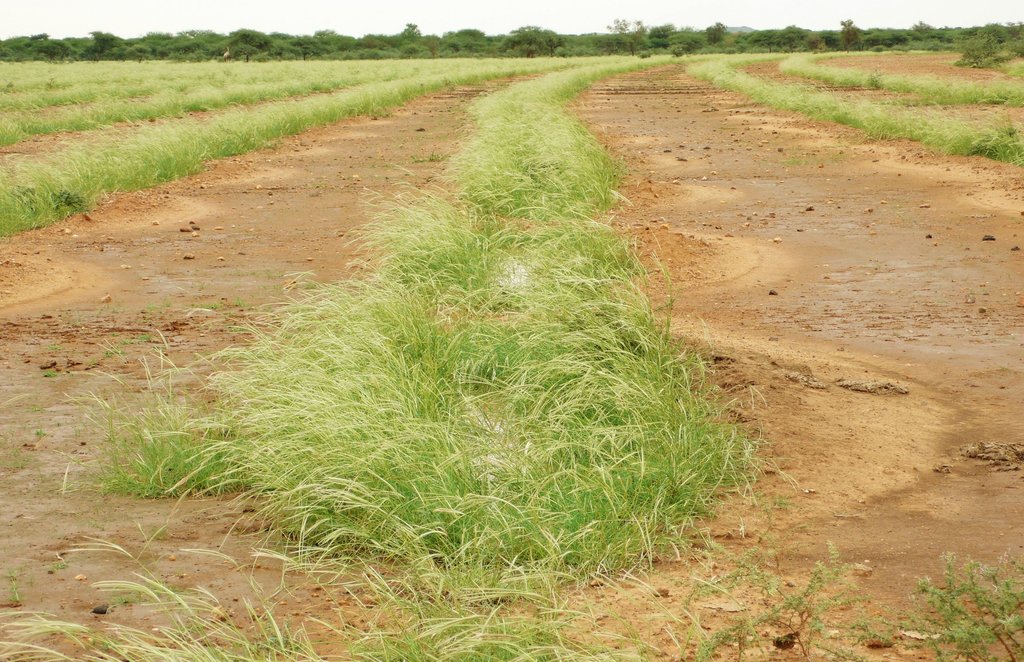
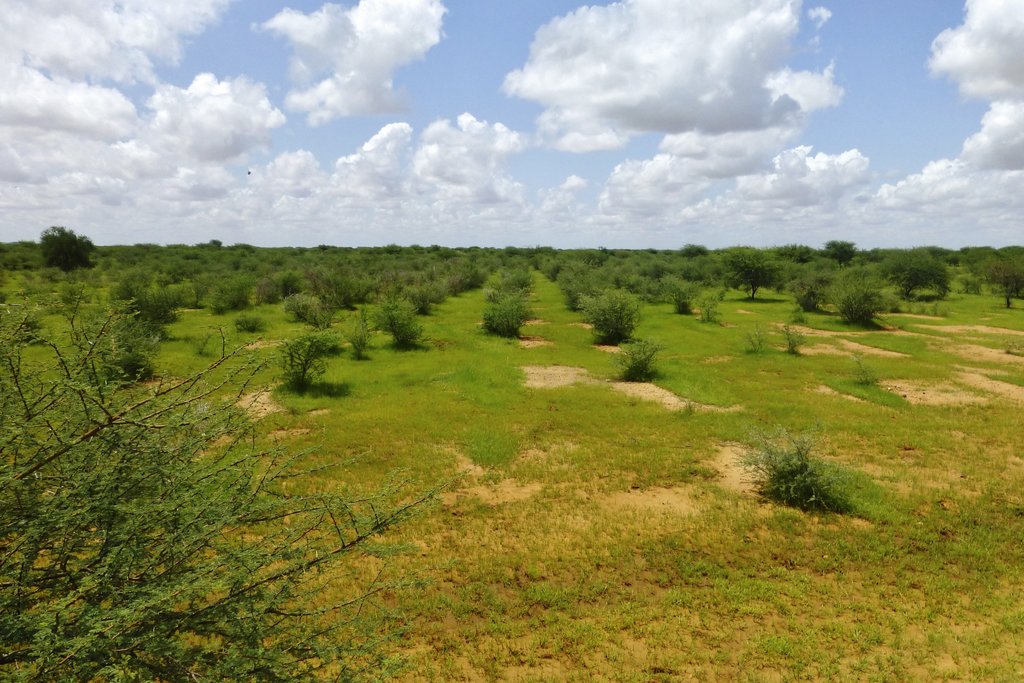
The Technology mechanizes the traditional technique of zai and semi circular bunds for water harvesting using a modified plow named Delfino3s pulled by a 180hp tractor. A normal plow on flat land excavates a symmetrical, continuous furrow, and earth piles up equally on both sides of the furrow. The Delfino3s plow has a single reversible plowshare that creates an angled furrow and piles up the excavated soil in half moon shaped ridges only on the downhill side. The plowing must be done along the contour to collect and slows down runoff water as it flows downhill. The plow’s blade moves in and out of the soil creating micro basins about 5 meters long, 50 cm deep, 50 cm wide and spaced 2-3 m. The ripper placed before the plow cracks up the soil to a depth of 70 cm facilitating the infiltration of water into the soil profile and the growth of deep roots. After plowing, the local population sows seeds of plants of indigenous species. They are sown along the ridges of the basins and in the furrow of the ripper. While for most species seeds are collected by the local population, for species rarely present in the region, seeds are purchased from tree nurseries. Sowing the manure of goat containing seeds has also been very successful with about 95% of all micro basin having at least one tree growing. The intervention on a big scale, the effects of water infiltration in depth, erosion reduction and vegetation growth, boost a long lasting rehabilitation process. Each day the Delfino plow can plow up to 20 ha, digging 6.000-7.000 micro basins. The speed, the capability to plow hard, abbandoned land, the effectiveness of the Delfino3s plow are its major advantages for the ecosystem rehabilitation process but require a big commitment. To make the best out of it, a great motivation and organizational work is necessary to: find great availability of land; train accuratelly the technicians; have well-rooted Subjects in the region. The technological aspect is just part of the recovery process, an important work with the Communities is required upstream and downstream. Communities are involved in the management process – in identifying the areas to be restored, clarifying the land uses of the affected areas, planning and implementing e.g. gathering and keeping seeds of local ecotypes, sowing, in the management of plantations and in the monitoring and evaluation of the results. Rules for SLM are adopted and respected by all. The Technology is applied in a degraded agro-sylvo-pastoral area of the Sahel Region, in the north east of Burkina Faso with 200-500 mm of annual rainfall. The soil is sandy-loam, strongly degraded with surface crust. The population is mainly composed of semi-nomadic herders. At the beginning of the project, the NGO Reach Italia was promoting schooling; they soon realized that during the dry season most kids left school and that to avoid it they should face food security and pasture improvement. So they started applying the Vallerani System and developped the participatory approach. The vegetation growth reduces the need for fodder search and long-range transhumance which also allows children to go to school regularly.The ecosystem rehabilitation effect of the technology help the communities to become more concious and resilient to the effects of climate change and prepared to cope with the socio-economic-environmental changes they are faced with.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
A short video that introduces the Vallerani System.The video has been shot in the project area.
日期:
14/05/2014
位置:
Oudalan, Burkina Faso
摄影师的名字:
Jonathan van Laamsverde
注释、简短说明:
The presentation of the ICARDA Minared project applying the Vallerani System for rangeland rehabilitation in the Jordan Badia.
日期:
16/06/2016
位置:
Badia, Jordan
注释、简短说明:
Reach Italia and Deserto Verde Burkinabé present the project of soil rehabilitation and food security in Burkina Faso. Italian text.
日期:
01/09/2009
位置:
Oudalan, Burkina Faso
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
布基纳法索
区域/州/省:
Sahel Region
注释:
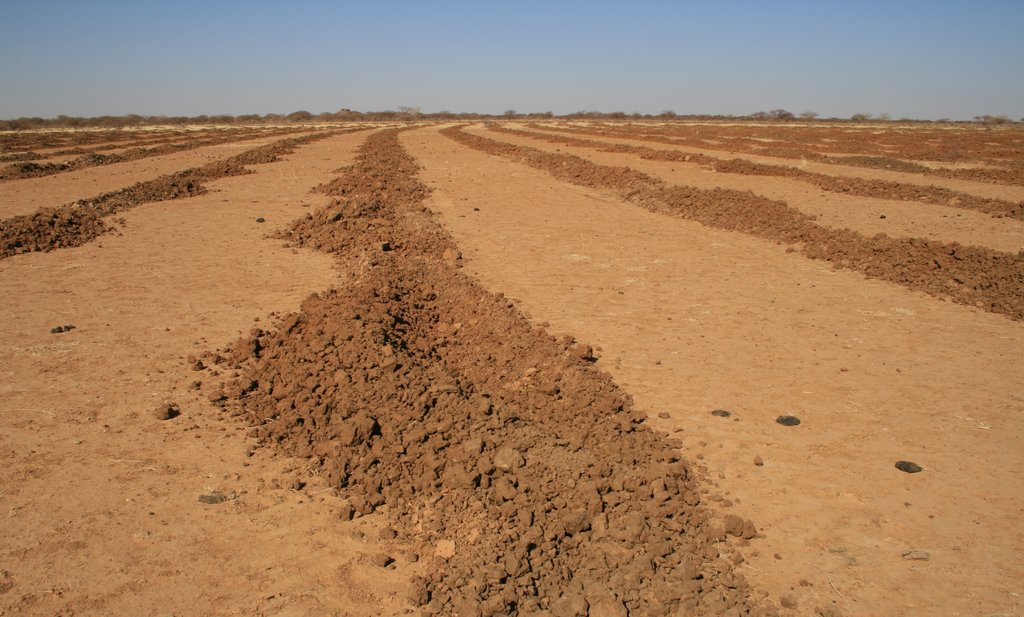
Since the project is going on since 2002, it is possible to see implemented sites in different stadium of rehabilitation. The plowing lines are clearly visible.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The Technology was introduced in the Region in an agro-sylvo-pastoral pilot project to fight against desertification by FAO in 1996-97.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧场:
- 半游牧/游牧
主要动物种类及产品:
Goats, cattle

不毛之地
具体说明:
Hard abbandoned land
注释:
Especially at the beginning of the project, some communities agreed to try the system on their most unproductive land. After seeing the results, they started to request the intervention on less degraded soil and on fields that are closer to their villages.
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Land degradation-desertification with reduction of vegetation cover in terms of plant density and species diversity is the main problem: disappearance of grasses and trees, reduction of the size of the plants that are resistant and of the biological activity of the soil. Runoff, water and wind erosion increase. Drought and irregular precipitation have heavy consequences on soil fertility, availability of water for humans and livestock, and recharging groundwater.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- 集水
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 100-1,000 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology in the Region is about 25.600 hectares up to 2017.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S2:堤、岸
- S4:平沟、坑

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失
- Eo:场外劣化效应

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pk:熟化和结壳
- Pi:覆土
- Pu:由于其他活动而导致生物生产功能的丧失

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, change of seasonal rainfall, droughts. Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), education, access to knowledge and support services.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
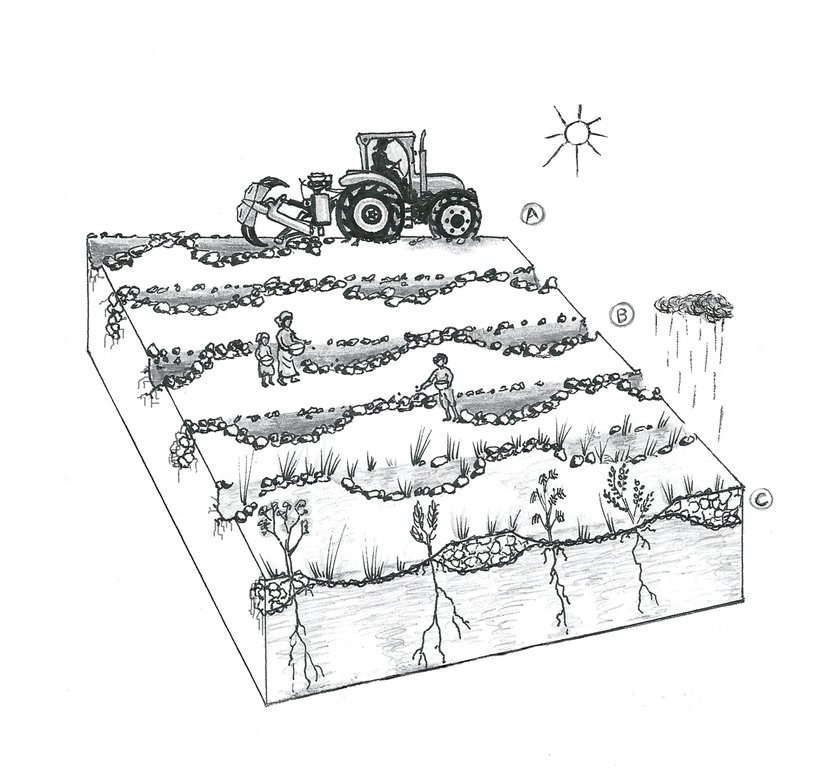
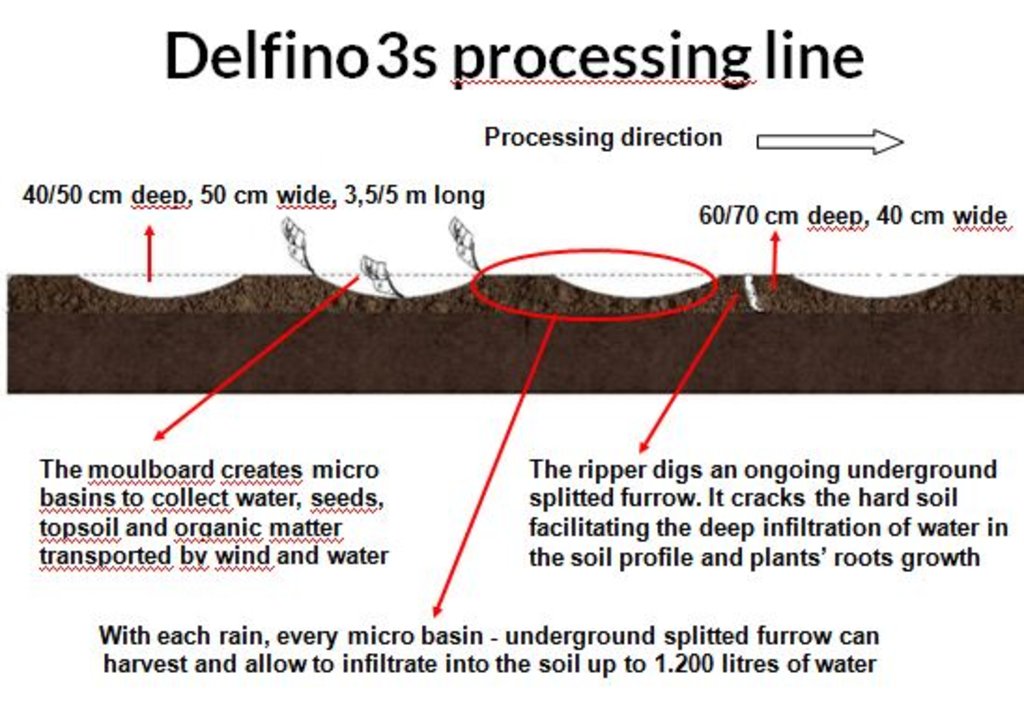
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
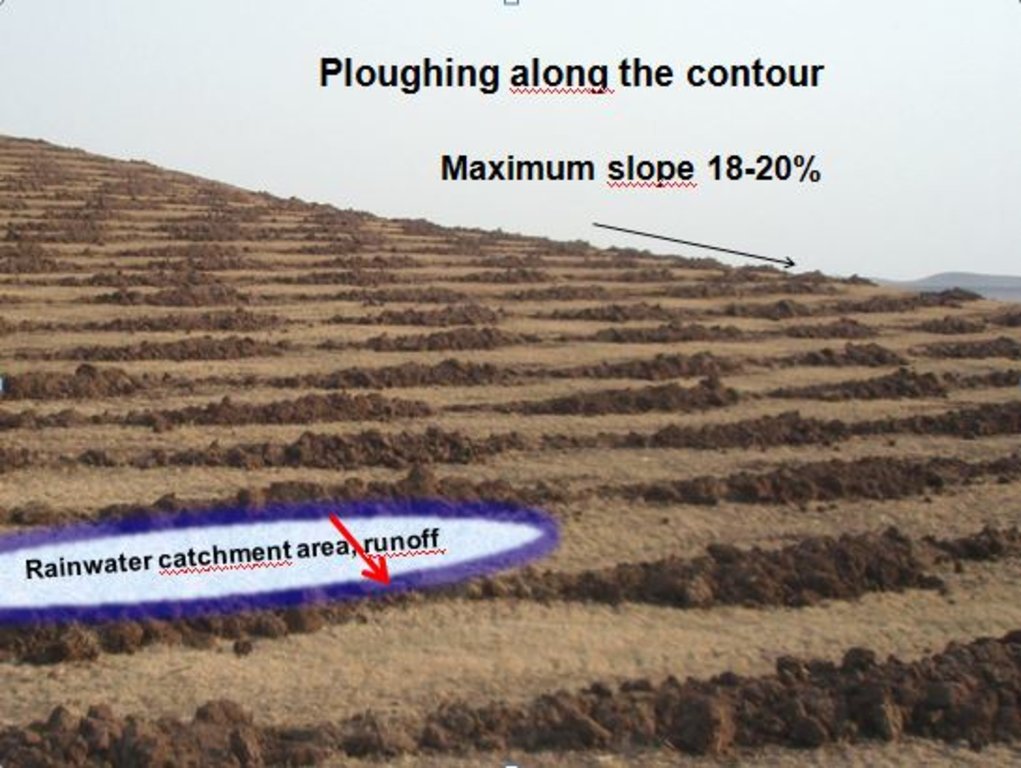
Drawing 1) A. The land chosen together with the local population is plowed with the special Delfino3s plow. The spacing between the plowed lines depend on: slope, soil and rain characteristics, purpose of the project. In average the inter-line is 4-6m wide. B. Local people sow seeds (collected from local trees or bought if species are rare) or goat dung containing seeds (collected in the night enclosures after feeding the goats shaking trees with ripe seeds). C. The micro basins collect the rain that falls into the crescents and up to 90% of the runoff water. The water easily penetrates into the soil profile, remains available to plant roots without risk of evaporation and eventually infiltrates to the groundwater. Drawing 2) All plowing measures are adjustable. Total length of work: 4/8 m. Tractor required: 180hp. Working speed: 4/7 Km/h which correspond to 1,5/2.5ha per hour. Weight of the plough: 1800 Kg. Drawing 3) To optimize run off harvesting and reduce water erosion, the ploughing must always be done along the contour. The bare soil between the tilled lines works as catchment area for the collection of runoff. To facilitate the execution of the plowing along the contour, nowadays there are new technologies such as laser guidance systems or GPS assistence.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
100 hectares
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.5
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Project planning, consulting and training | 其它措施 | Before starting |
| 2. | Plowing with the Delfino plow | 结构性的 | Dry season |
| 3. | Seed harvesting and storage | 农业学的 | When seeds are ripe |
| 4. | Missing seeds purchase in local markets or nurseries | 农业学的 | When seeds are ripe |
| 5. | Direct sowing | 农业学的 | Dry season |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Founders
注释:
The actual (2018) average cost of the implementation is $ 170 per hectare. This cost can be considerably reduced by around 22% in the case of an optimal use of the Technical Mechanization Unit, ie 800-1000 hours of work per year. This means that an operator who works with the plow Delfino has a gross investment cost which can vary according to its technical and organizational experience and by the amount of the plowed surface each year.
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pasture management to avoid overgrazing | 植物性的 | After the rain and in the dry season |
| 2. | Vegetation growth management | 植物性的 | During the first 3-5 years |
| 3. | Woodcut management | 植物性的 | After 4-7 years |
| 4. | Equipment maintenance (plow, tactor) | 管理 | Daily, weekly, seasonal |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Founders
注释:
Maintenance costs of plow and tractor greatly depend from the attention and technical skills of tractor drivers and mechanics and from the diligence and frequency of the maintenance activities of the implements. No other maintenance costs are forseen for the Technology.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Upfront costs for the aquisition of the required implements are around 40,000 EUR for the plow and 75,000 EUR for the tractor. Depending on the maintenance activities, the spares and fuel costs can be reduced. Fuel, oil and spares also greatly depend from the characteristics of the soil and the purpose of the project.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Dry season from oktober to may, rainy season from june to september. There's a great climate variability with unexpeced dry periods or areas in the rainy season. In the last years climate change effects are experienced in the region with raise in temperature, droughts and rain variability increase. Some Community claim that since the rehabilitation of big degraded areas it rains more regularly and abbundant.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Dori, Burkina Faso
农业气候带
- 半干旱
- 干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics. Average temperature 30°C
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Generally the watertable is lowering. Surface water is collected in boulies (ponds) for livestock and household activities. Its quality deteriorates during the dry season and its quantity decreases fast.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Up to 30-50 years ago biodiversity was reach and soil coverage higher.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 半游牧的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
During the dry season men often migrate(d) to the nearby mines or cities for off-site income. After the implementation of the Technology the need for seasonal migration reduced. Difference in gender involvement: the project involves reforestation and pasture improvement for the grazing of livestock which is a men dominated activity. Since 2010 women have sown and protected from grazing some special plants for medical and domestic use and as raw material for handcrafts. Population density: 10-50 persons/km2. Annual population growth: 3% - 4%. Off-farm income specification: The only activity people of the region are engaged in is goat and cattle breading. Crop production is practiced only for subsistence use.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之后的数量:
2-4 times
注释/具体说明:
Crop production and biomass augmented 2-4 times compared with traditional cultural techniques.
饲料生产
SLM之前的数量:
90kg/MS/ha
SLM之后的数量:
1250kg/MS/ha
注释/具体说明:
Grass fodder production increased by a factor of 5–30 compared with unmanaged land. The production of herbaceous biomass varied from 420 kg to 2.090 kg (dry matter) per ha; thus, on average, 1.250 kg of herbaceous biomass (dry matter) per ha developed on sites where the Vallerani system was deployed, compared with an average of 90 kg (dry matter) per ha in control plots. Vegetation is mainly distributed inside and around the micro basins.
饲料质量
SLM之前的数量:
12 floral species
SLM之后的数量:
44 floral species
注释/具体说明:
The application of the Technology boosts a regenaration process increasing year by year. Compared to the surrounding control rangelands, fodder quality and biodiversity increased with a high proportion of grassland species of good forage value, such as Panicum laetum and Schonefeldia gracilis, and the return of legume species such as Alysicarpus ovalifolius and Zornia glochidiata also testify the improvement of the quality of the reconstituted pastures.
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
The increase of fodder quantity and quality represents a surplus of 22–106 grazing days per tropical cattle unit per hectare. This extra fodder supply reduces the need to make long-range transhumance or cut shrubs to meet livestock needs for fodder, even in years where pasture is low. Livestock is fed with more and better quality fodder so its productivity and market price increase.
木材生产
森林/林地质量
SLM之前的数量:
20 trees/ha of 6 species
SLM之后的数量:
700 trees/ha of 14 species
注释/具体说明:
Significant improvement in forest cover (700 live trees and shrubbs per ha, on average) and biodiversity: trees are capable of spontaneous growth even with open access to grazing and in years of high water stress.
非木材林业生产
注释/具体说明:
Berries, gum arabica, resins, fruits.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
The increased fodder quantity, quality and biodiversity, the deep root system of the sown plants, increase resilience of the ecosystem and reduce the risk of production failure. The increased biodiversity, soil moisture and fertility increase the resilience of plants to attacks by pests, deseases and drought. Even in the case of severe drought, there are some plants that can be used as "emergency food" by humans and animals.
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
The implementation of the Technology gives the opportunity to diversify the production. Next to animal breeding, agriculture has intensified and in some villages the production of handicrafts, food processing, hunting and tourism activities are developping. Berries, gum arabica, resins, fruits enrich the family diet or can be sold at markets. Wild animals, insects, reptiles and birds have returned after decades and greatelly increased.
生产区域
SLM之后的数量:
25.600ha
注释/具体说明:
By the end of 2017 about 25.600 hectares of severelly degraded, abbandoned land has been rehabilitated.
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Local people attest that the rehabilitation of large areas of bare soil augmented the local rain amount and the water level in the wells.
家畜用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
The rain collected in the micro basins is available for livestock during the rainy season. The augmented rainfall also increases water availability in boulies (ponds).
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
No water is needed for the Technology except for rain.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
The implementation cost of the technology is not entirelly sustainable by Communities. donors and founders sustain the project. Large-scale application reduces the cost per hectare and increases the impact of actions in reversing the degradation–desertification trend. The cost of each plowed hectare.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Fodder increase in quality and quantity, improve animal health and productivity as well as their market price.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
The Technology increases income for herders and their families also thanks to diversification. More land is also used for agriculture. Selling or transformation of other products such as berries, fruits, gums, resins; hunting; new job opportunities in disadvantaged areas such as tractor drivers, social promoters, seed collectors...The community raises awareness and a potential for small business activities occurs, mainly among women.
经济差异
注释/具体说明:
Disadvantaged groups such as women start new economic activities such as mat production and sale at markets, medical plants and food production. They diversify their income and improve their status in the community.
工作量
SLM之前的数量:
5 micro basins/day
SLM之后的数量:
6.000 micro basins/day
注释/具体说明:
Each man can dig 5 micro basins per day doing a heavy work. The plow can dig 6.000-7.000 micro basins per day. As most rangelands, the area of the project has a low human density (29 inhabitants/km2) so people are responsible for seed collection and storage, sowing, the livestock management during the first growing phase, monitoring activities, a.s.o.
其它社会经济效应
Migration
注释/具体说明:
Increased and improved fodder availability reduces the need for long-range tranhumance and seasonal or definitive migration to areas with more work opportunities (e.g. mines), cities or other countries.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Food security improves with increased and diversified productivity and income. The increased fodder and crop quantity, quality and biodiversity, the deep root system and soil fertility, increase the resilience of the whole ecosystem. Even in the case of severe drought, there are some plants that can be used as "emergency food" by humans and animals.
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
Improved health especially due to better nutrition also for disadvantaged groups such as children and old people: bigger amounts, diversification, milk, vegetables. The reduction of dust storms also improves the health situation.
土地使用权/用水权
注释/具体说明:
Awareness rising and discussion of the theme are essential. Due to the great productivity of former degraded and often abandoned land, land use rules and water rights are clearly discussed and defined at the beginning of the project. Rules for SLM are adopted and respected by all; for example, it is forbidden to install camps in or near restored areas, to cut trees, and to mow for commercial purposes.
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
Shadow, green areas near the villages increase recreational opportunities.
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
It is essential to involve and give responsibility to local people in every step of the process. Comities and groups such as the women or seniors groups gain relevance and become essential for the sustainability of the project.
国家机构
注释/具体说明:
Collaborations with national institutions such as forestry direction, ministery of environnement and agricolture, research institutes, etc
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
All communities are involved in the management process – identifying the areas and the use of the sites to be restored, planning, and implementing (e.g. gathering and keeping seeds of local ecotypes, manure and sowing). Local villages are involved in the care and defence of new plantations and in the monitoring and evaluation of the results of vegetation growth. Ultimatelly they become responsable for the sustainable management of the whole area.
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
If land use and water rights are clearly defined, the increased availability of fodder reduces conflicts with neighbours and farmers.
社会经济弱势群体的情况
Community well being
注释/具体说明:
People have more confidence in the future, dignity and hope. The Community cohesion and identity is strenghtened and the community becomes more resilient to conflicts and disasters.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
SLM之后的数量:
360.000l/ha
注释/具体说明:
With each rain, each micro basin can collect up to 1.200l of water. Each hectare collects an average of 360.000 liter of rain, runoff included. Collected in the micro basin, the water has enough time to infiltrate in the soil profile and eventually in the water table. Local people assert that after the implementation of the Technology, the water level in the wells has raised.
水的回收/收集
注释/具体说明:
The Technology allows to harvest 100% of the rain falling in the micro basin and on the ripped furrow as well as up to 90% of the rain falling between the tilled lines. The bare soil between the tilled lines is essential as catchment area, to recieve rainfall and process runoff downstream. The micro basins collect up to 95% of rainfall.
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
5-15%
SLM之后的数量:
90%
注释/具体说明:
Plowing is done along the contour. This is essential to collect the runoff that flows between the tilled lines (catchment area). The distance between the lines can be between 4m and 12m depending from: slope, rain characteristics (quantity, intensity), soil type, surface roughness (runoff coheficient), the purpose of the project (type of plants desired). The technology allows to collect up to 90% of the runoff.
地下水位/含水层
注释/具体说明:
Local people assert that after the implementation of the technology, the water level in the wells has raised.
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
The rain collected in the micro basins infiltrates in the soil profile being accessible for seeds and roots without evaporating. After the first rains, the micro basins are quickly covered with high grasses that contribute to reduce evaporation.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Improved soil hydrodynamic properties: the relative size of capillaries by different soil levels increased and the soil water-retaining capability improved.
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Reduced soil loss through runoff reduction and wind erosion.
土壤压实
SLM之前的数量:
423
SLM之后的数量:
70
注释/具体说明:
At different depth soil compactness reduces from 6 (0 to 20cm) to 1.3 times (40 to 60cm)
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
Vegetation cover increase 5 to 30 times. Vegetation grows mainly inside and around the micro basins.
生物量/地上C
SLM之前的数量:
70 to 110kg/MS/ha
SLM之后的数量:
420 to 2090 kg/MS/ha
注释/具体说明:
The biomass production increases 5 to 30 times compared to the nearby unplowed soil. On implemented sites, biomass varies from 420 to 2090 kg / DM / ha, on average between 1000 and 1200 kg / ha against 70 to 110kg / DM / ha on control plots.
植物多样性
SLM之前的数量:
14 herbaceous, 6 woody species/ha
SLM之后的数量:
44 herbaceous, 14 woody species/ha
注释/具体说明:
Floral diversity increases from 14 to 44 species. With a high proportion of graminaceous species of good forage value and the return of more leguminous species. Concerning the diversity of woody plants the results show an average per hectare of 14 species on implemented sites and an average of 6 species on control plots.
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
A great increase of animal biodiversity: insects, birds, reptiles and mammals (such as squirrel, jackals, gazelle...) are observed in the implemented sites.
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
The increased vegetal and animal biodiversity, deep root system, soil fertility and water availability, increase the health and resilience capacity of the whole ecosystem.
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
Through water harvesting the rain is retained in the precipitation area and flood risk decreases. If flood occurs in the plowed area before the vegetation is well established, the micro basins can be washed out.
干旱影响
注释/具体说明:
Increased biodiversity, vegetation cover and soil fertility, deep root system and water storage in the soil profile, increase the resilience to drought of the whole ecosystem. During the project, in years of extreme drought, plants have reduced their growth but most of them survived, were used to feed animals and started growing again in the following rainy season.
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Minimal production of carbon dioxide compared with the potential gain.
火灾风险
注释/具体说明:
The implementing area remains open to lifestock (regulated pasture) to reduce the high production of grass that could favor the spread of a fire, herders also monitor the territory. There is a high level of community involvement and a growing ecological awareness.
风速
注释/具体说明:
The great number of growing trees reduce the wind speed.
微气候
注释/具体说明:
Local people attest that the Technology locally increased the amount of rain and reduced dust storms in number and intensity.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
Local people tell that the rehabilitation of large areas of bare soil augmented the local rain amount and the water level in the wells.
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
Wind intensity and dust storms reduction thanks to soil coverage and wind brake effect by trees and shrubs.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 非常好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 旱季 | 增加 | 非常好 |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 减少 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 适度 |
| 当地沙尘暴/尘暴 | 非常好 |
| 局地风暴 | 非常好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 不好 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The system includes the use of a heavy duty tractor and a special plow whose costs are high though difficult to sustain by the local population. Most financial costs are covered by founders and donors, the land user's partecipate to the project with their work so even if the benefits in the short term are fewer than in the mid and long-term, for them it is still very positive.
6.5 技术采用
- 10-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
330 villages and around 33.000 beneficiaries
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 50-90%
注释:
Except for plowing, the other activities part of the Technology are practicable by the population under an initial guidance of a promoter with specific training. These are done without any material incentives/payments. The technology is well known in the Region and there is an active participation of the local people and a strong demand for new interventions.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
其它(具体说明):
technical
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
The design of the plow has been adapted to increase the performance of the implement and reduce the running costs of plowing. The reversibility of the plowshare reduces the need for empty rides. The different parts of the plow are adjustable to adapt it to the needs of the project and the soil characteristics.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Higly degraded, abandoned land becomes fertile and rentable again. Fodder increases in quantity and improves in quality and lasts all year round. Food security also in drought years. Herds are healthier and more productive. Fodder and water availability for animals is closer to the villages. Some plants can be sown for different uses: crops, medicine or for the production of mats or other handcrafts products that can be sold. |
| Better life conditions, more income opportunities and diversification. Food is diversified and more nutritious. Less hunger and deseases. |
| Greater community cohesion and less migration, better environnemental conciousness and commitment, education and security. People gain back dignity, confidence in the future and hope. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The Technology allows the rehabilitation of rangeland and highly degraded areas in a fast and natural way on a large scale. This can boost a longlasting effect and the shift of the whole ecosystem. The Technology confers drought resilience and reduces the effects of climate change. It allows the sequestration of CO2 and can contribute to achieve the Land Degradation Neutrality Goals. |
| The partecipatory approach is essential for the sustainability of the project. The local Communities improve their life quality, awareness, cohesion and resilience. The need for migration is reduced and people has the chance to stay in their Lands. |
| The sown tree and shrub species are mainly indigenous and locally adapted species. Each specie can follow it's own growing laws and adaptation strategies. Through the tillage process the technology offers the highest degree of efficiency in the first years from processing. Its effects last for a long time so it does not need to be repeated on the same site. |
| The VS does not use any water (except rain) in countries where water is rare and precious. |
| The use of a mechanized implement allows to rehabilitate very hard, degraded and abbandoned land on large areas with reduced population. As the Delfino3s can plow strongly degraded land, the local people often ask to work their worse land which they would never be able to use. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Land that was unproductive and nobody claimed becomes productive: it can lead to misunderstandigs and conflicts. | Land use and production exploitation rules must be cleared and accepted by all Subjects at the beginning of the project. |
| Good pasture attracts animals and herders from the nearby Region (also from far away and abroad). | Rules must be clear. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The investmentand running costs for the machinery are high and cannot be covered by single land users or small Communities. | The projects must be financed by donors or founders. The Community can partecipate to some extent to cover the running costs. |
| The speed and effectiveness of the Delfino3s plow are its major advantages in the ecosystem rehabilitation process but can also be its major limitation. To make the best out of it, it is necessary to have a great availability of land (1.000-1.800ha) every year. | A big organizational capacity is needed. The spreading "like wildfire" that has characterized the case study was possible by the presence on the territory of an NGO already active and rooted in the territory for many years and by perseverance, respect and competence of all involved subjects. |
| Since great extentions will be processed, a big organisation is needed for all connected activities (awareness raising, seed collection and stockage, training, logistics, etc), | Must be well organized and should operate already before starting with plowing. |
| The professional level of the tractor drivers and the mechanics as well as the lack of a well-organized mechanical workshop and spares stock can lead to long interruptions of the work and high extra costs. | Professional technical trainings and monitoring are very important. The organization of a well managed mechanical workshop and spares stock are essential. This can also be a great development opportunity for the Region. |
| The increased amount of fodder can induce the shepherds to increase the number of animals. | An important work with the Communities is essential to achieve shared and sustainable management goals. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
4
- 与土地使用者的访谈
30
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
8
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
5
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Un "delfino" rinverdisce i deserti, Venanzio Vallerani, ISBN 978-88-95858-05-0
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
info@vallerani.com
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Récupération des sols fortement dégradés à des fins sylvo-pastorales, CILSS 2009
URL:
http://www.vallerani.com/wp/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/Rapport-Reach-Cills-2009.pdf
标题/说明:
GIZ, Good practices in soil and water conservation, pag. 22 seg.
URL:
https://www.giz.de/fachexpertise/downloads/giz2012-en-soil-water-conservation.pdf
标题/说明:
Using Mechanized Water Harvesting System (The Vallerani System ) for Rehabilitation of Degraded ASALs in Kenya
URL:
http://www.vallerani.com/wp/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/Meshack-Muga-Paper-25-Final.pdf
标题/说明:
Report for the Sino-Italian cooperation project, SFA, China
URL:
http://www.vallerani.com/wp/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/Report_in_English-10.pdf
标题/说明:
Global guidelines for the restoration of degraded forests and landscapes in drylands FAO, pag. 104 seg.
URL:
http://www.fao.org/3/a-i5036e.pdf
标题/说明:
Improved rainwater harvesting for fodder shrub production and livestock grazing: the Vallerani micro-catchment system in the Badia of Jordan
URL:
http://www.fao.org/family-farming/detail/en/c/1040697/
标题/说明:
Conedera, M., N. Bomio-Pacciorini, et al. 2010. Reconstitution des écosystèmes dégradés sahéliens. Bois et Forêts des Tropiques 304(2). Bois et Forêts des Tropiques 304(2). Bois et Forêts des Tropiques
URL:
http://www.vallerani.com/images/Reconstitution.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块