Soil pH management [英国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Tandra Fraser
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1727 - 英国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Tibbett Mark
m.tibbett@reading.ac.uk
Centre for Agri-Environmental Research, School of Agriculture, Policy and Development, University of Reading
Reading RG6 6UA, United Kingdom
英国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Centre for Agri-Environmental Research (CAER) - 英国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
University of Reading (University of Reading) - 英国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
03/05/2016
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷
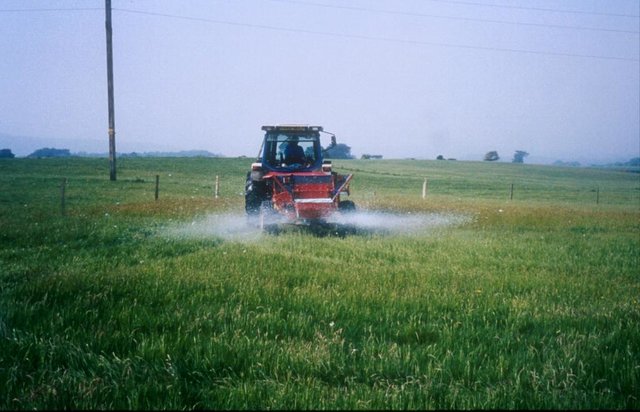

Soil pH management [英国]
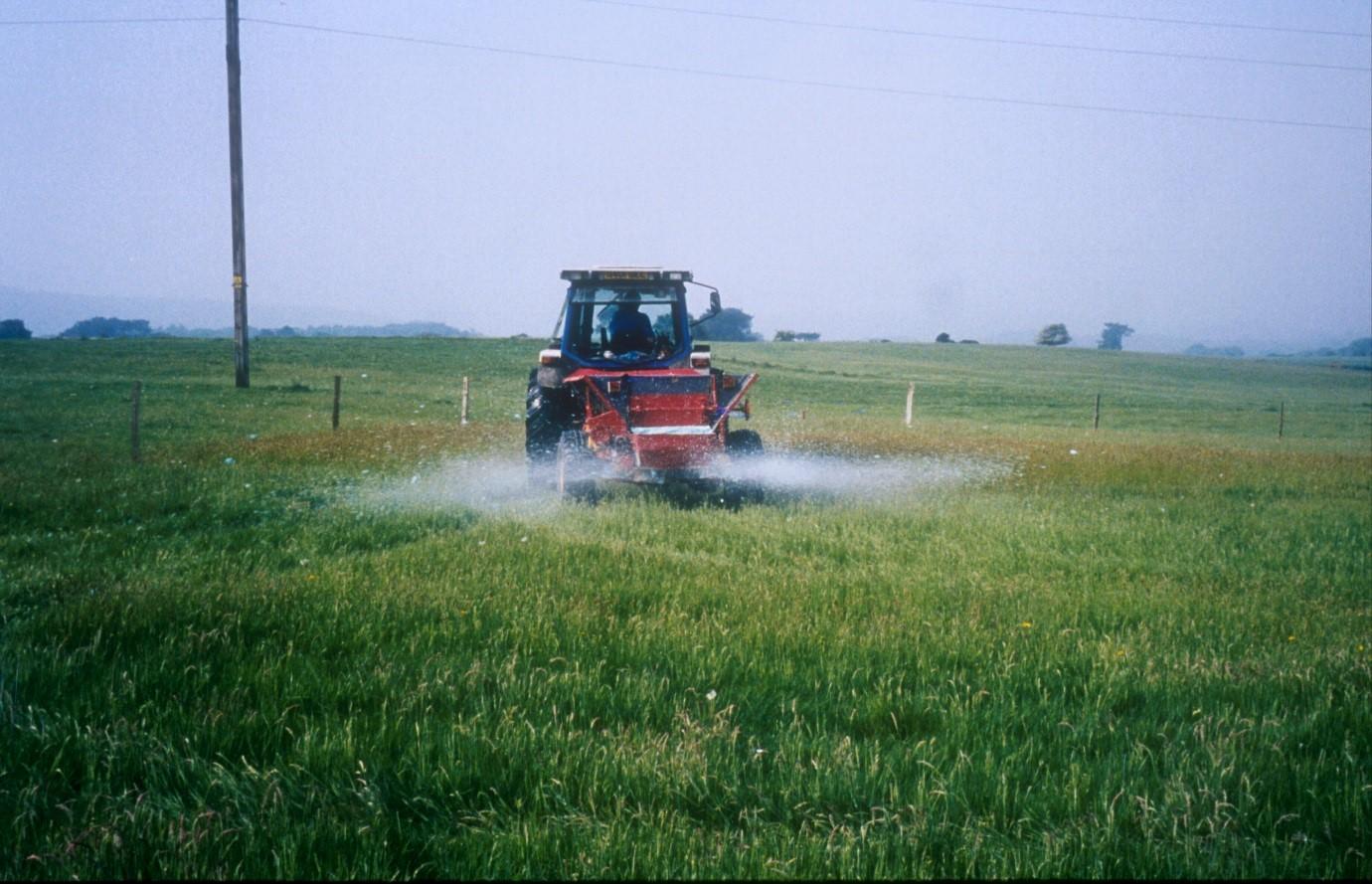
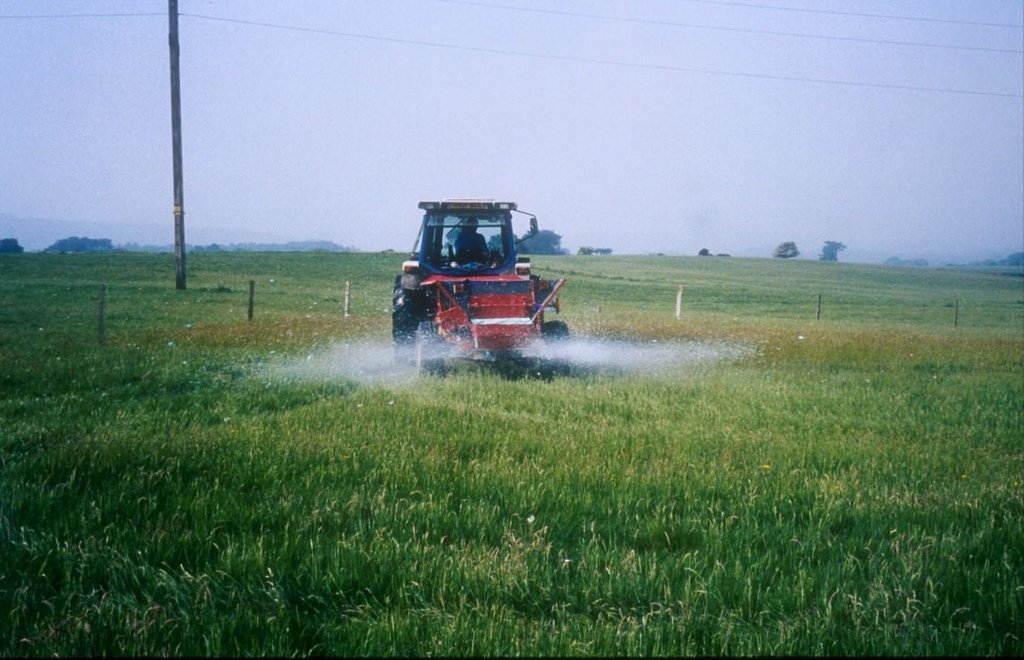
Acidification treatments were applied to improved pastures in an attempt to restore plots to low-intensity grazing land
- 编制者: Tandra Fraser
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Acidification treatments were applied to improved pastures in an attempt to restore plots to a semi-natural state
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Change in landuse from improved agricultural land to low input grazing land. Acidification treatments were applied to plots on the Isle of Purbeck that had previously been used for arable production and then high intensity grazing. The site is located on acidic fluvially-deposited soil and was in lowland heath until the middle of the 20th century at which time the land was tilled and treatments of rock phosphate, marl and chalk were added to increase soil pH and nutrient availability and improve the potential of the land for agricultural production.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of this technology was to convert the area from intensive pastureland to a semi-natural state with low intensity grazing through alteration of the soil pH. This change in land-use should have a positive effect on both above- and belowground biodiversity.
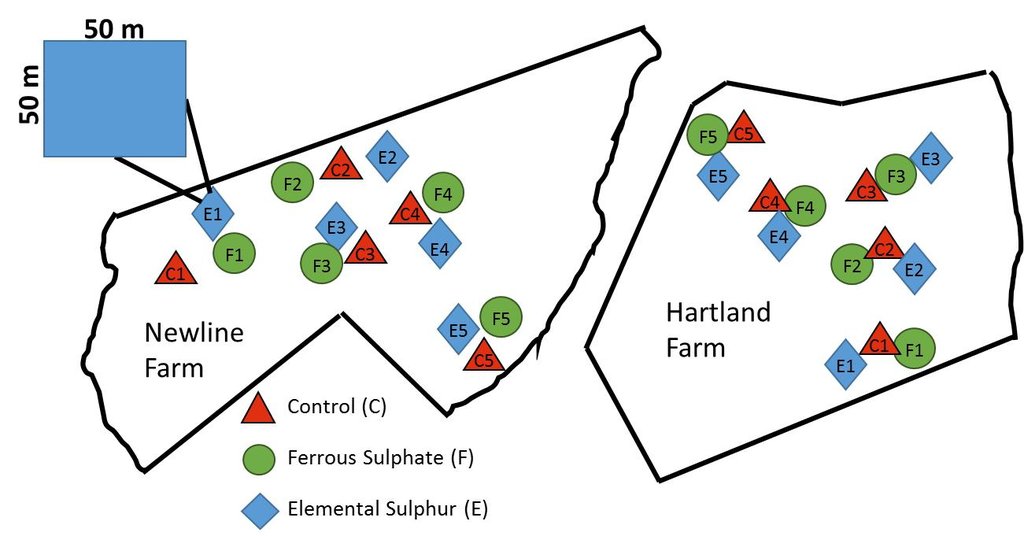
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Plots were established on two adjacent farms owned by National Trust near Wareham, Dorset (Newlines Farm and Hartland Farm). A control and two sulphur amendments were compared on plots on ten fields (five from each farm) on 50 m x 50 m plots. Elemental sulphur (Brimestone 90TM) or ferrous sulphate (Mistrale “Wet Copperas” 50TM) were applied at equal rates of 2000 kg ha-1 in May 2000 and a second application of 1600 kg ha-1 in March 2001.
Natural / human environment: The Isle of Purbeck is a multifunctional landscape with competing land uses including arable farming, livestock grazing, and recreational activities. Soil resources in the region have been under pressure from persistent physical and chemical manipulation, with consequences for soil biodiversity and function.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
英国
区域/州/省:
Dorset
有关地点的进一步说明:
Wareham
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧场:
- 半游牧/游牧
主要动物种类及产品:
Main species: Cattle
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Changing land use needs in a diverse landscape
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Changing land use demands, soil compaction on arable land, soil sealing, intensive agriculture, acidification of chalk hills by gorse
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Cattle
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: post-flooding
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- Soil pH management
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.6 m2.
This was a field experiment so treatments were only applied to a portion of this area.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M5:物种组成的控制/变化
注释:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Ca:酸化

生物性退化
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bh: loss of habitats, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline, Bl: loss of soil life
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ca: acidification
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Soil pH was previously increased for agricultural production. Land may be restored to a semi-natural production system by lowering soil pH.)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Intensively managed arable crops, low input pasture land)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Schematic representation of plot layout across Newline and Hartland Farm as control, ferrous suphate and elemental sulphur treatments.
Location: Near Warehame. Dorset, Ilse of Purbeck
Date: 21-3-2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: Soil biological functions
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Change of land use type: Intensive grazing (Gi) to extensive grazing (Ge)
Control / change of species composition: More diverse species mix
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fertilizer additions | 管理 | x2 |
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Monitoring | 管理 | Variable |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Fertilizer spreader
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The experiment was established in 1998 and costs are not available
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (10 m a.s.l)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
- National Trust
注释:
Own the land where the technology has been applied.
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
产品多样性
土地管理
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
社会文化影响
文化机会
娱乐机会
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
外来入侵物种
动物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Decreased spending on inputs where the only input in the system in dung from cattle grazing How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue grazing at a low enough density to allow adequate plant regrow |
| Decreased labour required for management |
|
Decreased compaction since regular use of tractors on site is no longer required How can they be sustained / enhanced? Attempt to minimizing compaction by grazing livestock |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The conversion in land use from a improved agriculture to a semi- natural low input grazing system should have a positive effect on above- and belowground biodiversity. |
| Considering that the Isle of Purbeck was historically a region of cultural importance, returning the system to a more natural state has important implications for the cultural and recreational value of the land. |
| Low input systems can increase resilience of the system to global change |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Decrease in economic returns | Application of lower rates of amendment at an increased frequency may be more manageable. |
| The sulphurous amendments may be difficult to apply evenly with a fertiliser spreader at such high rates. | Application of lower rates of amendment at an increased frequency may be more manageable. |
| May not be practical to apply such high rates of amendments on a landscape scale. | Grazing, mowing, and chemical herbicides are some options for slowing invasions. |
| Shrub encroachment (i.e. gorse; Alex europaeus) can be a problem when converting to low input pasture land in this region. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Over time nutrients are being drawn down but exporting meat off the land with no inputs | Periodic applications of nutrients may be required to ensure long-term fertility of the system |
| Land use change and restoration are slow process and may result in economic losses on managed lands |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Soil pH management [英国]
Acidification treatments were applied to improved pastures in an attempt to restore plots to low-intensity grazing land
- 编制者: Tandra Fraser
模块
无模块