Staggered Contour Trench [阿富汗]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Aqila Haidery
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
Jerma (Dari)
technologies_1715 - 阿富汗
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Sirat Aliaver
AKF
阿富汗
SLM专业人员:
Altaf Jalil
altaf.jalil@akdn.org
AKF
阿富汗
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Sustainable Land Management Project, Bhutan (SLMP)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Aga Khan Foundation (AKF) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Sustainable Land Management Institute Organistatio (Sustainable Land Management Institute Organistatio) - 阿富汗1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/10/2015
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
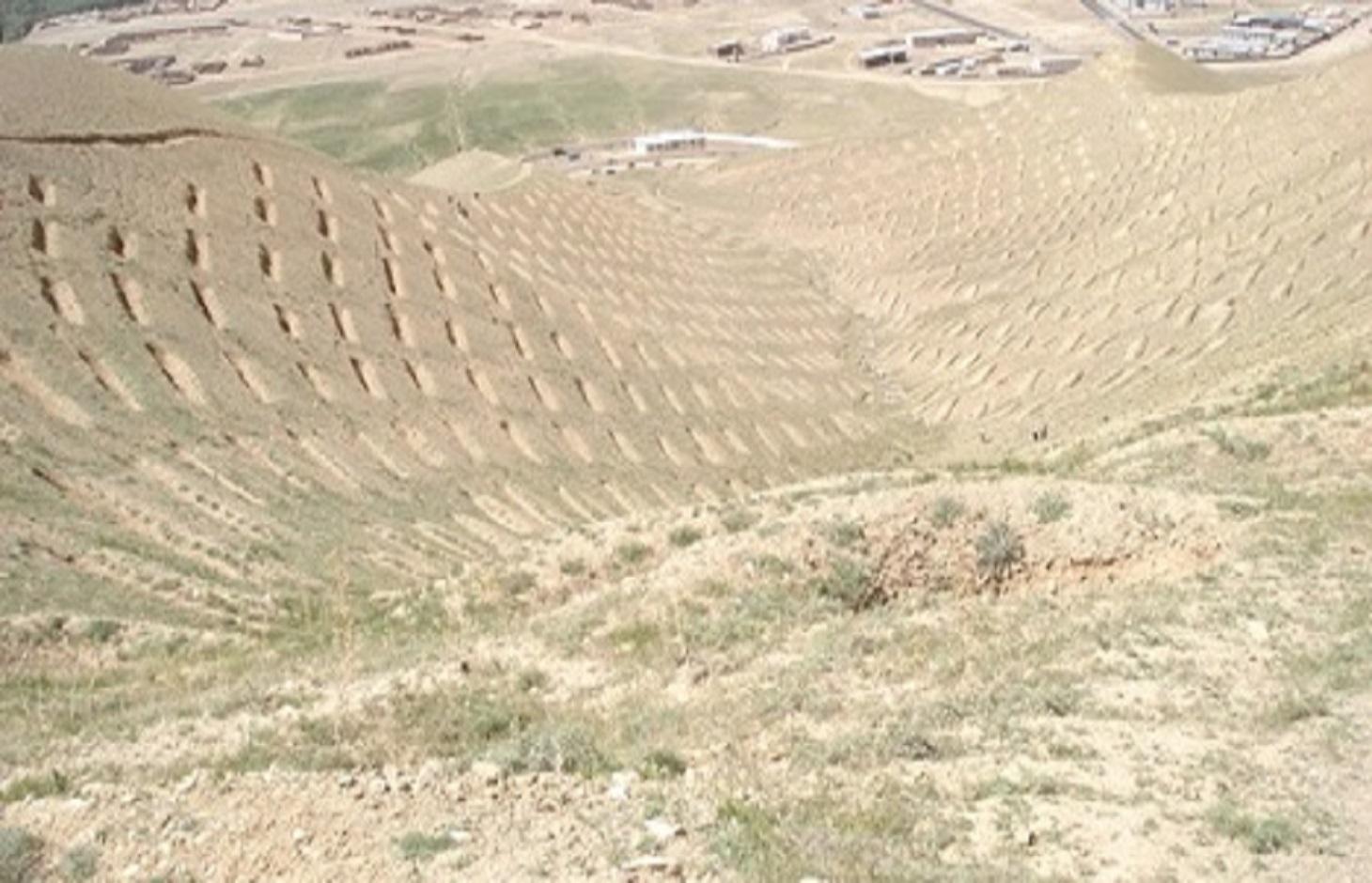
Earthen trenches with soil bunds built along contours in staggered design
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The SCTs technology is documented by Sustainable Land Management Project/HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation which is funded by Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC), with close support and cooperation of the Agha Khan Foundation (AKF). The staggered Contour Trenches (SCTs) were constructed at a degraded site in Bamyan center (Bamyan province) by Agha Khan Foundation (AKF) project with financial support of the Canadian International Development Agency (CIDA).
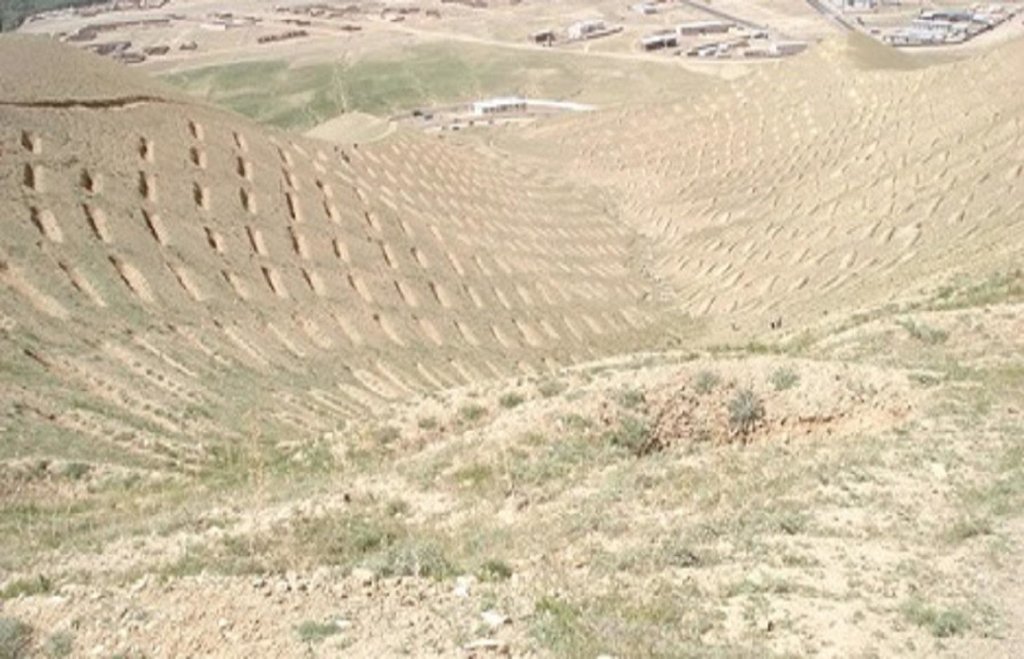
Totally 1470 contour trenches were constructed at the site, which has an area of 24 hectares.
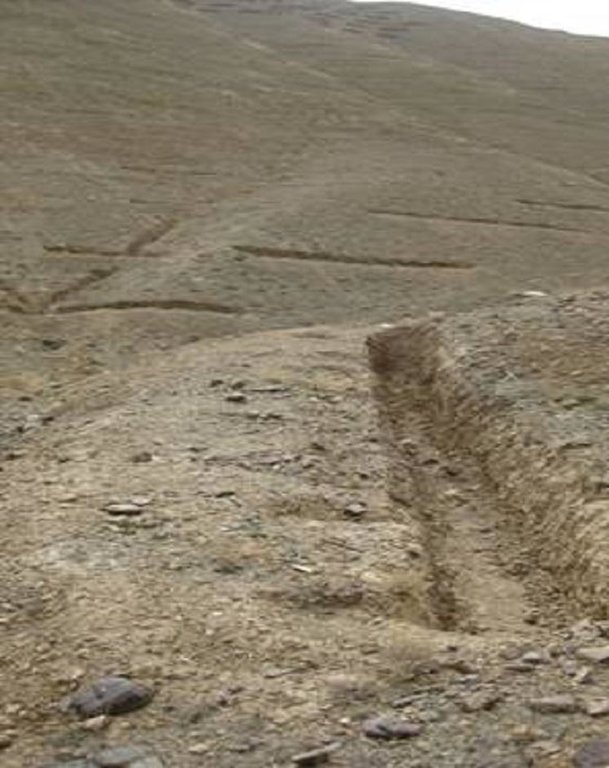
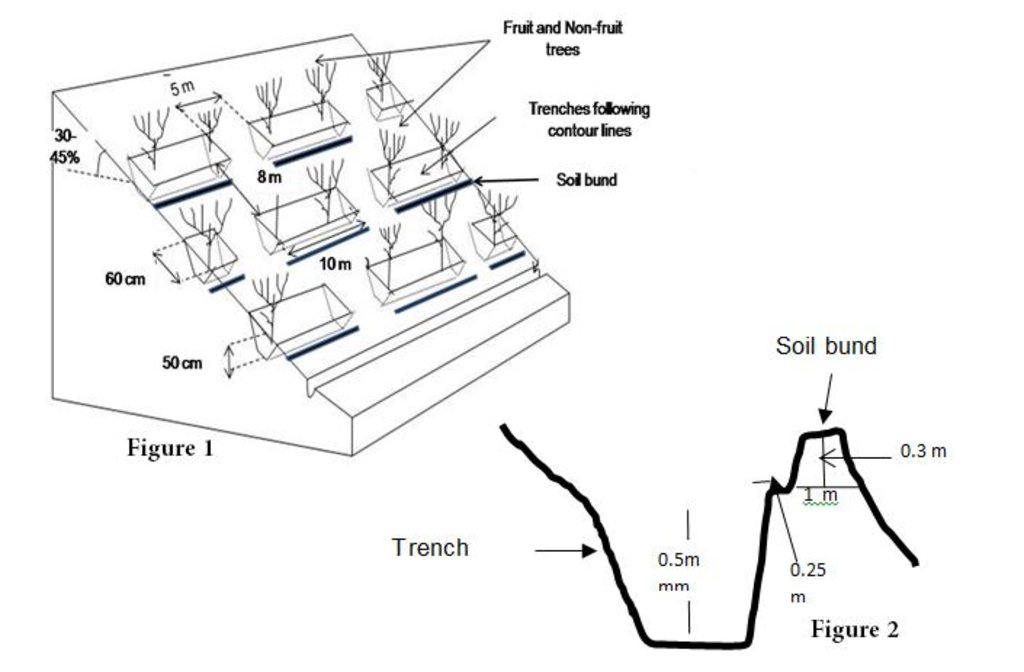
The size of each trench measured 10 m in length, 0.6 m in width and 0.5 m in depth. The trenches had soil bunds on the lower side having a width of 1 m and height of 0.3 m. Contour lines were prepared using an A-frame and lime and the spacing between two contour lines was 8 m considering the slope. All the trenches were dug out manually. Local people were employed for construction works. Along with the SCTs, other measures were applied such as plantation of fodder grass, shrub and non-fruit trees, gully plugs, water harvesting tanks and brushwood plugs. The area is excluded from grazing and shrub cutting.
The land was extensive grazing land before the project implementation and got extremely degraded due to a lack of management by the land users. There was rampant exploitation of natural vegetation for meeting domestic energy needs and for grazing. Droughts, which frequently occur in the region, contributed to the slow degradation of the vegetation.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of the technology is to reduce flash flood risks and improve land productivity (both upstream and downstream) so that more fodder, fuel wood and fruits could be produced and farmers affected by flash floods could grow more crops. The technology, which is part of a watershed technology system, helps in retaining runoff and sediment and improves soil moisture content. It also helps in water infiltration which eventually contributes to improved ground water recharge.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: SCTs were established in a step-wise manner; as follows: (1) Site surveying, (2) Site mapping, (3) Planning, (4) Marking contour lines with the help of an A-frame, and (5) Trench excavation and bund construction.
The establishment cost for staggered contour trenches, was about 15,500 USD or 645 USD/ha. Most of the money was spent on labour. There have been no expenses in maintenance of SCTs since their establishment in 2008.
Natural / human environment: The technology is applied in semi-arid condition as the area receives annual rainfall of about 400 mm to address land degradation. The site formally belonged to the state but the local communities have use rights. AKF is still maintaining the site and using it for training and demonstration purpose. Several exposure visits for SLM specialist, land users, students and teachers have been also organized at the site.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿富汗
区域/州/省:
Zai Mahmood village, Bamyan center, Afghanistan
2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 降低灾害风险
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Flash floods, gully/rill/sheet erosion, loss of natural vegetation and low productivity of the land due to degradation compounded by climatic factors.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Declining productivity of land resulting in shortages of fodder and fuel wood and loss of fertile land in the downstream areas due to flash floods.
Grazingland comments: The area is closed for livestock.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
Type of grazing system comments: The area is closed for livestock.
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: April to September
牲畜密度(如相关):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 区域封闭(停止使用,支持恢复)
- 横坡措施
- 地下水管理
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.24 km2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
A detailed staggered contour trenches layout and its specifications (Fig. 1), and the cross section of soil bunds (Fig. 2)
Location: Bamyan. Bamyan center/Bamyan province
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Technical knowledge required for SLM specialist: high
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Spacing between structures (m): 8
Bund/ bank: level
Spacing between structures (m): 8
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 ha
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of the contour trenches and construction of the soil bunds | 结构性的 | |
| 2. | Marking contour lines (A frame and lime) | 结构性的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Digging of the contour trenches and construction of the soil bunds | persons/day/ha | 100.0 | 6.43 | 643.0 | |
| 设备 | A frame and lime | ha | 1.0 | 1.8 | 1.8 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 644.8 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 4 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | No maintenance activities have been implemented for staggered contour trenches and soil bunds up to now. | 结构性的 |
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Despite the application of the structural measure of the SCTs AKF is still continuing its financial support for the plantation of the area. Thus irrigation which is a costly activity is still continued by AKF's support. The planted saplings of fruit and non-fruit trees are irrigated for six months/year, i.e. from April to September. Water is carried to the site by tankers. Each month, 75 tankers are used and the cost of one tanker is 12 USD or 600 Afghani. In addition, 16 persons are employed for one time irrigation.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Bamyan receives heavy snow falls and rain falls in winter season
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is very low - low
Soil drainage / infiltration is oor due to sealing
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Mainly men were involved in the activities due to cultural reasons.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
100% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: This is more applicable for poor small landholders or landless families.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
注释:
Formally, state owned. The site is now protected from open grazing and shrub cutting with support from the local communities.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
生产故障风险
产品多样性
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Decreased production area
水资源可用性和质量
家畜用水的可用性
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
文化机会
注释/具体说明:
As the site is greener now
娱乐机会
国家机构
注释/具体说明:
Especially of DAIL (Department of Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock) and the persons who visit the site
SLM/土地退化知识
livelihood and human well-being
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
注释/具体说明:
Runoff, dew, snow, etc.
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤覆盖层
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
动物多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
火灾风险
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
Due to better vegetation cover
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
注释:
SCT must be combined with vegetation and management measures
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The benefits stated are the combined impacts of all measures-structural, vegetative and management. SCTs have helped in the establishment of vegetative measures by contributing to increased soil moisture, reduced runoff and soil loss.
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The whole project activities were implemented by external supports
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: As the implementation of a watershed project requires high costs and investments which can not be affordable for the individual land users.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The land users views were not considered. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Helps in reducing flash flood risks due to less runoff How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper institutional mechanisms, involving the government, non-government and community institutions should be developed for sustaining project activities. Department of Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock DAIL; (Bamyan) should take lead |
|
Conserves soil and enhances soil cover and fertility leading to more on-site production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Vegetative measures should be strengthened |
| Complements re-greening efforts by reducing erosion and conserving moisture |
| The quality of contour trenches and soil bunds are very good and maintenance costs negligible |
| The site is used for demonstration, training and exposure visits |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Establishment costs are very high | Voluntary community contributions, if they have an active stake in the project, would reduce the costs, otherwise, there has to be external support at least for the establishment phase |
| Loss of land for production | Planting suitable plants inside the trenches and along soil bunds |
| Requires high level of technical knowledge for establishment | Practical training for the target groups |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块