Organic agriculture [斯洛文尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Matjaz Glavan
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Gudrun Schwilch, Ursula Gaemperli
Ekološko kmetijstvo
technologies_2795 - 斯洛文尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department for Agronomy, University of Ljubljana - 斯洛文尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
31/05/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
It is based on 5 years crop rotation, full absence of artificial plant protection products and mineral nitrogen and the circulation of nitrogen via organic manure, crops and residues.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
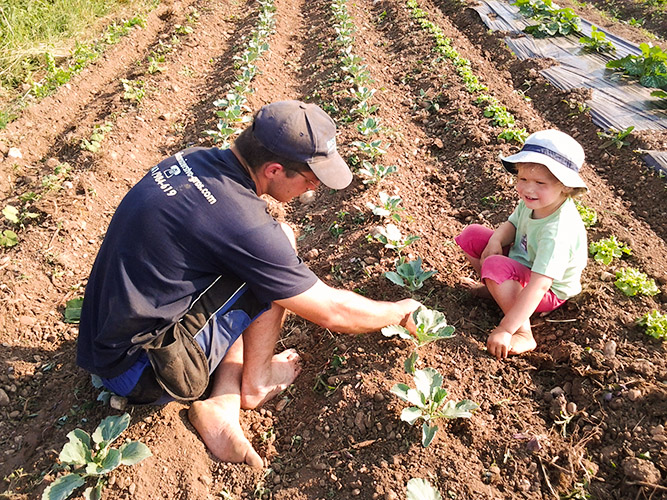
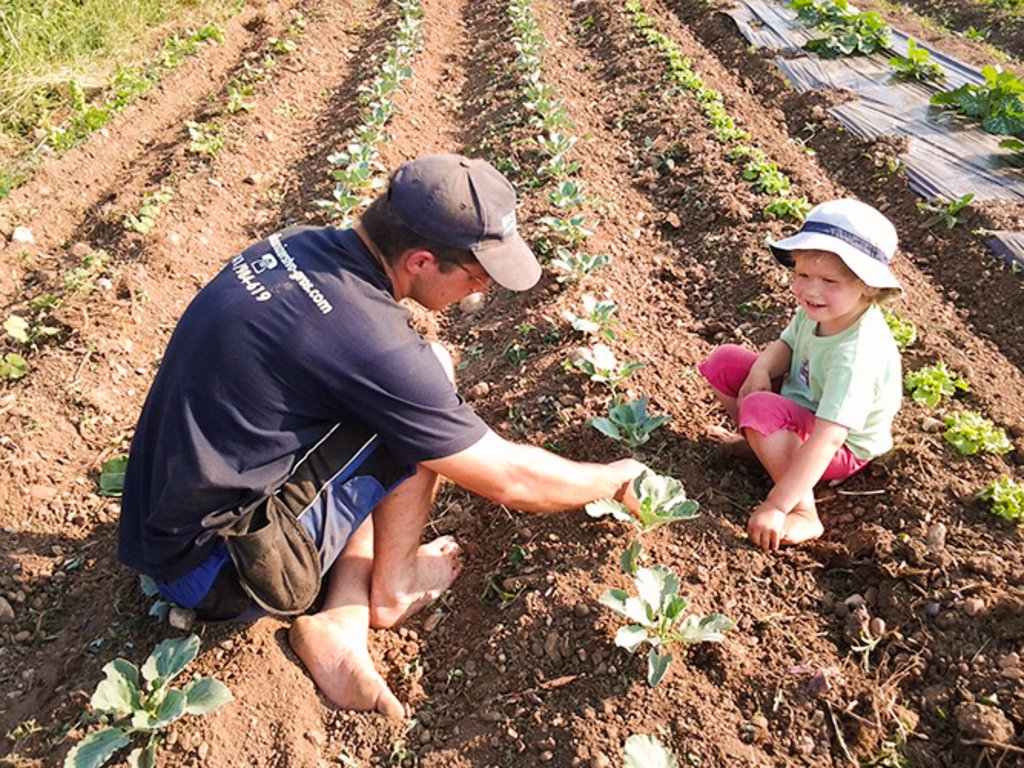
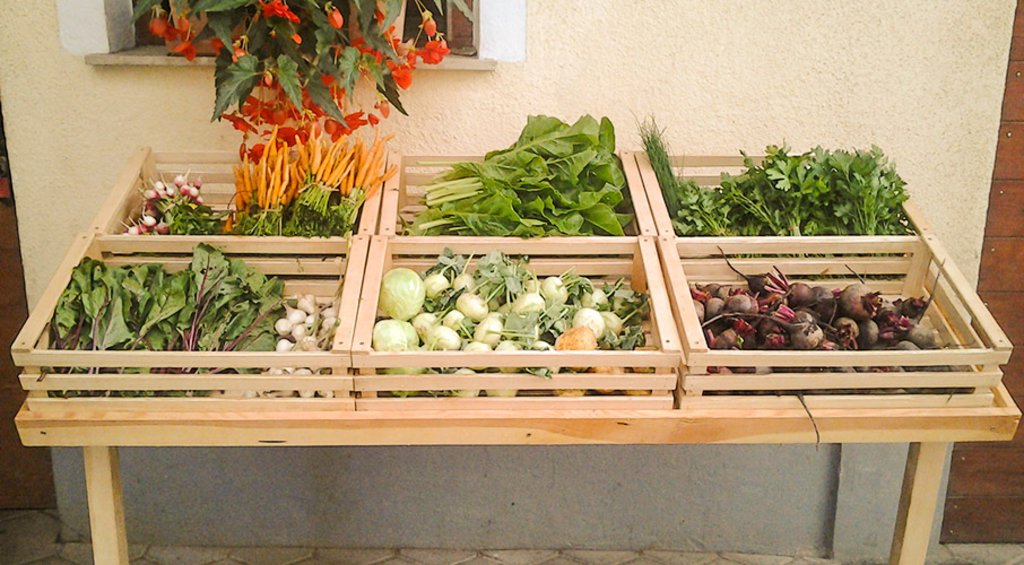
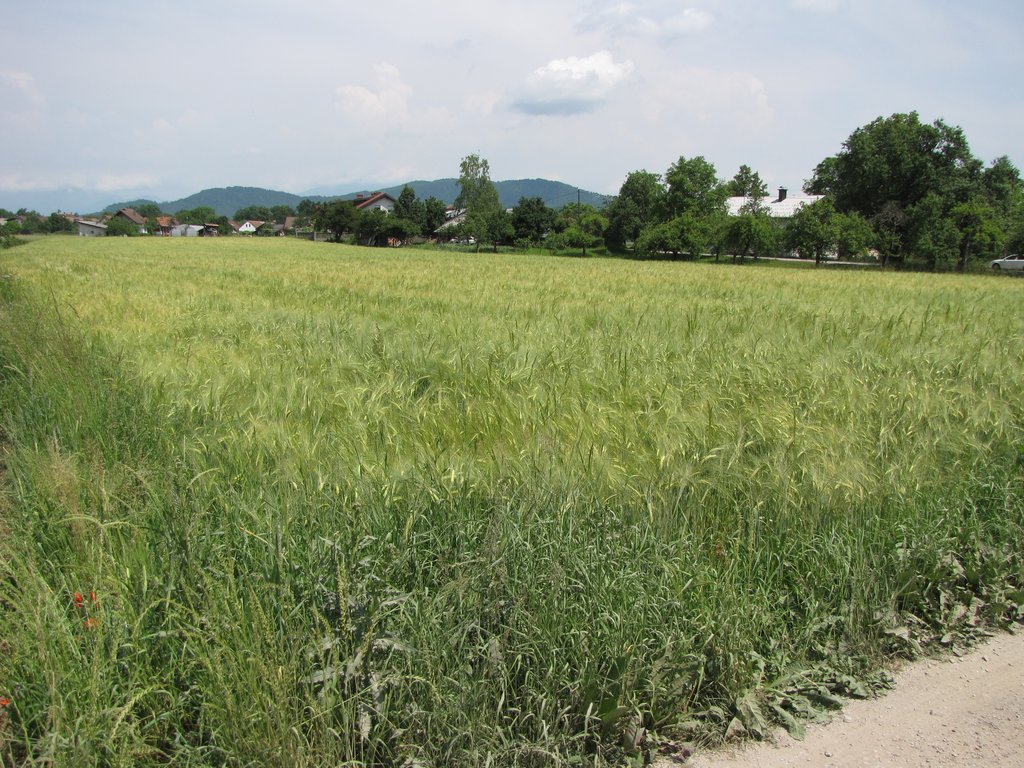
1.The technology is applied in the flatlands of Ljubljana with an average altitude of 350 m.a.s.l. The average annual precipitation is 1400 mm. The area is characterized with often stormy precipitation events and occasional droughts. Silty loam soils in the area are moderately deep to deep with medium soil organic matter. Area has good availability of surface water and groundwater of good drinking quality. Area has medium biodiversity without salinity and flooding problems. Sedentary agriculture with mixed or commercial agriculture is practiced with less than 10 percemt from off-farm activities. The examined farm household has an average wealth and is mechanized/motorized. The farm is run by middle aged and elderly mens. The farm household has good access to all services and infrastructure. Farm is of medium scale with land partly owned by the land users and partly leased from other private owners.
2. Main characteristics are
(1) full 5 year crop rotation
(2) at least 0.5 livestock units
(3) circulation of nitrogen via organic manure
(4) cycle of other nutrients closed as much as possible
(5) absence of artificial plant protection products and mineral nitrogen.
(6) nitrogen fixation leguminous in crop rotation
(7) production of local traditional species (buckwheat)
3. Purpose of the technology is to manage the land in a sustainable way with closed nutrient cycles and to increase the biodiversity. Organic matter increases organic matter and fertility of the soils. Reduced soil acidificatino, pollution, salinization and alkalinization. Reduced soil compaction, slaking and crusting of soils. Increased bio-productive function of soils. Increased vegetation cover, biomass and improves habitats with better quantity of species and its composition and diversity. The purpose is also to offer customers food of local and well known products without any use of chemically based plant protection.
4. Major activities:
(1) keeping of farm animals in stables for closing the N-balance
(2) a lot of further manual farm and cultivation work. Some of it is replaced by new machinery. This causes additional costs at the moment of establishment
(3) regular manual checking for pests, diseases.
5. Benefits are the closed N cycle and the CO2 sequestration - high organic matter content, lower loss of nutrients, higher biodiversity.
6. Farm users dislike lots of costs connected with the new machinery, lots of paper work for the certification, the pressure on productivity, a great deal of work with planning crop rotations and nutrient management, coping with pests and diseases. But they like the better price on the market.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
斯洛文尼亚
有关地点的进一步说明:
Municipality of Ljubljana
注释:
Georeferenced map locations are part of the same farm.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2008
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- Common agricultural policy
注释(项目类型等):
The land user saw the opportunity of capital city market and rising market of organic food in Slovenia. The subsidy payments accelerated the whole process of transformation from conventional to organic farm.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
cereals (wheat, barley) / buckwheat / peas / alfalfa / corn / potato / vegetable / in winter cover crops

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
主要动物种类及产品:
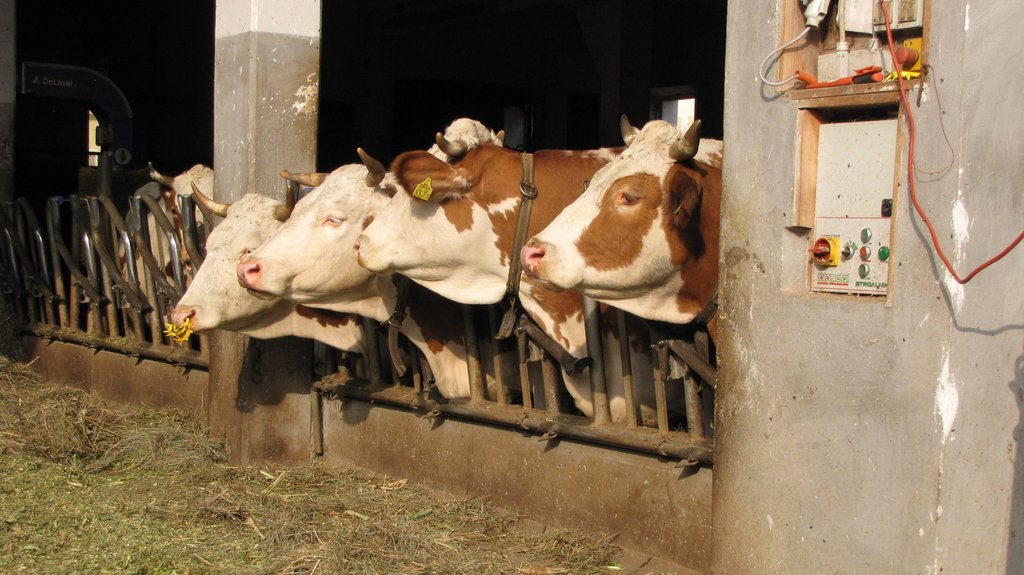
Dairy cows (milk, cheese). Due to the dispersed land parcels they are not able to implement grazing.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Vegetable on limited area is also irrigated.
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 轮作制度(轮作、休耕、轮垦)
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
Only one farmer of the village is engaged in organic farming.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Ca:酸化
- Cp:土壤污染

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pk:熟化和结壳
- Pu:由于其他活动而导致生物生产功能的丧失

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Infographic presents main activities taken place under organic farming technology (rotation, weed and pest control, animal welfare and use of organic fertilisers) . All of them finally result in benefits at the bottom of figure (local market, known origin of food, healthy food, food self-sufficiency).
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
24 hectares
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
EUR
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
50 EUR
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Exclusion of artificial chemiclas (plant protection products) | 农业学的 | all year around |
| 2. | Only organic N in use | 农业学的 | all year around |
| 3. | 5 year rotation | 农业学的 | all year arround |
| 4. | Winter cover crops | 农业学的 | in autumn, winter |
| 5. | Working with papers, records | 农业学的 | all year around |
| 6. | Animal stall reconstruction | 农业学的 | first year |
| 7. | machinery (cultivator, grubber, harrows) | 农业学的 | first three years |
| 8. | Plant protection preparations (for diseases and pests) | 农业学的 | First year |
| 9. | Further cost for diverse supplement activities (50% more work) | 农业学的 | all year around |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Working with papers, records | hour | 20.0 | 6.25 | 125.0 | 20.0 |
| 劳动力 | Further cost for diverse supplement activities | hour | 700.0 | 6.25 | 4375.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | machinery (cultivator, grubber, harrows) | pcs | 3.0 | 4000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Copper preparations (diseases) | ml | 100.0 | 0.2 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Naturalis (potato) | ml | 100.0 | 0.2 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Nivezal (potato) | ml | 100.0 | 0.2 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Animal stall reconstruction | pcs | 1.0 | 60000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Regular certifiaction control for organic production | pcs | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 76960.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Working with papers, records | 农业学的 | all year around |
| 2. | Equipment maintenance | 农业学的 | all year around |
| 3. | Only organic N in use | 农业学的 | all year around |
| 4. | Winter cover crops | 农业学的 | autumn, winter |
| 5. | 5 year rotation | 农业学的 | all year around |
| 6. | Buying plant protection products | 农业学的 | all year around |
| 7. | Further cost for diverse supplement activities (35% more work) | 农业学的 | all year aroud |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Working with papers, records | hour | 20.0 | 6.25 | 125.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Further cost for diverse supplement activities | hour | 490.0 | 6.25 | 3062.5 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | regular maintenance of machinery | hour | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Copper preparations (diseases) | ml | 100.0 | 0.2 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Naturalis (potato) | ml | 100.0 | 0.2 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Nivezal (potato) | ml | 100.0 | 0.2 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Regular certifiaction control for organic production | pcs | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 3697.5 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The reamining costs are coverd by subsidy payments.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour availability, price of organic plant protection products and fertilisers, price of the machinery
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1352.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Average annual period (1991-2000)
Majority of rainfall in autumn, followed by summer, spring and winter.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Ljubljana - Bežigrad
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Strong summer tunder storms, showers, local precipitation.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Production in comparison with conventional production is lower by at least 20 percent. As chemical plant protection is not applied the production can not be raised. And the cows eat only fodder coming directly from farm production without buying concentraded feed.
作物质量
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
They do not use mineral fertilizers. Thus, fodder quantity decreased slightly
饲料质量
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Organic technology requires the dairy cows stall reconstruction. On the same area only half can be kept compared to the conventional dairy.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Plant diseases or pests can develop very rapidly and if it can't be addressed in its early stage it can destroy the yield. Sometime it happens, when nothing succeeds.
产品多样性
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Farmer is saying that every technology has its pluses and minuses and on general he doesn't observe differences. It is never simple.
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的质量
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
The plant protection products and organic fertilisers and organic seeds are more expensive.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Due to regular customers, the location near the capital city and good prices income increases for 50% . Three persons are fully employed.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
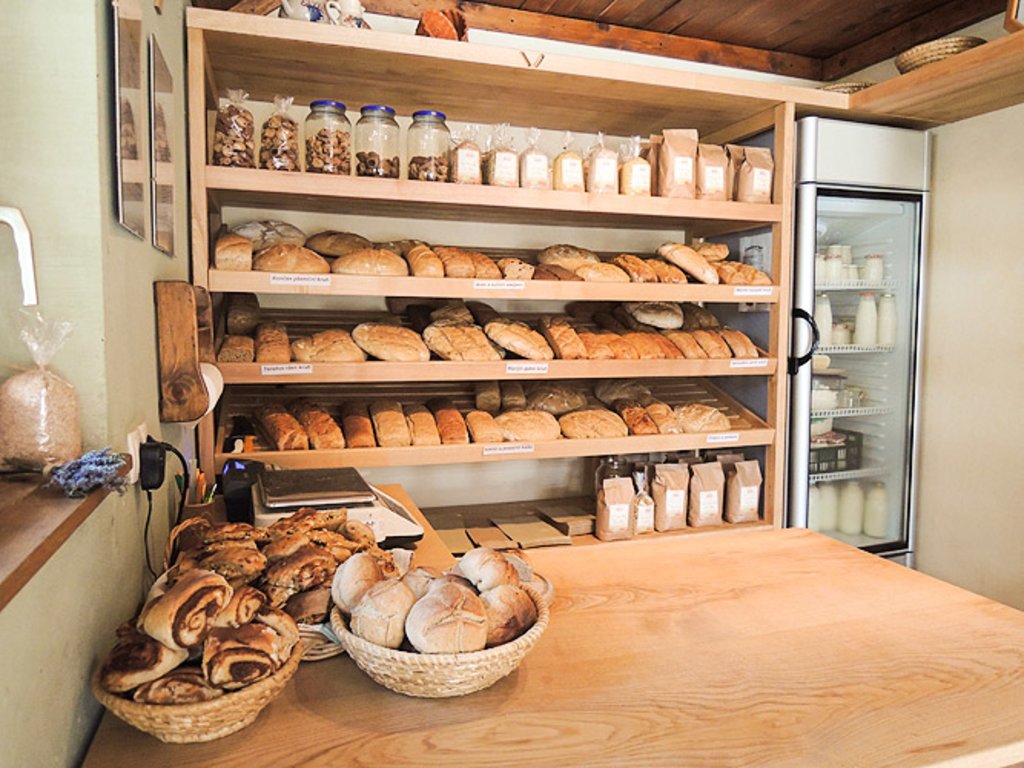
When they started with organic farming they started to produce dairy products (yogurt, cheese), flour and bread and vegetable. Before they produced only raw milk.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
A lot of hand/manual work in the field or at production of dairy product or bread.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
土壤
土壤堆积
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
碳和温室气体的排放
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 | |
| 季节性温度 | 夏季 | 增加 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
注释:
It is important that land user is engaged on market with self-promotion and good quality of product.
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
It is self-initiated as farm has its land on a water protection zone with many restrictions in management.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Lower use of plant protection products - less impact on bidiversity and water sources. |
| Quality of products. |
| Demand over organic food on the market is high, Farm is close (1 km) to capital city market. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Food produced without chemicals is of better quality and more interesting for the market. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Working force, especialy in vegetable production | New machinery, rotation |
| Shortage of nitrogen | fabaceae (legumes) as part of crop rotation |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| A lot of work force and expensive specialized machinery needed. | This is part of this technology. This can be overcome with higher prices of products. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
1
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块